applied kinesiology chapter 6
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
the ____ is much larger proximally than ______
ulna; radius
______ & _______ serve as proximal attachments of the elbow (origin)
scapula; humerus
____ & _______ serve as distal attachments of the elbow (insertion)
ulna; radius
________, _______, and ____ serve as proximal attachments for the radius and ulna (origin)
scapula; humerus; ulna
______ is the insertion for radioulnar pronators and supinators
radius
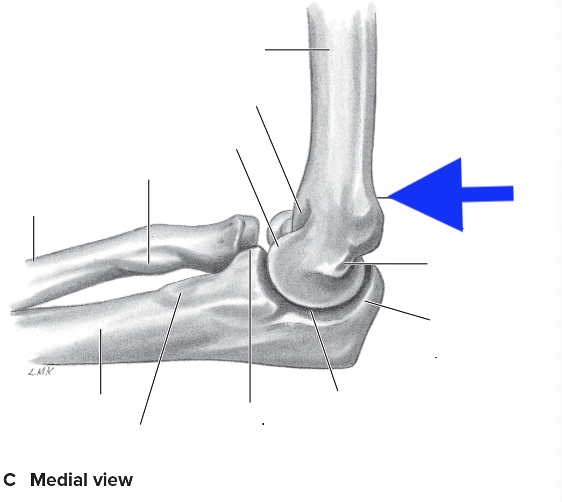
medial supracondylar ridge
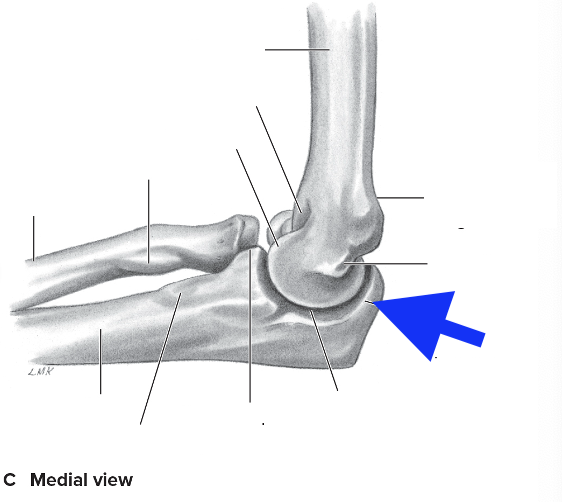
olecranon process
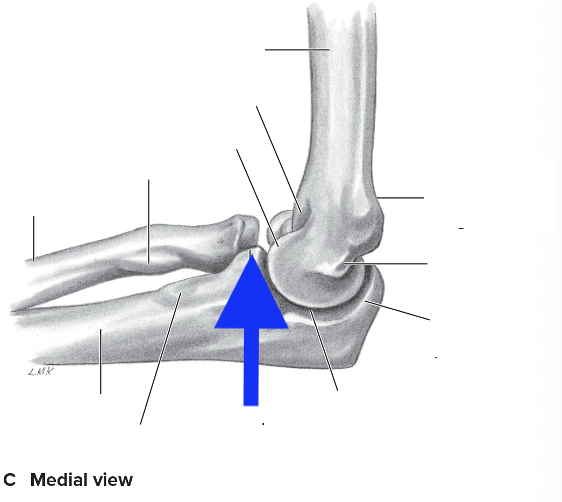
coronoid process
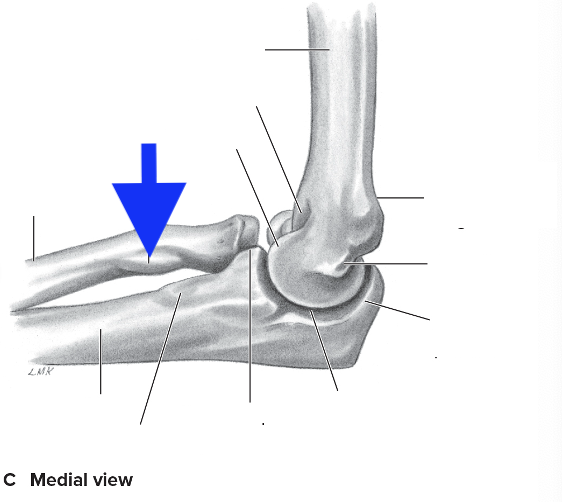
radial tuberosity
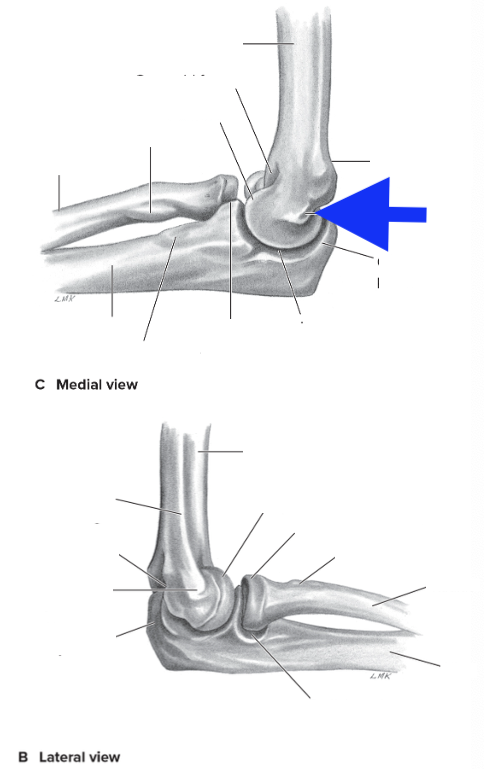
medial epicondyle
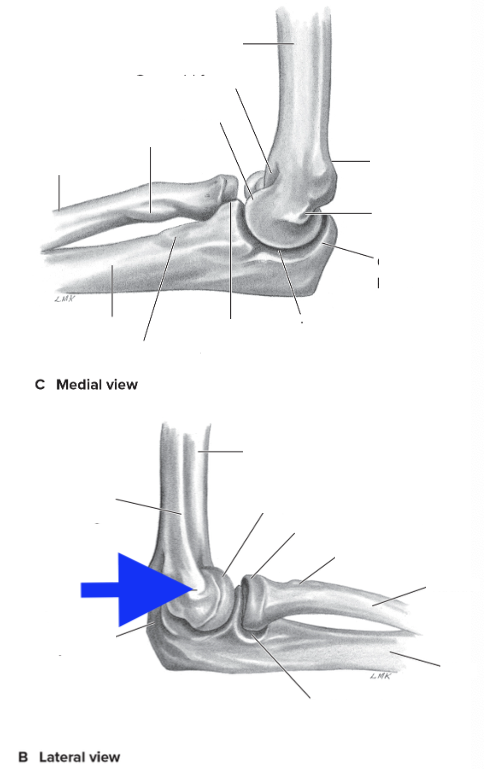
lateral epicondyle
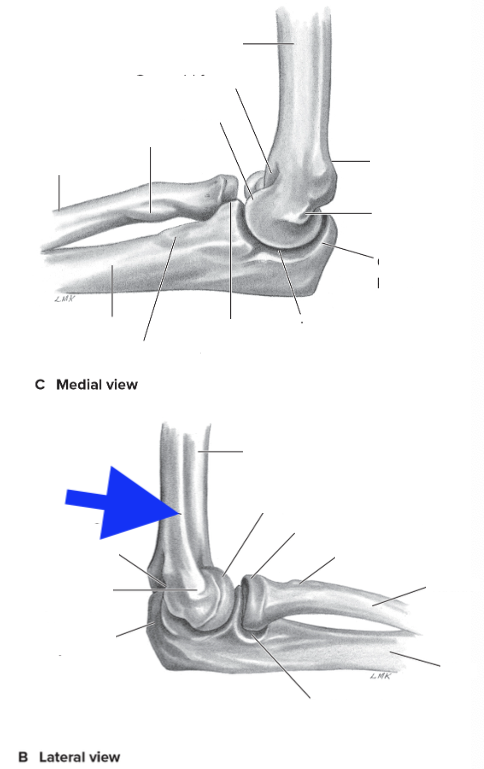
lateral supracondylar ridge
the elbow only allows ________ and _________ movements
flexion; extension
2 interrelated joints for the elbow
humeroulnar and radiohumeral
As elbow reaches full extension, the __________ _________ is received by __________ _____
olecranon process; olecranon fossa
With elbow in full flexion, __________ ________ fits into ________ _____
coronoid process; coronoid fossa
As elbow flexes 20 degrees or more, its bony ______ is unlocked, allowing for more side-to-side ______
stability; laxity
Stability in ______ is more dependent on the _______ (radial) collateral ligament & the _______ (ulnar) collateral ligament
flexion; lateral; medial
_____ collateral ligament is critical in providing _______ support to prevent elbow from _______ when stressed in physical activity
ulnar; medial; abducting
particularly crucial to high-velocity sporting activities requiring optimal medial elbow stability like baseball pitching
ulnar collateral ligament (UCL)
“Tommy John procedure” is conducted on what?
ulnar collateral ligament (UCL)
the “Tommy John procedure” is UCL surgical reconstruction using a tendon ______ such as ________ ______ tendon
graft; palmaris longus
_______ collateral ligament provides lateral stability & is rarely injured
radial
_______ ligament provides a sling effect around radial head for stability
annular
Elbow moves from _ degrees of extension to ___ to ___ degrees of flexion
0; 145; 150
In anatomical position, it is common for forearm to deviate laterally from arm 5 to 15 degrees
carrying angle
carrying angle is slightly greater in _________ limb than in __________ limb due to adaptive changes from ______ stress
dominant; nondominant; valgus