Year 1 Allied Sem 2 SAC 2
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Types of PPE used in healthcare?
Gloves, aprons, masks, protective glasses, surgical hats
Donning procedure?
Perform hand hygiene first. Put on a gown, then place on your face mask and fit it to the bridge of your nose. Next put on protective eyewear or a face shield. Finally, place on gloves.
Doffing procedure?
Start removing PPE in the patient's room as far away from the patient as possible. Take off gloves (remembering outside is contaminated) and discard. Perform hand hygiene. Take off gown and fold it into a bundle before discarding. Perform hand hygiene. Leave patients room, perform hand hygiene and remove face shield or protective eye wear. Perform hand hygiene, take off mask and perform hand hygiene
What is environmental cleaning?
the process of removing dirt and germs from surfaces to create a hygienic space that prevents the spread of infection for patients, visitors, and staff
Difference between low risk and high risk surfaces?
Low risk surfaces are not touched often such as often and administration areas, whereas high risk surfaces are frequently touched and come into contact with patient’s broken skin such as operating theatres and treatment rooms
Difference between disinfectant and antiseptic
Disinfectants are for hard, non-living surfaces, while antiseptics are for living tissues such as skin
Describe routine cleaning for low risk surfaces
walls, floors and ceilings should be vacuumed once a day to remove any debris, and then mopped using a diluted detergent.
Describe routine cleaning for high risk surfaces
should be cleaned more than once a day using a detergent solution for general purpose cleaning. Doorknobs, light switches and hand rails are high risk surfaces.
Describe enhanced cleaning
undertaken when there is an outbreak of infections to remove germs by thorough cleaning followed by disinfection. The disinfectant used should have antiviral activity. Wipe the area in solution using a disposable cloth, ensuring you wear gloves and a mask. Wash your hands thoroughly after.
Describe how to clean a blood spill
1. Apply the appropriate PPE
2. Ensure the affected area is safe and no further spill occurs
3. Use a disposable absorbent material to clean up the spill
4. Dispose of the contaminated material following the correct procedure
5. Clean the area using a detergent-disinfectant solution
6. Thoroughly dry the area or display the correct hazard signage
Describe process for changing linen on a hospital bed
Appropriate PPE must be worn, and linen removed should be immediately bagged into an appropriate laundry wastebasket. If the linen is contaminated with bodily fluids, it should be placed in a yellow biohazard bag. Hand hygiene should be performed immediately after handling the used linen.
How does a mechanical lift assist with movement?
assists the movement of people unable to move or stand by themselves using a sling and hoist. Eliminates the need for manual lifting that could cause injury, and provides stability during transfers from one location to another.
Safety considerations for mechanical lift
The sling and hoist must be appropriately sized for the patient's height and weight. Check the sling for rips, tears and faults.
How do slide sheets assist with movement?
used for the movement, repositioning and transfer of patients to reduce the risk of musculoskeletal injuries as not lifting is required. It also reduces the risk of skin tears (should not be in contact with bare skin) and ensures comfort during transfers.
How do chairs with armrests assist with movement?
provides support to help users get in and out of the chair, especially for those with mobility issues, by providing more stability.
Safety consideration for chairs with armrests
the chair must be sturdy and stable, and the height should be appropriate for the patient to place their feet on the floor.
How do wheelchairs assist with movement?
provides a mobility solution for those who cannot walk or have difficulty walking, allowing them to move independently.
Safety considerations for wheelchairs
Ensure the wheelchair is in good working order, sturdy, and no obvious signs of wear and tear present.
How do shower chairs assist with movement?
provide a stable, seated surface for those with mobility or balance issues. Reduce the risk of slipping and can enable patients to shower independently.
Safety considerations for shower chairs
Should be stable, appropriate for the patients size and if a safety belt is present it should be secured around the patient
How do mobility walkers assist with movement?
provide a stable frame for balance, distributing weight to reduce joint stress and allow for safer walks.
Safety considerations for mobility walkers
Ensure it is the appropriate height, and that breaks and wheels work correctly.
How do motorised beds assist with movement?
assist patients in movement or transferring and reduce the number of injuries to carers and staff.
Safety considerations for motorised beds
Bed should be suitable to the height of carer in a transfer, and brakes should always be engaged with rails up unless the bed is being moved
How do stretchers and gurneys assist with movement?
provide stable and secure way to transfer immobile or injured patients which makes the movement easier for both the patient and the handler. Ensures patients are moved gently and safely
Safety considerations for stretchers and gurneys
Check for correct assembly and stability, and that belts are used in a transfer if present. Side rails should be up when moving stretchers.
Safety and cleaning procedures for movement equipment
Clean equipment between patients immediately after use
Dispose of single use equipment
Perform regular checks and maintenance on equipment to ensure it is in good working order
Plan the movement before it occurs and ask for assistance if needed
Steps in assisting with movement
Prepare the environment
Explain the movement
Seek consent and cooperation
Assist with movement
Complete, evaluate and return equipment
How to prepare environment for a move?
Ensure all equipment is in the required place, clear room of clutter so that it is clean and ensure room is quiet for effective communication.
How to explain the movement?
speak directly to patient and inform them of what is happening. Ensure they are comfortable with the movement and aware what is happening. Refer to communication protocol.
How to seek consent and cooperation for movement?
seek consent and cooperation of a person before you can assist moving them. Ask if they are okay for you to touch them while you assist with the movement.
How to assist with movement?
maintain communication throughout the move by explaining the movement and providing a heads up of what is going to happen. Ensure they are comfortable by asking if they feel any pain or discomfort
How to reflect, evaluate and return equipment after movement?
Evaluate movement, return all equipment to designated area, clean equipment. Check equipment for any faults, report and tag to maintenance. If incident occurred, fill out report.
Main function of the digestive system
Ingest food, digest it into smaller molecules, and absorb the resulting nutrients
Ingestion
passing of food fluids from the mouth into the alimentary tract
Propulsion
the movement of the ingestion food/fluids along the tract (aided by peristalsis)
Digestion
breaking down of the food mechanically and chemically (enzymes)
Absorption
nutrients from digested foods entering the bloodstream
Elimination
undigested foods excreted after processing in the bowel
What are carbs broken down into and what do they do?
broken down into glucose which is the body’s main source of energy
What are lipids broken down into and what do they do?
broken down into fatty acids and glycerol which provide energy, aid in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins and facilitate nutrient transport.
What is protein broken down into and what do they do?
broken down into amino acids, which form the building blocks of enzymes and other proteins required for bodily functions such as enzymes.
Function of oral cavity
mechanical & chemical digestion. Tongue chews and swallows. Teeth tear, grind, cut and break down food.
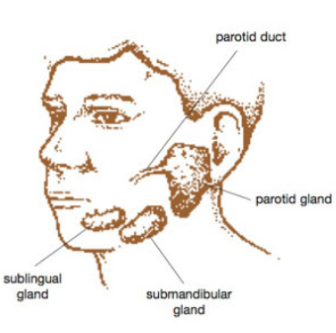
Function of salivary glands
produce saliva to begin chemical digestion and moisten food for mechanical digestion. Saliva contains water to moisten food, mucous to bind food into a bolus, salivary amylase to begin breaking down starch and antibacterial compounds to reduce microbes in mouth.
Locations of salivary glands
Function of oesophagus
transport food and liquid from mouth to stomach using peristalsis - a series of wavelike muscle contractions that push food downward
Function of stomach
Muscular organ that stores food after swallowing. Churns and mixes food using strong muscular contractions (mechanical). Secretes gastric juices containing HCl to create acidic environment, pepsin to break down proteins and mucus to protect the stomach lining (chemical). Food turns into chyme.
Function of pancreas
produces amylase (break down carbs), lipase (break down fats) and trypsin (break down protein) which are released into the duodenum. Bicarbonate is also released to neutralise stomach acid in chyme
Function of liver
produces bile, stores nutrients (e.g. glycogen), detoxifies harmful substances and processes nutrients absorbed in small intestine.
Function of gallbladder
stores and concentrates bile, which is released into duodenum via bile duct when fatty foods enter small intestine.
Function of bile
produced by liver, stored in gallbladder to emulsify fats by breaking large fat droplets into smaller ones to increase surface area for more effective digestion.
Function of small intestine
digestion of proteins, carbohydrates and fats and absorption of nutrients
What does each section of the small intestine do?
duodenum receives chyme from stomach, bile from bile duct and digestive enzymes from pancreas. Jejunum is main site for digestion and absorption of nutrients. Ileum absorbs remaining nutrients and bile salts.
Function of large intestine
absorbs water and salt from undigested food to form solid faeces. Also houses gut flora that break down some fibre to produce vitamin K and B vitamins. Compacts waste material and stores it in the rectum, defecation occurs through anus.
What is faeces?
solid waste eliminated from the body after digestion and absorption are complete.
Describe how nutrients are absorbed in the small intestine
The inner lining of the small intestine is covered in villi and microvilli to greatly increase surface area. Each villus contains a central core with a network of blood capillaries and a central lacteal. Water soluble glucose and amino acids enter blood capillaries, and fatty acids are absorbed into lacteals as part of the lymphatic system.