SPA 3101 Final Exam
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
True or False: A myofibril is comprised of myosin, actin, sarcomeres, and fascicles.
False: Fascicles are actually the bundles of myofibrils that make up muscles. Smallest→Largest: Myofilaments(Myosin + Actin) →Sarcomere(contractile unit)→Myofibrils(chains of sarcomeres)→Muscle Fiber→Fascicle→Whole Muscle
Boyle’s law states…
There is an inverse relationship between pressure and volume at constant temperature.
Aspiration pneumonia occurs more often…where and why?
In the right lung due to the wider, shorter, more vertical bronchus.
Functional Residual Capacity
Volume of air remaining in the lungs AFTER a normal passive exhalation. FRC=ERV+RV
Residual Volume
The air you can NEVER exhale.
Expiratory Reserve Volume
The extra air you CAN exhale forcefully after a normal recoil exhale.
Lungs expand due to…
Negative pressure that keeps lungs attached inside the thoracic cavity. Pleural linkage.
Skeletal Muscle mainly involved in….
VOLUNTARY movement.
Biological functions of the respiratory system
Breathing, airway protection, humidifcation, filtering of air, pressure regulation, smell.
NON-biological functions of the respiratory system
Speech production, voice production, singing, laughing, crying, breath hold for certain tasks.
Lung-thorax unit is closest to equilibrium at…?
40% of Vital Capacity
Fibrous Joints
The only joints that do NOT contain an articulatory space. Non-moving
Which division of the pleura lines the inside of thoracic cavity?
Parietal
Hyaline cartilage
Susceptible to ossification. Smooth, most common, found in joints and ribs, nose, trachea.
Elastic Cartilage
Flexible, found in epiglottis and pinna, recoils to shape.
Fibrocartilage
Strongest, dense collagen; found in intervertebral discs, menisci
Cartaliginous Joints
Slightly moveable, bones joined by cartilage; hylanie and fibrocartilage;
Synovial Joints
Most movement; fluid filled capsule; hinge, ball & socket, pivot, gliding, condyloid
The amount of air in the lungs after a tidal expiration is
Functional residual capacity
The lungs are a highly_________ structure.
Passive and elastic
The diaphragm is in a dome shaped position
At rest
Diaphragm attaches to the sternum at the:
Xiphoid process
Which of the following is a muscle used in active expiration:
Quadratus lumborum
Carina is considered part of the:
Lower airway
Primary muscles of quiet expiration are:
No muscles. Lungs and rib cage recoil do the work.
When would the abdominal muscles become active during speech?
At low lung volumes.
Hyaline, fibrous, and elastic are all types of…
Cartilages
The smallest contractile unit within a muscle is a…
Sarcomere
The transverse plane divides the body into:
Upper and lower sections
The _______ nerve innervates the diaghragm and emanates from the _______ level of the vertebral column.
Phrenic; cervical
The Sternocleidomastoid muscle
Has an attachment in the neck and is active during forced inspiration. It increases the size of the thoracic cavity.
External intercostals
Active during both quiet AND forced INSPIRATION. Front pocket orientation. Lift ribcage up to increase thoracic volume.
Internal intercostals
Active during ONLY FORCED exhalation. Back pocket orientation. Pull ribcage down to decrease thoracic volume. Deep to the external intercostals.
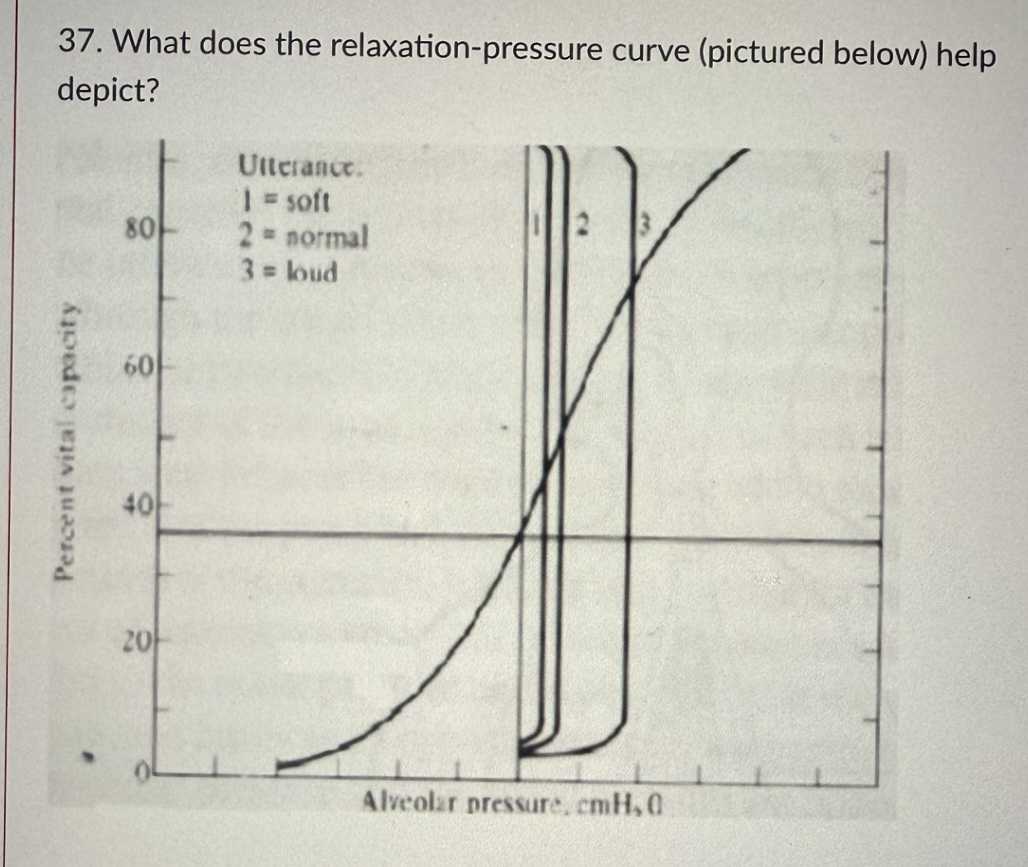
The relaxation pressure curve shows:
The non-muscular forces acting on the lung-thorax unit.
If I wanted to speak softly at 60% vital capacity what forces would be at work?
Elastic recoil and inspiratory checking
How do you calculate inspiratory capacity? (IC)
IC=TV+IRV IC is the MAX you can inhale starting from the end of a normal exhale.
TV Tidal Volume. How do you find it?
TV=TLC-(IRV+ERV+RV) The amount of air you inhale or exhale during a normal, quiet breath. Typical adult is 500mL.
Functional Residual Capacity
The amount remaining after a tidal exhalation. ERV + RV = FRC
Speech Breathing Process
Diaphragm contracts
Lung volume increases
Air flows into the lungs
Lung thorax unit decreases
Functional residual capacity reached
Expiratory muscles contract
According to the myoelastic aerodynamic theory of voice production, opening and closing of the vocal folds is due to _________
Subglottal air pressure build up, elastic recoil, and Bernoulli effect
Both the epiglottis and the thyroid cartilage are essential structures for phonation.
False
The lateral cricoarytenoid muscle is important for the position and support of the larynx.
False
The perceptual correlate of intensity is loudness.
True
The posterior cricoarytenoid muscle has an attachment at the muscular process of the arytenoid.
True
Using a strobe light during laryngoscoppy allows for visualization of the vocal folds in slow motion.
True
Flexible laryngoscopy allows for assessment of laryngeal function during conversational speech.
True
The omohyoid muscle is an extrinsic suprahyoid muscle.
False
The anterior digastric muscle is an intrinsic muscle of the larynx with a point of attachment on the hyoid bone
False
As mass per unit increases, stiffness increases, and fundamental frequency decreases.
True
Which of the following vocal folds configurations would have a larger glottis?
Vocal folds fully abducted.
What is the space beneath the vocal folds extending to the first tracheal ring?
Subglottal space
The ______ is the part of the thyroid that descends posteriorly and inferiorly, attaching to the cricoid cartilage.
Inferior Cornu
All of the following affect the fundamental frequency of the vocal folds except….?
Endoscopy
On average the female voice’s fundamental frequency during reading is:
200-275 Hz
All of the following are mechanisms for increasing pitch except…
Increasing mass
Which layer of the vocal fold is active?
Thyrovocalis
Lowering the pitch of your voice involves ______ the vocal folds.
Relaxing
The rocking motion of the ______ cartilage relative to the ______ cartilage can increase pitch.
Thyroid and cricoid
Which of the following consist of only EXTRINSIC infrahyoid muscles?
Omohydoid, thyrohyoid, sternothyroid, sternhyoid
The anterior portion of the vocal folds attaches to the ____ cartilage and the posterior portion attaches to the arytenoid cartilages at the ____.
Thyroid; Vocal process
Which of the following consists of only muscles used in adduction:
Oblique interarytenoid; transverse arytenoid; lateral cricoarytenoid
The glottal fry register is characterized by all of the following except:
All of the above are true about the glottal fry register.
Each of the following are joints within the laryngeal mechanism.
A and B
The muscles of the larynx are innvervated by the ____ branch of the _______nerve.
Recurrent laryngeal; vagus
The geniohyoid is important for what function”
Elevating the laryngeal complex
The posterior cricoarytenoid is innvervated by the _____ and has a synergistic relationship with the diaghpragm which is innervated by the __________.
Recurrent laryngeal nerve; phrenic nerve
______ and ______ are two OBJECTIVE acoustic measures of phonation.
Fundamental frequency; intensity; jitter; shimmer;
Name two SUBJECTIVE descriptive measures of phonation.
Glottal fry; breathiness; hoarseness; hyponasality; tremor; resonance; vocal effort;
Which of the following is biological function of the larynx?
Thoracic fixation; Swallowing; Coughing; Breathing
The inferior orbicularis oris is less mobile than the superior orbicularis oris.
False
Both muscular force and gravity are involved in the production of non-nasal speech sounds.
False
The zygomatic, levator labii superioris, depressor labii inferior, and risorius are facial muscles primarily innervated by CN V.
False
The parietomastoid suture is a fibrous joint containing a large articulatory space.
False
The posterior cricoarytenoid and the lateral cricoarytenoid are essential for production of voiced sounds.
False
A retrognathic or class II malocclusion occurs when the maxilla lies anteriorly to the mandible.
True
Vowels are generally voiced and are produced with very little airflow constriction.
True
The primary mover muscles for production of /s/ and /z/ are inferior longitudinal and superior longitudinal.
True
Temporalis
Elevator
Mylohyoid
Depressor
Medial pterygoid
Elevator
Anterior belly of the digastric
Depressor
Masseter
Elevator
Lateral pterygoid
Depressor
Linguapalatal
Tongue to alveolar ridge
Linguadental
Tongue to teeth
Labiodental
Lip to teeth
Linguavelar
Tongue to soft palate
The temporomandibular joint is formed by the
Condyloid process of the mandible and the temporal bone
The function of the hyoglossus muscle includes all of the following:
Draw the tongue down and back