Populations in ecosystems:
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
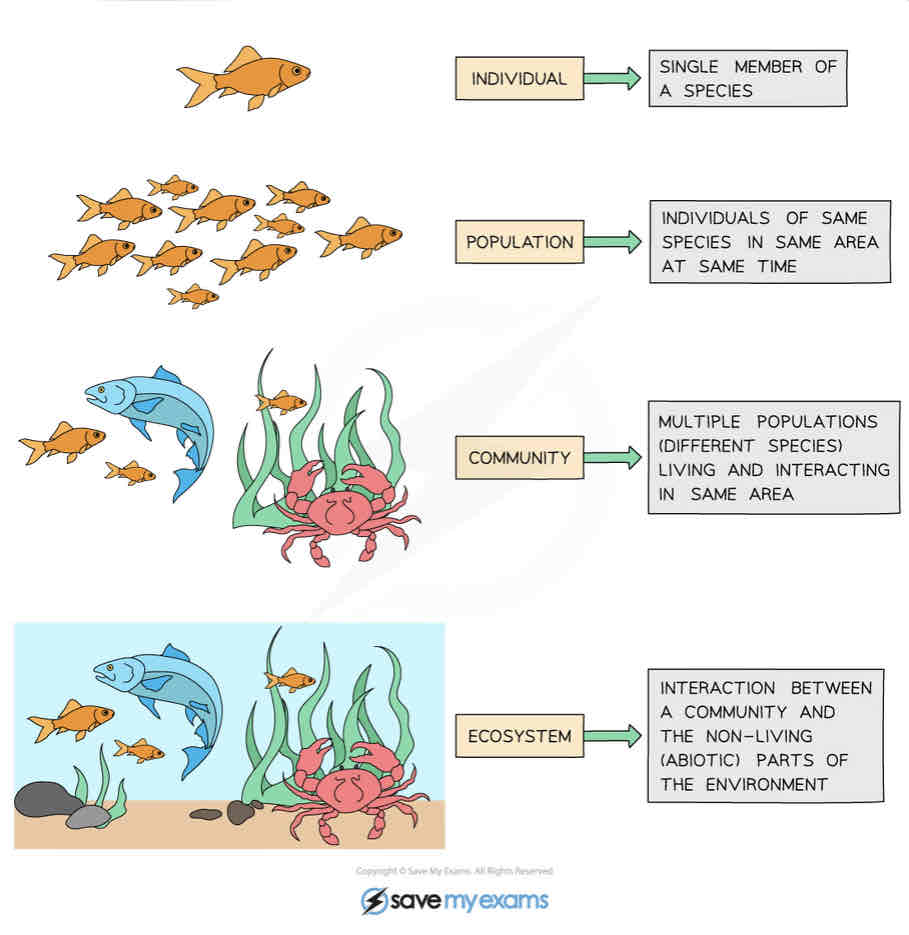
Define species:
A group of organisms that can interbreed to produce fertile offspring
Define population:
Individuals of the same species in the same area at the same time
Define community:
Multiple populations of different species living in the same area
Define ecosystem:
The interaction between a community and the non-living parts of the environment.
Read through this: ( do you understand)
Yes
Define habitat:
Place where organism lives
Define niche :
The role of an organism in the ecosystem, where is lives and what it does.
Define environment:
Set of conditions that surrounds an organism, containing the abiotic and biotic factors
What are biotic factors :
Living parts of the environment
What are abiotic factors?
The non-living parts to the environment.
Define biosphere:
The areas of the earth that are occupied by living organisms
Why do we use logarithms ?
Used to compare data that has a large range. When converted to log we can read the points off the graph more accurately.
What is the competitive exclusion principle ?
Two species or organisms cannot occupy the same niche as one will always outcompete the other.
What is an advantage that two species occupy different ecological niches ?
They won’t compete for the same resources such as food and water, therefore they will have a greater chance of survival and more likely to pass on their advantageous alleles to their offspring
What does a demographic transition graph show ?
The link between the birth rate, death rate and population changes ( immigration and emigration)
What is the carrying capacity of a population ?
the maximum number of individuals that the environment can sustain.
See hand written notes for human population growth in booklet
Ok
What are these example of : predation, competition, disease, new pathogens, food ability ?
Biotic factors (living)
What are these examples of: water, minerals in the soil, water, humidity, temperature ?
Abiotic factors ( non living)
What are the 5 abiotic (non-living) factors that can affect population size ?
temperature
Light
pH
Wind
Humidity
How does water affect population size ?
When there is little water, populations are small of only one species that is well adapted to dry conditions.
How does light effect population size ?
Light is a source of energy for the light-dependant reaction of photosynthesis. So an light intensity increases the rate of photosynthesis also increases. So the plants grow, which means their is grater food for animals to feed on. So the animals carrying capacity increases .
How does temperature affect population size ?
Each species has a different optimum um temperature, if changed (high), enzymes will denature and reduce carrying capacity of species. If temp is low, enzymes work slowly so metabolic rate of species is reduced. So reduced carrying capacity.
Competition is a ……………… factor
Biotic
What is competition ?
It’s when 2 or more individuals fight to get the same resource as its in short supply.
True or false, During competition, ‘ the more similar the individuals are, the more intense the competition is’
True
What is intraspecific competition ?
Competition between individuals of the SAME species.
Why is intraspecific competition good ?
As the individual who is stronger and better adapted will survive, as pass on their advantageous alleles onto their offspring.
What is interspecific competition ?
Competition that occurs between individuals of different species.
Why is interspecific competition seen as less fierce ?
As the individuals competing are probably from different habitats, and because they are differnt species, they will have multiple different food resources.
What is succession ?
The process in which an ecosystem changes over time.
What is the first species that appears to colonise the area in succession ?
Pioneer species
Describe the process of succession ;
firstly the pioneer species colonises the area
The pioneer species then die and this changes the abiotic conditions which makes the land less hostile.
New species are now able to colonise the area and outcompete the pioneer species
Then when these organisms dies, they add more nutrients to the soil ( humus) so larger plants can grow
The ecosystem then increases in species diversity
Eventually a climax community is reached
This is when the abiotic factors are fairly constant and the community is relatively stable.
What is the mark-recapture method ?
It’s a method used to estimate the size of a population where fast-moving organisms are involved.
Describe the mark-recapture method;
firstly the animals are caught in an ethical, safe way that doesn’t cause any harm to the animals.
Then you would mark the animals in a non-toxic way that wouldn’t make them stand out to predators.
Then release them back into their natural habitat.
Then wait a certain period of time to allow the animals to be evenly distributed among the rest of their population.
Then recapture the animals and count how many have a mark.
Then use this equation to estimate the population size: Number caught in 1st capture x number caught in 2nd capture / no of animals marked in 2nd capture
What is conservation ?
protection of species and habitats to maintain biodiversity
Describe how succession is used as a method of conservation ?
this is when there is deliberate interference to prevent the ecosystems from developing further.
This can be achieved through letting animals graze on the land or setting controlled fires to certain areas of land so that the pioneer species can be conserved again.
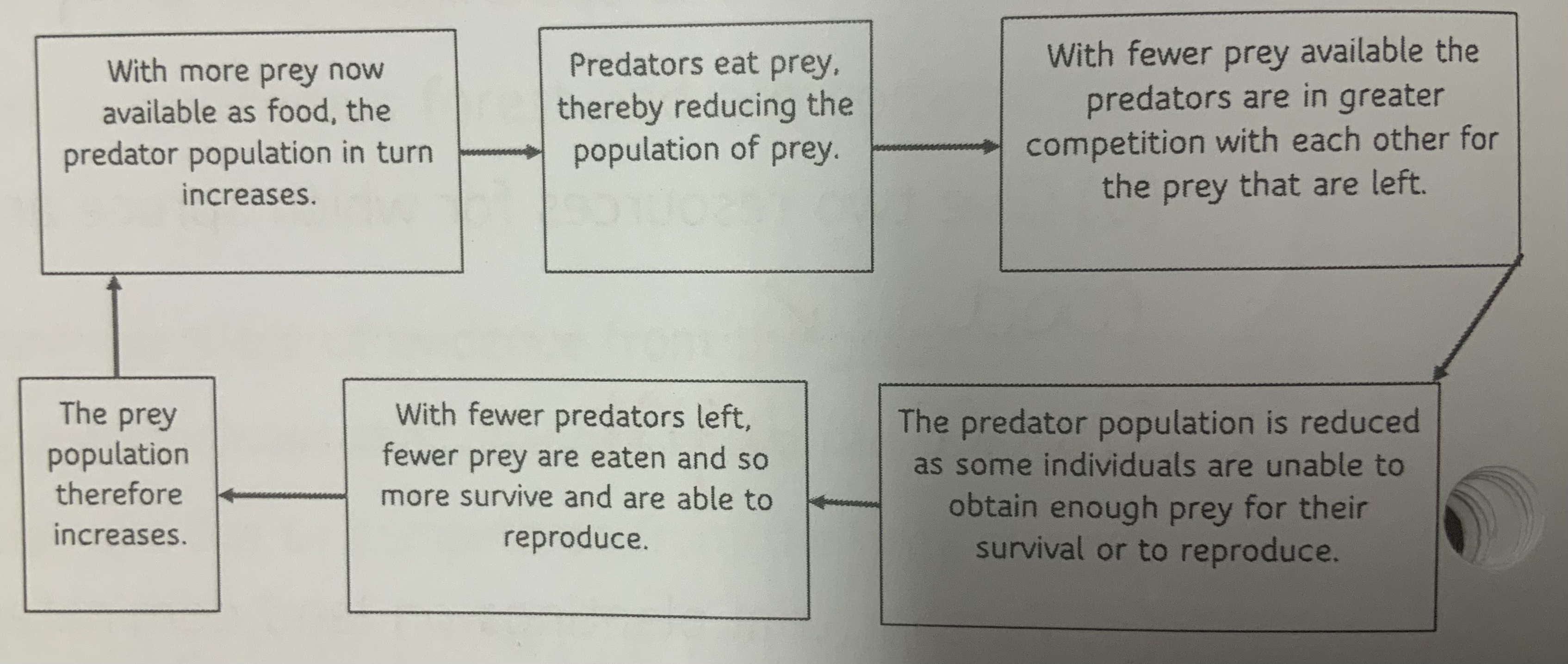
What is predation ?
It’s when an organism kills and eats another organism as a source of food .
What are two main features of a predator-prey cycle ?
that the number of predators in usually lower than the prey
The number of predators increase when the prey increase.
How is the predator-prey cycle important for evolution ?
the prey that are better suited and are able to escape the prey are more likely to survive and reproduce. And pass on their advantageous alleles to the offspring.
Do you understand ?
Yes
What is the equation for population size when using a Quadrat ?
Population size = mean number of organisms in all Quadrats x total size of area where organism lives / area of one Quadrat