Anatomy L4 Ear Anatomy and Equilibrium/Balance
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
what are the regions of the ear?
external/outer ear
middle ear
internal ear
what structures compose the outer ear?
auricles (aka pina or helix)
external auditory meatus
tympanic membrane (TM)
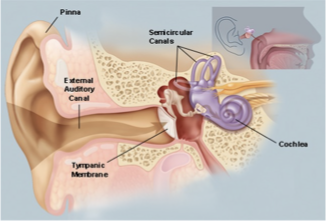
what is the function of the auricles?
collect sounds
what part of the auricles is devoid of cartilage?
lobule aka the ear lobes
what is the function of the external auditory meatus?
conducts sounds to the tympanic membrane
describe the external auditory meatus
a curved tube of cartilage (lateral 1/3) & bone (medial 2/3) leading into temporal bone
what are ceruminous glands?
glands that secrete cerumen aka ear wax
how does hearing sounds work in the external ear?
the auricle will collect sound and direct it to the external auditory meatus where the sound will continue to flow down to the tympanic membrane
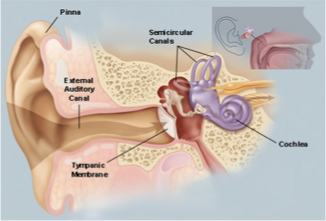
what is the shape of the TM?
cone shaped
the middle ear contains
the tympanic cavity
auditory ossicles
what are auditory ossicles?
tiny mobile bones
malleus, incus, stapes
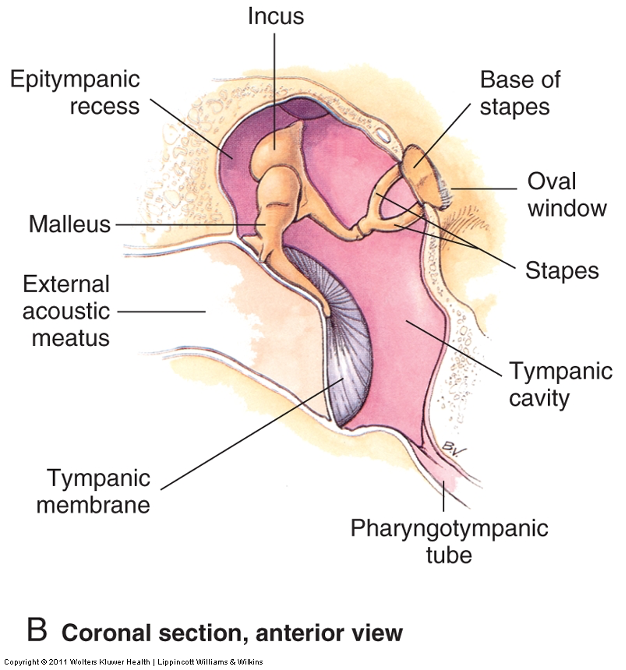
what are some important structures of the TM?
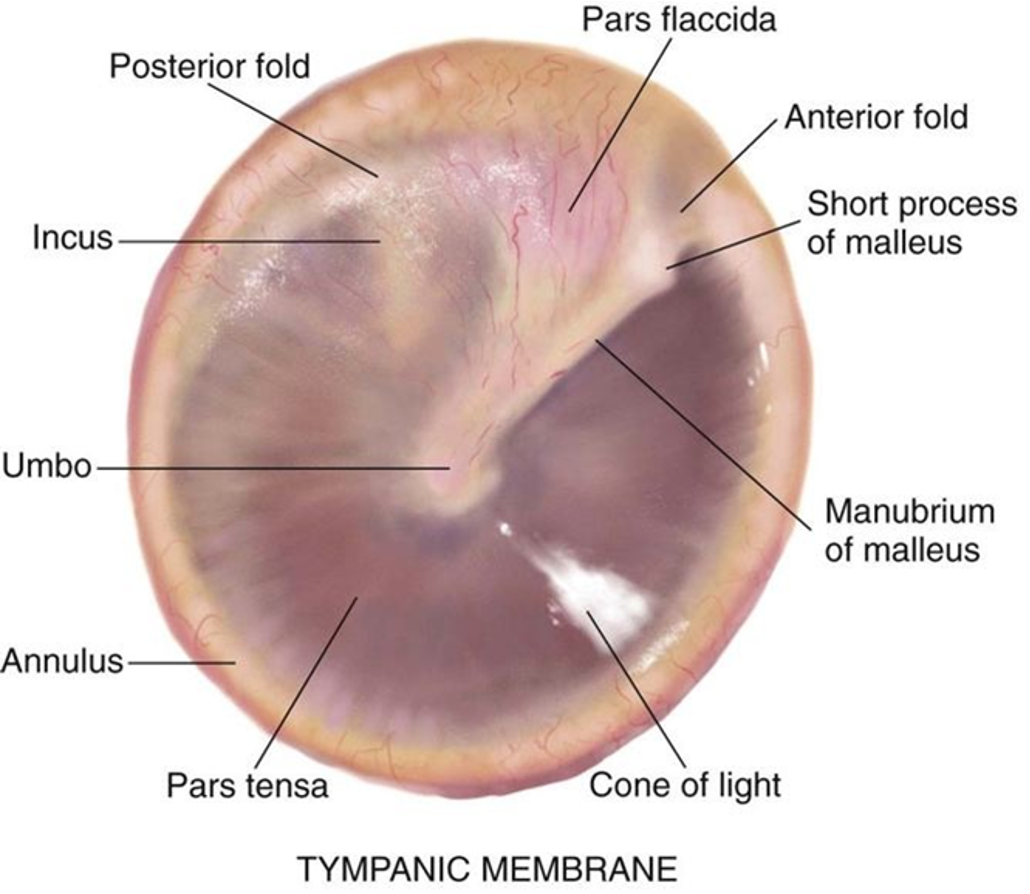
what is the function of the TM?
separates the external ear from the middle ear
transmits sound from air to the ossicles
what is a perforation?
a hole
what is the eustachian tube? what does it do?
aka:
auditory tube
pharyngotympanic tube
Connects the middle ear to the nasopharynx
Equalizes pressure in the middle ear
Allows air to move the TM during valsalva
the internal ear contains
3 semicircular canals
vestibule
cochlea
cochlea duct
what is the function of the 3 semicircular canals?
aid in equilibrium
what planes are the 3 semicircular canals? function
anterior: detects nodd up and down
posterior: detects tilting left and right
lateral: detects shaking side to side
the the 3 semicircular canals are involved in what type of equilibrium?
dynamic equilibrium
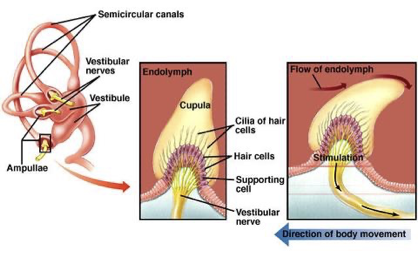
what are the organs found in the the 3 semicircular canals?
the ampulla which contains the:
crista ampullaris
contain hair cells covered in cupula (gelatinous)
what is the cochlea divided into?
Oval window (entrance)
Round window (exit)
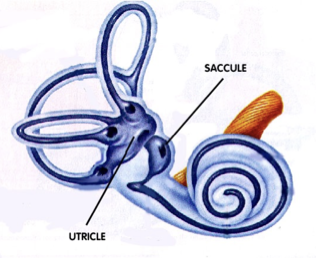
what is the vestibule divided into? what do they detect?
Utricle
detects side to side and back and froth movement
Saccule
detects up and down movemnets
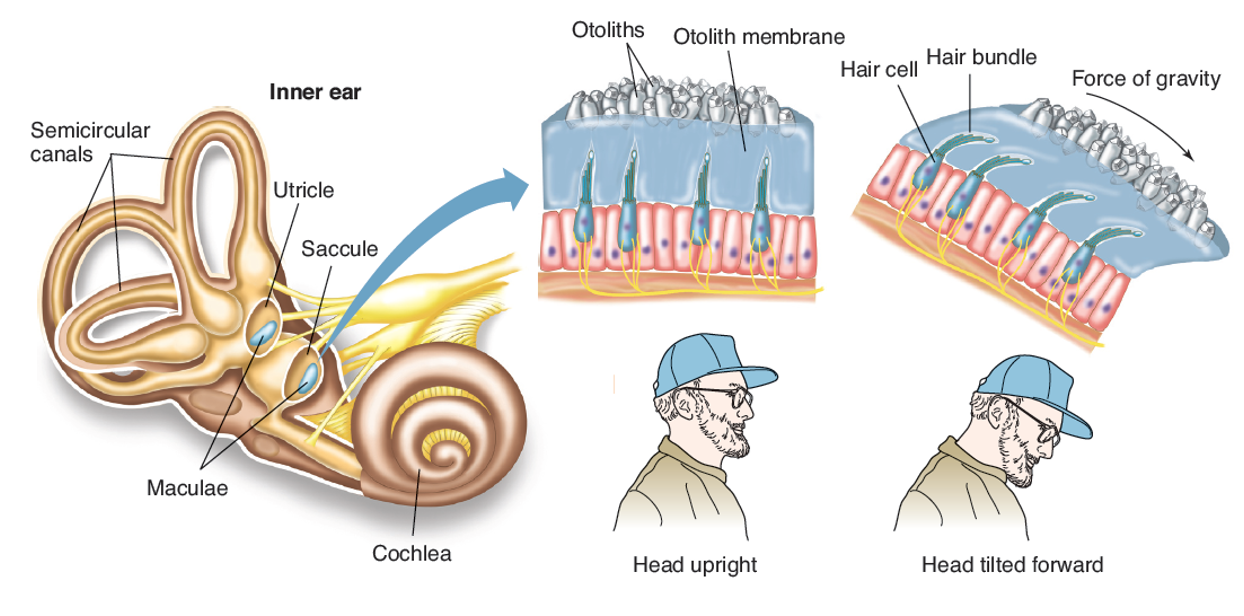
what are otoliths?
hard, calcium carbonate structures
where are otoliths located?
saccule and utricle
aka the vestibule
what are otoliths sensitive to?
to gravity and static/linear acceleration
what stimulates hair cells when the head moves?
otoliths
what is the cochlea duct divided into?
scala vestibuli
scala media
scala tympani
where are the stereocilia located?
the corti in the cochlea duct
what serves as a receptor for sound?
stereocilia
the cochlear hair cells
what does the stereocilia do?
converts vibration into nerve impulses
the sense of equilibrium consists of what?
static (head straight) equilibrium and dynamic equilibrium
what is static equillibrium?
the position of the head is sensed while head and body are still
what is dynamic equillibrium?
when the head and body move or rotate, the motion is detected, aiding in balance
what is the ampullae responsible for?
balance
what is the cupula responsible for?
balance