Periodic trends stack
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
the column down a periodic table is called a
group
the row across the periodic table is called a
period
what do all atoms of the same group have in common?
they all have the same number of valence electrons
what do all atoms of the same period have in common?
they have the same amount of electron shells
locate the alkali metals group on the periodic table
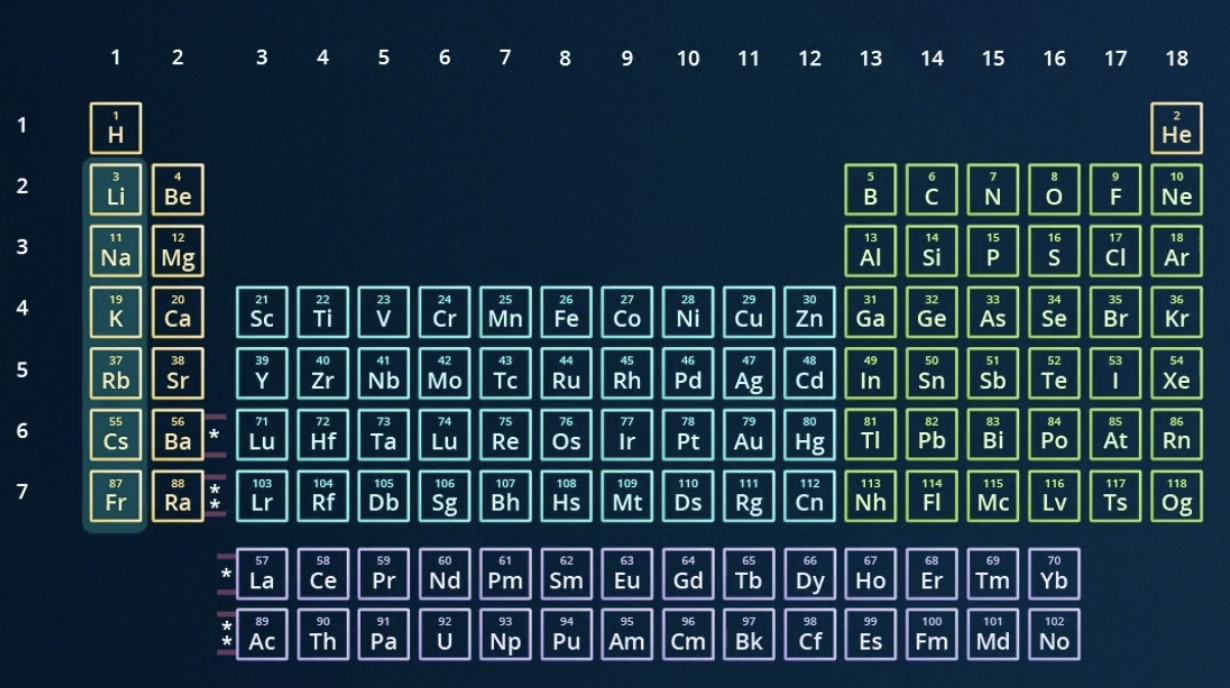
*EXCLUDES HYDROGEN
locate the alkaline earth metals on the periodic table
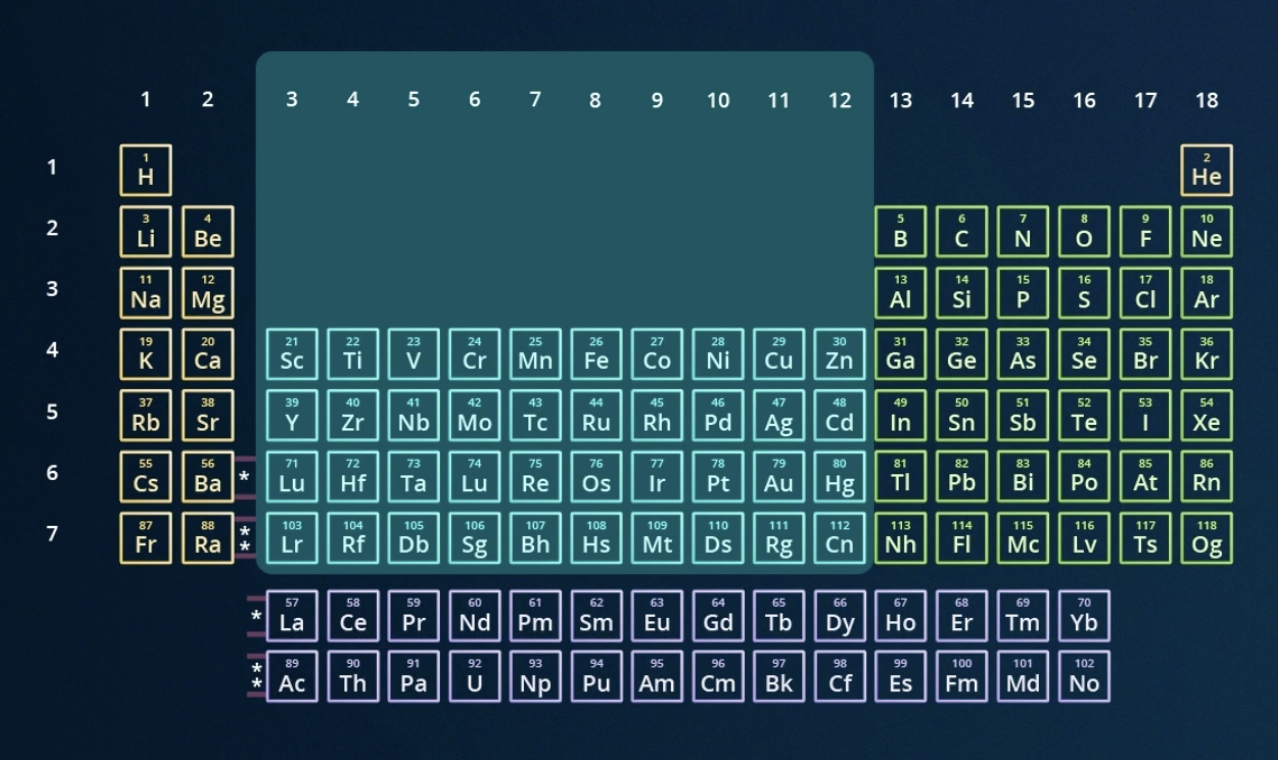
locate the transition metals on the periodic table
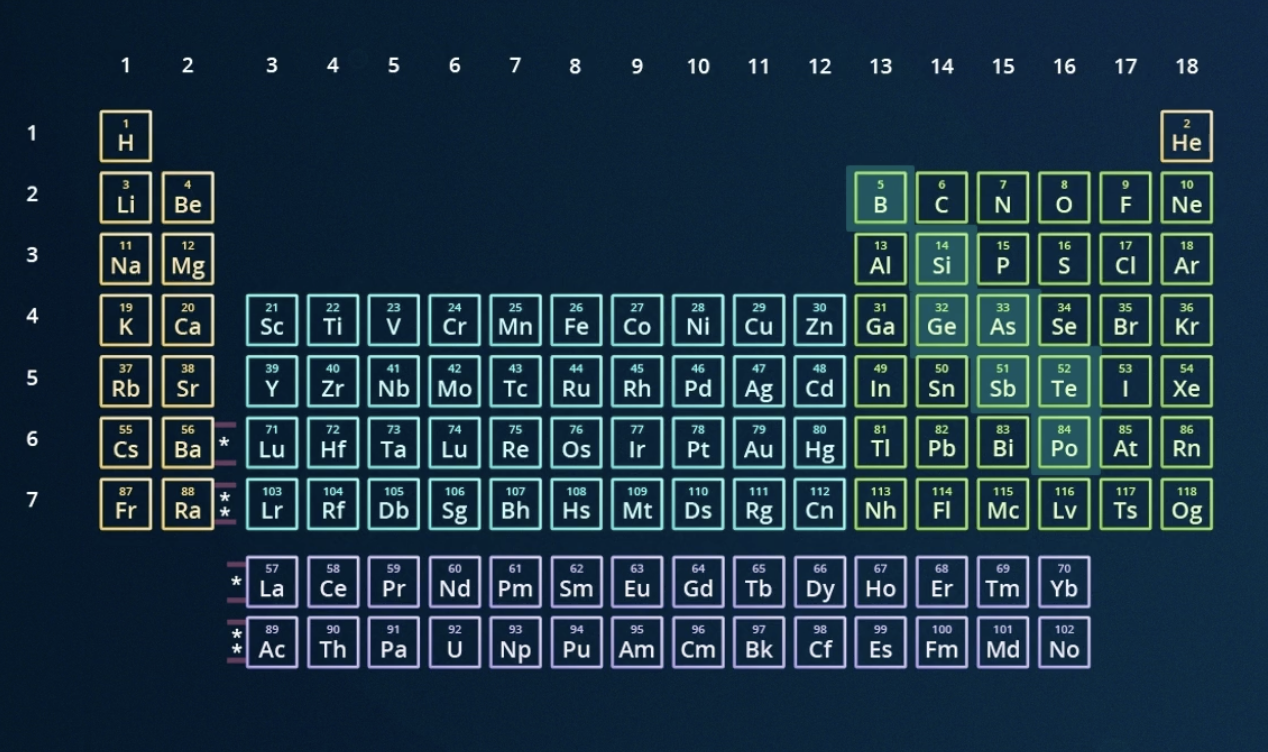
locate the metalloids on the periodic table
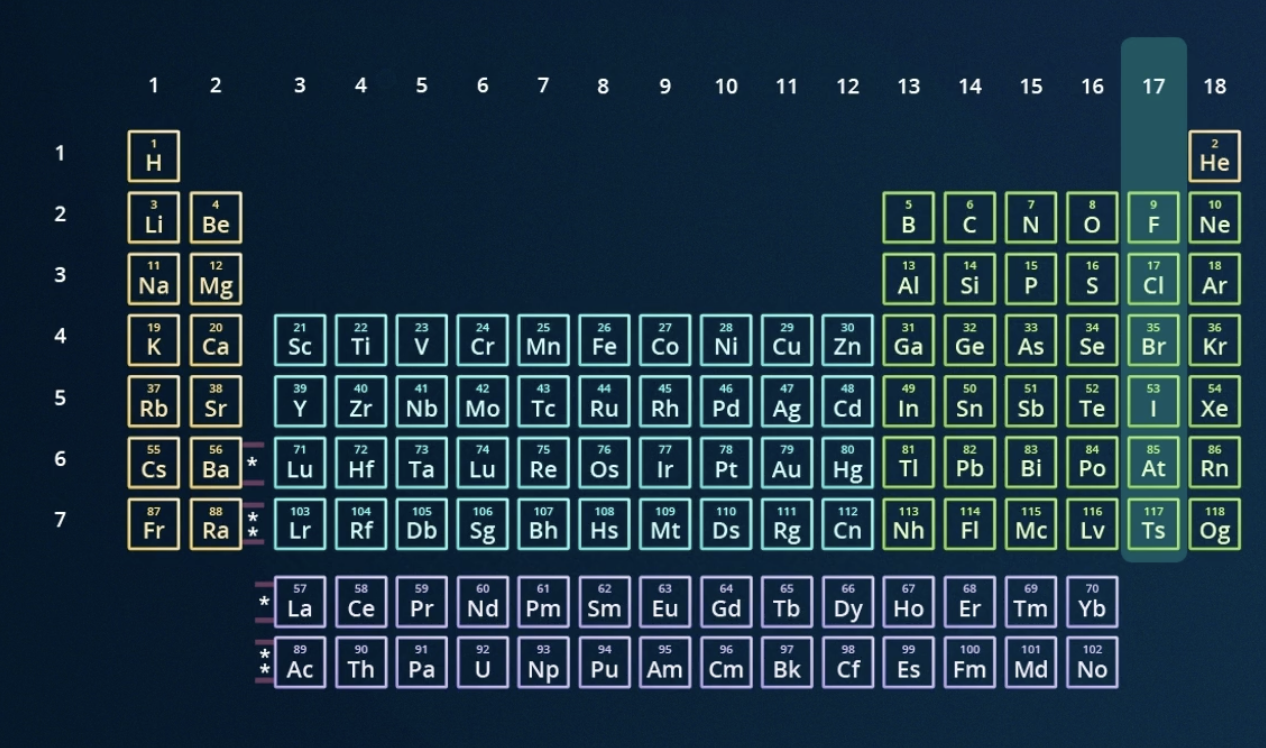
locate the halogens on the periodic table
locate the noble gases on the periodic table

which periodic group has the trait of multiple oxidation states?
transition metals
why is it that an atom can have multiple oxidation states?
it has several electrons with similar energies - very easy to have different amounts of electrons interact
true or false - all the transition metals have colour
false - row 4 transition metals are colourless (the rest do have colour)
locate the inner transition metals on the periodic table
what is the difference between valence electrons of a transition metal and an inner transition metal?
transition metal
VE in outermost D orbital
inner transition metal
VE in inner F orbital
locate separately, the lanthanides and actinides on the periodic table
ll
list all the diatomic atoms
HAVE NO FEAR OF ICE COLD BEER
hydrogen
nitrogen
fluorine
oxygen
iodine
chlorine
bromine
list the 6 common properties of metals
malleable and lustrous
good conductor of electricity and heat
form basic oxides
form cations via loss of electrons
solid at room temperature *exception of mercury
High melting and boiling points
list the 6 common properties of non-metals
brittle and dull
poor conductor of electricity and heat
forms acidic oxides
forms anions via gaining electrons
gas/solid at room temp
*exception of bromine
low melting and boiling points
explain the atomic radius trend on the periodic table and the cause for the trend
R decreases from left to right
as you go left, there are more protons to pull the electrons closer in
R increases from top to bottom
as you go down there are more electron shells
what is effective nuclear charge?
the amount of positive charge experienced by an electron
what is the formula for effective nuclear charge? (Zeff)

describe the nuclear charge trend on the periodic table
increases from left to right
decrease from top to bottom
REVERSE FROM ATOMIC RADIUS
what does it mean when 2 atoms are isoelectric?
they have an identical number of electrons, while having a different number of protons
what is ionization energy/ionization potential?
the energy needed to remove an electron from an atom
describe the ionization energy trend on the periodic table
Increases from left to right
decreases from top to bottom
what is the trend for 2nd, 3rd, 4th etc ionization energies of an atom?
as the number of ionization energies increases, the energy needed to remove the electron does too
why are group 15 and alkaline earth elements an exception to the ionization energy rules?
group 15 - half filled orbitals are more stable than non half or full orbitals
alkaline earth metals - have full orbitals
define electron affinity
the amount of energy released when an electron is added to an atom
describe the electron affinity trend on the periodic table
increases from left to right
decreases from top to bottom
what is the exception to the electron affinity trend?
of the same period, an atom missing one electron to fill/half-fill an octet will have a higher affinity than the atom with an already filled/half-filled octet
what periodic group has a negligible electron affinity? why?
noble gases - complete valence shells
define electronegativity
the ability of an atom to attract electrons in a bond
describe the electronegativity trend on the periodic table
increases from left to right
decreases from top to bottom
what is the directionality of the metallic character trend?
decreases from left to right
increases from top to bottom
what is the directionality of the non-metallic character trend?
increases from left to right
decreases from top to bottom