Chapter 16- The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle, Mitosis, and Meiosis
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
What is cell division?
the process of making daughter cells from a parent cell
What did scientists observe in Eukaryotic Cell division?
Noticed a cyclic pattern→ Cell Cycle
What can be observed via a microscope during the cell cycle?
Chromosomes becoming compact
How many human chromosomes?
46 homologous chromosomes.

What are the chromosomes called in humans?
44 chromosomes are called autosomes.
2 are the sex chromosomes.
What does autosome mean?
non-sex chromosomes in all chromosomes
What does Karyotype mean?
reveals the number of chromosomes in an actively dividing cell
How to write the Karyotype of a Human somatic cell?
2n=46
(2n)=Ploidity
46= total number
What is Ploidy?
number of chromosomes in homologous chromosomes
Diploid or 2n- humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes
Haploid or n- gametes have 1 member of each pair of chromosomes or 23 total chromosomes
What are the phases in cell division?
G1, S, G2, Mitosis, and Cytokinesis.
What is interphase?
G1+S+G2
You do not see the chromosomes in interphase
you see chromatin
What happens in the G1 phase?
Cell growth: a mother cell has 6 chromosomes, 2 sets of 3 each.
ploidy: 2n=6
What happens in the S phase?
DNA replication
chromosome replication produces 6 pairs of sister chromatids
After replication, two copies stay joined to each other
What happens in the G2 phase?
Replication is completed. The cell prepares to divide.
synthesizes proteins needed during mitosis and cytokinesis
What happens in Mitosis?
Nucleus breaks apart, and the replicated chromosomes condense in preparation for mitosis.
separation of sister chromatids
What happens in cytokinesis?
Indentation and separation
Two daughter cell are made
What are the checkpoints in the cell cycle?
G1, G2, and M
What is the G1 checkpoint?
Detects mutation and DNA repair, and has more preparation
major checkpoint
What are the checkpoint proteins?
CDK/Cyclin complex- responsible for advancing a cell through the phases of the cell cycle.
CDK is a Kinase (alone= inactivated)
Cyclin helps make it active.
Only activated when everything is good
Cyclin is degraded after the cell enters S phase and mitosis
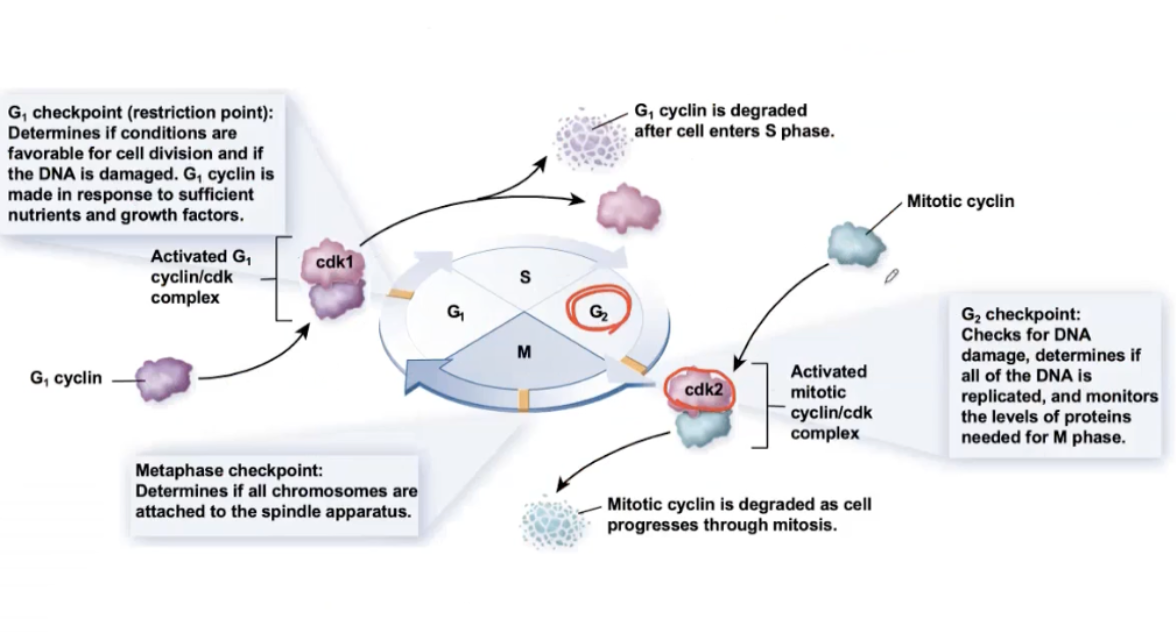
What happens when the CDK/Cyclin complex is persistently active?
Cancer
What happens to the karyotype in mitosis?
The remains the same.
Changes during mitosis:
Chromatin condenses to a chromosome
chromatids tightly associated at centromere (DNA)
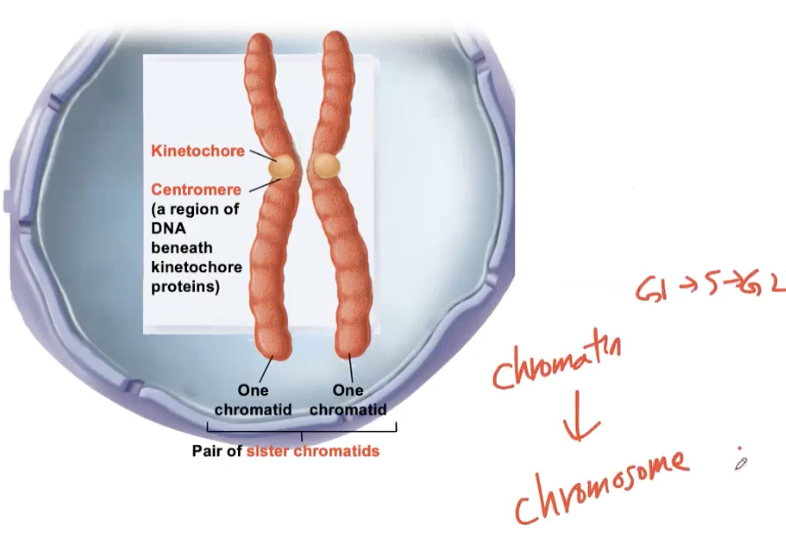
Structure of Chromosome
Kinetochore- protein
Centromere- DNA under the Kinetochore
Centromere serves as an attachment site for the kinetochore (protein) used in sorting chromosomes
Mitosis cycle
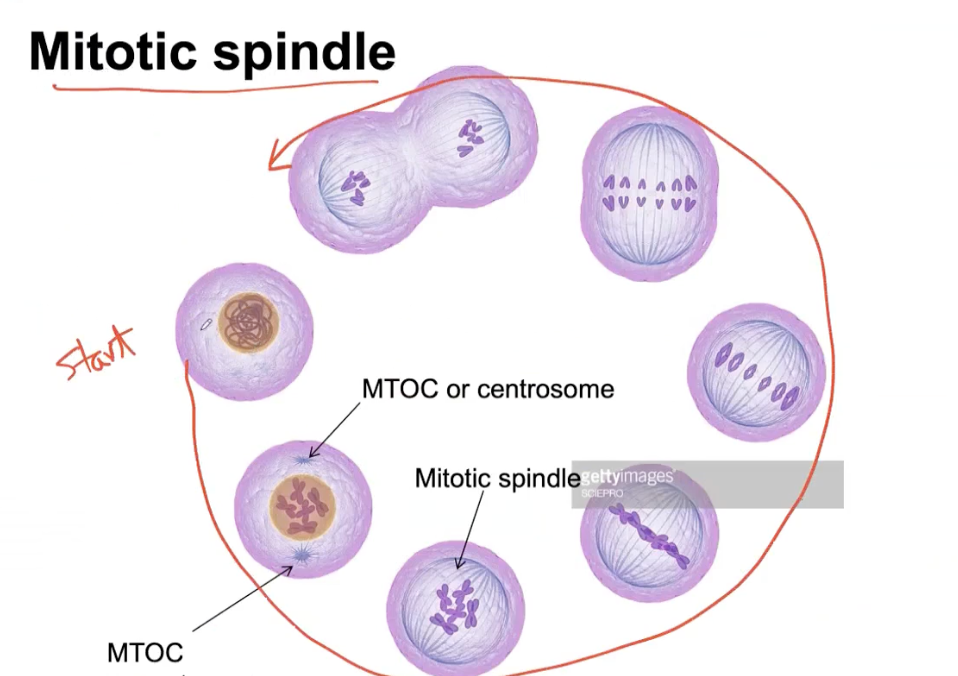
What is a mitotic spindle?
Composed of microtubules
binds to Kinetochore
What are centrosomes?
Microtubule-Phasorganizing center (MTOCs)
duplicated at the beginning of M phase
What are the phases in Mitosis?
Prophase, Prometaphase, Metaphase, Anaphase, and Telophase
What is prophase?
Nuclear membrane breakdown
Chromosome formation
Sister chromatids condense, and the mitotic spindle starts to form. The nuclear envelope begins to dissociate into vesicles. Nucleolus is no longer visible.
What happens in prometaphase?
The nuclear envelope has completely dissociated into vesicles, and the mitotic spindle is fully formed. Sister chromatids attach to the spindle via kinetochore microtubules.
What happens in metaphase?
Sister chromatids align along the metaphase plate
What happens in anaphase?
Sister chromatids separate, and individual chromosomes move towards the poles as kinetochore microtubules shorten. Polar microtubules lengthen and push the poles apart.
What happens in Telophase?
Chromosomes decondense, and the nuclear envelope re-forms.
What happens in cytokinesis?
separates the mother cell into two daughter cells, which begins with a cleavage furrow in animal cells.

B: 4 sister chromatids are made and held together at the centromere
What is required in sexual reproduction?
a fertilization event in which two haploid gametes unite to create a diploid cell called a zygote
What is the ploidy in Meiosis?
2n=46
egg: n=23
sperm: n=23
What is Meiosis?
the process by which haploid cells are produced from a cell that was originally diploid
Meiosis process
Chromatids stay together in Meiosis 1.
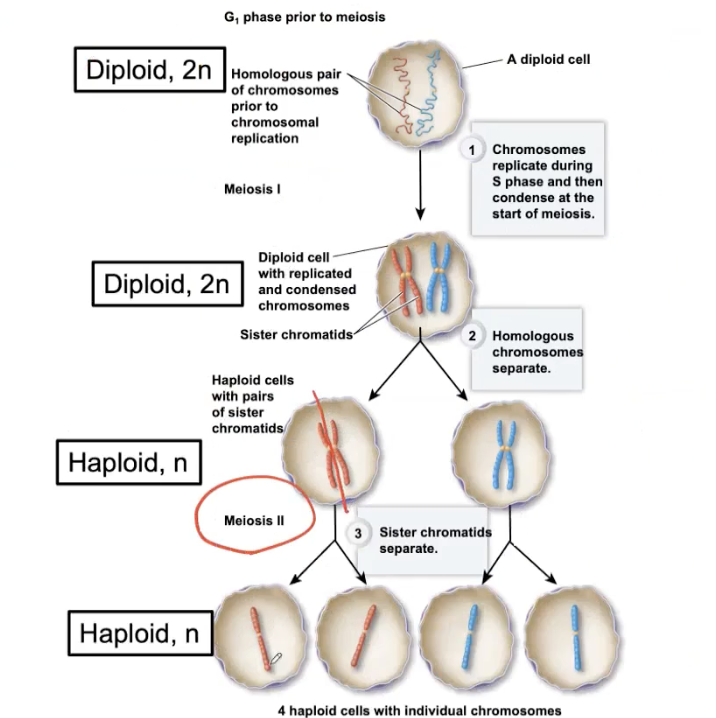
What is the similarity between Meiosis and Mitosis?
Begins after a cell has progressed through the G1, S, and G2 phases of the cell cycle (Interphase)
Note there is no interphase between meiosis I and meiosis II
What are the unique features of meiosis?
during synapsis, homologous pairs form a bivalent (aka: tetrad)
Crossing over (recombination)
Reductive division
What does bivalent or tetrad mean?
Homologous pairs of sister chromatids associate with each other, lying side by side to form a bivalent or tetrad.
Process is called synapsis
What happens during Meiosis?
Homologous chromosomes condense
Synapsis begins
Bivalent/ tetrad is formed
Crossing over occurs (Meiosis I to Meiosis II)
The chiasma becomes visible as chromosome arms separate during late prophase.
What is crossing over?
Physical exchange between chromosome pieces of the crossing bivalent
may increase the genetic variation of a species.
Meiosis I
Homologous chromosomes synapse to form a bivalent and undergo crossing over of their arms. Chromosomes condense, and the nuclear envelope begins to dissociate into vesicles
occurs in prophase I (early event)
The nuclear envelope completely dissociates into vesicles, and bivalents become attached to kinetochore microtubules
occurs in prometaphase I
Metaphase I
Bivalents randomly align along the metaphase plate. Each pair of sister chromatids is attached to one pole.
Anaphase I
Homologous chromosomes separate and move toward the opposite poles.
Telophase I and cytokinesis
The chromosome decondenses, and the nuclear envelope re-forms. The 2 daughter cells are separated by a cleavage furrow.
What is the result of Meiosis I?
Two haploid cells, with no pairs of homologous chromosomes
Meiosis II
Prophase II
sister chromatids condense, and the spindle starts to form. The nuclear envelope begins to dissociate.
Prometaphase
nuclear envelope completely dissociates. sister chromatids attach to the spindle via the Kinetochore microtubules.
Metaphase II
Sister chromatids align along the metaphase plate. Each pair of sister chromatids is attached to both poles.
Anaphase II
Sister chromatids separate, and individual chromosomes move towards the poles as the kinetochore microtubules shorten. Polar microtubules lengthen and push the poles apart.
Telophase II and cytokinesis
Chromosomes decondense, and the nuclear envelope reforms. Cleavage furrows separate the 2 cells into 4 cells.
What is the difference between Meiosis and Mitosis?
Mitosis produces two diploid daughter cells that are genetically identical
Meiosis produces four haploid daughter cells. (Not identical chromsomes)
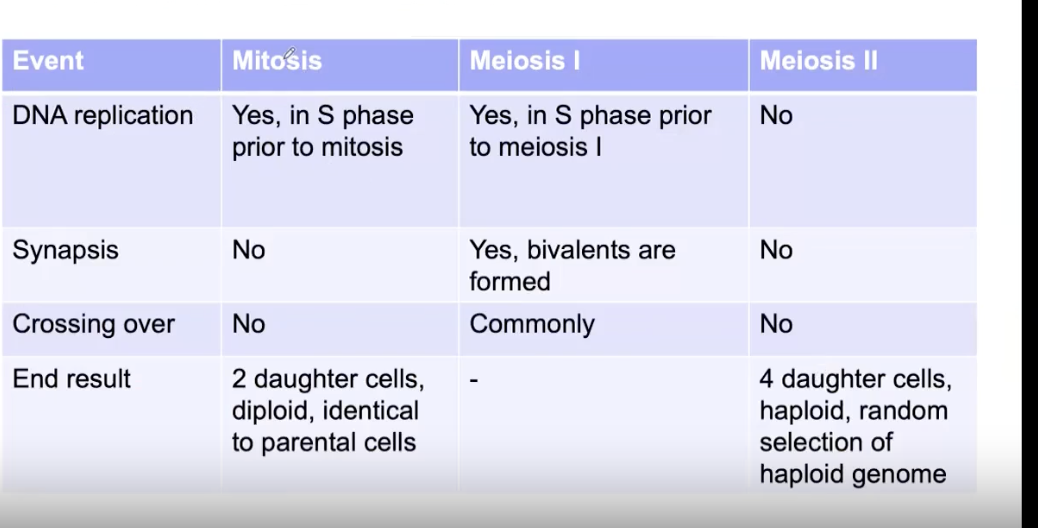
Table of similarity and differences.