Vertebrate Zoology Exam 1 - Clades & Synapomorphies
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Other flashcards for Vertebrate Zoology can be found under the tag "11:216:325"
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Cyclostomata
Clade comprised of Hagfish (Myxiniformes) and Lungfish (Petromyzontiformes)
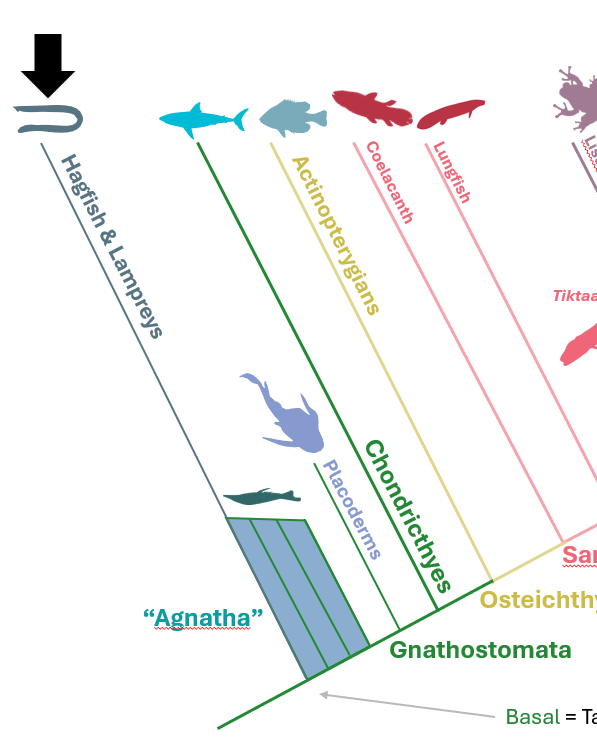
What are some defining characteristics of Cyclostomata?
Cyclostomata = extant jawless vertebrates
Single median nostril
Branchial basket (arch that supports gills)
Gill arch skeleton lateral to/outside of gill tissue (instead of medial/inside of)
Unique tongue that is NOT homologous with the gnathostome tongue
* Image includes Chondrichthyan diagrams (B&D) for comparison
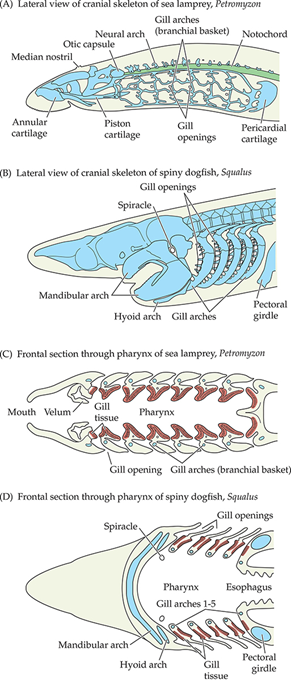
“Hagfish” refers to what clade?
Myxiniformes
What are the two major genera of Hagfish (Myxiniformes)?
Eptatretus and Myxine
What are some defining characteristics of Myxiniformes?
SYNAPOMORPHY: SLIME GLANDS
The slime chokes and deters gnathostome predators
Single median nostril
Pharynx and gill slits are posterior to the head
Single median fin
Pre-anal fin (the only extant vertebrates to have one)
Teeth arranged horizontally <—>
No larval stage
Reduced features (such as no eyes)
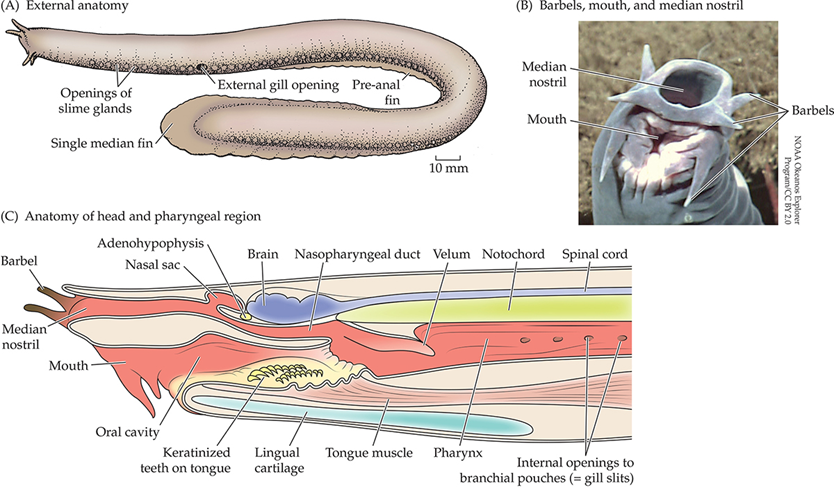
“Lampreys” refers to what clade?
Petromyzontiformes
What are the two major genera of Petromyzontiformes?
Petromyzon (meaning “stone sucker”) and Lampetra
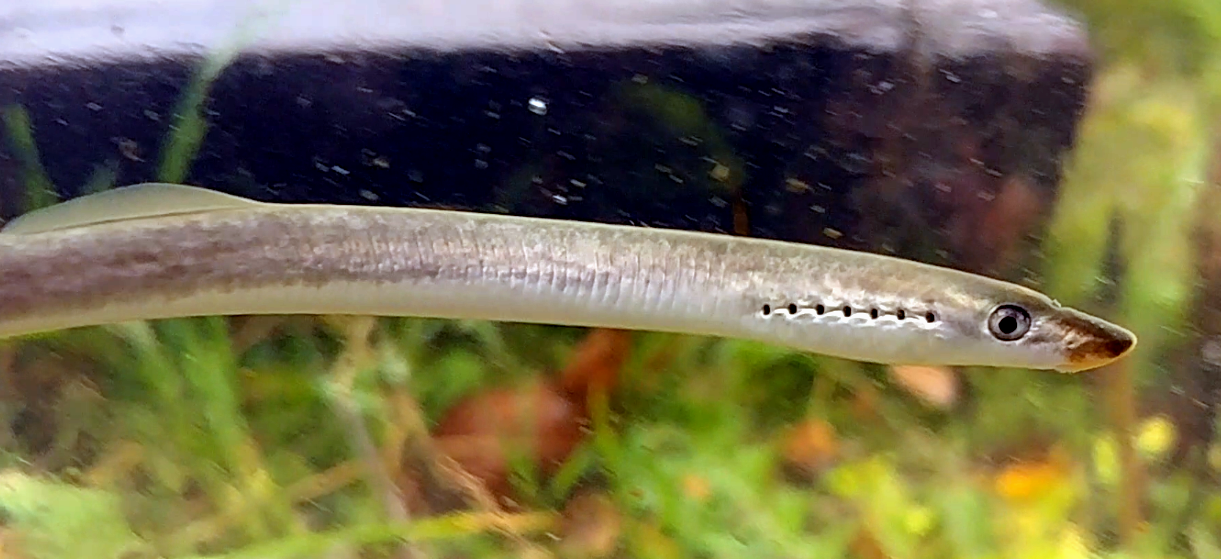
Image: Lampetra planeri

What are some defining characteristics of Petromyzontiformes?
SYNAPOMORPHIES:
7 pairs of gill pouches
Round mouth located at bottom of buccal funnel
Buccal funnel displaced the single median nostril to the top of the head
Well developed eyes w/ color vision
Pineal eye homologous to pineal gland of mammals
Larvae are filter feeders that use velum to pump water for filter feeding
Parasitic species feed on fluid
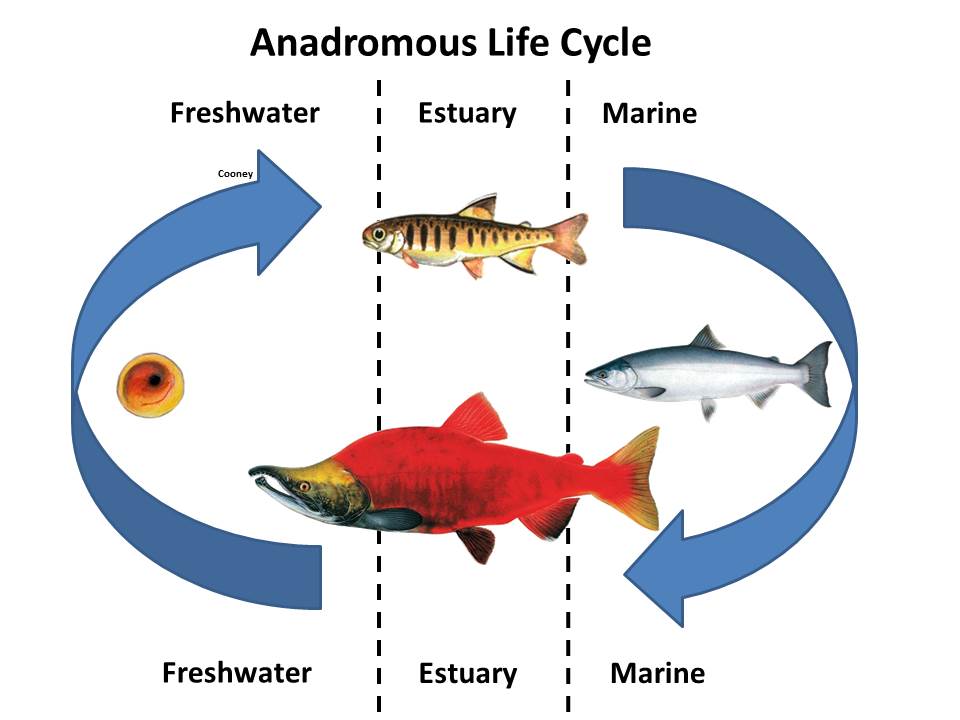
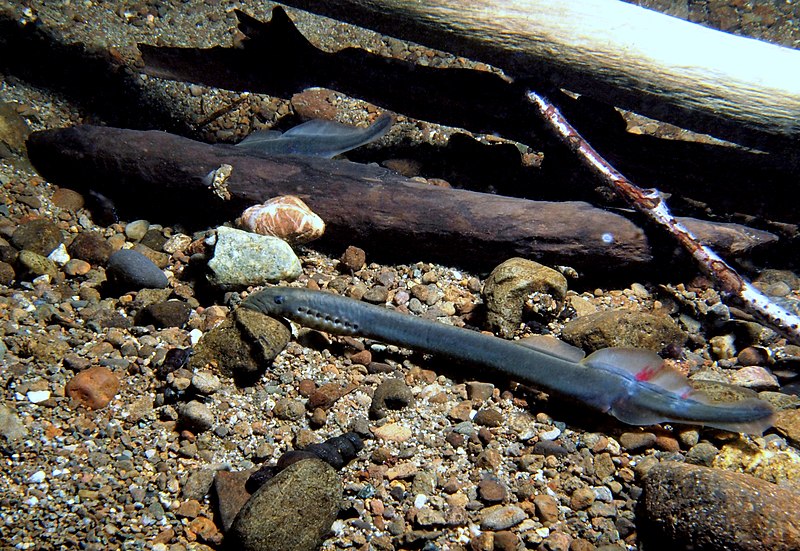
Anadromy
Spawning occurs in freshwater, larvae grow in freshwater, but adults live in the ocean
Freshwater <—> Ocean
Potamodromy
Life cycle entirely in freshwater
EX: Potamodromous lampreys live in large lakes and ascend rivers and streams to breed

Cryptobranchidae
Clade of hellbenders and giant salamanders, within Caudata
Sirenidae
Clade of sirens, within Caudata
What is unique about Sirenidae compared to the rest of Caudata?
They lack hindlimbs and the pelvic girdle
Ambystomatidae
Clade of mole salamanders, within Caudata
Proteidae
Clade of mudpuppies, within Caudata
Amphiumidae
Clade of amphiumas, within Caudata
Amphiumas - elongated equative salamanders lacking gills
Plethodontidae
Clade of lungless salamanders, within Caudata
Contains 2/3 of extant salamander species