Research Methods Final
1/261
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
262 Terms
Bivariate correlations
associations that involve exactly two variables
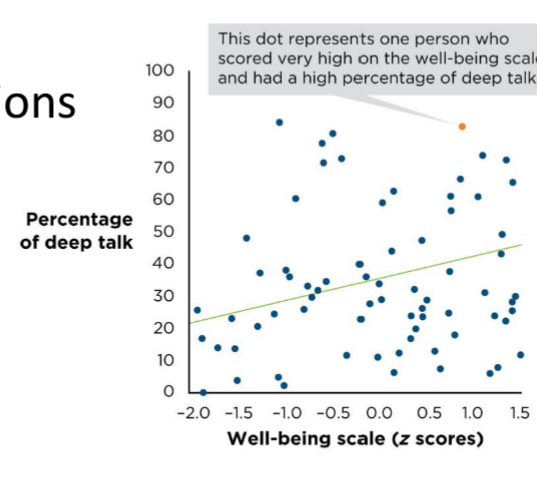
What relationship is shown?
positive correlation
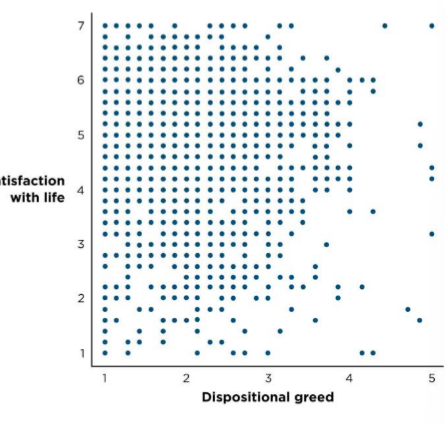
What relationship is shown?
weak negative correlation
What makes a study correlational? (have)
having two measured variables
Construct Validity
measurement of variables
reliability of measure
measurement of correct measure
evidence for face, concurrent, discriminant, and convergent validity
Statistical Validity
strength of relationship
precision of estimate
outliers?
restriction of range?
association curvilinear?
Effect Size
strength of association btwn 2+ variables
larger effect sizes are more importent
CI - 0
95% CI does include 0 → good chance of finding no difference btwn groups if experiment is run again
95% CI does not include 0 → statistically significant association
Curvilinear Association
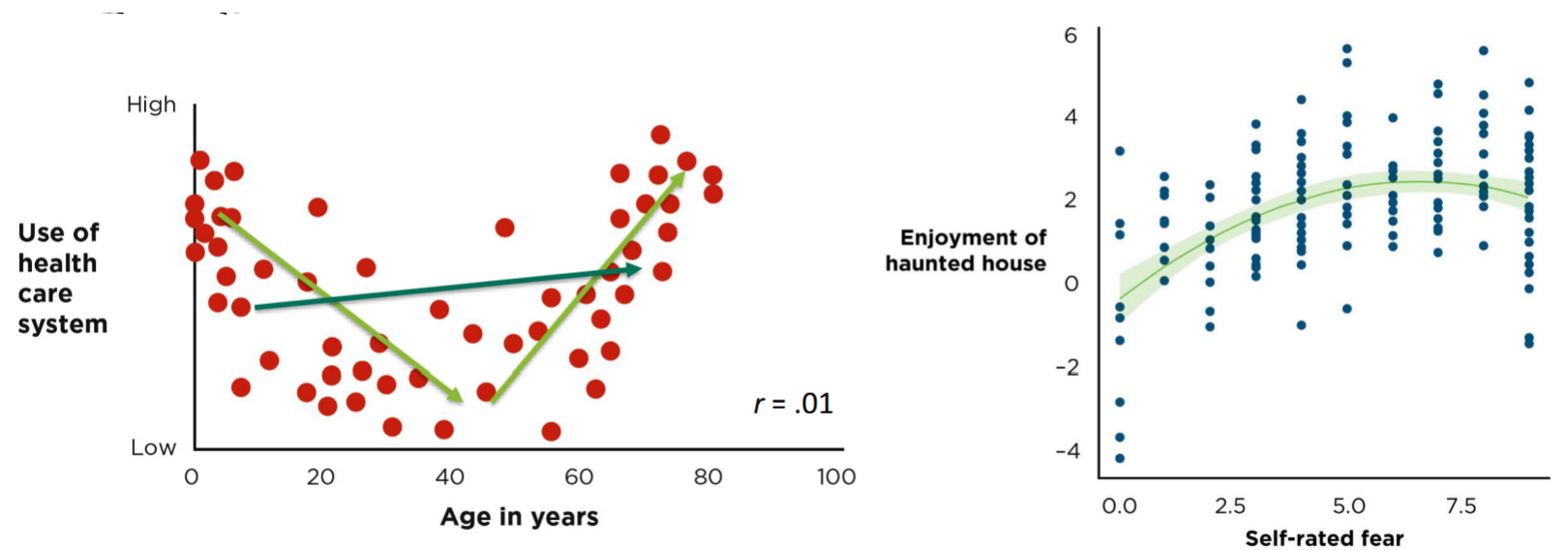
Three Causal Criteria
Covariance - no relation, no causation
Temporal Precedence - what came first
Internal Validity - no alternative explanations for the relationships
External Validity
generalizability, moderating variables
Moderating Variable
variable that effects the experiment
interaction
Multivariate Designs
involve more than 2 measured variables
longitudinal → temporal precedence
multiple regression → rule out 3rd variables
pattern and parsimony → dif correlations support one cause theory
Longitudinal Design
measuring same variable in the same people at several different times
developmental psychologists, closer to causal claim
used for variables that people cannot be randomly assigned to - preferences, smoking
Longitudinal Design Results
cross-sectional correlations
autocorrelations
cross lag correlations
Cross sectional correlations
relation btwn two variables measured at the same timepoint. no temporal precedence inferences
Autocorrelations
relation of a variable with itself over time
both variables are consistent over time
Cross Lag Correlations
relation btwn an earlier measure of one variable and a later measure of a second variable
temporal precedence inferences
Longitudinal Studies - Causation
covariance - significant cross sectional correlations
temporal precedence - significant cross lag correlations
internal validity - 3rd variables may be involved and must be considered w subsequent analyses
Multiple Regression Analyses
multivariate regression
helps rule out a 3rd variable - indicates whether a 3rd variable affects the relationship
does not establish causation - no temporal precedence, only considers the 3rd variables specifically analyzed
adds more predictors to a regression, regression in pop media
Criterion Variables
dependent
Predictor variables
independent
Beta
used to test for 3rd variables, indicates relationship btwn predictor variable and criterion variable
similar interpretations to r
b = non standardized β. cannot compare b vals on the same table, can compare β vals on the same table
If Beta is close to 0
the third variable is not significant
Regression analysis
helps control for several 3rd variables at once
examines beta’s for all other predictor variable → which factors most strongly predict the factor under investigation
Regression in Popular Media Articles
analyses and results are elaborated in a narrative way
controlled for, adjusting for, considering
Establishing Causation Gold Standard
randomized experiment
Parsimony
simplicity, occam’s razor
Pattern and Parsimony
useful for getting causality
based on summation of studies
Pattern and Parsimony in Popular Media
journalists do not always fairly represent
often report just one study - selective presenting on only one part - missing the cumulation
Mediator vs. Third Variables
multiple regression, SEM
sim - multivariate research designs, detected w multiple regression
dif - 3rd var are external to the bivariate correlation (problematic), mediators are internal to causal variable (not problematic)
mediators are fine, third variables fuck up the study
Mediators vs Moderators
mediators - why
moderators - for whom, when
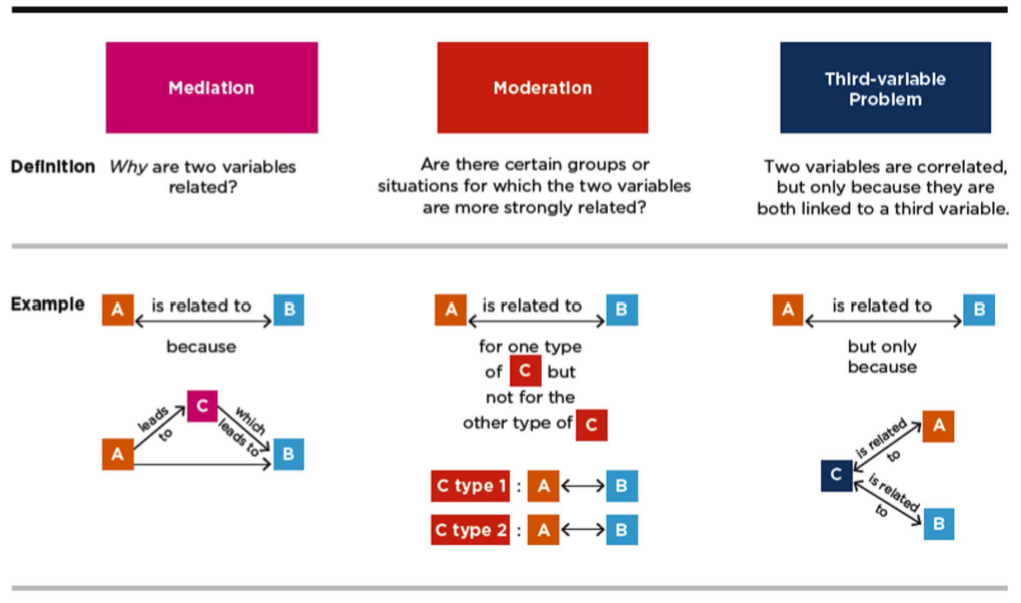
Multivariate Designs and Validities
Internal validity
Construct validity - all measured variables
External validity - random sample
Statistical validity - CI, p, β, replication
Quasi-Experiments
experiments where there is not full control over the IV (quasi-independent variable)
ex. nudging people towards organ donation (some countries are opt-out of giving donations), psychological effects of cosmetic surgery, pop shows and suicide, investigating the effect of legislation on opioid abuse (nonequivalent control group, interrupted time series)
Quasi-Experiment Internal Validity
selection effects - independent groups only, unaccounted for dif btwn groups, wait list designs
design confounds
maturation threats
history threat
regression to the mean
attrition
testing and instrumentation
observer bias, demand char, placebo effects
Why do Quasi-Experiments?
real world opportunities, external validity, ethics, construct validity (great for qIV), statistical validity
Quasi-Exp vs. Correlational Study
both may use independent groups, neither use random assignment (pre-existing groups) nor manipulated variables
quasi target specific subjects/groups
Participant Variable
categorical, levels are measured rather than manipulated
used in studies for documenting similarities and differences assoc with social identities
Quasi-IVs vs. Participant Variables
Quasi-independent variables focus more on potential interventions (e.g., laws) and less on individual differences
Small N Designs
very small sample: low as one. HM (memory), Piaget (child dev), Ebbinghaus (forgetting curve)
each participant is treated separately, data for each individual is presented, careful designs, therapeutic settings
Large-N Designs Differences from Small-N
group participants, data represented as group averages, large samples → precise estimate, basic and applied research

Balancing Priorities in Case Study Research
experimental control, manipulation, and replication → spec tasks assessing dif types of memory
studying special cases
Disadvantages of Small-N Studies
Internal validity - patient often has many issues
External validity - difficult to generalize results → triangulation
Stable Baseline - Small-N Design
multiple stable observations before starting a treatment
issue with regression to the mean
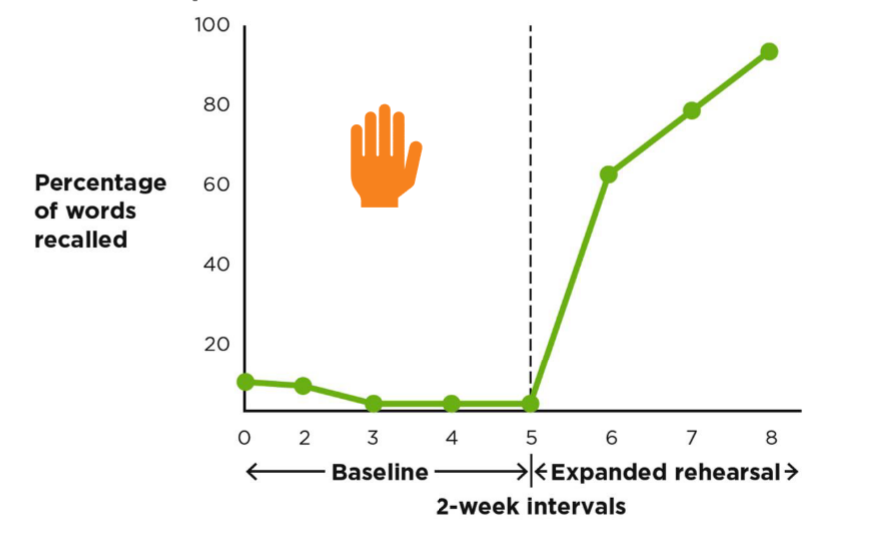
Multiple-Baseline Designs - Small N
beginning of intervention is staggered across situations, times, and contexts
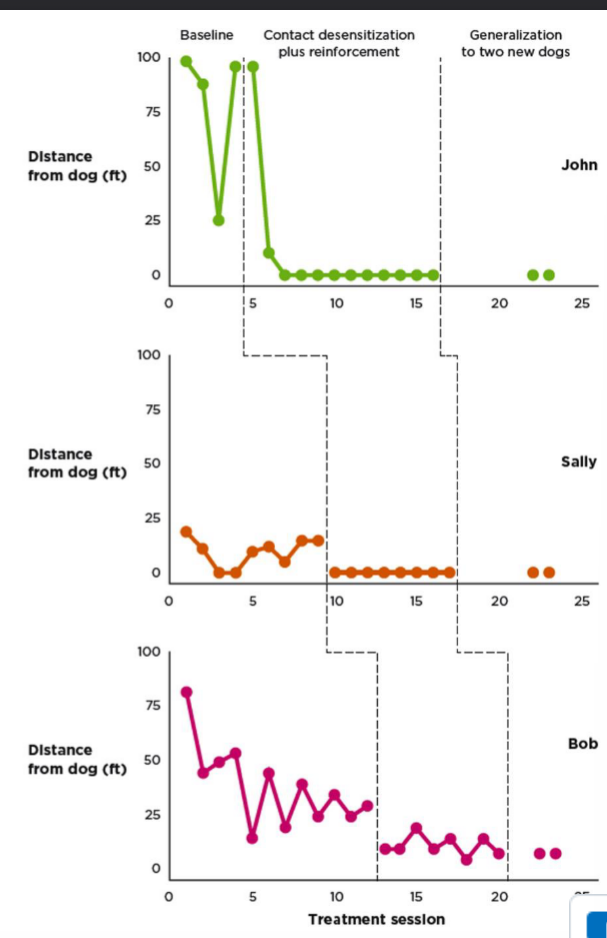
Reversal Design - Small N
treatment is removed to see if the behavior reverts
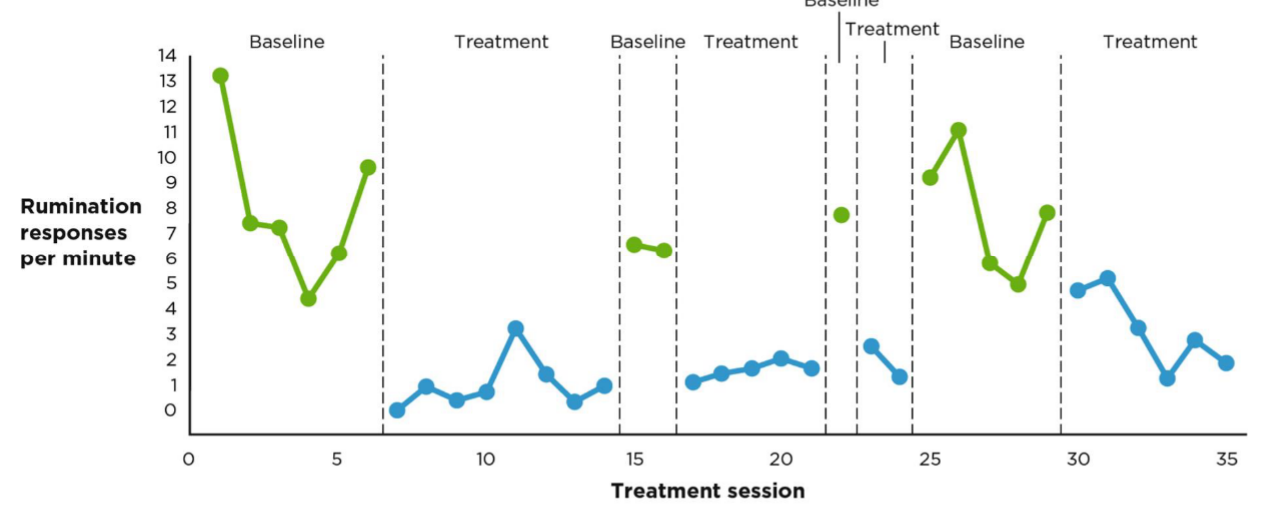
Small-N - Validities
Internal - high if carefully designed
External - problematic depending on goal. triangulation
Construct - high if using precise definition and observations
Statistical - visual summary of results and assessment of improvement, non assessed with traditional inferential stats
Replicability/Reproducibility of Results
A study and its results can be repeated with similar outcome
Direct Replication
exact, close replication of the original study
Conceptual Replication
Same research question investigated with different procedures
Replication plus extension
replication of a previous study with additional questions
Replication Projects
recent trend in psychological science
one study, many labs
many labs, many studies
Why Might a Study Not Be Replicable?
contextually sensitive effects
number of replication attempts - only one may be inconclusive
issues with original study
Meta-Analysis
statistical analysis that combines results of multiple scientific studies - published and unpublished
NOT a review article
Strengths and Limitations of Meta-Analysis
file drawer problem - overestimate true effect size as only positive results were published
Replicability and Popular Media
journalists do not always consider the importance
many only report on the latest not the summation of the body of literature
Research Transparency and Credibility
Communality - make data public
Disinterestedness - share data even when the results do not support the hypothesis
Potential issues - underreporting null, harking, small samples, p-hacking
HARKing
hypothesizing after results known

Using Small Samples

Underreporting Null Effects

p-hacking

Necessity of External Validity
generalizing to other participants - 89% underrepresentated (WEIRD)
from sampling strategy not sample size
generalizing to other settings
ecological validity
Does a study have to be generalizable to many people?
theory testing mode - test association or causal claims. Internal > external
generalization mode - for generalizing findings from sample to population
Does a study have take place in a real world setting?
Ecological Validity
aspect of external validity in which the focus is on whether a laboratory study generalizes to real world settings
Generalization Mode
frequency claims always, sometimes association and causal claims
sample is crucial
WEIRD
Western Educated Industrialized Rich Democratic
External Validity - Real World
field setting, high external validity
ecological validity - may not generalize
prioritize real world relevance and ecological validity
Experimental Realism
when laboratory research is just as realistic as research conducted in the real world
Lab studies prioritize ________ and ________ validity.
precision, internal
Theory Testing - Real World
prioritize internal validity - experimental realism
create artificial situations to minimize confounds
increasing the number of IVs
Non-Equivalent Control Group Interrupted Time-Series Design
quasi-experiment
2+ groups without random assignment
measured on DV before, during, and after interruption
Nonequivalent Control Group Pretest/Posttest Design
quasi-experiment
1+ treatment group, 1 comparison group, no random assignment
1+ pretest, 1+ posttest
Interrupted Time Series Design
quasi experiment
measured on DV before, during, and after the “interruption”
Wait-List Design
experimental design for studying therapeutic treatment
random assignment, some get immediate treatment, some get treatment after a delay
Nonequivalent Control Group Pretest/Posttest Design
quasi experiment
1+ treatment, 1+ comparison, NOT random assignment
1+ pretest, 1+ posttest
Simple Experiment Examples
Exposure to peers’ pro-diversity attitudes increases inclusion and reduces the achievement gap
Infants make more attempts to achieve a goal when they see adults persist
Manipulated variable
controlled, independent
contains levels (conditions)
Measured variable
recorded, dependent, outcome
Control Variable
any variable that an experimenter holds constant
Experiments - Causal claims
experiments establish covariance, temporal precedence, and establish internal validity if well designed and therefore support causal claims
Groups of an experiment
control - no treatment
treatment - 1+ treatment conditions
comparison - placebo
Design Confound
variable that systematically varies with IV - alternative explanation
issue for internal validity
Selection Effect
avoid with random assignment
or matched groups - put in groups then randomly assign from those groups
In an experiment where participants were shown one of three potential photos of a person (face titled up, face looking straight, face titled down) with the same facial expression shown in each and recorded how dominant the person appeared using the criteria “this person would enjoy having control over others” as the participant response, what is the independent variable?
the degree of face tilt
Why would faces of the same expression be used in a study testing the effects of head tilt on perception of how dominant a person is?
to prevent facial expression from being a confound in the study
Independent groups design
between subjects, between groups design
2+ groups, each experience 1 level of the independent variable
IGD Posttest Only
participants are randomly assigned to IV groups and tested on the DV just once
better for time limited/searching tasks

On plots the x axis is normally…
Independent
IGD: Pretest/Postest Design
participants are randomly assigned to at least 2 different groups and are tested on the key dependent variable twice (one before IV, one after)
Want: same before IV, markedly different after IV exposure
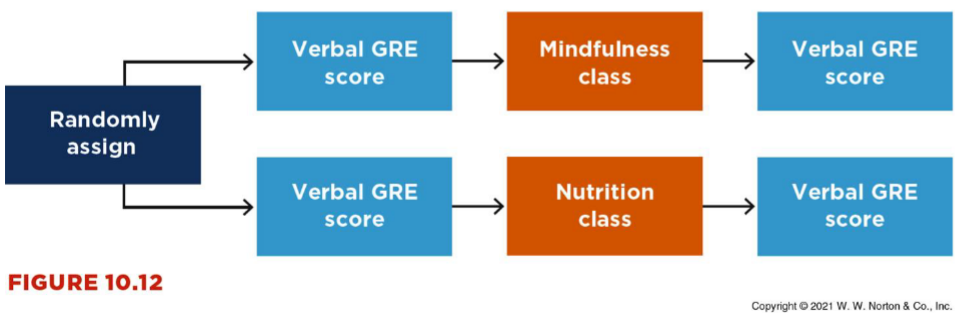
Within Groups Designs
repeated measures, concurrent measures
covariance, temporal precedence, internal validity - order effects (avoid by counterbalancing → up internal validity)
Adv: participants in groups are equivalent (same participants), require fewer participants
Disadv: order effects, may not be practical/possible, experiencing all levels of the IV changes
the way participants act - guess hypothesis
Repeated Measures
participants are measured on DV more than once, after each exposure to each lvl of the IV
Concurrent Measures
participants are exposed to all levels of IV at the same time - single preference is DV
measure once
Order Effects
when being exposed to one condition affects how participants respond to other conditions
practice/fatigue, carryover
Practice Effects
Fatigue, participants get better or worse at a task due to practice or fatigue
Carryover effects
contamination carrying over from one condition to the next
Counterbalancing
full - all possible combinations are representing
partial = some of the possible orders are represented - latin square = every condition appears in each position at least once
Validities
• Construct validity: How well were the variables measured and manipulated?
• External validity: To whom or what can the causal claim generalize?
• Statistical validity: How much? How precise? What else is known?
• Internal validity: Are there alternative explanations for the results?
Construct Validity - Variables
dependent - how well were they measured?
independent - how well were they manipulated?
Manipulation checks, pilot studies