oncology
1/251
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
252 Terms
Gene mutations caused activation of ___ or loss of ____ gene function
oncogene
tumor suppressors
True or false
In the plateau growth phase, you have longer tumor doubling times
True
it outgrew its blood supply
When can you intervene when looking at the graph
10 to the 9th-10 to the 12th
True or false
chemo and radiation are most effective during the plateau growth phase
False
most effective during the growth phase. that is why debulking surgery is important
What is required for tumor growth and metastasis. Hint this stage is induced by tumor hypoxia
Angiogenesis
50% of what 2 breeds will develop cancer at some point of their lives
Boxers and golden retrievers
What is the only cancer that is inheritable from parents?
Renal cyst adenocarcinoma and nodular dermatofibrosis of German Shepherd dogs
Three viruses considered carcinogens
Papillomavirus
FeLV
FIV
What cancers do you see in animals who have exposure to environmental tobacco smoke?
Lymphoma
oral SCC in cats
2, 4-D, causes what cancers (pesticide herbicide insecticide)
Lymphoma
transitional cell carcinoma
Cat has intraocular trauma such as lens rupture. They are likely to develop
Intraocular sarcoma
True or false
Metallic implants is considered a carcinogen
True
UV exposure causes what cancers
SCC
cutaneous Hemangiosarcoma
sparse hair covering and light pigmented animals
If you are treating an animal with radiation what risk are they having?
can develop late radiation tumor
mostly sarcomas
List four types of cancer cell types
Epithelial
round cell
mesenchymal
endocrine
Cells in clusters and clumps round nuclei with moderate cytoplasm
Epithelial tumors (usually end with the carcinoma)
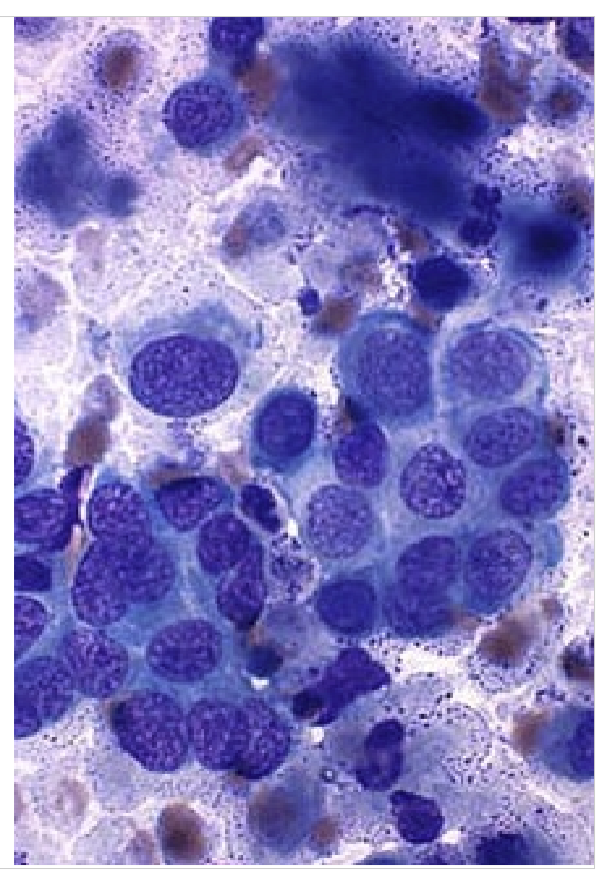
Do epithelial tumors exfoliate well
Yes
Usually singular elongated cells with cytoplasmic tails
Mesenchymal
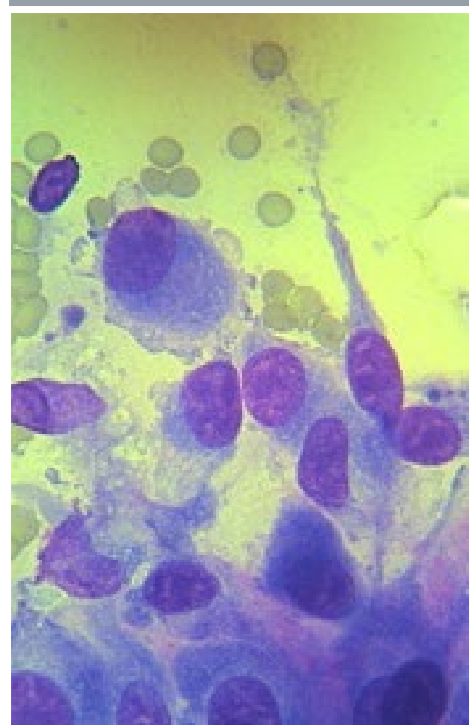
What type of tumors arise from connective tissue?
Mesenchymal (spindle cell)
usually end with sarcoma
Do mesenchymal tumors exfoliate well
No
List five types of round cell tumors (LIMPH-T)
plasma cell
lymphoma
mast cell
histiocytoma
transmissible venereal tumor
± melanoma
discrete small to medium sized cells
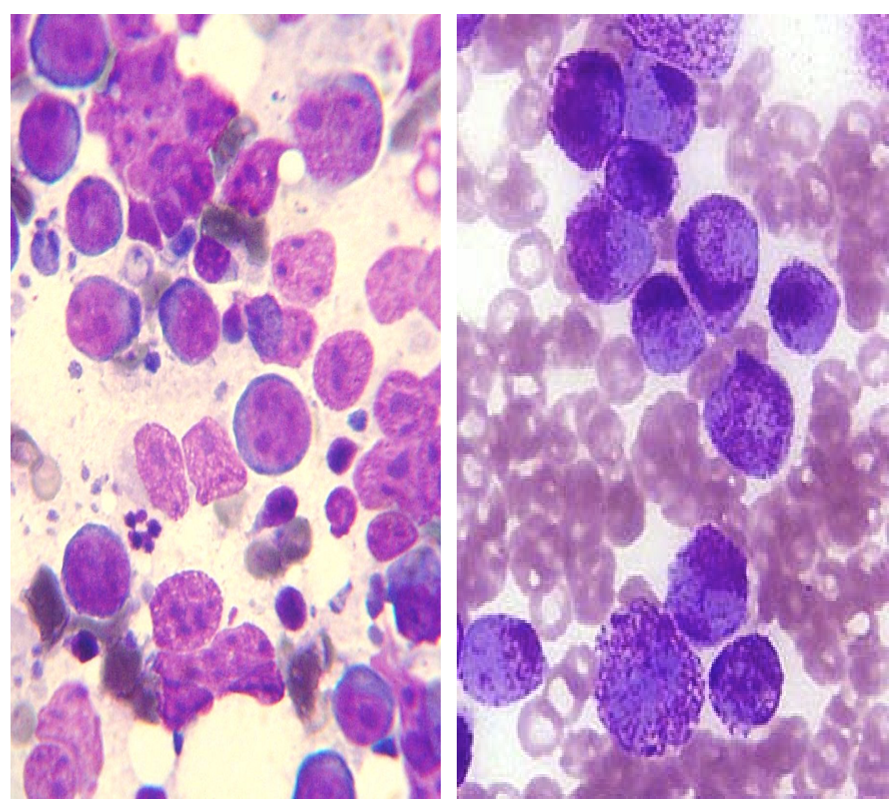
Do round cell tumors exfoliate well?
Yes
Free naked nuclei in a sea of cytoplasm
Endocrine tumors
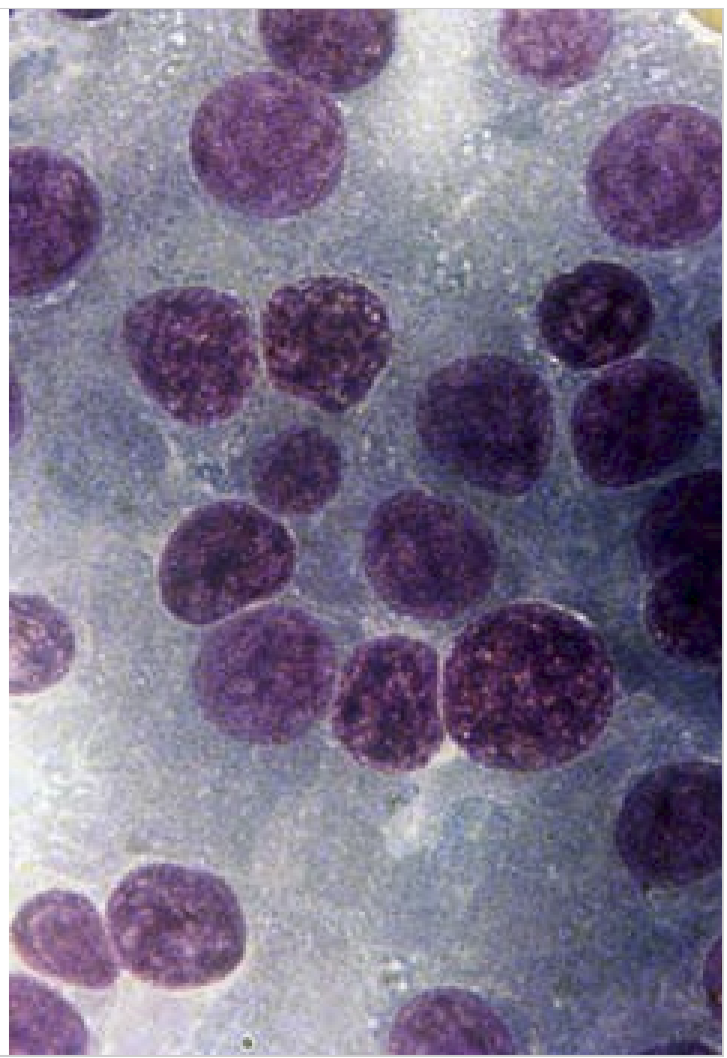
When presented with the mass, what are the three things you do in order?
Diagnosis (what is it?)
staging (extent of disease)
treatment (options are expectations)
only way to obtain a grade
Histopathology via biopsy
What type of tumor is highly responsive to radiation therapy?
Lymphoma
Also good for brain and nose since not accessible for surgery
True or false
remission means no evidence of cancer anywhere in the body
True
Three things chemo can provide you
induce and maintain remission
delay metastasis
control local disease
True or false
chemotherapy is a primary treatment for the majority of tumors
False surgery is the primary treatment
Chemotherapy side effects (BAG)
Bone marrow
alopecia (hair follicles)
GI (intestinal epithelium)
targets rapidly dividing cells
Why do you have to wait between intervals when administering chemo?
Have to give time for normal cells to recover
Formula to dose chemotherapy
MG/M2 (body surface area)
What is metronomic chemotherapy?
Continued low-dose treatment with a antineoplastic drug combined with an NSAID
Targets = angiogenesis (due to the low dose this is the target instead of cytotoxic feature, slows everything down)
What is a common indication for metronomic chemotherapy?
Incomplete resection of soft tissue sarcoma
Hemangiosarcoma
Standardized way to look at to see and measure tumors to see if they are responding to chemotherapy
Recist criteria
When you give chemotherapy when do the WBC hit their lowest point
5-7 days
Note: anemia is rare and non-life threatening due to lifespan of 120 days
You do a CBC what are your cut offs to delay treatment?
Less than 2000 neutrophils or
less than 50,000 platelets
What constitutes as an emergency in chemotherapy?
Neutropenia plus fever
risk of sepsis greatest impatience with less than 1000 cells
Where does the source of infection come from for them to be sepsis?
from the GI tract
No more neutrophils in the GI tract leading to translocation
You do a CBC and have less than 1000 neutrophils client has no fever or illness. what do you do?
Oral antibiotics (broad spectrum) and dose reduction
if animal has fever or illness, present you hospitalize
If animal has 1000-2000 neutrophils with no fever or illness what do you do?
No treatment needed
True or false
Alopecia side effect in animals is rare
True
more commonly see loss of whiskers and eyelashes
also, and maybe Toy breed dogs
When would you come see GI signs after chemotherapy
3 to 5 days
What agent causes sterile hemorrhagic cystitis
Cyclophosphamide
What causes hepatotoxicity and significant myelo suppression
Lomustine
Cisplatin toxicity
Nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity
pulmonary edema in cats that is fatal
cisplatin makes cats go splat
Which causes neural toxicity
Vincristine
5FU
Doxorubicin toxicities
cumulative Cardiotoxicity
Nephrotoxicity in cats
severe vesicant
anaphylaxis
Which drug is an enzyme that is only effective against lymphoma/leukemia
L asparginase
How common is canine lymphoma?
Second to only skin cancer
True or false
intact females have decreased for lymphoma
True
True of false
Most animals present with enlarged lymph nodes, but are clinically well
True
others can have nonspecific signs and PU/PD
84% in dogs have what form of lymphoma
Multicentric (generalized)
two differentials for solitary or regional lymphadenopathy
local infection or inflammation
metastatic disease
What diagnostic test is often diagnostic for lymphoma?
Cytology
avoid mandibular lymph nodes if multiple nodes are enlarged
After cytology what is the 2nd best diagnostic test for lymphoma
Flow cytometry
Differentiates between T cell, B cell and if large or small
Flow cytometry comes back as homogenous population or if it comes back with heterogenous population of lymphocytes. What would these mean?
Homogenous = neoplasia
Heterogenous = reactive disease
What does PARR test detect
Clonal population of lymphocytes
low sensitivity, high specificity
main difference between this and flow cytometry is that this test does not require live cells
Most common type of lymphoma classification you will see
Diffuse large cell B cell lymphoma
second = diffuse acute large T cell lymphoma
True or false
Flow cytometry can detect CD 34+ on lymphocytes
True
What diffuse change would you see with lymphoma during ultrasound of organ architecture
Swiss cheese appearance
True or false
Barely do bone marrow staging for lymphoma
True
Stage two lymphoma
Multiple notes on one side of the diaphragm
Aka. regional lymphadenopathy
Stage three lymphoma
Multiple notes on both sides of the diaphragm
aka. generalized lymphadenopathy
stage four lymphoma
liver and spleen involvement (lymph nodes do not need to be involved)
stage five lymphoma
involvement of any non-lymphoid tissue W
Which dogs do worse, B cell or T cell
T cell
Treatment of choice for lymphoma
chemotherapy
Multi agent protocol
C = cyclophosphamide
H = hydroxydaunorubicin
O = Oncovin (vincristine)
P = prednisone
Gold standard treatment 90% remission rate
How many cycles for CHOP
repeat five week cycle four times for a 19 week protocol
Most effective drug for a single agent protocol
Doxorubicin
given every 2-3 weeks
MST shorter due to quicker resistance
Steroids alone response rate
50%
MST = 1-3 months
True or false
Do not give steroids without diagnosis or if owner wishes to pursue with chemotherapy
True
it decreases remission rates with other chemo protocols by 50% due to resistance now being made
Good rescue protocol if animal gets out of the remission after CHOP
Tanovea
Dog goes out of remission after CHOP therapy (ie three months after) what protocol should you use?
Do CHOP again
Is lymphoma often found in the lung
No
thats why two view radiographs are sufficient because only looking at the nodes
True or false
like dogs and cats lymphoma is also mainly multicentric/nodal
False
multicentric/nodal form is rare
What type of cats develop spinal mediastinal, peripheral nodes, ocular and renal lymphoma
usually younger cats with FeLV
Which type of cats develop nasal, alimentary lymphoma
usually older cats without FeLV
True or false
Environmental tobacco smoke increases cats risk to lymphoma
True
Older cat with GI lymphoma are they usually FeLV positive or negative
Negative
Which sex is more predisposed to lymphoma, male or female cats
Male
note: breeds DSH and siamese
Why is biopsy often required for feline lymphoma whereas in dogs psychology is good enough for diagnosis
nodular presentation is rare so you need to go get a biopsy internally from wherever the lymphoma is
True or false
Expect shorter survival times with lymphoma and FeLV/FIV together
True
Does immuno phenotype of lymphoma matter in cats for prognosis
No
True or false
A full staging diagnostic is often indicated in cats
True
unlike dogs, they can have it in one area or spread all over the body
lymphocytes (small cell) grade
low-grade
What is high grade
Lymphoblast (large cell)
Feline GI lymphoma occurs more in small or large intestine
small intestine
What is more aggressive, small cell or large cell lymphoma?
Large cell
Protocol for small cell lymphoma
Chlorambucil and prednisolone
Protocol for large cell
CHOP
Good prognosis with 90% treatment response with clinical signs resolving in 1-3 months of treatment initiation
MST = greater than two years
small cell or large cell lymphoma?
This small cell lymphoma prognosis
What is the response rate and MST for large cell lymphoma?
Response rate = 30-50%
MST = 3-5 months
What imaging device can you use to diagnose nasal lymphoma?
CT scan
rhinoscopy for biopsy
Treatment for nasal lymphoma that is not systemic
Radiation therapy
MST = 1.5-3 years good prognosis
if systemic add chemotherapy CHOP protocol
three year old cats comes in with muffled heart and lung sounds. FeLV test was positive.
what should be on the top of your differential?
Mediastinal lymphoma
How can you diagnose mediastinal lymph node
fine needle aspiration of the pleural fluid
what results of the cytology would indicate a mediastinal lymphoma?
intermediate to large lymphocytes (CHOP protocol)
small lymphocytes indicate chylous like effusion
When is the only time you will do a single excisional biopsy that is also therapeutic
single node enlargement in felines (Hodgkin’s like lymphoma)