Alkenes- chemistry
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
two types of bonds when orbitals overlap in cov bond:
Sigma bonds (σ)
Pi bonds (π)
formation of pi-bonds (π)
Side- ways overlap of two p-orbitals
∴ electron density is above and below the molecule
formation of sigma bonds (σ-bond)
end-on overlap of orbitals
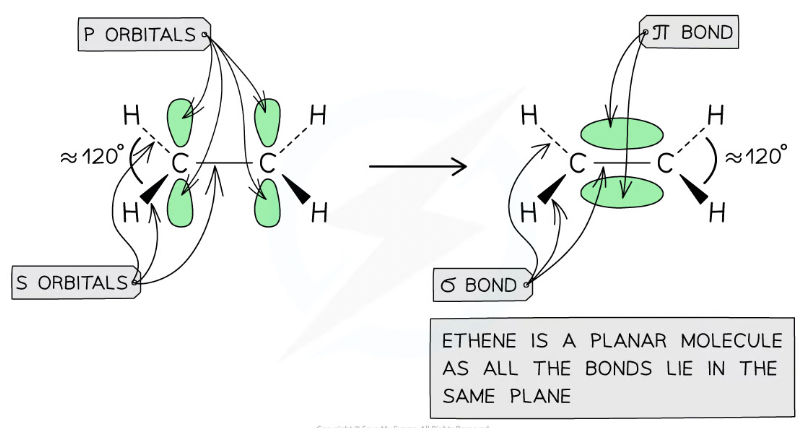
carbon- carbon bond in alkenes
carbon atoms use only three of their electron pairs to form a σ bond, each carbon atom will have a p orbital which contains one spare electron
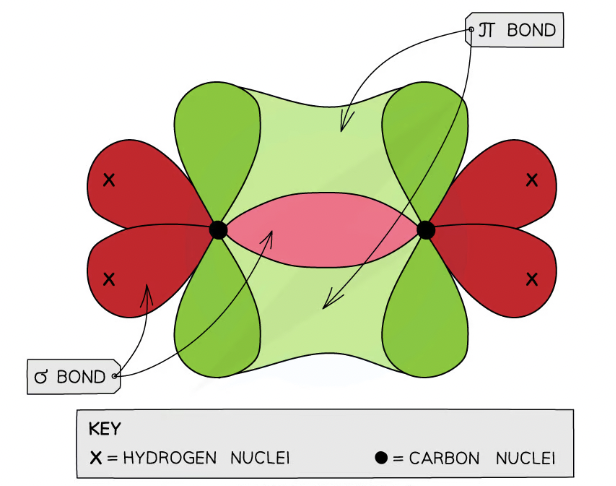
What is a double bond?
combination of a σ and π bond
What is a triple bond?
combination of one σ and two π bonds
Why does bond strength change from single < double < triple bond?
increased electron density around the carbon-carbon bond, making the bond stronger and more difficult to break
What is bonding of carbon of an alkene?
double bond has three σ bonding pairs of electrons
Two pairs forming σ bonds with other atoms
One pair forming σ bonds with the other carbon atom of the double bond
The three bonding pair of electrons are in the plane of the molecule and ___ each other
repel
What is the name + bond angle of alkenes?
planar arrangement with bond angles of 120o
fourth π bonding pair forms the double bond in combination with the carbon-carbon σ bond
Ethene’s bonding
Carbons use 3 of 4 electrons to form σ bonds ( 2 σ with H and 1 σ with other carbon)
fourth electron from each carbon atom occupies a p orbital which overlaps sideways with another p orbital on the other carbon atom to form a π bond
means that the C-C is a double bond: one σ and one π bond
What is stereoisomerism?
Compounds with same structural formula but different arrangement in space
Types of steroismicsm:
Geometric isomerism
Optical isomerism
What is geometric isomerism:
Can occur with compounds that contain a double bond because there is restricted rotation around the double bond
named depending upon which side of double bond branches lie
cis meaning
latin for on this side
trans meaning
latin for across
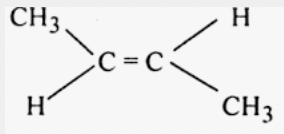
trans-but-2-ene
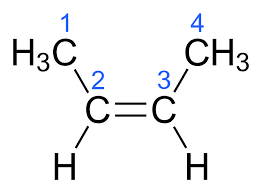
cis-but-2-ene
Difference between cis/ trans and E/Z
Cis / trans isomerism occurs where two of the atoms or groups of atoms attached to each carbon atom of the C=C bond are the same
E / Z isomerism is an example of stereoisomerism where different atoms or groups of atoms are attached to each carbon atom of the C=C bond
The cis / trans naming system can still be used with three atoms / groups of atoms but only if:
Two of the three atoms or groups of atoms are the same
These two atoms or groups of atoms are on opposite sides of the double bond

we look at the atomic number of the first atom attached to the carbon in question ∴
The higher the atomic number; the higher the priority
What is E and Z?
Z - highest priorities are opposite each other ———
E- highest priorities are at angles to each other ╲
how to write E and Z notation
e.g.
E-2-bromo-1-propen-1-ol
Z-2-bromo-1-propen-1-ol
if its H2 and H3 what has higher priority?
neither
look at next atom
What in hydrogenation?
reaction between an alkene and hydrogen is known as hydrogenation or reduction
As well as a nickel catalyst, this requires a temperature of 200 °C and a pressure of 1000 kPa
Application of hydrogenation
production of margarine from vegetable oils
Vegetable oils are unsaturated and may be hydrogenated to make margarine, which has a higher melting point due to stronger London Dispersion Forces
By controlling the conditions it is possible to restrict how many of the C=C bonds are broken and produce partially hydrogenated vegetable oils which have which have the desired properties and textures for margarine manufacture
What is halogenation?
reaction between alkenes and halogens is known as halogenation
reaction occurs readily at room temperature and is the basis for the test for unsaturation in molecules
What is halogenation an example of
electrophilic addition where an electrophile ('electron seeker') joins onto to a double bond
What does halogenation form
dihaloalkane
What can halogens be used to test for?
If a molecule is unsaturated
What halogen is used to test for unsaturated + how is it done?
Br2 is an orange or yellow solution, called bromine water
The unknown compound is shaken with the bromine water
If the compound is unsaturated, an addition reaction will take place and the coloured solution will decolourise e.g. 1,2-dibromoethane
What is hydrohalogenation?
Reaction of alkenes readily with hydrogen halides such as HCl and HBr to produce halogenoalkanes
What is hydrohalogenation an example of?
electrophilic addition reaction that occurs quickly at room temperature
Hydrohalogenation reactions in alkenes

Order of fastest to least fast of hydrogen halides and why?
FAST- HI > HBr > HCl- SLOW
due to the increasing bond strength of the hydrogen-halogen bond, so the weakest bond reacts most easily
What is hydration?
When alkene is converted to alcohol
e.g. of hydration
Treated with steam at 300 oC
Pressure of 60 atmospheres
Sulfuric acid (H2SO4) / phosphoric acid (H3PO4) catalyst
—> water is added across the double bond
The reaction processes via an intermediate in which H+ and HSO4- ions are added across the double bond
The intermediate is quickly hydrolysed by water, reforming the sulfuric acid
Hydration in alkenes equations
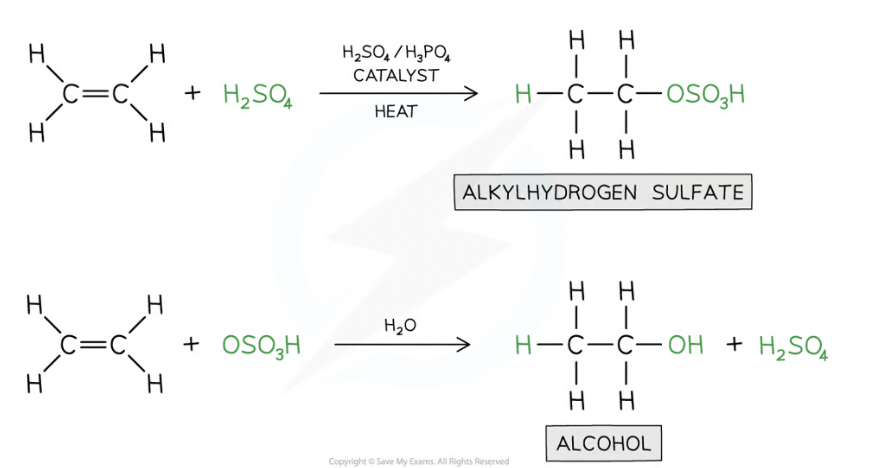
Use of hydration
important industrial reaction for producing large quantities of ethanol, a widely used solvent and fuel
The process is much faster and higher yielding that producing ethanol by fermentation
If ethene monomers react what is the name of the polymer formed
Polythene
what do curly arrows represent?
movement of pair of electrons
what is an electrophile?
Atom which is attracted to an electron rich atom, where it accepts a pair of electrons to form new cov bond
electrophilic addition definition
addition of an electrophile to an alkene double bond, C=C, which is an area of high electron density which makes it susceptible to attack by electrophiles. The double bonds breaks forming a single C-C bond and 2 new bonds from each of the two carbon atoms
what is carbocation
an ion that contains a pos charged carbon atoms
A double bond of an alkene is an _____
area of high electron density / high neg charge
electron-deficient species will accept what?
lone pair of electrons
what are electrophiles
means “electron loving”
species either have full pos charge or slight pos charge on one or more their atoms
alkenes undergo addition reactions when approached by ____ and therefore undergo __________
electrophiles
electrophilic addition
1st stage of electrophilic addition
pos charge on electrophile is attracted to the electron density in the double bond
as electrophile approaches the double bond, electrons in A-B bond are repelled towards B
pi bond break and A bonds to carbon, forming carbocation
Two electrons in A-B bond move to B forming B- ion
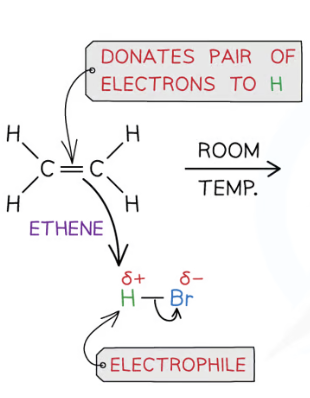
2nd stage of electrophilic addition
The B- ion acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carboncation
Lone pair of electrons on the B- ion are attracted towards pos charged carbon in the carbocation causing B to bond to it
both electrons in bond joins B- to the carbocation ion come from B-, the bond is a co-ordinate bond
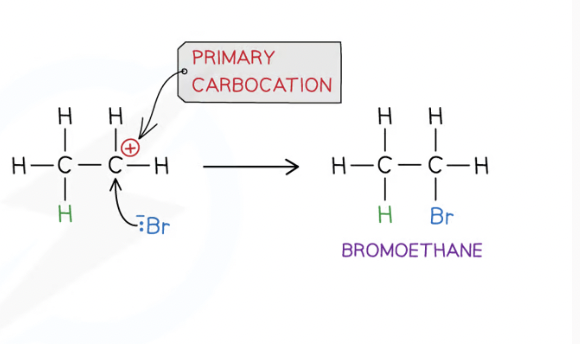
what is a nucleophile?
species that donates a lone pair of electrons to form a covalent bond with an electron deficient atom
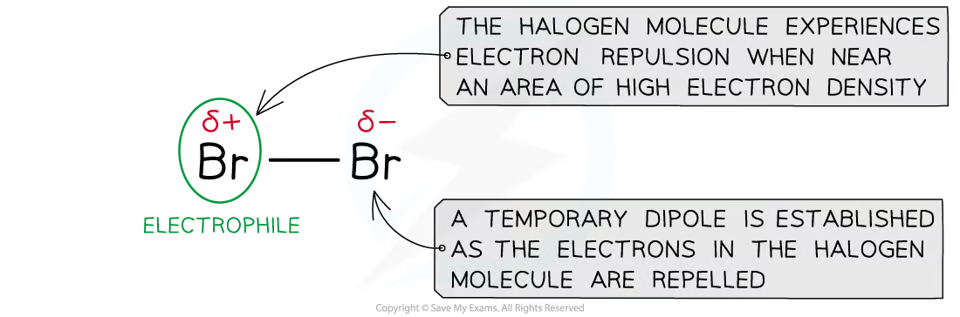
Electrophilic addition of halogens
mechanism for the electrophilic addition of halogens (and hydrogen) is the same as the electrophilic addition of hydrogen halides with one key exception:
Hydrogen halide molecules have a permanent dipole (as shown above)
Halogen molecules have a temporary (or induced) dipole caused by the repulsion of the halogens electrons by the high electron density C=C bond
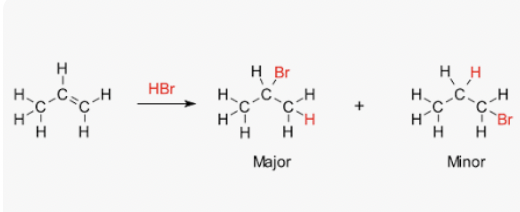
Asymmetric molecules addition
If e.g. HBr is added to one → 2 possible products can be formed
1 product is favoured over other and will be formed in greater amounts
Amount of each product is decided by intermediate carbocation
e.g. propene + Hydrogen bromide
2-bromopropane
1-bromopropane
Markownikoff’s rule:
when hydrogen halide reacts with an unsymmetrical alkene, the hydrogen of the hydrogen halide attaches to carbon that is attached to most hydrogen atoms and least carbon atoms
The major product will be the one that forms from _____
most stable carbocation (molecule in which a carbon atom has a positive charge and three bonds)
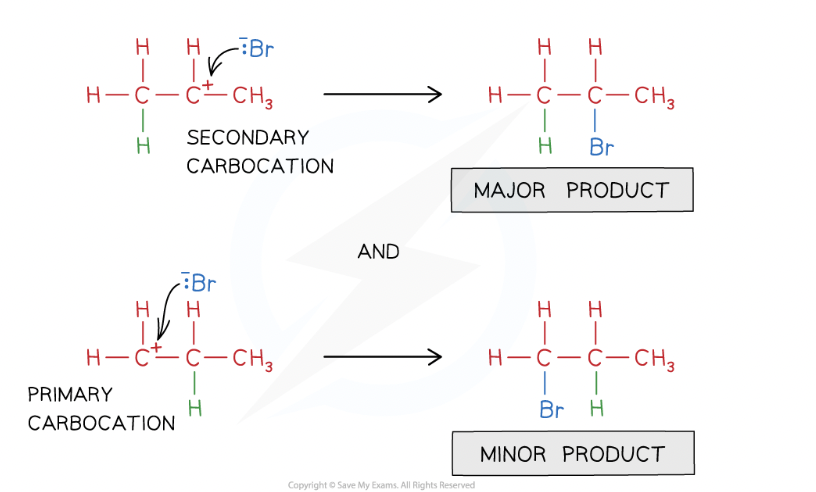
carbocation stability comes from ____
number of electrons releasing groups surrounding it
alkyl groups are what and why?
electron releasing groups as the electrons stabilise the pos charge by reducing it
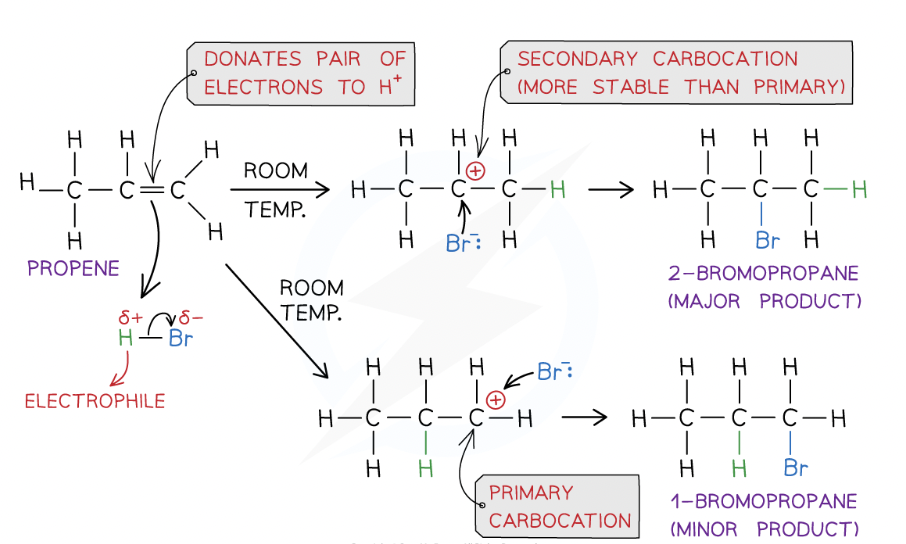
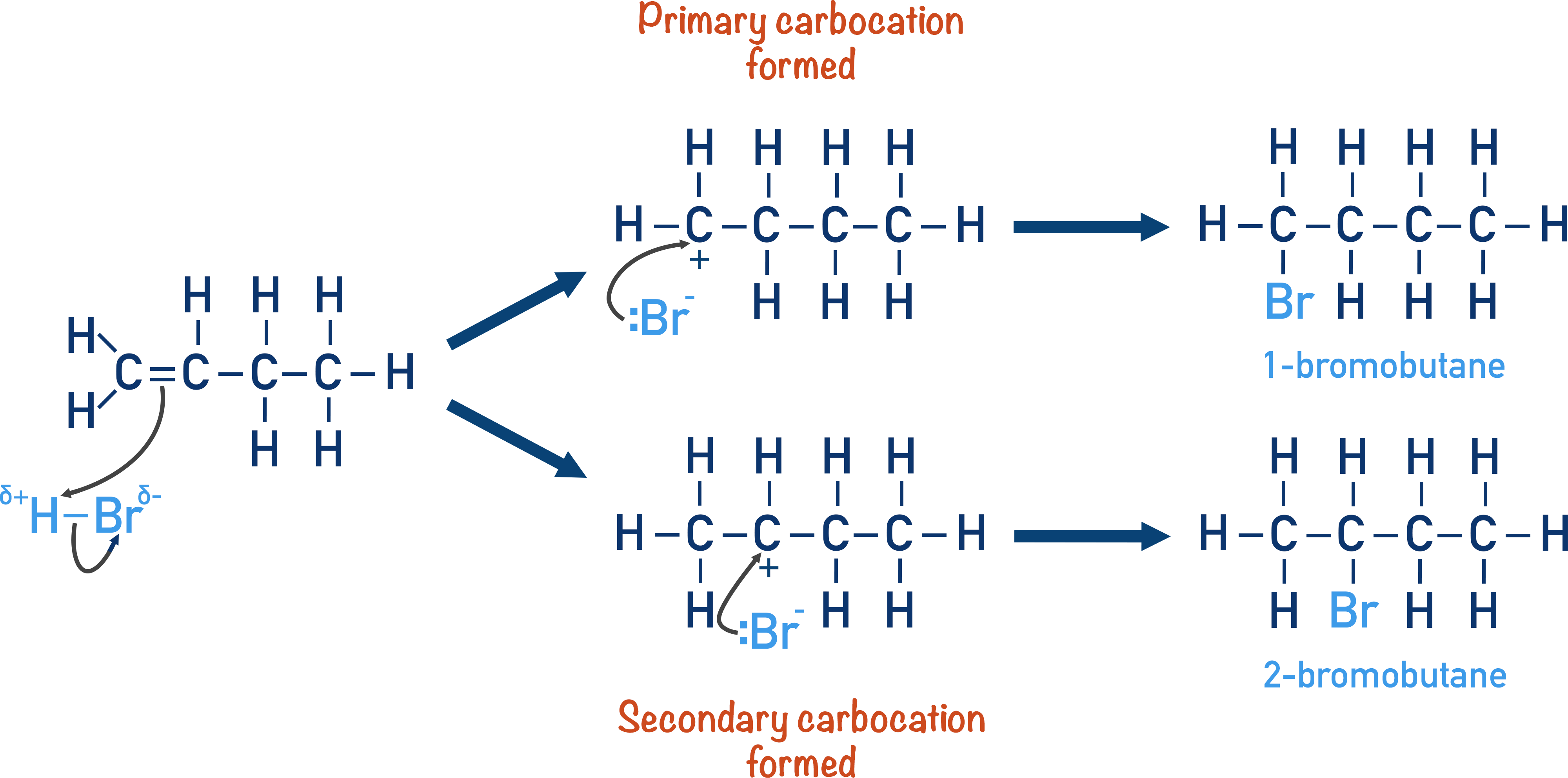
The mechanism for the electrophilic addition of hydrogen bromide to propene, showing the formation of the major and minor products can be shown as:
stability of the carbocation intermediate is as follows:
tertiary > secondary > primary
Primary carbocation
pos charge is on carbon atom at the end of the chain
secondary carbocation
pos charge is on carbon atom with 2 carbon chains attached to it
Addition polymerisation definition
is the reaction in which many monomers containing at least one C=C double bond form long chains of polymers as the only product
polymer definition
long-chain molecule that is made up of many repeating units
general formula for addition polymerisation
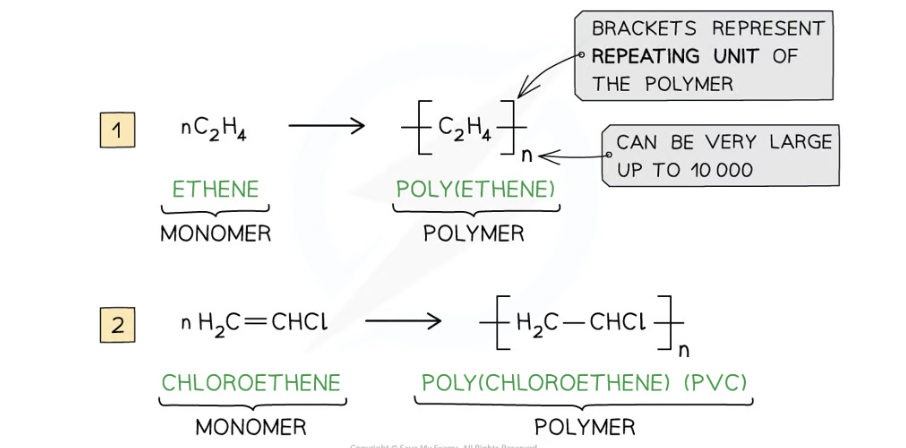
How many products does addition polymerisation form?
1
____ ____ of many polymers makes them ideal for certain use but what does this problem cause
low reactivity
disposal as a lot of polymers are non-biodegradable- environmental problems of waste plastic killing marine animals
polymer disposal: landfill sites
not ideal and various initiatives are being introduced aiming to reduce this method of waste disposal in general as well as with specific regard to polymers
recycling
reduces the amount of waste that it going to landfill sites
reduce the use of finite resources (Lots of polymers are made from the products of cracking crude oil and it's fractions)
time-consuming as they have to be sorted into the different categories
After sorting, the polymers are chopped, washed, dried, melted and then cast into pellets ready for use
Certain polymers can cause problems when recycling due to their chemical composition, e.g. PVC contains a large amount of toxic chlorine which can be released
Combustion
Since they have a large amount of energy stored within the polymer chains, these polymers can be incinerated
Formation of HCl/products of combustion cause acid rain
Formation of CO2/gases that cause global warming / greenhouse gases OR Formation of CO
Feedstock
where waste polymers are broken down, by chemical and thermal processes, into monomers, gases and oils
products are then used as the raw materials in the production of new polymers and other organic chemicals
major benefit of feedstock recycling, compared to other methods of polymer disposal, is that it works with unsorted and unwashed polymers
Bioplastics
polymers that are made from plant starch / cellulose, plant oils and plant proteins
provide a renewable and sustainable alternative to the current polymers which are predominantly based on finite resources such as crude oil
Biodegradable polymers
polymers can be broken down over time by microorganisms
polyester and polyamide condensation polymers are considered to be biodegradable as they can be broken down using hydrolysis reactions
This is a major advantage over the polymers produced using alkene monomers (polyalkenes)
When polyesters and polyamides are taken to landfill sites, they can be broken down easily and their products used for other applications
Compostable polymers
Compostable polymers are commonly plant based
Plant starch is being used in the production of biodegradable bin liners
Sugar cane fibres are replacing polystyrene in the production of disposable plates and cups
Compostable polymers degrade naturally leaving no harmful residues
Photodegradable polymers
Photodegradable polymers contain bonds that are weakened by absorbing light / visible radiation
This starts the breakdown of the polymer
A lot of photodegradable polymers are oil-based
In certain cases, an additive that absorbs light is mixed into the polymer to promote degradation
poly(chloroethene)
PVC / poly(vinyl chloride)
can make polymer flexible or rigid
uses- pipes, films and sheeting, ducts and profiles
poly(propene)
children’s toys, packaging crates, guttering
polystyrene/ poly(phenylethene)
packaging material, food trays + cups
poly(tetraflurethene)
non-stick frying pan
Why is poly-ethanol soluble but poly-1-ene is insoluble in water?
Soluble polymers has an alcohol group which can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules
Possible advantage and disadvantage to environment of disposing of polymers by combustion?
Advantage: Can make heat which is used to make steam to turn turbines to generate electricity
Disadvantage: Using up finite resources of oil to make polymers or toxic gases produced when combusted
Is electrophilic addition homolytic or hetrolytic and why?
Heterolytic, because curly arrows movement of pair of electrons, so bond breaks when both electrons to one of the bonded atom
Using Markownikoff’s rule why is one product major?
Tertiary carbocation is more stable than a secondary carbocation
Biodegradable polymers are often made from plant material and break down through microbial action to produce CO2 and water. People claim these polymers are carbon neutral, why can this can be true and untrue?
True- amount of CO2 released when polymer degrades is = to amount of CO2 taken in by plant photosynthesising
Untrue- Harvesting crop/ manufacturing + transport of crop/polymer likely use fossil fuels therefore more CO2 is emitted than absorbed
Despite having a C=C bond, why cant molecule demonstrate E/Z isomerism
each carbon of C=C double bond does not have different group attached to it
Why cant a molecule be cis or trans?
Each C atom of a C=C bond must have 2 different subsitiution groups
electrophilic addition
Radical substitution produces a mixture of organic products. Suggest two reasons why.
further substitution OR produces different termination products OR More than one termination step✔ substitution at different positions along chain