Bio 1 Chapter 5 the structure and function of large biological molecules
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
125 Terms
what are 4 classes of biological molecules all living things are made up of?
carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids and proteins
within cells, small organic molecules are joined together to form?
larger molecules
what are macromolecules?
large molecules composed of thousands of covalently connected atoms
molecular structure and function are?
inseparable
what is a polymer?
a long molecule consisting of many similar building blocks
These small building block molecules are called?
monomers
which 3 of the 4 classes of life’s organic molecules are polymers?
carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids
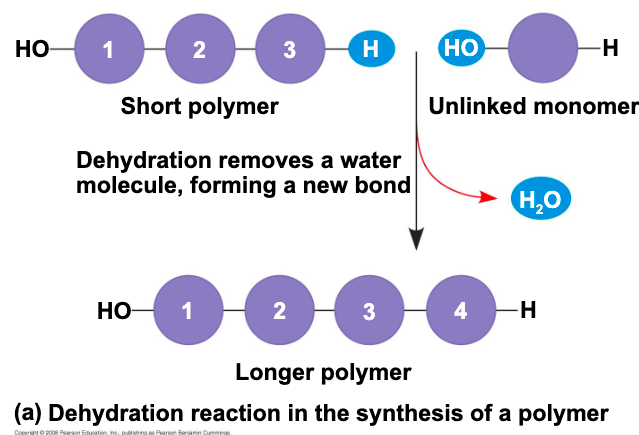
what occurs when two monomers bond together through the loss of a water molecule
a condensation reaction or dehydration synthesis
what are macromolecules that speed up the dehydration process?
enzymes
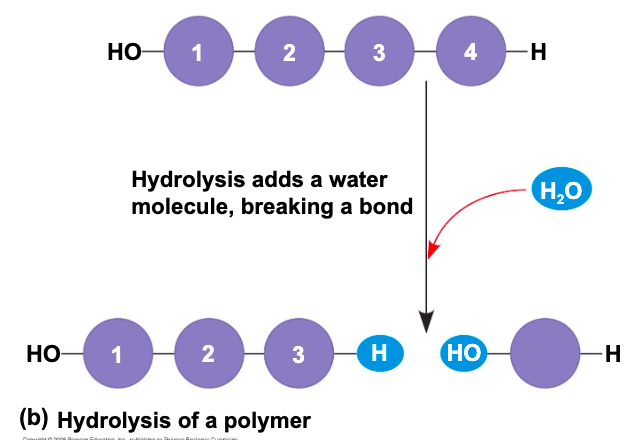
polymers are disassembled to monomers by ___ which is a reaction that is essentially the reverse of the dehydration reaction
hydrolysis
(B)
(b) hydrolysis of a polymer (peep photo)
each cell has thousands of different kinds of
macromolecules
macromolecules vary among cells of an?
organism, vary more within a species, and vary even more between species
an immense variety of polymers can be built from?
a small set of monomers
COH include?
sugars and the polymers of sugars
the simple COH are?
monosaccharides, or single sugars
COH macormolecules are ___ , polymers composed of many sugar building blocks
polysaccharides
monosaccharides have __
molecular formules that are usually multiples of CH2O
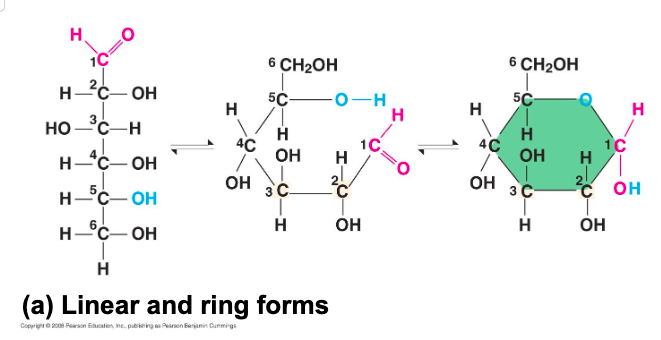
what is the most common monosaccharide?
Glucose (C6H12O6)
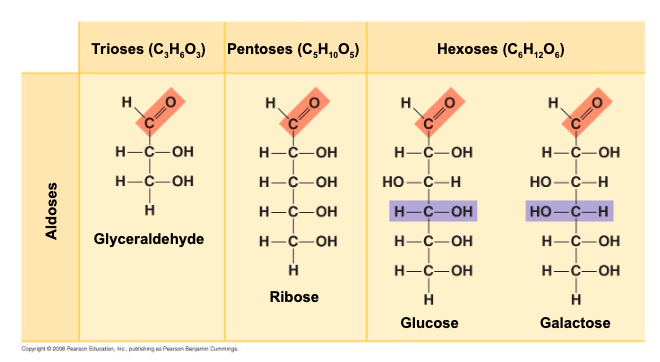
how are monosaccharides classified by?
the location of the carbonyl group (as aldose or ketose )
the number of carbons in the carbon skeleton
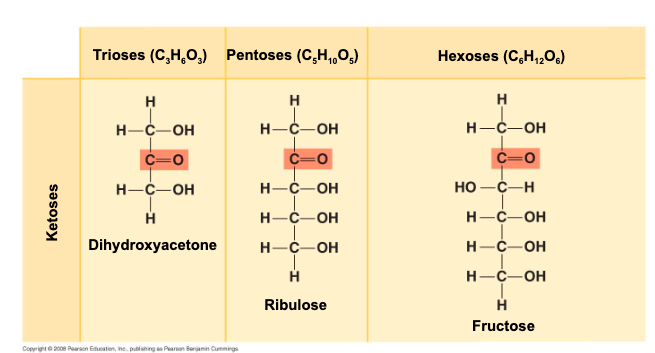
though often drawn as linear skeletons, in aqueous solutions many __
sugars form rings
monosaccharides serve as a ?
major fuel for cells and as raw material for building molecules
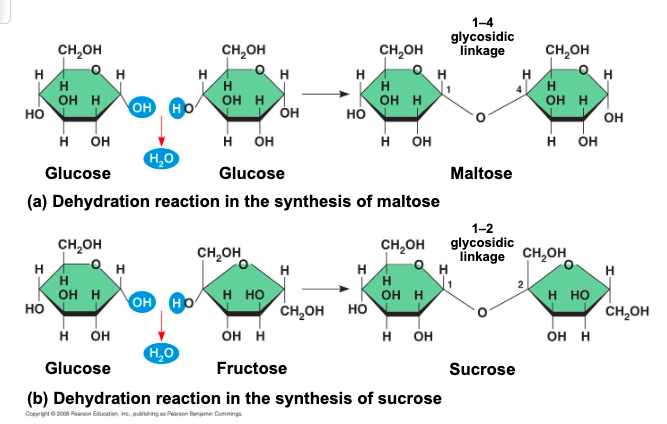
a disaccharide is formed when a
dehydration reaction joins 2 monosaccharides
the covalent bond is called a
glycosidic linkage
polysaccharides are the
polymers of sugars, have storage and structural roles
the structure and function of a polysaccharide are
determined by its sugar monomers and the positions of glycosidic linkages
what is starch?
a storage polysaccharide of plants consists entirely of glucose monomers
plants store surplus starch as
grunles wihtin chloroplasts and other plastids
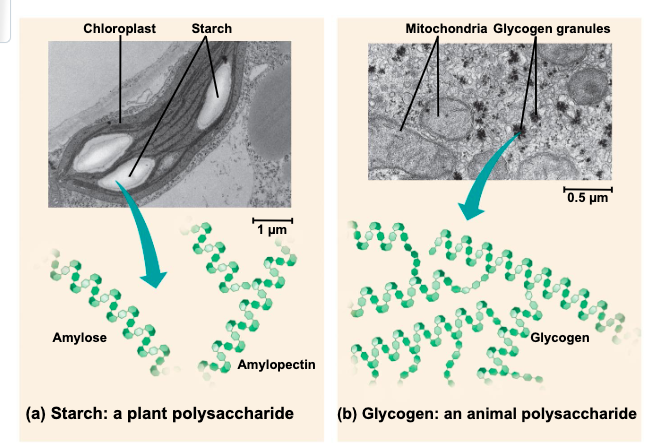
what is glycogen?
a storage polysaccharide in animals
humans and other vertebrates do what?
store glycogen mainly in liver and muscle cells
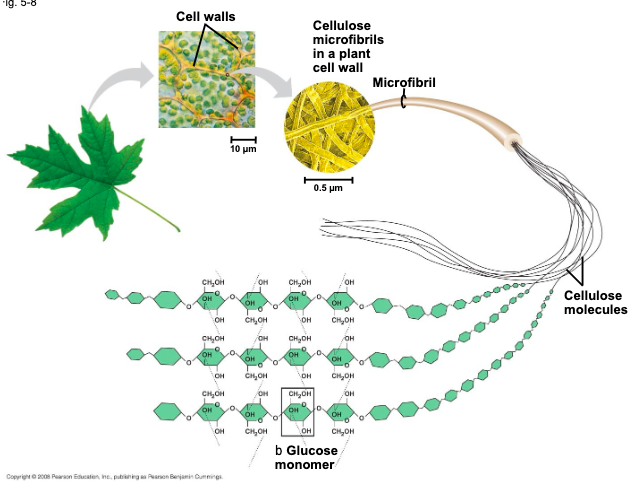
the polysaccharide ___ is a major component of the tough wall of plant cells
cellulose
like starch, cellulose is a?
polymer of glucose, but the glycosidic linkages differ
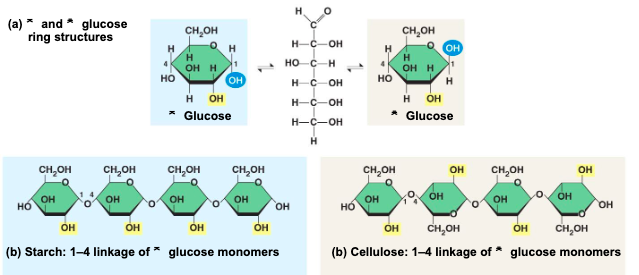
the difference of structural polysaccharides is based on
two ring forms for glucose: alpha and beta

polymers with alpha glucose are
helical
polymers with beta glucose are
straight
in straight structures,
H atoms on one strand can bond with OH groups on other strands
parallel cellulose molecules held together this way are grouped into
microfibrils which form strong building materials for plants
enzymes that digest starch by
hydrolyzing alpha linkages cant hydrolyze beta linkages in cellulose
cellulose in human food passes through the
digestive tract as insoluble fiber
some microbes use
enzymes to digest cellulose
many herbivores from cows to termites have
symbiotic relationships with these microbes
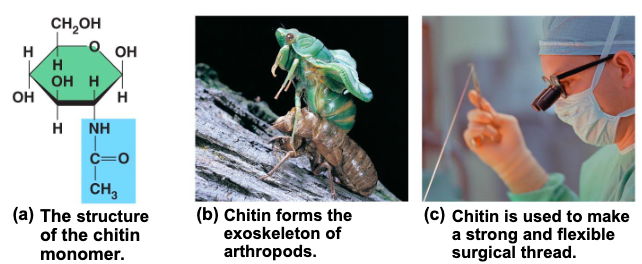
what is chitin
another structural polysaccharide is found in teh exoskeleton of arthropods / also provides structural support for the cell walls of many fungi
lipids are the one classs of large biological molecules that
do not form polymers
the unifying feature of lipids is having little or
no affinity for water
lipids are hydrophobic because
they consist mostly of hydrocarbons, which form nonpolar covalent bonds
the most biologically important lipids are
fats, phospholipids and steroids
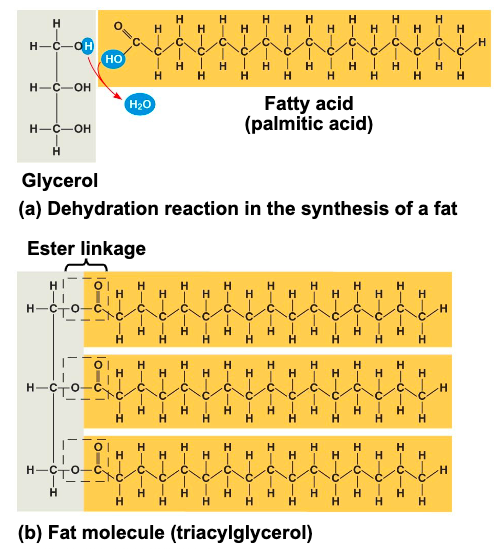
fats are
constructed from 2 types of smaller molecules, glycerol and fatty acids
what is glycerol
a 3 carbon alcohol with a hydroxyl group attached to each carbon
what is a fatty acid
consists of a carboxyl group attached to a long carbon skeleton
fats separate from water because
water molecules form hydrogen bonds with each other and exclude the fats
in a fat, 3 fatty acids are joined to
glycerol by an ester linkage, creating a triacylglycerol, or triglyceride
fatty acids vary in
length (number of carbons) and in the number and locations of double bonds
saturated fatty acids have the
maximum number of hydrogen atoms possible and no double bonds
unsaturated fatty acids have
one or more double bonds
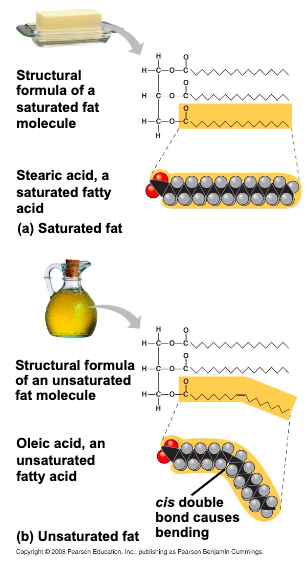
fats made from saturated fatty acids are called
saturated fats and are solid at room temp.
most animal fats are
saturated
fats made from unsatirated fatty acids are called
unsaturated fats or oils and are liquid at room temp
plant fats and fish fats are
usually unsaturated
a diet rich in saturated fats may contribute to __ through plaque deposits
cardiovascular disease
__ is the process of converting unsaturated fats to saturated fats by adding hydrogen
hydrogenation
hydrogenation vegetable oils also creates
unsaturated fats with trans double bonds
these trans fats may __ than saturated fats to cardiovascular disease
contribute more
the major function of fats is
energy storage
humans and other mammals store their fat in
adipose cells
adipose tissue also cushions
vital organ and insulates the body
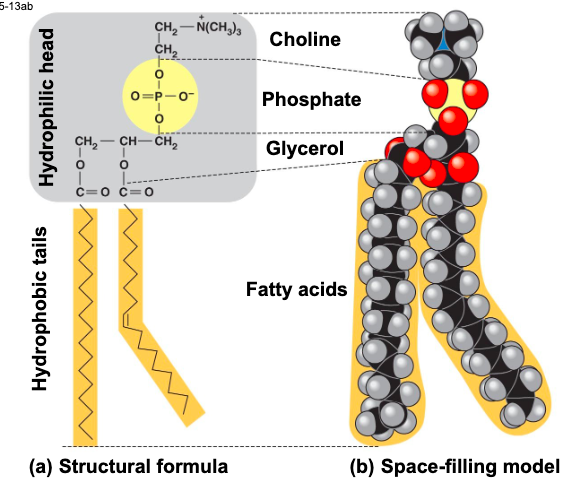
in a phospholipid,
2 fatty acid and a phosphate group are attached to glycerol
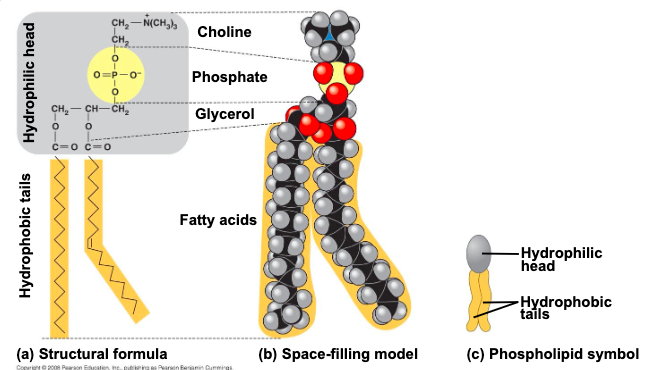
the 2 fatty acid tails are hydrophobic, but the
phosphate group and its attachments form a hydrophilic head
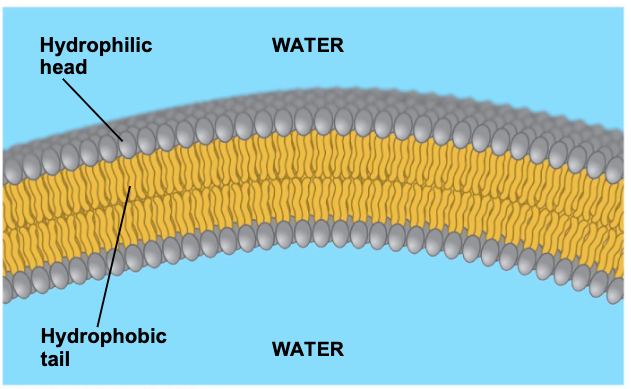
when phospholipids are added to water they
self assemble into a bilayer, with the hydrophobic tails pointing toward the interior
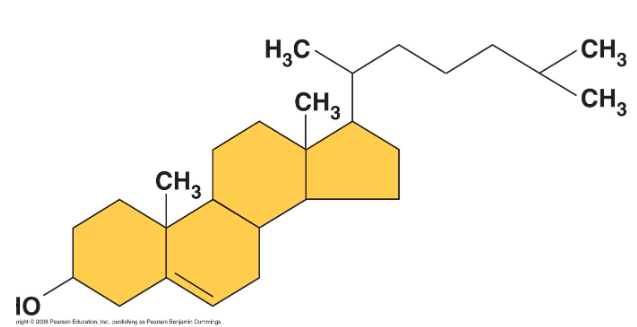
what are steroids
are lipids characterized by a carbon skeleton consisting of 4 fused rings
what is cholesterol
an important steroid, is a component in animal cell membranes
although cholesterol is essnetial in
animals, high levels in the blood may contribute to cardiovascular disease
portein account for more than
50% of the dry mass of most cells
protein functions include
structural support, storage, transport cellular communications, movement and defense against foreign substances
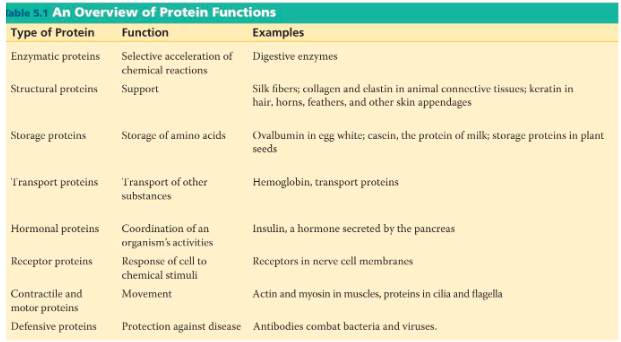
what are enzymes
a type of protein that acts as a catalyst to speed up chemical reactions
can perform their functions repeatedly functioning as workhorses that carry out the processes of life

polypeptides are
polymers built from the same set of 20 amino acids
a protein consists of
one or more polypeptides
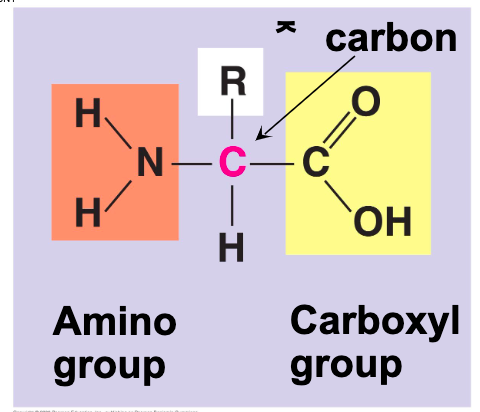
what are amino acids
are organic molecules with carboxyl and amino groups
differ in their properties due to differing side chains called R groups
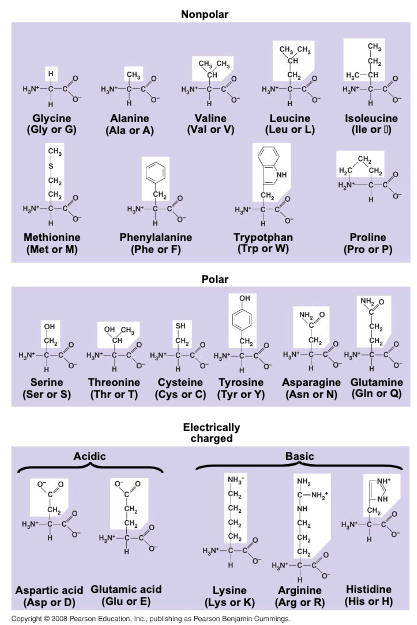
amino acids are linked by
peptide bonds
a polypeptide is a polymer of
amino acids
polypeptides range in length from a few to
more than a thousand monomers
each polypeptide has a
unique linear sequence of amino acids
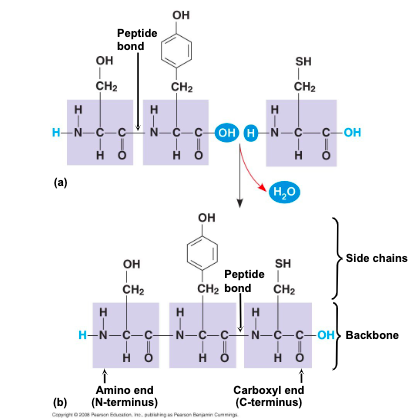
a functional protein consists of
one or more polypeptides twisted, folded, and coiled into a unique shape
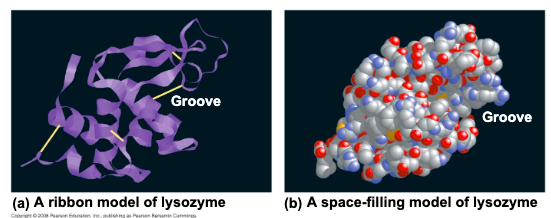
the sequence of amino acids detemrines a
proteins 3 dimensioanl structure
a proteins structure determine its
function
the primary structure of a protein is its
unique sequence of amino acids
secondary structure (found in most proteins) consists of
coils and folds in the polypeptide chain
tetrtiary structure is determined by
interactions among various side chains (R groups)
quaternary structure results when a
protein consists of multiple polypeptide chains
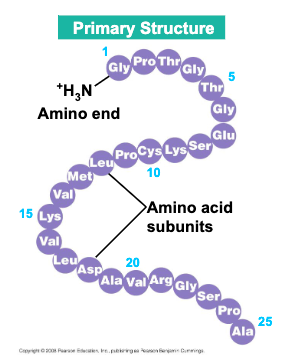
primary structure is the
sequence of amino acids in a protein, is like the order of letters ina long word
primary structure is determined by inherited genetic information
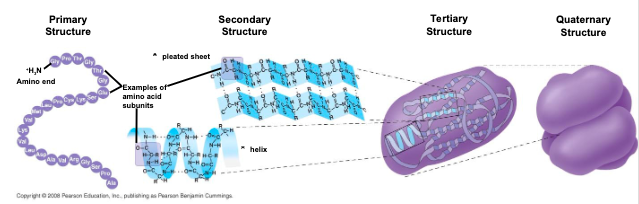
the coils and folds of ___ result from hydrogen bonds between repeating constituents of the polypeptide backbone
secondary structure
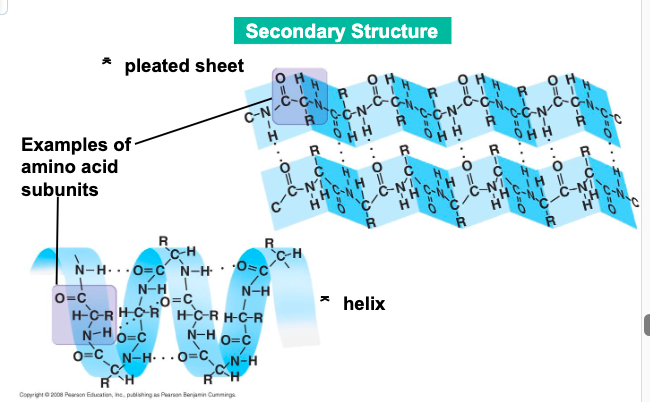
typical secondary structures area coil called
an helix (alpha sign) and a folded structure called a pleated sheet (beta sign)

__ is determined by interactions between R groups, rather than interactions between backbone constituents
tertiary structure
these interactions between R groups include hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, __, and van der Waals interaction
hydrophobic interactions
strong covalent bonds called __ may reinforce the proteins structure
disulfide bridges
results when 2 or more polypeptide chains form one macromolecule
quaternary structure
collagen is a fibrous protein consisting of
3 polypeptides coiled like a rope
hemoglobin is a globular protein consisting of
4 polypeptides: 2 alpha and 2 beta chains
what is sickle cell disease
an inherited blood disorder results from a single amino acid substitution in the protein hemoglobin
a slight change in primary structure in can affect a proteins structure and ability to function
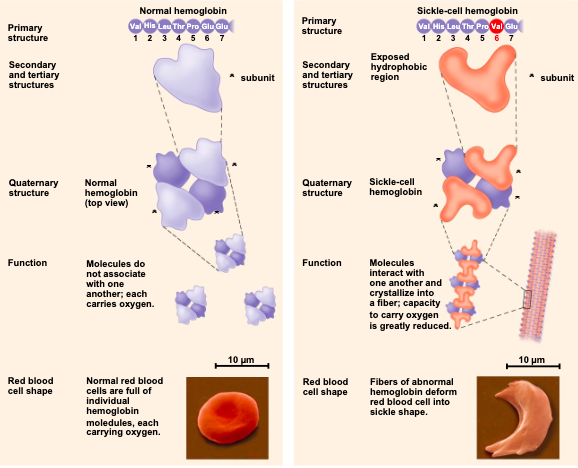
in addition to primary structure, physical and chemical conditions can
affect structure
alterations in pH, salt concentration, temp., or other environmental factors can
cause a protein to unravel