Ch. 39 Neurons
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Afferent Neurons
Sensory receptors→ interneurons
Interneurons
Integrates message in CNS
Efferent neurons
Carries signals away from Interneurons to effectors (muscles and glands)
Motor neurons
Efferent neurons that carry signals to skeletal muscles
Dendrites
Recieves signals
Axon
Carries signals away from cell body to another neuron/effector
Axon terminal
Connects neurons with another
Glial cells
Non-neuronal cells that provide nutrition and support to neurons
Astrocytes
In CNS. Covers surface of blood vessels to provide physical support
Oligodendrocytes
In CNS. Wrap around axons to for myelin sheaths and nodes of ranvier
Schwann cells
In PNS. Form myelin sheaths
Resting potential
When neuron isn’t stimulated.
Range from -40 to -90mV
Avg: -70mV
created by sodium-potassium pump: 2 K+ in, 3 Na+ out
Ion leak channels- allows more K+ to diffuse out than Na+ in
Action potential
When neuron transmits electrical impulse and a change in membrane potential occurs.
positive charges outside the membrane flow in (depolarization)
Eventually it reaches threshold (10-20mV)
Voltage gated Channels
When neurons are stimulated, K+ and Na+ channels open and close causing membrane potential changes
found on axon and axon hillock
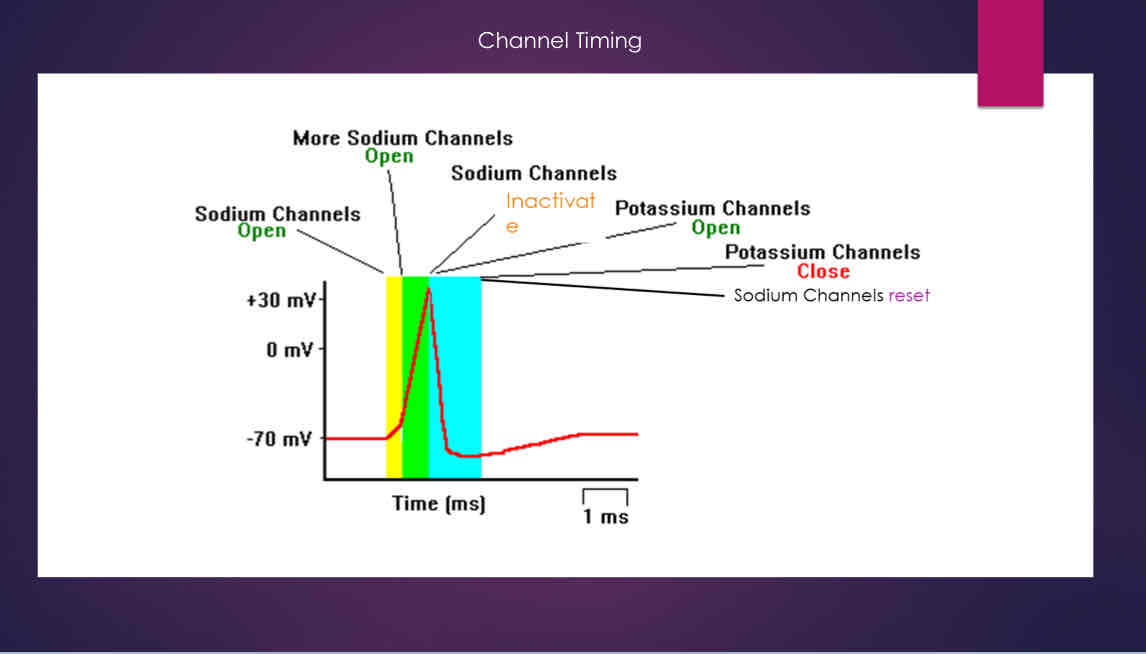
Channel Timing
Action potential explained
Once threshold is reached, action potential fires and membrane potential increases.
Hyperpolarization
Potential Dallas dropping below -80mV
Refractory Period
Cell can’t be restimulated
Frequency of Action potentials
The greater the stimulus, the more action potentials per second
Saltatory conduction
Allows action potentials to hop rapidly along myelin-coated axons.
voltage gated channels at nodes of ranvier allows action potentials to happen at these points
Synapse
When neuron communicates with another neuron/effector.
occurs by direct electrical flow or through a neurotransmitter
Electrical Synapses
Plasma membranes of presynaptic and postsynaptic cells are in direct contact.
When electrical impulse arrives at axon terminal, gap junctions allow ions to flow between cells
Chemical Synapses
Pre and postsynaptic cells are separated by a synaptic cleft.
an neurotransmitter is released, and the postsynaptic cell can create a new electrical impulse
Neurotransmitters
Open and close ligand-gated ion channels
Excitatory Postsynaptic Potential
Change in membrane potential that pushes neuron closer to threshold.
occurs when ligand-gated Na+ channel opens, causing depolarization
Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potential
A change in membrane potential that pushes neuron farther from threshold.
occurs when ligand-gated ion channel opens and allows Cl- to flow in and K+ out (hyperpolarization)
Summation
Sum of EPSP and IPSPs