IFR Know All
1/221
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
222 Terms
Fixation
Applying full concentration to one single instrument
Omission
Excluding one or more instruments from scan
Emphasis
Relying on instrument that you readily understand even if it provides inadequate information
Control instruments
Attitude indicator, taachometer, manifold pressure
Performance instruments
Heading indicator, turn coordinator, airspeed indicator, turn coordinator, airspeed, altimeter, vertical speed indicator
Pitch Instruments
Airspeed, Attitude, Altimeter, VSI
Bank Instruments
Attitude, heading indicator, turn inductor
Power Instruments
Airspeed, Tachometer, Manifold Pressure
Magnetic Compoass Errors
Magnetetic Deviation
Magnetic Vartiation
Magnetic Dip
Oscillation
North & South Turning Errors
Acceleration/Deceleration Errors
Pitot Static Instruments
Airspeed, Altimeter, and Vertical Speed Indicator
Types of Airspeed
Indicated
Calibrated
Equivalent
True
Ground
Types of Altitude
Density
Absolute
True
Pressure
Indicated
Calibrated
Altimeter errors
High to low look out below
Cold to warm clear the sky
Pitot tube blockage
Ram = Airspeed drops to 0
Ram & Drain = Airspeed will act as an Altimeter
Vacuum failure
Attitude & Heading will fail
Panel lights will come on
The vacuum gauge will drop to 0
Shear drive will break
possible engine damage
Gyrospoic Instruments
Attitude, Heading, Turn
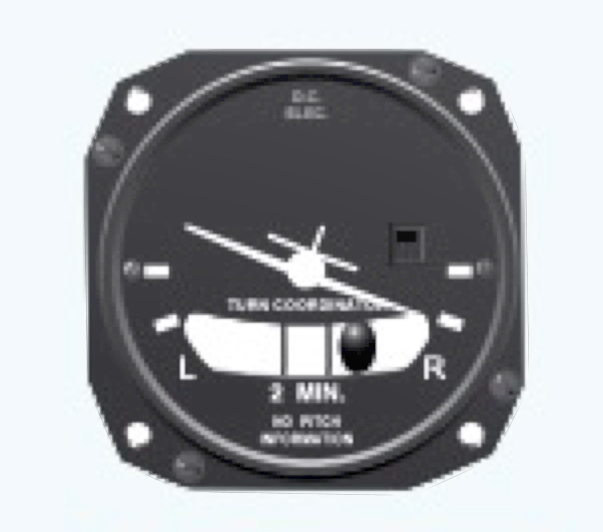
Skid
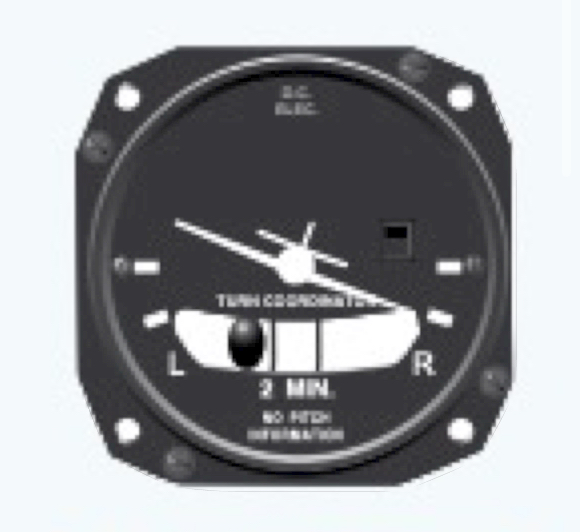
Slip

VOR
Radials in all directions
Identify with morose code.
cone of confusion
OBS must be aligned
VOTS
VOR test facility ±4
Found in chart supplement gives off 1 radial 360 from or 180 to
VOR ground checkpoint
±4
found in chart supplement
VOR Airborne checkpoint
±6
found in the chart supplement
Dual VOR check
Within 4
Using two VORs against each other
VOR check
Date
Error
Place
Signature
Distance measuring Equipment (DME)
Typically paired with VOR
It uses slant range to measure
Limited to the line of sight
will read 6000 when over the point
morse codes ins transmitted every 30 seconds
Speed is measured by how fast the signal goes from plane to station and back
Course Deviation Indicator (CDI)
Tells you how far off course you are
Each dot is 2 degrees
full scale is 10 degrees
must be half-scale deflection or less to be established
200 ft per dot per nautical mile
turn towards the needle for correction
Non-Directional Beacons
ground based receiver always paired with ADF
Reverse Sensing
Occurs when you’re flying reciprocal of intended course
Automatic Direction Finder (ADF)
Automatically & continuously displays the relative bearing from the aircraft to the station
Automatic Direction Finder use
operates off low AM frequency
ADF will point to the station no matter what
Must constantly monitor Morse code
limited to line of sight
points towards lightning because its static
deflects off mountains
If paired w/ILS its considered a compass locator
Homing
not using any wind correction only following the needle
Tracking
Using wind correction to stay on course
Instrument Landing System (ILS)
Precision appraoch with vertical and lateral guidance that can descend you down to minimums
GLAM = glideslope, localizer, approach lighting system, marker beacons
Glideslope
Provides vertical guidance Allows you to descend to your decision altitude
Localizer
Provides lateral guidance
located on the departure end of the runway
4x more sensitive than VOR
If the localizer fails, the IFR approach is not authorized
Approach lighting System (ALS)
Helps transition between instrument to visual approach
It can help in estimating flight visibility if you know the dimensions of the specific ALS configuration
Precision Approach Lighting System
Lighting starts 2400 to 3000 ft from runway
SLASR
Simplified short approach lighting system w/ runway alignment indicator lights
ALSF
Approach lighting system w/ flashing lights
MALSR
Medium-intensity approach lighting system w/ runway alignment indicator lights
Non-Precision Approach Lighting System
Lighting starts 1400 to 1500 ft from the runway
MALSF
Medium intensity approach lighting system w/ flashing lights
MEA-Minimum En-route Altitude
The lowest published altitude between radio fixes that guarantees adequate navigational signal reception and obstruction clearance of 1,000’ in non-mountainous and 2,000’ in mountainous terrain
MOCA-Minimum Obstruction Clearance Altitude.
Ensures reliable navigation only within 22 NM of facility and obstacle clearance
MAA-Maximum Authorized Altitude
Max usable altitude or flight level for an airspace structure or route segment for which adequate reception of navigation aid signals is assured
MRA- Minimum Reception Altitude
The lowest altitude at which an intersection can be determined
MCA- Minimum Crossing Altitude
The lowest altitude at certain fixes at which an aircraft must cross when proceeding in the direction of a higher minimum en route IFR altitude
OROCA- Off Route Obstacle Clearance Altitude
Provides obstacle clearance of 1,000 and 2,000 but may not provide signal coverage from ground-based nav aids, ATC radar, or communications
MSA- Minimum Safe Altitude
Found on approach plates and provides 1000’ terrain clearance within 22NM of the airport, used for emergency purposes
What reports must always be made to ATC?
M-Missed Approach
A-Altitude Changes VFR on top
T-True Airspeed change +/- 10 knots or 5%
H-Holding: time and altitude when entering or leaving the holding fix C-Cannot maintain a 500fpm climb/descent
A-altitude and time when at holding fix or CLEARANCE LIMIT L-Leaving an assigned altitude
L-Lost comm. nav, equipment
S-Safety of flight, including un-forecasted weather
When does night time begin?
Between end of evening civil twilight and begging of morning civil twilight
When can you log night landings
Between 1 hour after sunset and 1 hour before sunrise
When is an IFR rating required
In Class A airspace
Operating under IFR
Anytime the weather is beneath VFR minimums: Ceiling below 1000’ or visibility less
than 3 miles
Anytime you are operating special VFR at night
What are the recency-of-experience requirements to be PIC of a flight under IFR?
Within the preceding 6 months of the flight, 6 instrument approaches and holding procedures and intercepting and tracking courses must be completed either in actual IMC, in VMC while using a view limiting device, or in a flight simulator/FTD
Define “appropriately rated safety pilot.”
The safety pilot must possess at least a private pilot certificate with the category and class ratings appropriate to the aircraft being flown and he/she must have adequate vision forward and to each side of the aircraft.
If a pilot allows his/her instrument currency to expire, what can be done to become current again?
If you fail to meet the instrument experience requirements for more than 6 months, the only way to reestablish currency is with an IPC
What aircraft/instruments/equipment are required for an IFR Flight?
Generator/alternator
Radio
Altimeter (adjustable)
Ball (inclinometer)
Clock w/ hours, minutes, and seconds
Attitude indicator
Rate of turn indicator
Directional gyro
*DME is required at or above FL240 if VOR navigation is required
What records must be kept concerning VOR checks?
Signature, location, error, date
Describe gyroscopic instruments
powered by an engine driven vacuum pump with the
exception of the turn coordinator which is electrically powered
Magnetic variation
Difference between Magnetic north and true north
Magnetic deviation
Errors produced by magnetic interference from other magnetic fields such as those caused by electrical equipment or metal structures.
Magnetic dip errors
While flying a north heading and turning to the left, the compass will initially show a turn in the opposite direction and lag behind the turn. When on a south heading, the compass will lead the turn and show that the turn is being made much faster than it is.
Norterly turn error
UNOS
Acceleration error
ANDS
What would happen if the VOR station were undergoing maintenance?
It may translate a Morse Code of TEST ( ‒ • ••• ‒ ) or the code may be removed
entirely
What does it mean if there is only a single coded identification every 30 seconds on a VORTAC station?
The VOR function is not working but the DME function is working
What are the limitations of a VOR
Line of sight
Pilot error
Cone of confusion
What are the limitations of a VOR
the actual distance between the aircraft and the ground station (as opposed to the horizontal distance).
What does RAIM stand for?
Receiver
Autonomous
Integrity
Monitoring
What is the purpose of RAIM
The purpose is to determine the accuracy or “integrity” of the GPS signal. It does this by comparing the signals from the 5 satellites.
What does FDE stand for?
Fault
Detection and
Exclusion
Purpose of FDE?
RAIM detects an error but does nothing about it except warn you. ____ is a function of some RAIM-capable GPS. It requires 6 satellites so that info from the faulty satellite can be excluded.
What does WAAS stand for?
Wide
Area
Augmentation
System
Where could you find the GPS requirements for GPS?
(AIM 1-1-17)
How do we verify that we will have RAIM during the flight?
FSS Briefers can provide RAIM predictions for a 3 hour period Alternatively, go to AUX page 3 on the GNS 430 and use the RAIM prediction tool
What are the benefits of WAAS capable GPS?
More precise than RAIM
Provides lateral and vertical navigation without the temperature errors associated with
Baro-Vnav
No RAIM prediction necessary
An airport that only has a GPS approach may be selected as an alternate
What are the visual components of the ILS?
approach lighting system, VASI/PAPI, and precision approach runway
What are the range components of the ILS?
marker beacons/compass locator and/or DME
Lateral and vertical guidance: localizer and glideslope
What is the distance threshold for the outer marker?
4-7 miles – usually at the glideslope intercept position
What is the distance threshold for the middle marker?
Middle marker: 3500’ – represents the decision altitude (200’ above TDZE)
What is the distance threshold for the inner marker?
Located between the MM and the landing threshold – represents the DH for a CAT II ILS approach
What are substitutes for an ILS outer marker?
Compass locators, DME, VOR, GPS, Precision Approach Radar (PAR), or Airport Surveillance Radar (ASR)
Where is the localizer antenna array located
The departure end of the runway aligned with the centerline
What is the course width of a localizer signal?
between 3° and 6° so that at the landing threshold, the total width is 700’
What is the sensitivity differences between the CDI tuned to a VOR and a CDI Tuned to a LOC?
Full scale deflection represents at least 10° when tuned to a VOR and only 2.5° when tuned to the localizer.
What is the usable range of the glide slope?
10 NM
Where is the glideslope equipment located?
Between 750’-1250’ from the approach end of the runway and 400-600’ to one side of the centerline
What are the dimensions of the glideslope course?
The total width is 1.4° therefore, full scale deflection represents at least .7°
What is an ILS reflection error?
Radio waves can bounce off of surface vehicles or other aircraft leading to erroneous indications
What is an ILS false course error?
Intercepting the GS at other than the published altitude can cause confusion because the GS equipment inherently produces various courses at higher vertical angles.
What is a Simplified Directional Facility (SDF)?
It provides lateral guidance similar to a localizer but is less accurate because the course is fixed to either 6° or 12°. The SDF antenna may be offset from the runway centerline but usually not by more than 3°. There is no vertical guidance.
What is a Localizer Type Directional Aid (LDA)
More precise than an SDF because the course is usually between 3°- 6° just like a localizer (hence, localizer type). An ___ may also provide a glideslope for vertical guidance in some instances. These are published as LDA/Glideslope and are characterized as APVs (approaches with vertical guidance). NOT ALIGNED WIITH THE RUNWAY
What is the minimum visibility needed to takeoff in part 91?
NONE
What are the 2 different types of departure procedures?
Obstacle Departure Procedure (ODP)
Standard Instrument Departure (SID)
What criteria determines that you will remain clear of obstacles when flying an ODP?
1. Cross the departure end of the runway at or above 35’ AGL
2. Make the first turn no earlier than 400’ AGL (unless otherwise specified)
3. Maintain climb gradient of at least 200fpnm (unless otherwise specified)
What is the pilot’s responsibility concerning ODPs?
1. Determine that an ____ has been published
2. Determine whether or not to fly it, even if not issued by ATC in a clearance. Pilots are encouraged to fly ____ at night, in MVFR and IFR conditions
3. Determine aircraft performance is adequate for the procedure
4. Be aware of low close-in obstacles
How would you know if an ODP has published for an airport?
The T symbol in the notes section of an IAP means that the takeoff minimums are not standard.
What are the dimensions of victor airways?
begin at 1200’ AGL and extend up to 17,999’ MSL. The width is 8nm
How does the vacuum system operate
An engine driven vacuum pump creates suction. Air is pulled through a filter and then directed to the instrument case. Rotor vanes on the gyros catch the air like a water wheel and cause it to rotate at a high speed. In the Archer IIIs, there is also an electrical vacuum pump to be used as a backup.
When navigating from VOR to VOR, when do you change frequencies to maintain Course guidance?
At that point depicted on the airway as the changeover point In the absence of a changeover point, the halfway point on the airway Whenever there is a bend in an airway