Earth Materials - Mineral Genesis (Exam 2)
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What are the 4 main ways minerals can form?
solid-solid reactions, crystallization from a liquid, deposition from a vapor (no intermediate liquid), precipitation from a fluid such as H2O or CO2
what does polymorph mean
minerals in different forms with the same composition but different structures
what is polymorphic transformation/solid-solid reaction
when one polymorph transforms into another
what controls the conditions which a particular polymorph is stable?
temperature and pressure
name 3 polymorphs of SiO2
quartz (trigonal), tridymite (triclinic), cristobalite (tetragonal)
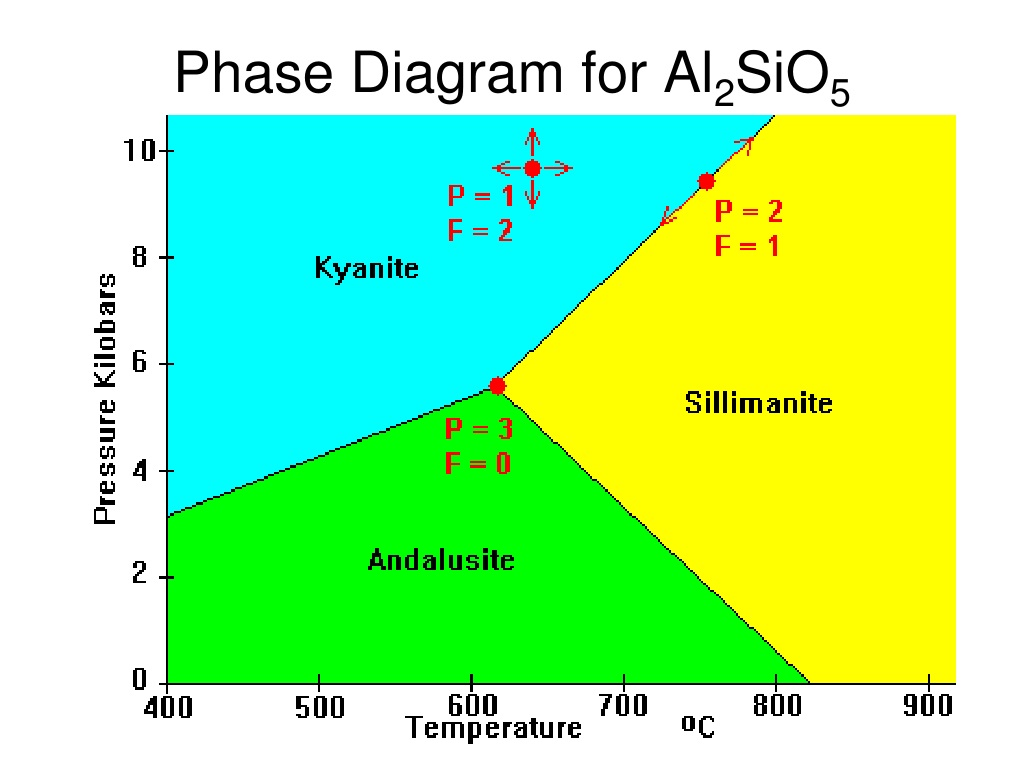
name 3 polymorphs of Al2SiO3
kyanite, sillimanite, andalusite
draw the Al2SiO3 phase diagram
what are the 3 energy states
unstable, stable, and metastable
what is Gibbs Free Energy
measure of chemical energy, all chemical systems tend naturally toward states of minimum free energy
At higher temperature, the phase with larger entropy (S) will have (higher/lower) G
lower
at higher pressure, the phase with the lower volume will have the (higher/lower) G
lower
smallest volume means (highest/lowest) pressure
highest
largest volume means (highest/lowest) pressure
lowest
largest entropy means (highest/lowest) temperature
highest
smallest entropy means (highest/lowest) temperature
lowest
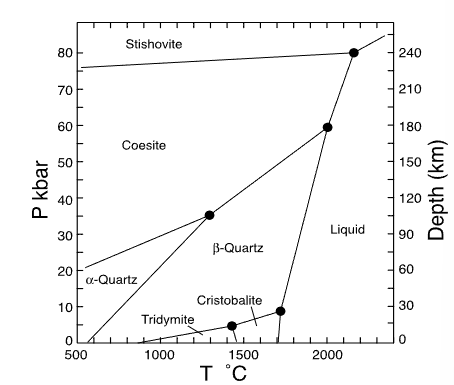
which mineral has the smallest volume?
stishovite
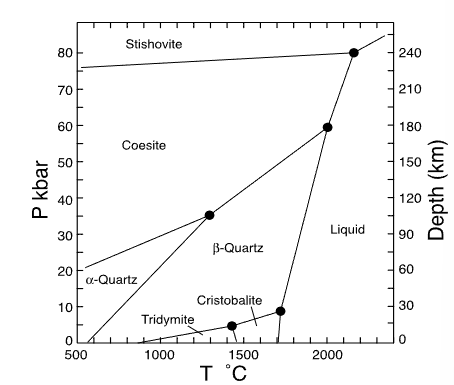
which mineral has the largest volume?
tridymite
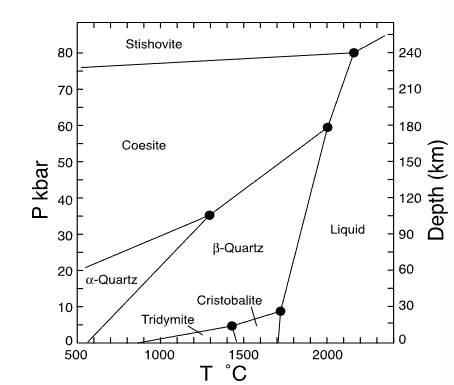
which mineral has the smallest entropy?
alpha quartz
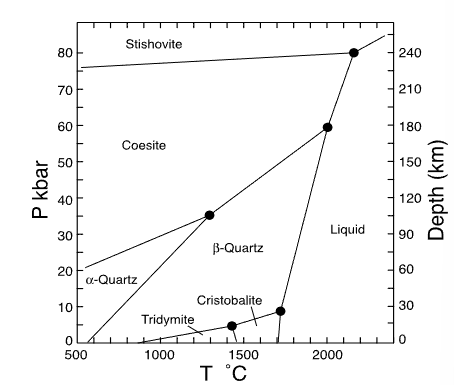
which mineral has the largest entropy?
liquid
what are the 2 polymorphs of CaCO3
aragonite and calcite
what are the 3 types of polymorphic transformations?
reconstructive transformation, displasive transformation, order-disorder
give the mineral names of an example of solid-solid reaction involving more than one phase
albite, jadeite + quartz
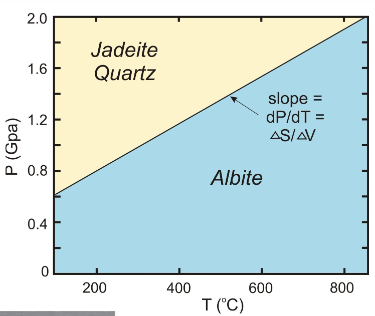
which indicates higher pressure?
jadeite + quartz
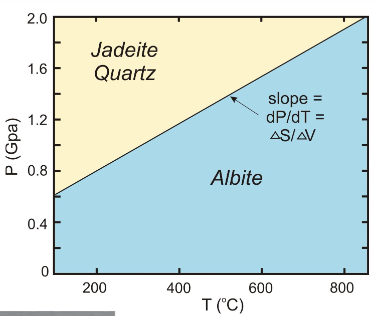
which has a smaller volume?
jadeite + quartz b/c the pressure is higher
what is nucelation
formation of new minerals
why do displasive and order-disorder transformation NOT require nucleation?
bonds stretch or shrink but do not break in displasive transformation (beta-quartz to alpha-quartz)
atosm order on different crystallographic sites in order-disorder (sanidine to orthoclase to microcline)