Laboratory Safety, Emergency Procedures, and Waste Management Guidelines
1/146
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
147 Terms
Safety Agreement
A document that outlines the responsibilities of students regarding safety in the laboratory, including wearing appropriate personal protective equipment and following laboratory instructions.

Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Items such as laboratory gowns, safety goggles, gloves, and masks that must be worn to ensure safety during experiments.

Laboratory Guidelines
Rules that govern the borrowing of materials, use of reagents, and proper conduct within the laboratory.
Borrowing of Materials
The process by which students must complete a waiver and requisition form to borrow materials for experiments, ensuring they are returned in good condition.
Reagents and Supplies
Chemicals and materials needed for experiments that must be handled according to specific guidelines to prevent contamination and ensure safety.
Emergency Procedures and First Aid Techniques
Protocols that outline steps to take in case of accidents or emergencies in the laboratory.
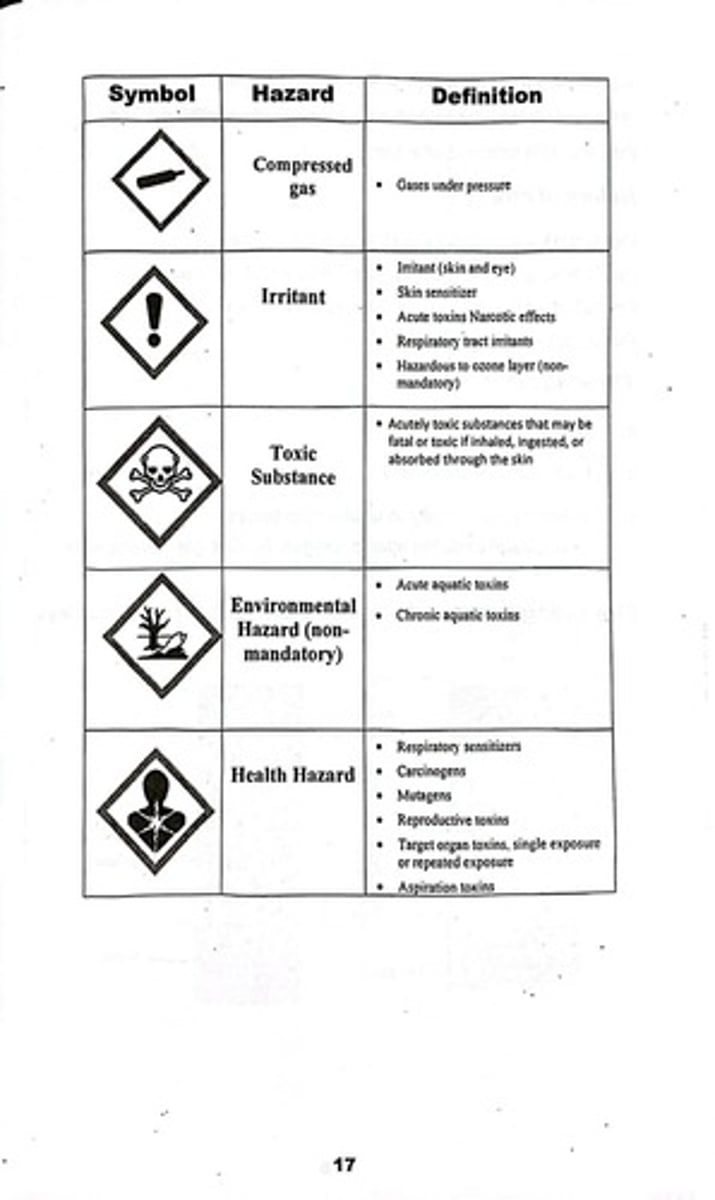
GHS Hazard Symbols
Symbols that indicate the hazards associated with chemicals, as defined by the Globally Harmonized System.
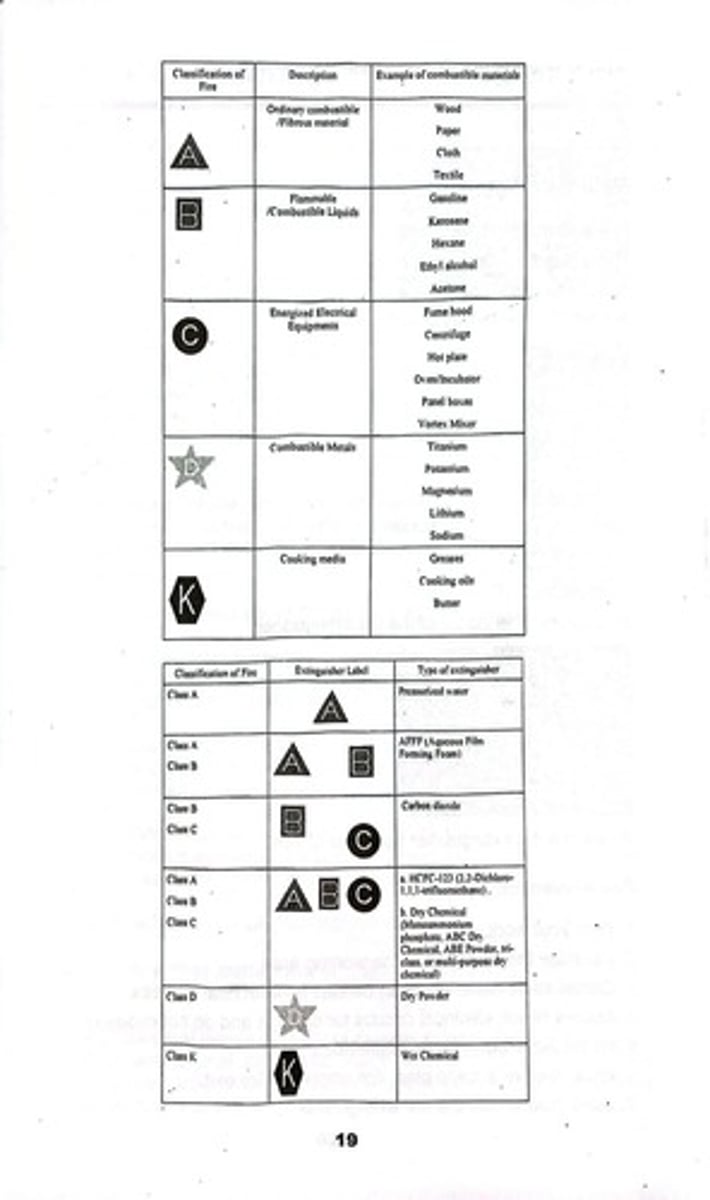
Fire Safety and Prevention
Guidelines that outline how to prevent fires and respond to fire emergencies in the laboratory.

Health Care Waste
Waste generated in the laboratory that requires special handling and disposal procedures to ensure safety and compliance with regulations.
Emergency Hotline Numbers
Contact numbers that should be readily available for immediate assistance in case of emergencies.
Inspection of Borrowed Apparatus
The process of checking borrowed laboratory equipment for damage before and after use.

Chemical Labels
Information on reagent bottles that must be read carefully to ensure proper handling and usage.

Weighing Chemicals
The practice of using weighing boats or watch glasses instead of weighing directly on the pan to prevent contamination.
Contamination Prevention
Methods to avoid cross-contamination of reagents, including using assigned spatulas and droppers.
Documentation of Breakages
The requirement to report any breakages of laboratory equipment to the laboratory assistant for proper record-keeping.
Requisition Form
A form that students must fill out to request materials needed for their experiments.
Laboratory Assistant
A person responsible for assisting students in the laboratory, including handling materials and equipment.
Waiver
A document that students must complete to acknowledge their understanding of laboratory safety guidelines before participating in experiments.
Utilization of Laboratory Facilities
The effective use of laboratory resources to minimize waste and maximize safety during experiments.
Accident Prevention
Strategies implemented to reduce the likelihood of accidents occurring in the laboratory.
Signature over Printed Name
The formal way of signing a document that includes both a handwritten signature and the printed name of the individual.
Instructor's Copy
The version of the safety agreement or waiver that is retained by the instructor after signing.
Student's Copy
The version of the safety agreement or waiver that is retained by the student after signing.
Breakage Reporting
The process of informing the laboratory assistant about any breakages during the conduct of the experiment.
Chemical Amount
Get only the exact amount of chemicals needed for the experiment.
Reagent Labels
Read the labels of the reagent bottles properly before use.
Fume Hood
Always use a fume hood when performing experiments that produce obnoxious and toxic fumes.

Hand Washing
Always wash your hands with soap and water immediately after performing the experiment and removing all PPE.
Laboratory Waste Disposal
Dispose of laboratory wastes properly in designated trash cans and biohazard containers.
Laboratory Gown
Provides protection of skin and personal clothing from incidental contact and small splashes.
Laboratory Safety Mask
Protects against organic solvent fumes and should be worn when weighing out powders or changing solutions.
Goggles or Safety Glasses
Protect your eyes from dust and other elements that might cause irritation.
Laboratory Gloves
Nitrile gloves protect against most chemicals; rubber gloves protect against mild corrosive material.
Removing PPE Sequence
The order for removing PPE: Laboratory Gloves, Goggles or Safety Glasses, Laboratory Gown.

Eating and Drinking Prohibition
Eating, drinking, and chewing gum is prohibited inside the laboratory.

Emergency Awareness
Be aware of the location of all fire extinguishers, exits, and first aid cabinet in case of emergency.
Locker Use
Place all belongings in the assigned locker while conducting the experiment.
Working Area Clearance
Clear your working area and put chairs at the designated location.
Change Gloves
Change gloves when torn or heavily contaminated.
Laboratory Waste Types
Trash can (black bag) for non-infectious waste; yellow bag for potentially infectious wastes; biohazard containers for blood components.

First Aid
The immediate care of a person who has been injured or has suddenly taken ill.

Life threatening emergencies
Situations that require immediate action of the rescuer as well as complex medical follow-up.
Potentially serious situations
Situations that are not life-threatening but require medical care.
Simple first aid
Situations that require basic first aid and self-care.
Goals of First Aid
To restore and maintain vital functions, prevent further injury, and make the victim as comfortable as possible.
ABC of basic life support
Open Airway, Breathing, and Circulation are always the first priority.
Order in which First Aid should be provided
1. Assess victim for signs of life. 2. Restore respiration if breathing has stopped. 3. Restore heart activity if there is no discernible heartbeat or pulse. 4. Stop bleeding. 5. Treat for shock.
1st degree burn
Limited to the outer layer of the skin (epidermis); skin is red and tender, may have swelling without blistering.

Treatment for 1st degree burn
Flush the burned area with cool water or apply cool, wet compress on the skin. Cleanse the burned area. Rescuer may use Aloe vera, aspirin or ibuprofen to alleviate the pain.
2nd degree burn
Involves both the epidermis and underlying dermis; skin shows redness, tenderness, and significant blistering.
Treatment for 2nd degree burn
Rinse the area with cool water; gently wash with soap and water then rinse again. Apply antiseptic and sterile dressing. Do not apply ointments or household remedies.
3rd degree burn
Destruction of the full thickness of the skin and may damage underlying tissue; skin may be blackened or white and leathery feeling.
Major burns treatment
Remove the victim from the fire or other source of injury; apply cool compress briefly to bring skin temperature back to normal.
Chemical Burns treatment
Place the burned area under cool, running water and continue flushing for at least 15 minutes.

Electrical Burns
Often deeper and more serious; all electrical burns must be examined by a physician.
Ingestion of Chemicals
A situation where a person has consumed harmful chemicals.
Emergency Procedures
Evacuate the area if not trained to handle the problem; alert others and call the fire department.
Assessing the situation
The ability of the rescuer to assess the situation and make proper decisions without delay.
Signs of life
Indicators that a victim is alive, which should be assessed first in emergency situations.
Respiration restoration
The process of restoring breathing if it has stopped.
Heart activity restoration
The process of restoring heart activity if there is no discernible heartbeat or pulse.
Stopping bleeding
The action taken to control blood loss in an injured person.
Treating for shock
The process of providing care to a victim who may be in shock due to injury or trauma.
Ingesting Chemicals
If the victim is conscious and not convulsing, immediately have the person ingest 1-2 glassfuls of milk or water to dilute the chemical.
Inducing Vomiting
NEVER induce vomiting; it is frequently dangerous to the victim, particularly if corrosive materials have been ingested.
Transporting Victim to Hospital
Bring the victim to the hospital together with the chemical container.
Inhalation of Chemicals
Evacuate the area and move the victim into open air and call medical assistance.
CPR for Non-Breathing Victim
If the victim is not breathing, perform CPR until medical team arrives.
Mouth-to-Mouth Resuscitation
Be careful to avoid exposure to chemical poisoning via mouth to mouth resuscitation; use a mouth-to-mask resuscitator if available.
Maintaining Airway
If the victim is breathing, loosen victim's clothing and maintain the airway.
Positioning Victim
Lay the victim flat on his/her back. Place one hand under the neck and lift, with the other hand on the victim's forehead to tilt the head backward into maximum extension.
Flushing Chemicals from Eyes
Immediately flush eyes thoroughly with a gentle stream of clean, cool water for at least 20 minutes without delay.
Irrigation of Eyes
Hold eyelids apart and roll eyeballs around during irrigation to wash the entire surface.
Washing Alkaline Solutions from Eyes
Wash alkaline solutions for longer periods of time as they are more hazardous than acid solutions.
Neutralizing Solutions for Eyes
Do not use neutralizing solutions.
Rinsing Chemicals from Body
Immediately rinse affected areas thoroughly under emergency shower for at least 20 minutes without delay.
Removing Contaminated Clothing
Remove contaminated clothing while rinsing.
Neutralizing Chemicals on Body
Do not use neutralizing chemicals.
Electrical Shock Injuries
Take fast action because electrical shock injuries can cause burns and can cause a person's lungs and/or heart to stop functioning.
Approaching Electrical Shock Victim
NEVER approach or touch a person who is in contact with live electrical equipment.
Shutting Off Power Source
Locate and shut-off power source first.
Disconnecting from Live Electrical Source
If power shut-off is not possible and you believe it can be done without personal risk, you may use a non-conducting object to disconnect the person from the live electrical source.
Controlling Bleeding Wounds
Control bleeding with direct pressure on the wound with a sterile gauze pad for at least 5 minutes.
Elevating Injured Limb
If the injury is on the arm or leg, elevate it above the level of the heart.
Removing Objects from Cuts
Do not remove any object such as glass or wood from a cut; removal should be done by medical personnel.
Lying Down for Heavy Bleeding
If a person is bleeding heavily, have the person lie down with feet elevated.
Keeping Victim Warm
Keep the victim warm and calm.
Applying a Tourniquet
NEVER apply a tourniquet.
Handling Seizures
When a person starts to convulse, do not attempt to restrain them.
Protecting During Seizures
Move any objects which may injure the person and pad the patient's head with clothing or paper.
Opening Patient's Mouth
Never try to open the patient's mouth or place items between his/her teeth.
Monitoring After Seizure
Allow the seizure to take its course and then monitor the patient's breathing and pulse.
Fundamental Rule of First Aid
Victim should not be moved but should be treated where she lies except when the person must be moved from explosion, fumes or other life-threatening hazards.
Short-Distance Transport
If possible, short-distance transport should be accomplished on a firm surface such as a stretcher, or a board that will provide even support for the entire body.
Dragging Victim to Safety
If the victim must be dragged to a safe place, pull him/her lengthwise, not sideways.
Using a Blanket for Transport
If possible, try to place a blanket under the person so that the edge of the blanket is pulled carrying her weight.
Moving with Spinal Injury
In a situation where spinal injury is suspected and the patient must be moved, the spine and the neck must be kept in alignment.
Not Moving the Neck
Do not move the neck.
Explosive
Self-reactive substances, Organic peroxides.
Flammable
Flammable gases, aerosols, liquids, and solids; Pyrophoric liquids or solids; Self-heating substances; Substances that emit a flammable gas upon contact with water; Organic peroxides.
