main groups of life
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
(phylum) porifera
-sponges
-basal w no special tissues
-only specialized cells
-one way in and out→not blind gut
Filter feeder
Water passes through their system and the filter out the food they wants and food they dont
Cnidaria
-sea nettles, jelly fish, etc.
-radial symmetry
-specialized tissues
-one way in and out
-first organisms to have a body w 2 layers
Alteration of generations - Cnidarians
Polyp→medusa
Cnidocytes
-What Cnidarians use to grab prey
-stinging structure(tentacles)
Protosomes
-Animals where the mouth developed first
-contains nephrozoans and ecdysozoa
Blind gut
-cnidarians
-one hole for everything
Through gut
-Anus AND mouth
-One for eating one for shitting
Nephrozoa(NS)
-through gut animal with
Bilateral symmetry
Throught guts
The coelom-body cavity filled with fluid and internal organs
Blastula and gastrula
Start as a blastula-hollow ball one cell thick
Triple a in thickness
Hole punched through and is now a gastrula→forms digestive tract
Spiralia
-a big clade of protosomes→are nephrozoan
-contains
Flatworms
Molusks
Annelids
Gastropods
Bivalves
Flatworms
-No respiratory or circulatory system
-First animals that can pee with flame cells
-have nervous system
Cephilization
Having sensory system around the head(like our nose and eyes)
Annelids
-segmented worms
-septa→internals walls
-cuticle to avoid drying out-respiration
-some with gills
-closed circulatory system
Mollusks
-sister to annelids
-radulla-’tongue’ covered with teeth
contains:
Chitons
Cephalopods
Gastropods
Bivalves
-Mantle-reproductive system
-All have open circulatory systems except cehpalopods
Cephalopods
-squids, octopus
-foot becomes feeding structure
-mantle becomes jet propeller
-some with shells other have them greatly reduced
Colour changing
-mollusks
Gastropods
-group of mollusks
-slugs and snails
-defined by torsion-body twists so anus is on the head
Bivalves
-clams, scallops, etc.
-shell enclosed whole body
Chitons
Small mollusks w segmented shells
Ecdysozoa
-major group within protosomes
-contains
Nematodes
Arthopods
Nematodes
-roundworms
-piercing mouthparts
Arthopods
3 main lineages
Tardigrades
Velvet worms
True arthopods
Tradigrades and Velvet worms are not true arthopods
-very large group
-crustaseans, insects, arachnids
Arthopod features
Contains
Exoskeleton
Moulting
Limb segmentation
Body segmentation
Open circulation
Chelicerae
-Major phylum of arthopods
-piercing mouthparts with venom ous enzymes
-spiders, centipedes, millipedes
Exoskeleton and moulting
-dedicated to movement
-made of chitin
-limited growth→moult
-moulting:shedding exoskeleton
Segmented limbs
-Like joints that they can bend to help with mobility
-stiff
Segmented bodies
Segmented into tagmata Similar to the head abdomen and thorax
Echinoderms
-sea urchins, sea stars, sea cucumbers
-Water vascular system
-Most don't have anuses
-have statocysts
-Can fragment but needs part of the center of their body
-not hermaphrodites
Stacocysts
Allows animal to tell if their upside down or right side up
Water vascular system
-pumps blood through feet to move
-also used as their heart and lungs
Hermaphrodites
Has both male and female reproductive parts
Chordates
-Our closest relatives
-contains
Lancelets
Agnathans
Chonorichthyes
Osteichthyes
Tetra pods
Amnitoes
Sauropsids
Mammals
Lancelets
Simplest vertavrate wo a brain heart or skull
Agnathan
Have
True hearts
Brains
Skulls
Sensory structures
Chonorichthyes
-Sharks
-first vertabrates with jaws
Osteichthyes
-With actuals bones→not cartilage
-thin and feathered out
-most fish
-lobe finned fish and lung fish
Tetrapods
-lobed finned fish that adapted to live on land
-silver fish 🤢
Amnitoes
-Produces amniotic egg:embryo covered in waterproof membrane
Sauropsids
Modern reptiles and birds
Mammals
-Produces milk
-has fur
Marsupials
First group of animals with placentas→mammals
Monotremes
Egg laying mammals
Neotny
Slowing growth
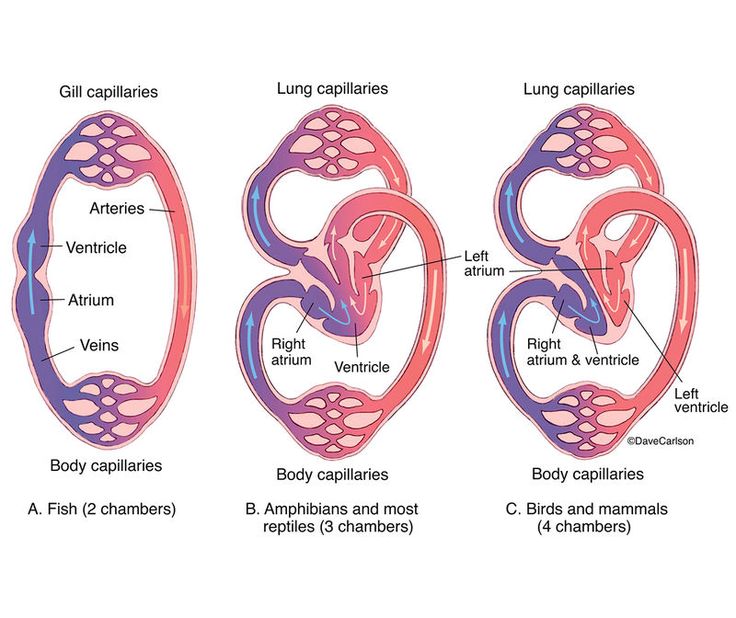
chamber heart
-Water fish:2 chambers, one loop around, blood goes to the heart→gills→body→back to heart
-amphibians and most reptiles:3 chambers, 2 loops, blood enters heart→oxegynated and deoxygenated blood mix in the ventricle→half the blood loops around to the lungs and back→other half loops to the body and back
-mammals:4 chambers, ventricle has a wall between so all blood is oxygenated, blood enters heart into the left ventricle and passes the lungs→goes into right ventricle and loops to the body→back to the left ventricle
Siphon
-in gastropods, cephalopods, bivalves
-lets water (and some air) flow to and from the mantles cavity
Mandibulates
-sister to chelicerae
-3 tagmata
-jaws and antennae
Tagmata
Arthopod body parts are split into tagmata but not all have 3 tagmata, just insects
-thorax, head, abdomen
Lissamphibia
Group of tetrapods that include all amphibians