11.3 M phase
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
M-Cdk
self-reinforcing cyclin-Cdk complex
explosive activity increase = abrupt transition from G2 to M phase
Prophase
phase in which phosphorylations by M-Cdk often occurs
Phosphorylation
process done by M-Cdk to certain substrates involved in prophase processes
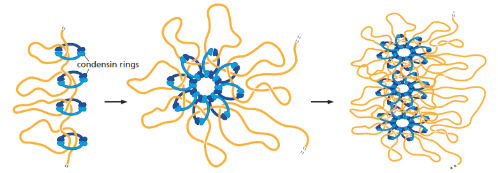
Condensins
its phosphorylation triggers assembly of its complexes onto DNA
promote condensation of chromosomes during prophase
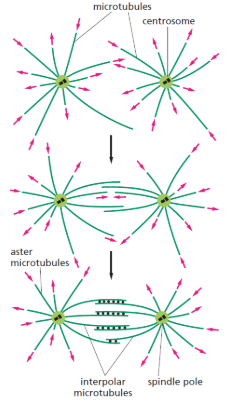
Microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs)
its phosphorylation facilitates the formation of spindle fibers
for when MTs of centrosomes interact with one another
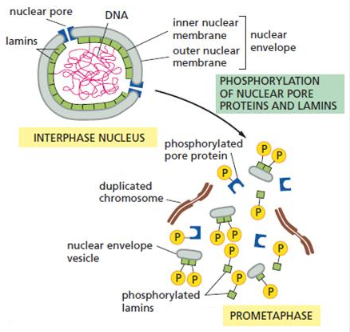
Lamins
its phosphorylation results in nuclear membrane disassembly
Prometaphase
phase that starts abruptly with breakdown of the nuclear envelope
when MTs attach to chromosomes
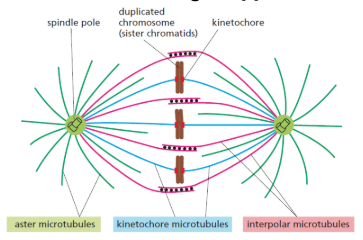
Kinetochores
protein complexes that assemble on the centromeres of duplicated chromosome
recognizes specific DNA sequence at the centromere
Metaphase plate
Formed when chromosomes line up at spindle equator halfway between the spindle poles
Event defines beginning of metaphase
Colchicine
drug that blocks tubulin addition
tubulin loss continues while metaphase spindle disappears
Sister chromatids
part of DNA that’s suspended under tension as they oscillate back and forth even after they are aligned
Securin
inhibitory protein bound to separase before anaphase
Separase
proteolytic enzyme that destroys cohesin
Anaphase-promoting complex (APC)
complex involved in ubiquitylation of certain proteins in anaphase
phosphorylation activated by M-Cdk
Ubiquitylation
process that causes proteins to be targets for proteasomes destruction
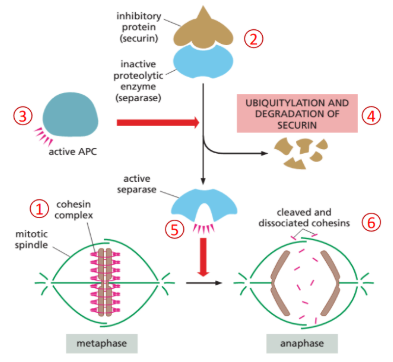
6 steps of sister chromatids separation
Cohesins hold sister chromatids together
Securin bind and inhibits separate from destroying cohesins
Anaphase-promoting complex (APC) is activated by M-Cdk
Ubiquitylation of securin catalyzed by APC
Securin destructed by proteasomes
Active separase cleave cohesin complexes to let sister chromatids be pulled apart
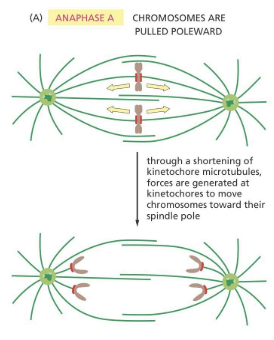
Anaphase A
anaphase stage when kinetochore MTs shorten
attached chromosomes are pulled poleward
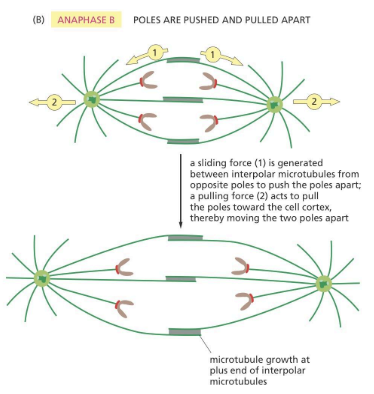
Anaphase B
anaphase stage when spindle poles move apart
involves kinesin and dynein
Kinesin
motor protein in anaphase B
pushing spindle poles apart
Dynein
motor protein in anaphase B
pulls the actual poles apart
Spindle assembly checkpoint
checkpoint that controls onset of anaphase and exit from mitosis
eg. chromosome missed by the spindle sends “stop” signal to
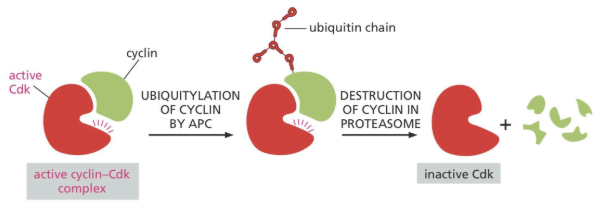
4 steps of M-Cdk inactivation
Phosphorylated active cyclin-Cdx present
cyclin-Cdx ubiquitylated by APC
M cyclin degraded
Inactivated M-Cdk complex exit mitosis
Telophase
phase when:
chromosomes decondense
mitotic spindle disassembles
Nuclear membrane re-forms
nuclear pore proteins & nuclear lamins are dephosphorylated