Section C - Coasts
1/190
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
191 Terms
What is a coast?
Where land meets sea made of saltwater.
What is the difference between a river and coast?
A river is a channel of freshwater flowing downhill whereas a coast is where land meets sea made of saltwater.
Define: Wave
Movement of water molecules caused by wind transferring energy to water as it blows over. This causes friction on water’s surface, causing ripples to form.
How are waves formed?
They’re formed by the wind blowing over the sea, transferring energy form the wind to the water. This creates friction on the waters surface, causing ripples to form, known as waves.
What does the size of a wave depend on?
Fetch.
Strength of wind.
How long the wind has been blowing for.
Speed of the wind.
What is the fetch of a wave?
How far the wave has travelled.
Name the 2 types of wave.
Constructive and Destructive.
Does the swash build or destroy the beach?
Build.
Does the backwash build or destroy the beach?
Destroy.
Does the swash or backwash build the beach?
Swash.
Does the swash or backwash destroy the beach?
Backwash.
Does the swash or backwash move up the coast, towards the beach?
Swash.
Does the swash or backwash move away from the beach and back to sea?
Backwash.
Does a constructive wave have a strong or weak wash?
Strong wash.
Does a constructive wave have a strong or weak backwash?
Weak backwash.
Does a destructive wave have a strong or weak wash?
Weak wash.
Does a destructive wave have a strong or weak backwash?
Strong backwash.
Describe features of a constructive wave.
Strong wash, weak backwash.
Long wavelength.
Low energy.
Shorter.
Far apart.
Less frequent.
Gently spill over onto the beach.
Build up the beach.
Describe features of a destructive wave.
Strong backwash, weak wash.
Short wavelength.
High energy.
Taller.
Close together.
Very frequent.
Break and crash.
Destroy the beach.
Are constructive waves high or low energy?
Low energy.
Are destructive waves high or low energy?
High energy.
Are constructive waves frequent or infrequent?
Infrequent.
Are destructive waves frequent or infrequent?
Very frequent.
Are constructive waves taller or shorter?
Shorter.
Are destructive waves taller or shorter?
Taller.
Are constructive waves close together or far apart?
Far apart.
Are destructive waves close together or far apart?
Close together.
Do constructive waves have a short or long wavelength?
Long wavelength.
Do destructive waves have a short or long wavelength?
Short wavelength.
Do constructive waves gently break and crash or gently spill over?
Gently spill over.
Do destructive waves gently break and crash or gently spill over?
Break and crash.
Do constructive waves build or destroy the beach?
Build the beach.
Do destructive waves build or destroy the beach?
Destroy the beach.
Compare two features of destructive and constructive waves.
Destructive waves are steeper and higher whereas constructive waves have a lower height.
Destructive waves have high energy whereas constructive waves have lower
energy.
Constructive waves help to build up the beach whereas destructive waves destroy/remove material.
Constructive waves are spilling whereas destructive waves are plunging.
Destructive waves are closer together but constructive waves are far
apart.
Destructive waves have a shorter wavelength whilst constructive waves ave a longer wavelength.
Constructive waves have strong swash whereas destructive waves have
strong backwash.
What is the lowest part/base of a wave?
Trough.
What is the top part of a wave?
Crest.
What type of orbit does water move in out at sea?
Circular orbit.
Why does water move in a circular orbit out at sea?
There’s less friction in deep water.
Do waves get taller/bigger or shorter/smaller in shallow water?
Taller and bigger.
Why does land slows down the water?
Due to friction.
What type of orbit does water move in shallow sea?
Elliptical orbit.
Does the trough of wave slow down or continue to move at the same speed when it hits land?
Slow down.
Does the crest of wave slow down or continue to move at the same speed when it hits land?
Continues to move forward at the same speed.
Explain how waves break.
Waves start out at sea, moving in a circular orbit.
As waves approach the shore/land, friction slows down the trough of the wave.
This causes the water to move in an elliptical orbit until the top of the waves breaks over.
Define: Weathering
Breakdown of rock in situ.
Describe freeze thaw weathering.
Water gets into a crack in the rock and freezes when the temperature drops.
The ice in the rock expands, creating more weaknesses in the rock and causing the crack to widen.
Process repeats until the rock eventually splits.
What is chemical weathering?
Slightly acidic rain chemically reacts with the rock and rots it away.
Define: Erosion
The breakdown of rock.
What is hydraulic action?
Sheer force of waves banging against a cliff.
What is abrasion?
Waves throw rocks at the cliff, eroding it.
What is attrition?
Pebbles/rocks in the seawater hit and knock against each other, making them smoother, smaller and rounder.
What is corrosion?
Sea water is slightly acidic so dissolves rocks.
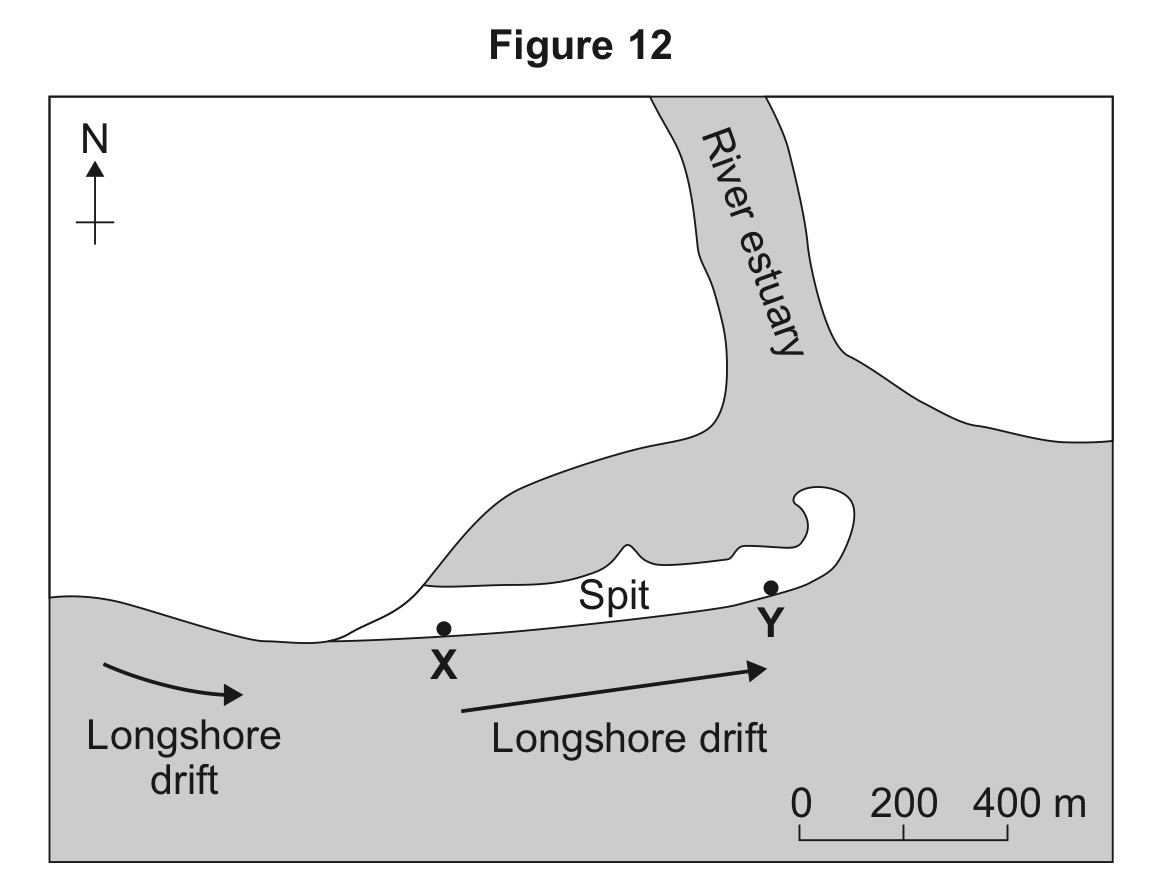
Suggest one reason for the difference in sediment see between location X and Y.
Longshore drift carries the lighter material much further along the spit.
Heaviest material is only carried a short distance.
Greater erosion/attrition as sediment is carried further along the coast.
Define: Transportation
Movement of rock/materials by the seawater.
What is traction?
Large boulders roll along the seabed.
What is saltation?
Pebbles bounce along the seabed.
What is solution?
Chemicals dissolve in the water and are carried along.
What is suspension?
Particles are suspended and carried along by the river.
What is longshore drift?
Transportation of sediments along the coast in a zig zag movement.
Explain how longshore drift occurs.
Longshore drift is the transportation of sediments along the coast in a zig zag movement.
Prevailing wind determines the angle of waves approaching the beach.
Swash brings up sediment to beach.
As swash dies, backwash carries sediments away at right angle, pulled by gravity.
Process repeats to create zing zag movement.
Define: Deposition
When the water’s velocity drops and loses energy, it drops the sediment (sand, rocks, pebbles etc.) it had been carrying.
What is mass movement?
Downslope movement of sediment (rocks, soil) caused by gravity.
What is a landslide?
Blocks of rock slide downhill, lubricated by heavy rain which saturates the soil to weaken the slope.
What is a slumping?
Occurs after heavy rain weakens the slope and saturates the soil, causing materials to move down a curved cliff in a rotational manner.
What is a rock fall?
Fragments of rock break off from the cliff surface due to freeze thaw weathering and fall down with no contact to the cliff.
Is hard or soft rock more resistant to erosion?
Hard rock.
Is hard or soft rock less resistant to erosion?
Soft rock.
Does hard or soft rock create high, steep, tall cliffs and rugged landscapes?
Hard rock.
Does hard or soft rock create smoother, lower, gentle cliffs?
Soft rock.
What is a discordant coastline?
Alternating type of rock.
What is a concordant coastline?
The same type of rock throughout.
What type of coastline do headlands and bays form on?
Discordant coastline.
Give examples of soft rock.
Clay + Sandstone.
Give examples of hard rock.
Granite + Limestone + Chalk.
What is often found on bays?
Beaches.
Where are beaches found?
Bays.
Why are beaches often found on bays?
Wave energy is weak at bays as headlands block the winds. This means constructive waves with weaker wave energy occur at bays to form beaches.
What is a bay?
Crescent shaped indentation, often beaches found here.
What is a crescent shaped indentation, where beaches are often found?
Bays.
What is a headland?
Pieces of hard rock jutting/sticking out at sea.
What is a piece of hard rock jutting/sticking out at sea called?
Headland.
Are headlands and bays depositional or erosional landforms?
Erosional.
Define: Landform
Unique, natural features on the Earth’s surface.
Give examples of erosional costal landforms.
Headlands and Bays.
Wave cute platforms.
Caves, arches, stacks and stumps.
Give examples of depositional costal landforms.
Beaches.
Sand dunes.
Spits and Bars.
Describe the formation of headlands and bays.
Forms on a discordant coastline meaning it has alternating rock types.
Soft rock like sandstone is less resistant to erosion than hard rock like granite.
Abrasion and hydraulic action quickly erode the soft rock, leaving behind the hard rock.
This forms headlands, which is a piece of hard rock jutting/sticking out at sea + Bays, which are crescent shaped indentations.
Beaches are often found on bays because constructive waves occur here. This is because wave energy is weaker as the winds are blocked by the headlands.
What is a wave cut platform?
Smooth area of rock at the base of a cliff; exposed at low tide.
Are wave cut platforms exposed at low or high tide?
Low tide.
Are wave cut platforms depositional or erosional landforms?
Erosional.
Describe the formation of a wave cut platform.
Strong waves bang against the base of a cliff between the high and low tide mark.
This results in abrasion and hydraulic action eroding the cliff base.
This forms a wave cute notch (dent in a cliff) that widens over time as a result of continuous hydraulic action.
It eventually undercuts cliff for an unstable overhang of hard rock to form.
Eventually, the overhang collapses due to gravity, no support and weathering on top.
Fallen rocks settle at base and are exposed at a low tide.
At high tide, rocks are eroded by abrasion, smoothing out the rock.
Leaves behind a smooth wave cut platform, exposed at low tide.
The cliff continues to retreat as process repeats.
What is a stack?
A tall isolated column hard rock.
Put these in order of formation: Arch, Stump, Cracks, Stack, Headland, Cave
Headland, Cracks, Cave, Arch, Stack, Stump.
Are caves, arches, stacks and stumps erosional or depositional landforms?
Erosional.
Describe the formation of a stump.
A headland is a puce of hard rock jutting out at sea.
The headland is eroded by abrasion and hydraulic action, creating weaknesses in the rock and therefore forming large crack.
Erosional processes continue to weaken the rock and create further cracks, forming a cave, that widens and deepens with more erosion.
The sea then cuts through the cave to the other side of the headland, forming an arch.
On top of the arch, freeze thaw weathering occurs whilst erosion occurs at the base, making the arch less stable/weak and more likely to collapse.
Eventually, the heavy rock at the top of the arch collapses due to the weathering, erosion, gravity and no support.
This leaves a stack which is a pillar/column of detached, isolated hard rock.
Weathering and erosion occur on the stack, undercutting the column to leave a stump behind, disconnected from the headland.
Are beaches depositional or erosional landforms?
Depositional.
What does a beach form between?
High or low tides.
What is a beach?
A depositional landform that forms between high and low tide levels.
Name the 2 types of beaches.
Sandy + Pebble/Shingle.
Describe the features of a sandy beach.
Formed in sheltered bays by low energy constructive waves.
Deposit sediment onto the beach to build it.
Sand dunes found here.
Fairly, flat profile.
Describe the features of a shingle beach.
High energy, stronger constructive waves.
Remove finer sediment from the beach and leave behind the large pebbles.
Berms found here.
Steep profile.