Biology Mini-Test Revision #1
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
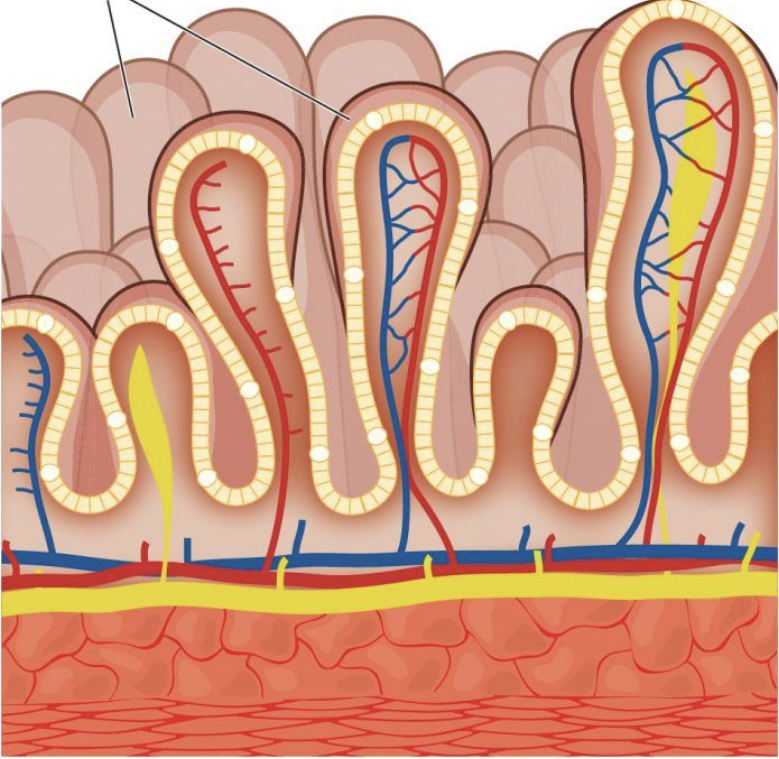
picture
ileum
affects of THINNESS on exchange surfaces
reduced diffusion distance, thus accelerating the rate of diffusion across surface.
affects of MOISTURE on exchange surfaces
ensures gases can dissolve (in the liquid) and can pass through the semi-permeable membrane.
affects of LARGE SURFACE AREA on exchange surfaces
increases the rate of diffusion by expanding the area that molecules are able to move around
cells in tissues
are generally similar in both function, and structure
1st statement of cell theory
all organisms are comprised of cells
2nd statement of cell theory
all cells are derived from pre-existing cells
lysosome function
exclusive to animal cells, breaks down and decomposes waste using enzymes referred to as ‘hydrolases’.
bronchi
main passage way carrying oxygen from the trachea to the bronchioles. (big tube)
bronchioles
secondary pathway breaking off from the bronchi to deliver oxygen to each individual alveoli
gas exchange
respiratory system converts oxygen into carbon dioxide
alveoli
minuscule sacks of air contained within the lungs, perform as the primary site of gas exchange
physical digestion
does not alter the chemical structure/composition of food; involves the mechanical breakdown of food
examples of physical digestion
chewing and swallowing
chemical digestion
alters the chemical structure/composition of food, by using digestive secretions to breakdown complex molecules
examples of chemical digestion
protein macronutrients are broken down into amino acids (takes place ion small intestine)
ileum
responsible for the absorption of nutrients contained in food
lacteal
specialised lymphatic capillaries essential for absorbing, and transporting lipids, other nutrients and antigen related molecules
blood vessels
delivers oxygen, and micronutrients to the rest of the body’s cells, as well as carrying out the removal of wasted byproducts
wasted byproducts removed by blood vessels
carbon dioxide
components of digestive system
mouth, oesophagus, stomach, small and large intestines
components of respiratory system
lungs, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, diaphragm, voice box, throat, nose/mouth
cell wall
outermost barrier of plant cell
inner barrier of plant cell
cell membrane
lysosomes
membrane-bound organelle that contains enzymes responsible for breaking down biological polymers
biological polymers broken down by lysosomes
proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and lipids