Exam 1 Chapter 3 (Prokaryotic Cell)
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
prokaryotic cell
no nucleus or membrane bound organelles
older
small
rigid cell wall
Prokaryotic cells
are in domains achaea and bacteria
Appendages (external structures) of prokaryotic cell
flagella
pili
fimbraie
periplasmic fluid
Flagella
Motile
Used for movement and attachment
Pilli
Tube structure used in horizontal gene transfer
used for attatchment
Cell envelope consists of
glycocalyx
Cell wall
Cell membrane
Glycocalyx
Mixture of proteins + sugars
Coating in exterior of cell
types of glycocalyx
slime layer
capsule
Slime layer
Loose mesh network of proteins + sugars
Capsule
Dense mesh network of proteins + sugars
More protective
slippery
Harder to grab
Bigger
Harder to engulf
Cell wall
protection of cytoplasmic membrane from environmental stress
Determines shape of cell
Forms a mesh like structure
Cell wall keeps prokaryotes from
lysing from osmotic pressure
Two types of cell wall
Two types
Gram + (pink)
Gram - (purple)
Gram +
teichoic acid and peptidoglycan
thick
Gram -
lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
thin
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
causes immune cells to freak out and release signals
can cause fevers, hemorrhaging, and septic shock
Acid fast
mycolic acid
waxy coating
stain gram +
hydrophobic
Difference between gram + and acid fast
Acid fast has mycolic acid
Name of genus that has mycolic acid
Mycobacterium
Carbol fushin
Acid fast stains binds to colic acid
Antibiotics are
Hydrophilic
Cytoplasm consists of
matrix
ribosomes
Inclusion bodies
nucleoid region
endospores
All cells have
Ribosomes
Nucleoid region
Contains DNA
Endospore
Only spore former
Why are endospores important?
preserve genetic information for future generations
allow cells to survive in harsh environmental conditions
Morphology
Coccus
Bacillus
Vibrio
Coccabacillus
Spirllium
Spirochete
Coccus
Round

Bacillus
Rod

Vibrio
Curved rod

Coccabacillus
Short rod

Sprillium
Spiral
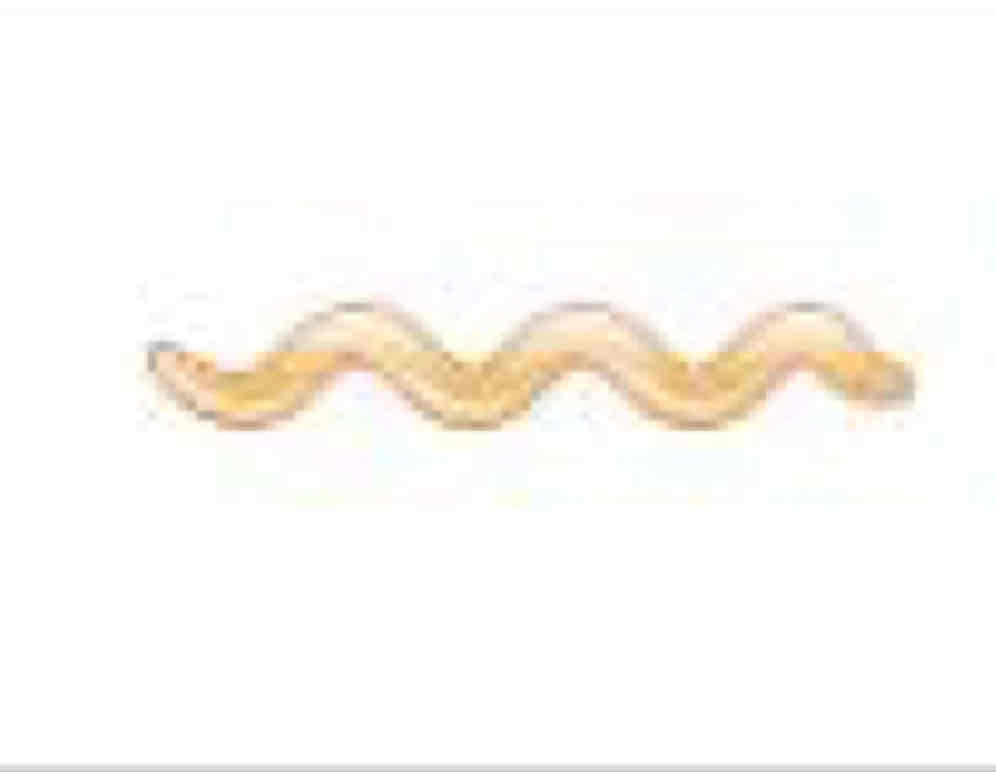

Spirochete
Helical shape
Cell arrangements
Coccus
Diplococcus
Tetrad
Streptococcus
Staphylococcus
Bacillus
Streptobacillus
coccus
single coccus

diplococcus
pair of two cocci

tetrad
four cells in a square

streptococcus (important)
chain of cocci

staphylococcus
cluster of cocci

bacillus
single rod

streptobaccillus
chain of rods

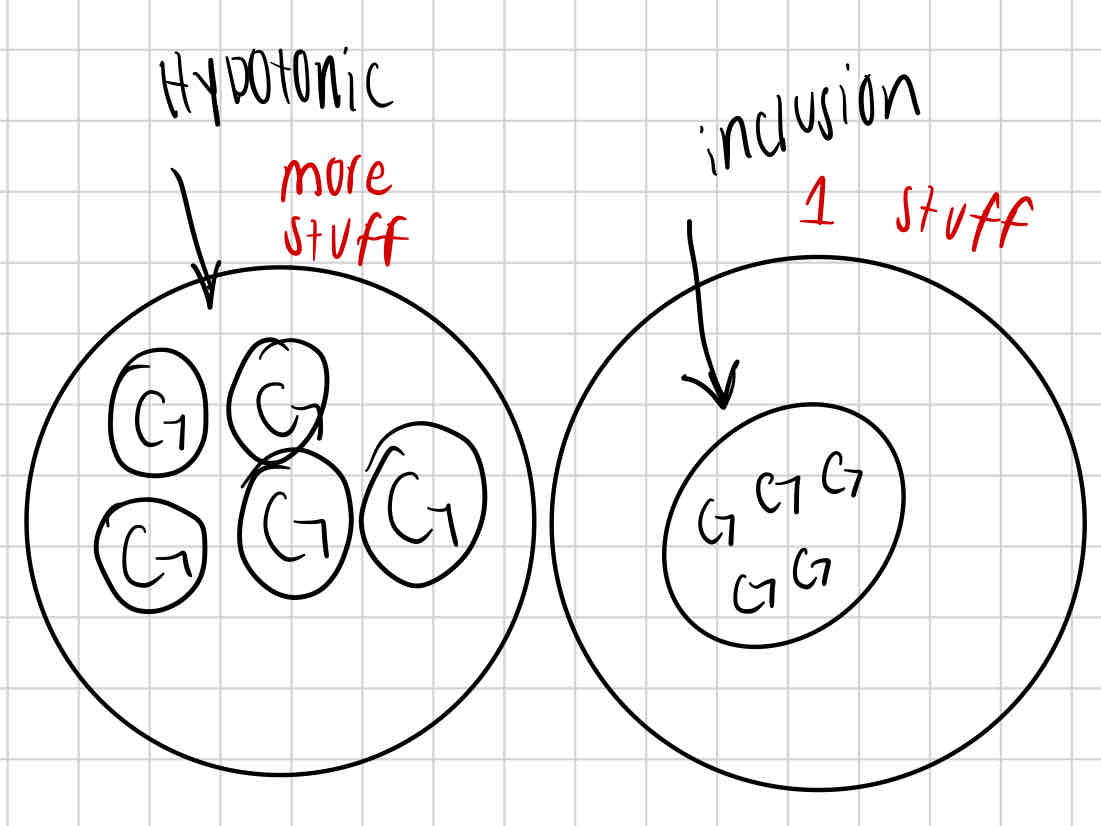
osmotic pressure
water moves across the cell membrane to areas of high solute concentration
hypotonic solution
water moves into the cell
cell can burst or die due to too much water
cell wall attempts to stop cell membrane from expanding
hypertonic
water moves out of cell
cell membrane detach from cell wall leading to a shrunk cytoplasm
isotonic
cell stays the same
inclusion
help reduce osmotic pressure by storing excess nutrients or solutes in a condensed form, lowering concentration of free solutes in the cytoplasm
endospores
form because of loss of nutrients
sporolation
process of forming spores
sporolation process
DNA replicates
Membranes form around DNA
Forespore forms additional membranes
Protective cortex forms around spore
Protein coat forms around cortex
Spore is released
Example bacterias ( Endospores)
Genera Bacillus and Colstridium
B. anthracis - anthrax
C. tetani - tetanus
C. difficile - pseudomembranous colitis
C. perfringens - gas gangrene
C. botulinum - botulism
Temperatures (vegetative vs endospores)
vegetative = sensitive to extreme temperatures and radiation
endospores = resistant to extreme temperatures and radiation
Gram stain (vegetative vs endospores)
vegetative = gram-positive
endospores = do not absorb gram stain
Water (vegetative vs endospores)
vegetative = normal water content and enzymatic activity
endospores = dehydrated, no metabolic activity
Growth (vegetative vs endospores)
vegetative = active growth and metabolism
endospores = no growth or metabolic activity
macrophages
marines of the immune system
cytokines
massive release of cytokines over the body send patient into crisis = lower blood pressure
Water
Always go to where there is more stuff (solute)
Can cross plasma membrane slowly but consistently
All cells are in
a hyptonic solution
A hypertonic environment will cause prokaryotic cells to go through
Plasmolysis
Prokaryotic ribosome
70S
Antibiotics target
70S (prokaryotes)
Ribosomes
Perform translation
DNA →(transcription) mRNA →(translation) protein
Bacillus + clostridium
Can form endospores