Exam 5 Digital Imaging
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
121 Terms
absorption material is the part that decides if the IR is direct or indirect technology (made of DELS)
TFT flat panel digital image detector
what are the three components of each DEL
detector surface area
capacitor
TFT
stores electrical charge until read-out
capacitor
what is the job of the detector surface area
capture signal
isolates each DEL
reacts like a switch (sends charges to image processor)
Thin Film Transistor (TFT)
layer of microscopic detector elements each containing their own TFT
Active Matrix Array (AMA)
Process of a direct system
x-rays photos are absorbed by photoconductor
photoconductor converts the photons into an electrical signal, which is then stored in the DELs
information is sequentially discharged and read-out with dedicated electronics
low noise, high-sensitivity: amplifiers perform read-out amplification, and analog-to-digital conversion
Line scanning sequence (lifeguard telling the swimmers at the top to go)
what is the main photoconductor for the direct system
amorphous selenium (a-se)
describe the process of an indirect system
photons strike the scintillator
scintillator converts photons into light
light is then converted into an electrical charge by a photodetector
electrons stored into the capacitor within the DEL until the time for line sequencing and read out
T/F TFT arrays are the same for both systems
True
Gd2O2S (unstructured and turbid)
Gadolinium Oxysulphide
what does the gadolinium oxysulphide detector do
air pockets allow light (indirect) to escape laterally before it reaches the TFT surface, reduces efficiency, lowers spatial resolution
Csl (structured)
thallium doped cesium iodide
most popular a-Si detector
Csl
describe the process of using the Csl detector
tubules act as a guide for light (indirect) form the scintillation layer, almost no light speed, increased efficiency, increased spatial resolution (higher DQE)
non-functioning pixels
dead pixels
what are some of the reasons that cause dead pixels
dust, scratches, static damage, chemical corrosion, age
what are the software programs that identify and isolate dead pixels
interpolation (fills in dead space using surrounding pixels as a guide)
gain calibration
“flat-fielding” corrects flaws in the detector
gain calibration
what makes gain calibration important
removes potential of having artifacts that interfere with diagnoses
removes densities on an image by taking out the unwanted densities and leaving only diagnostic information
faint image from previous exposure still visible, previous image’s signal not getting completely erased (double exposure artifact)
image lag
what are the causes of image lag
rapid succession of images
overexposure in an area with little beam attenuation (lead marker)
ways to prevent image lag
increase time between exposures
proper collimation
appropriate technical factors
how to correct image lag
detector software
dark noise
offset correction
how much noise can be tolerated in the image
Signal-to-noise ratio
relationship between noise and patient exposure
inversely proportional
a decrease in noise leads to what in patient exposure
higher exposure (high mAs, less noise)
spatial resolution and DQE are what type of measurements
numerical measurements for performance
how efficiently a system converts the x-ray input signal into a useful output image
Detective Quantum efficiency (DQE)
Higher DQE = ___ quality images at lower doses
higher
Increased DQE (higher DQE) does what to patient dose
lowers it
anything that has a DEL, assessment of quality of a flat-panel detector
fill factor
a fill factor is a ratio of ___ areas to the __ __ area of the DEL
sensitive, non-sensitive
High fill factor does what to DQE
increases it
what are the things that a high fill factor effects
high contrast resolution (increased SNR)
less patient exposure and dose
measures from the center of one DEL to the center of an adjacent DEL
DEL pitch
DEL includes both ___ and ___ areas, unlike Fill Factor
sensitive, non-sensitive
spatial resolution =
½ times the DEL pitch
equation for DEL pitch
SR=1/2P
what are the alternative options to TFT indirect technology (replace flat panel array)
CCD and CMOS
describe the process of the CCD device
x-ray photons interact with scintillation material
signal transmitted by the lenses or fiber optics to the CCD
lenses reduce image size
image is transferred to small capacitors where light is converted into an electrical charge
charge is released sequentially line by line and sent to ADC
which of the two is more susceptible to noise
CMOS
what is the basic construction and function of CMOS
light photons stored in individual capacitors within each pixel
each pixel has its own amplifier that converts light photons into electrical signal
created voltage from amplifiers is converted by the ADC
between CCD and CMOS which is more sensitive to light
CCD
between CCD and CMOS which uses more power
CCD
between CCD and CMOS which is more expensive
CCD
between CCD and CMOS which has a greater pixel fill factor
CCD
difference between cassette-based vs cassette-less PSP
cassette processing with a reader vs internal processing of plate without a cassette (they are both still PSP because they utilize photosimulation of the imaging plate)
Film or PSP the cassette doesn’t need to be light-tight and is read with a CR reader
PSP
Film or PSP may be single or double emulsion
film
Film or PSP barium fluorohalide is the active element
PSP
Film or PSP cassette needs to be completely light tight and must be processed in a dark room
Film
Film or PSP usually just a single emulsion
PSP
Film or PSP silver halide is the active element
film
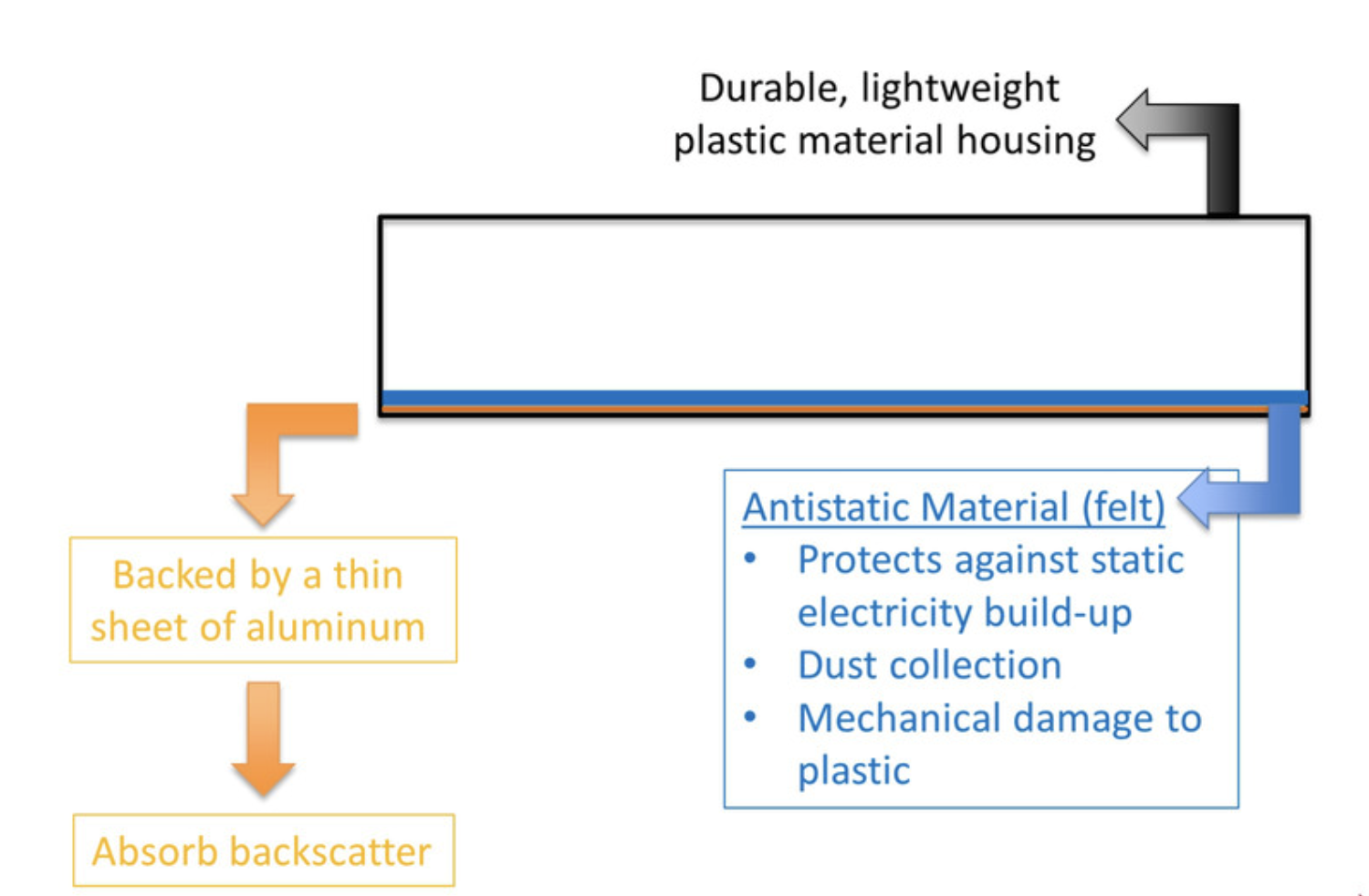
its durable, lightweight and plastic material
the antistatic material
protects against static electricity
dust collection
mechanical damage to plastic
backed by a thin sheet of aluminum
absorbs back scatter
structure and function of the PSP cassette
the protective layer (1st)
thin, tough clear plastic (protects phosphor layer)
phosphor layer (2nd most important layer)
active layer, barium fluorohalides work here (traps electrons during the exposure)
light reflective layer (3rd)
some detail is lost in this step
sends light forward once its released from the reader (black, reduces light spread)
conductive layer (4th)
absorbs and reduces static electricity
support layer (5th)
semi-rigid material for plate strength
light shielding layer (6th)
prevents light from erasing data and leaking through the back
backing layer (7th)
soft polymer, protects back of cassette
barcode must be scanned and connected to patient position from the exam menu
(barcode may be linked with patient info)
cassette based
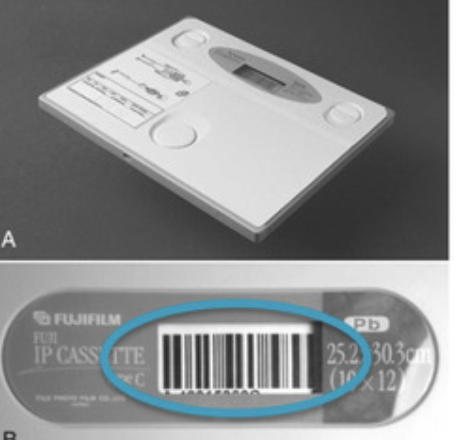

match the exam to the patient through the worklist
no barcode on the plate
cassette-less
what are orientation markers
cassette-based systems- colored marker or sticker (indicates appropriate orientation of cassette in relation to patient)
requires less post-processing manipulation when oriented correctly
smallest imaging plate possible = ___sampling rate
highest
how ist eh entire cassette read
by the CR reader
the size of the matrix determines the ___ of the pixels
size
fitting the matrix within our cassette size is going to influence __ ___
spatial resolution
if the matrix is 512 × 512
cassette is 14×17
creates ___ pixels
less spatial resolution
bigger
if the matrix is 512 × 512
cassette is 10×12
creates ___ pixels
more spatial resolution
smaller
how is film different from CR when the image is being taken
light from intensifying screen +photons interact with silver halide
electron ejected from halide
attracted to sensitivity speck
silver ions attracted to now negative charge
how does photostimulation work
some light is given off when XR strikes PSP
fluorohalides luminesce from XR interaction
not all of the energy is released with the light
trapped energy forms latent image
what are the four steps of reading and erasing the imaging plate
using laser to read the plate
digitizing the signal
erasing the image
preprocessing, processing, and forwarding
single laser scan that radiates imaging plate
point scan
scan that has a photomultiplier tube
point scan
scan that has several linear laser units and optical light collection lenses
line scan
scan that has a ccd linear array photodetector collecting equipment
line scan
movement of the laser across the imaging plate “scan”
fast scan direction
movement of the imaging plate through the reader “translation” or sub-scan direction
slow scan direction
Light Amplification of Stimulated Emission of Radiation
LASER
what is the main purpose of a laser
release stored electrons
what does beam shaping optics do
ensures the same beam output no matter the location (consistent spatial resolution)
what are the three steps to beam shaping
shaped by special optics that keep the beam size, shape, and speed largely independent of beam position
beam deflector- moves laser beam rapidly back and forth across the IR to stimulate the phosphors
light collection optics- direct released phosphor energy to an optical filter and then to photodetector
imaging plate is scanned with__ light in a raster pattern, the light that is emitted is __ when its relaxed into lower energy levels
red, blue
converting light signal to an electrical signal
digitization
returns electrons to lower energy state (removes image from plate)
erasure
how often should the erasure process occur
once a week to remove buildup of background signal and scatter
(surface of imaging plate is flooded with light)
exposure
photostimulation of IR
enter IR into reader
Laser excited electrons to release latent image
photodetector captures emitted light
signal is digitized
plate erased
preprocessing, processing, and forwarding the image
the whole process of taking an image
the ___ the phosphor layer
the ___the pixel size
the higher the resolution
thinner, smaller
sampling frequency must be greater than 2x the frequency of the input signal (changing the sampling frequency affects the spatial resolution of the image)
nyquist theorem
more data in our bins (more sampling frequency) = ___ accurate representation of signal coming off the plate
more
sampling occurs less than twice a cycle
results in lost information and a fluctuating signal
when the signal is reproduced, frequencies above the nyquist frequency
(grid errors)
aliasing
five causes of PSP artifacts
imaging plate
image processing
plate reader
printer
operator (picnic)
image processing errors
incorrect LUT selected
inappropriate technique
inappropriate positioning
plate reader errors
white lines are parallel to direction of plate travel
double imaging plates loaded into single cassette
insufficient erasure after exposure
incorrect alignment of grid lines to laser scan direction
printer errors
fine white lines- debris on mirror in the laser printer (on hard copy images)
operator error (PICNIC)
Problem In Chair, Not in Computer
insufficient collimation
exposure on the wrong side of the cassette
underexposure= quantum mottle
image display in DR is ____ of image acquistation
independent