community health
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Primary prevention
-delay onset of disease, REVERSE or arrest its progress
-routine care, mouth guards, sealants, fluoride for prevention, health education
Secondary prevention
-terminate disease process, RESTORE tissues as normal as possible
-fluoride for incipient caries, sealants for incipient caries, perio debridement, night guards, restorations
Tertiary prevention
-REPLACE lost tissues
-crowns, partials, dentures, implants
optimal fluoride level in drinking water?
0.7ppm
Five dimensions of health model
-physical, intellectual/mental, emotional, social, spiritual
(Pie… so scrumptious)
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
-physiological, safety, love/belonging, self-esteem, self-actualization
(Pumpkin spice latte… so scrumptious)
Stages of learning theory
Unawareness
Awareness
Self-interest
Involvement
Action
Habit
Which is set first, objectives or goals?
Goals, then measurable objectives
Formative evaluation
-internal evaluation during PLANNING
Summative evaluation
-evaluation AFTER IMPLEMENTATION
Type 1 examination
complete examination
-need mirror, explorer, light, radiographs, study models, tests
-seldem ever used in pubic health settings
Type 2 examination
limited exam
-need mirror, explorer, light, bwx, and selects PAs
Type 3 examination
inspection
-need mirror, explorer, and light only
-MOST COMMON in community health
Type 4 examination
screening
-need light and tongue depressor only
-too unreliable for community health
Which types of examination must be done if treatment is planned?
Type 1 or 2
Presence or absence of condition
simple index
all past and present evidence of condition (dmft)
cumulative index
Conditions that will not change
Irreversible index
Conditions that can be changed
Reversible index
Ramfjord teeth
3, 9, 12, 19, 25, 28
Oral Hygiene Indices
PHP
PI
OHI
VOLPE MANHOLD INDEX
Gingivitis Indices
GI
GBI
SBI
EASTMAN INTERDENTAL BLEEDING INDEX
Periodontal indices
PI
PDI
PSR
CPITN
Dental Caries Indices
Cambra
DMFT/DMFS
deft
RCI
Dental fluorosis indices
Dean's Index of Flurosis
Null Hypothesis
Stated as a negative outcome
Research hypothesis
Stated as a positive outcome
random sample
-every subject selected independently and randomly
Stratified sample
subgroups in the population are represented proportionally in the sample (age, gender, income, etc…)
Systematic sample
obtained by selecting every nth (number) individual from the population
Judgemental Sample
Selected by personal judgement of who would be a typical participant
Creates bias
Convenient sample
only surveying people who are easily accessible
Historical Research Design
-looks at incidence and prevalence of disease in a population over time
Descriptive Research Design
-describe the presence and distribution of a disease or health condition at one point in time
-uses the survey method
Retrospective research design
investigates possible causes of disease
longitudinal research design
a group is observed over a long period of time
can be a double blind study
Quasi experimental research design
Study that does not have a control group
UNETHICAL
pilot study
a trial run in survey research
IRB: institutional review board for ethical implications
Categorical Variable (Qualitative)
Has no numeric representation (color, rating, etc…)
Dichotomous variable (Qualitative)
Places subject into only TWO groups (male/female, pass/fail, etc…)
Continuous variable (Quantitative)
A variable (such as age, test score, or height) that can take on a wide or infinite number of values.
Discrete Variable (Quantitative)
assume values that can be counted
-expressed as whole numbers
Nominal scale
Categories have NO rank or order
Ordinal scale
Categories have rank ORDER
Interval Scale
Same as ordinal scale, equal distance between units. No absolute zero point
Ratio scale
Same as interval scale, PLUS absolute zero point
Ungrouped frequency distribution table
Data presented with each individual score
Grouped frequency distribution table
Data presented within the range
Cumulative frequency distribution table
Frequency of occurrence of scores including any given value in the data set
Normal distribution (Gaussian distribution)
Symmetrical and unimodal
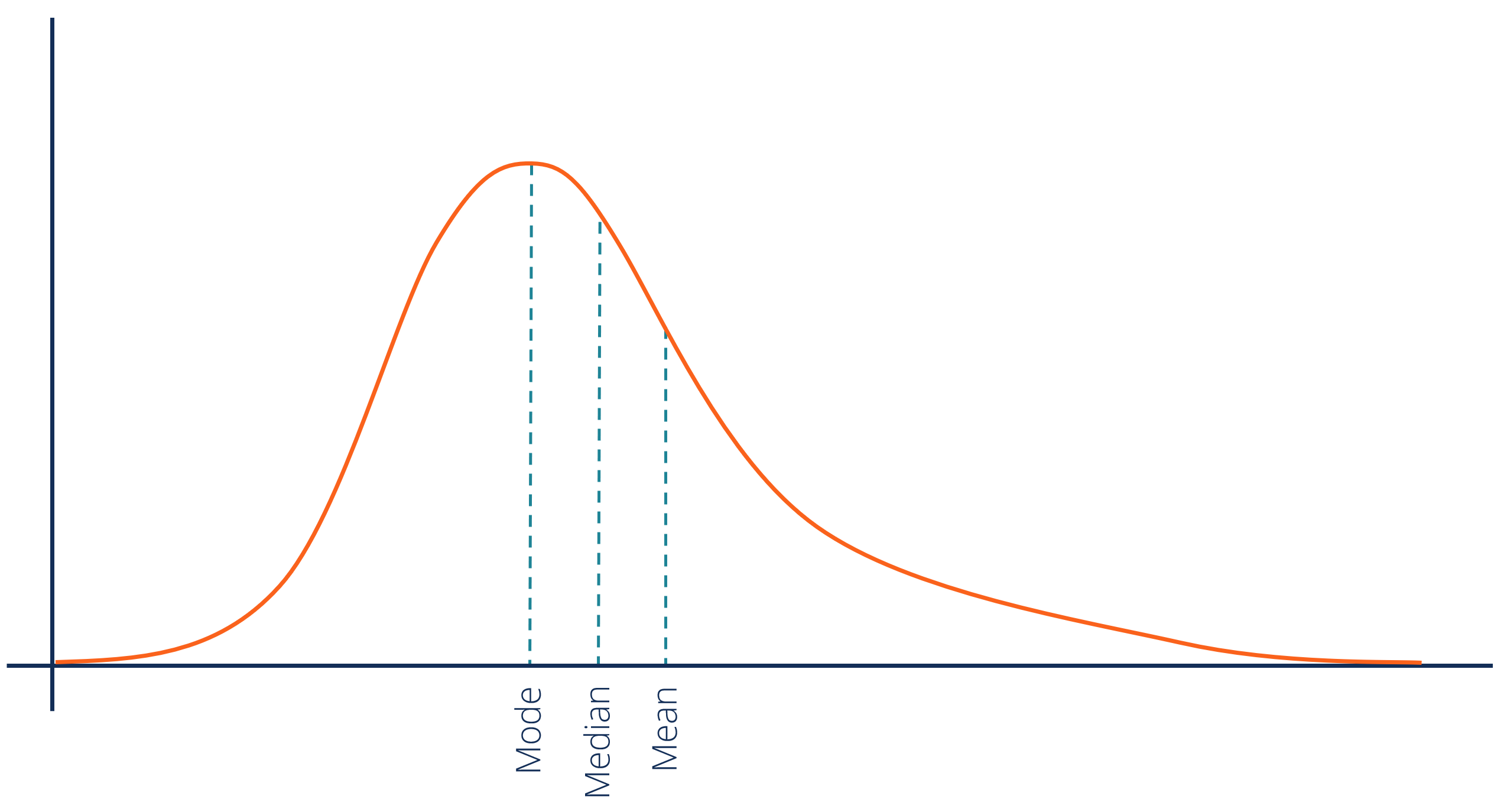
Positively Skewed
Negatively Skewed
Range
Subtract the lowest number from the highest number
Standard deviation
Square root of the variance, most common and useful
Strong correlation
R is closer to 1
Weak correlation
R is closer to 0
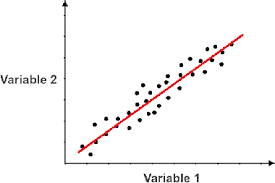
Positive Correlation, as X increases/decreases, Y increases/decreases
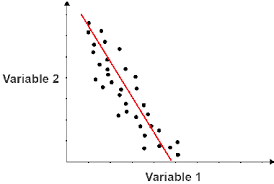
Negative Correlation, as X increases/decreases, Y decreases/increases
Internal Validity
Accuracy of a study’s results
External validity
Accuracy of generalizing the results to the population
INTRA-examiner Reliability
Consistent performance by the same investigator
INTER-examiner reliability
Consistent performance by different investigators
Calibration
Establishing a relationship between a measuring device and the units of measure
Endemic
Low but constant presence of disease in a geographic region
Epidemic (outbreak)
Occurrence of disease in excess of normal in a community or region
Pandemic
An epidemic where the disease may cross international boarders to affect several countries