Lab 8 - Skeletal Muscles
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Muscle Fiber (Muscle Cell)
Skeletal muscles are made up of elongated muscle cells called muscle fibers. Inside of muscle fibers are the proteins responsible for contraction.
Endomusium
The endomysium is a delicate layer of connective tissue that surrounds each individual muscle fiber, providing support and facilitating the exchange of nutrients and waste between the fibers and blood vessels.
Fascicle
A bundle of muscle fibers grouped together. Each is surrounded by a layer of connective tissue called the perimysium.
Perimysium
The perimysium is a connective tissue sheath that encases a group of muscle fibers, forming a fascicle, and provides structural support and protection.
Epimysium
The epimysium is a dense layer of connective tissue that surrounds an entire muscle.
Orgin
The origin is the fixed attachment point of a muscle, usually located on a bone, from which muscle contraction generates movement.
Insertion
The insertion is the movable attachment point of a muscle, typically located on a bone, where contraction of the muscle causes movement at a joint.
Action
The action of a muscle refers to the specific movement it produces when it contracts, influencing the position or posture of body parts.
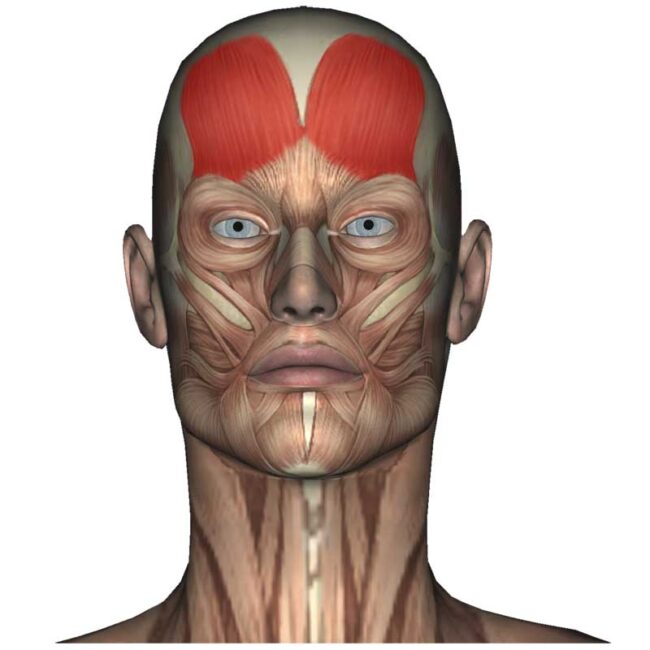
Frontalis
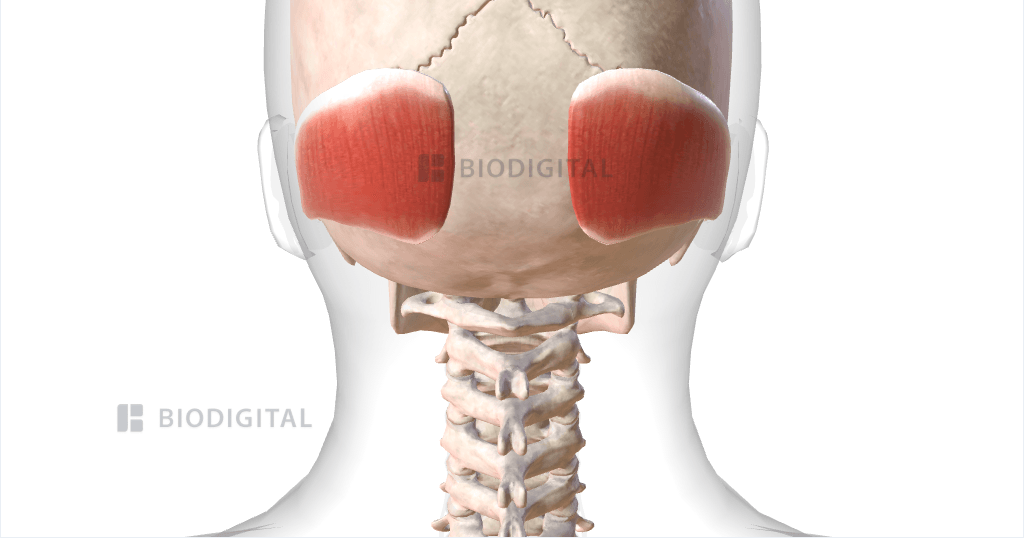
Occipitalis
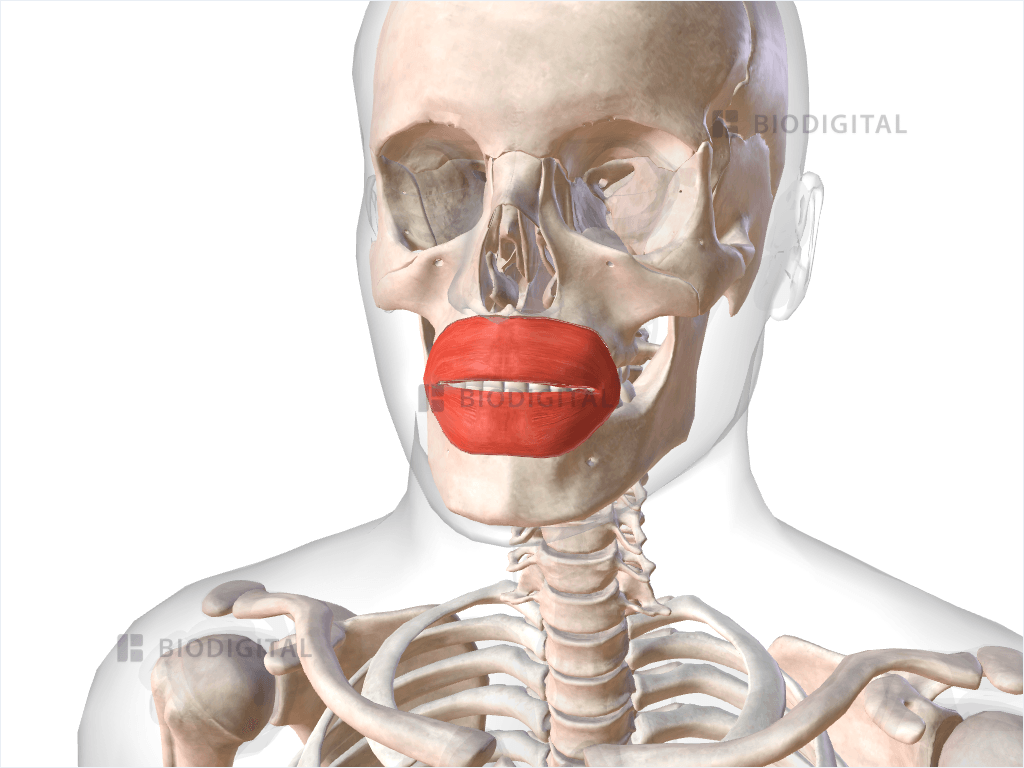
Obicularis oris
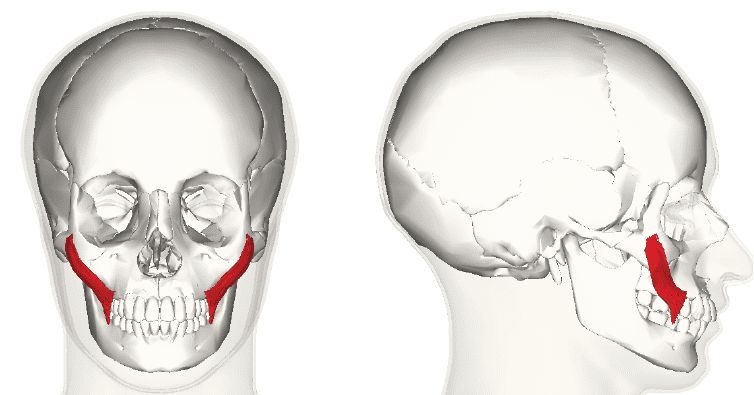
Zygomaticus major
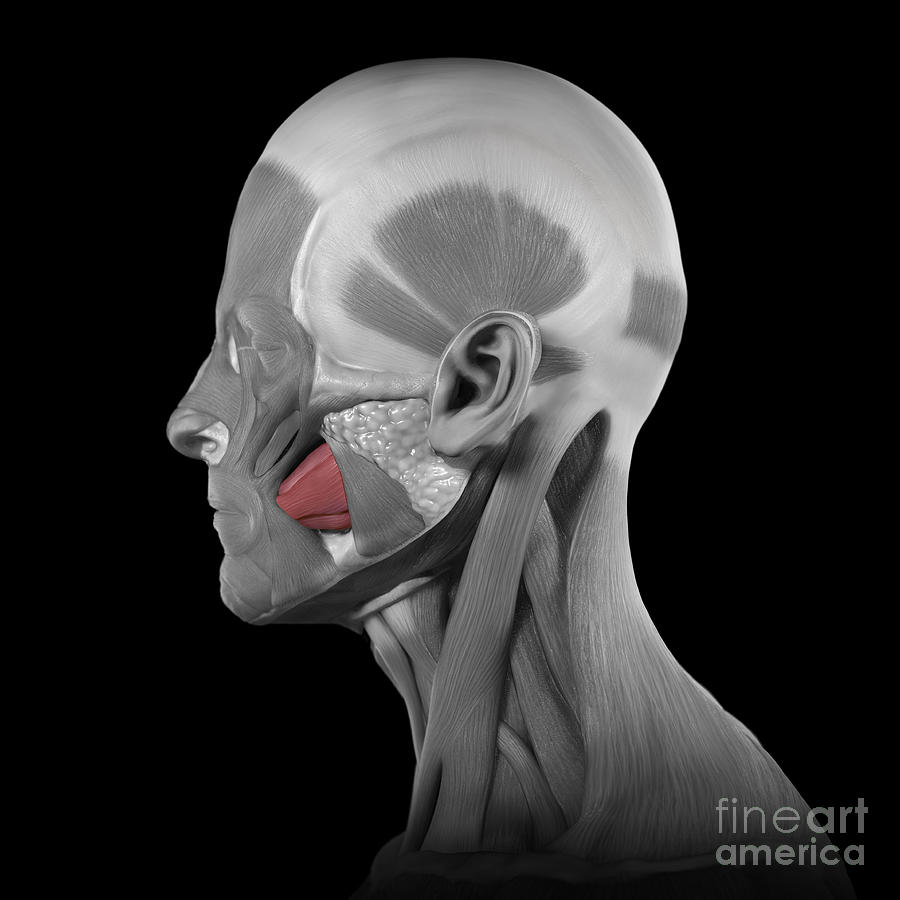
Buccinator
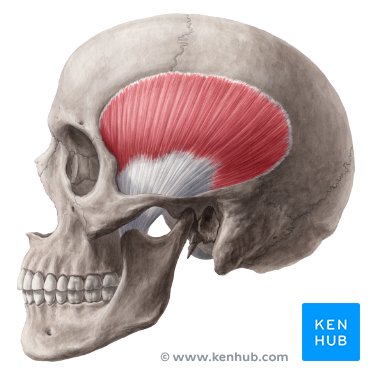
Origin, Insertion, Function
Temporalis - origin is the temporal fossa and the temporal line of the skull. Insertion is at the coronoid process of the mandible. It functions to retract the mandible.
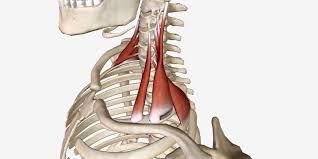
Scalenes (3)
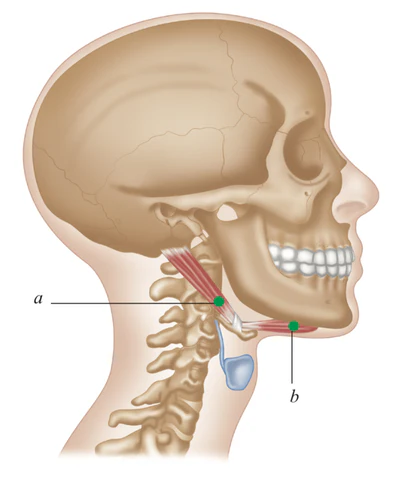
Digastric
Origin, Insertion, Function
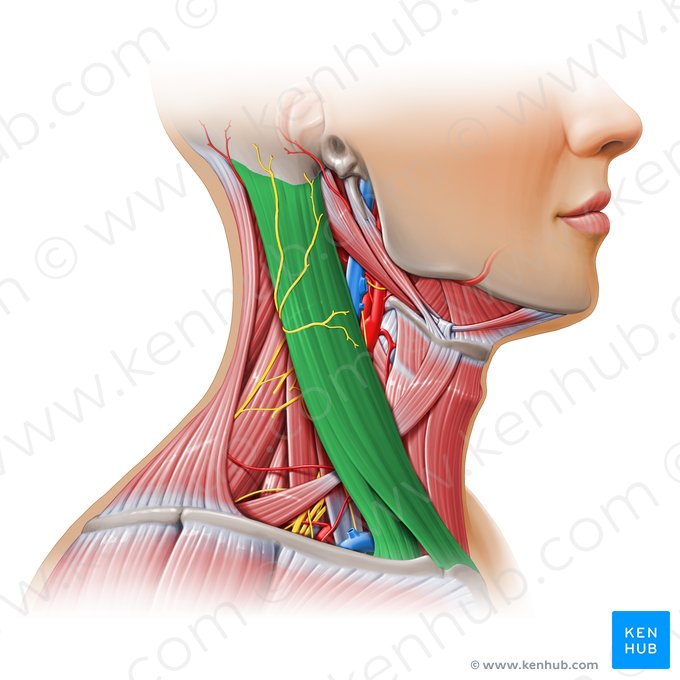
Sternocleidomastoid
origin is the manubrium of the sternum and the clavicle. Insertion is at the mastoid process of the temporal bone. It functions to flex and rotate the head.
Origin, Insertion, Function
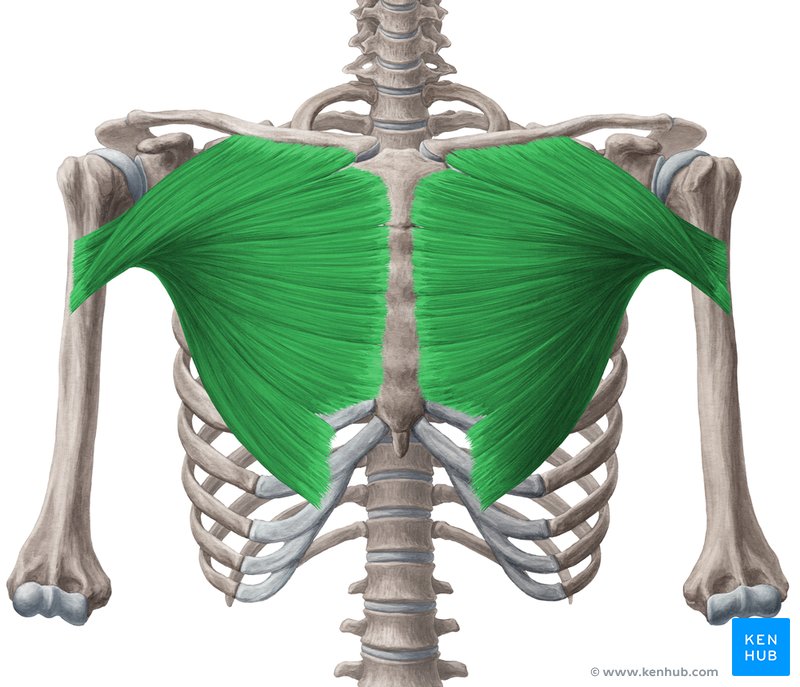
Pectoralis major
origin is the clavicle, sternum, and ribs. Insertion is at the greater tubercle of the humerus. It functions to flex, adduct, and medially rotate the arm.
Origin, Insertion, Function
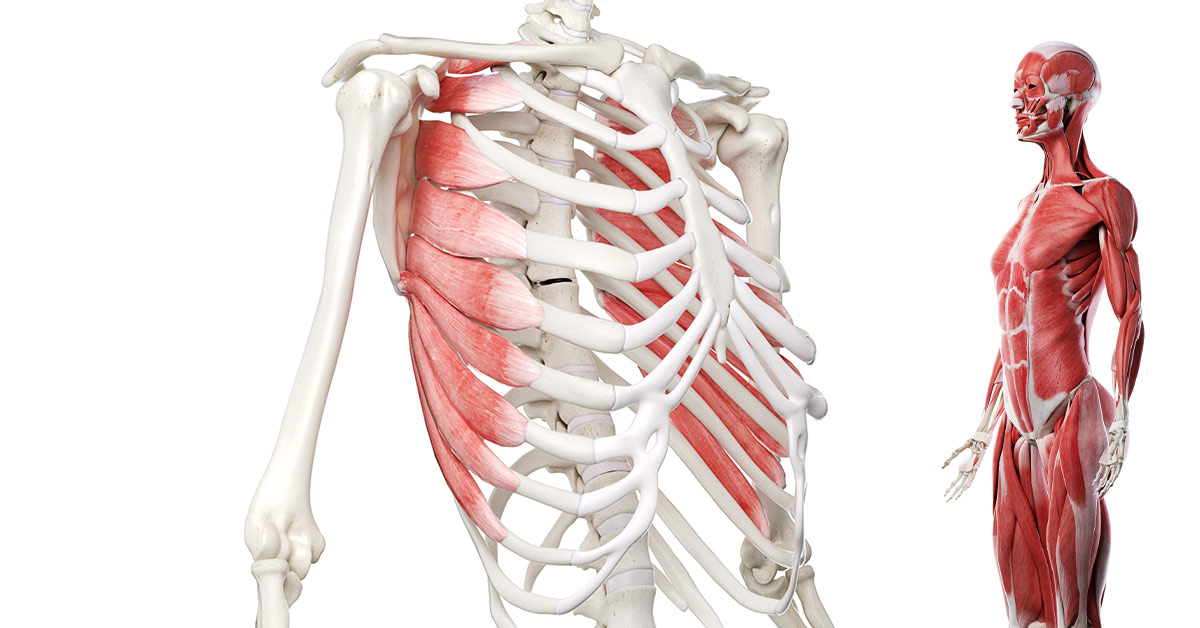
Pectoralis minor
origin is the third to fifth ribs. Insertion is at the coracoid process of the scapula. It functions to stabilize the scapula and assist in respiration.
Origin, Insertion, Function
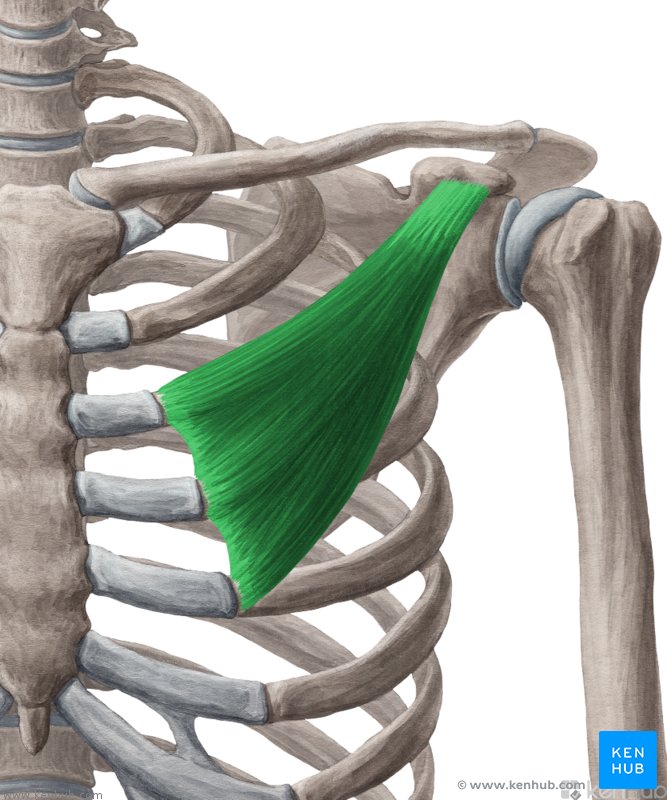
Serratus anterior
origin is the lateral surfaces of the upper eight or nine ribs. Insertion is at the medial border of the scapula. It functions to protract and stabilize the scapula.
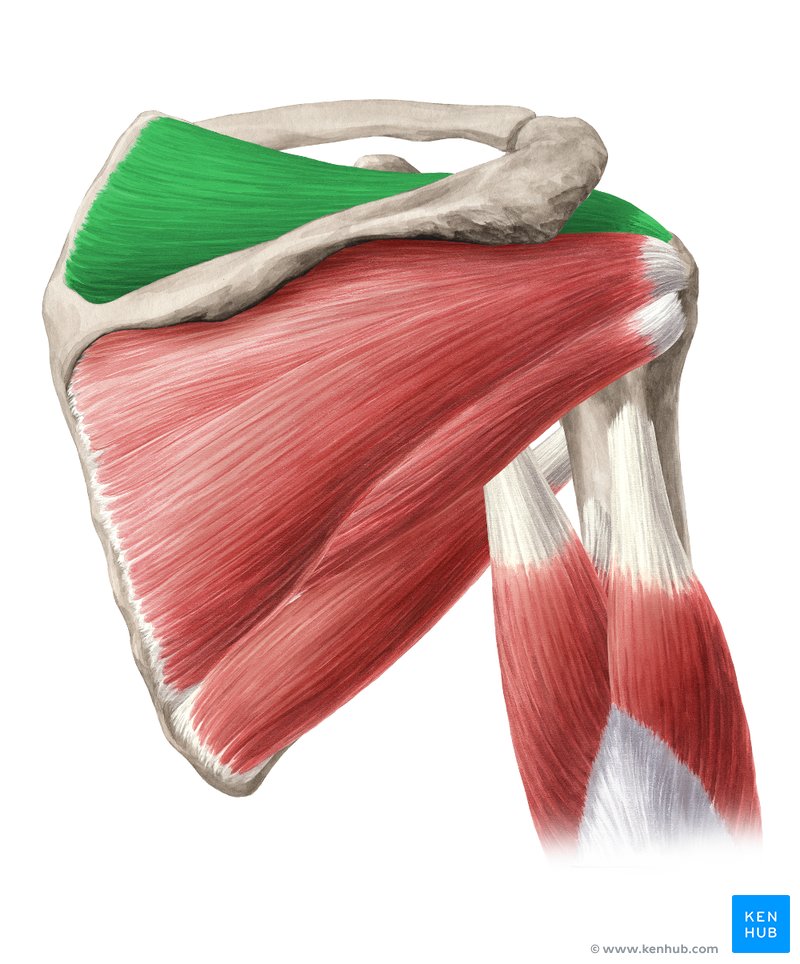
What are the Rotator Cuff muscles?
Supraspinatus,
Infraspinatus,
Teres minor,
Subscapularis
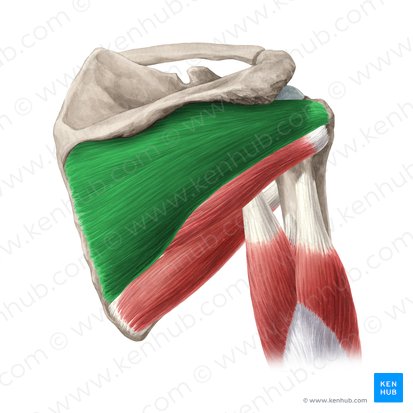
Origin, Insertion, Function
Supraspinatus is a rotator cuff muscle that originates from the supraspinous fossa of the scapula and inserts on the greater tubercle of the humerus. It functions to abduct the arm and stabilize the shoulder joint.
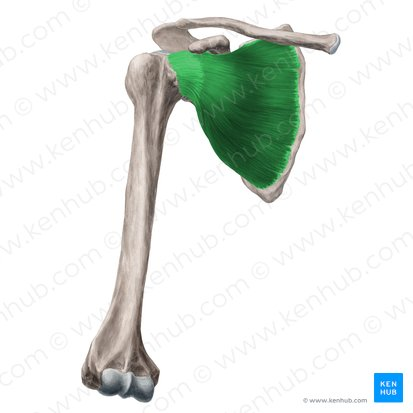
Origin, Insertion, Function
Infraspinatus is a rotator cuff muscle that originates from the infraspinous fossa of the scapula and inserts on the greater tubercle of the humerus. It functions to externally rotate the arm and stabilize the shoulder joint.
Origin, Insertion, Function
Teres minor is a rotator cuff muscle that originates from the lateral border of the scapula and inserts on the greater tubercle of the humerus. It functions to externally rotate the arm and stabilize the shoulder joint.
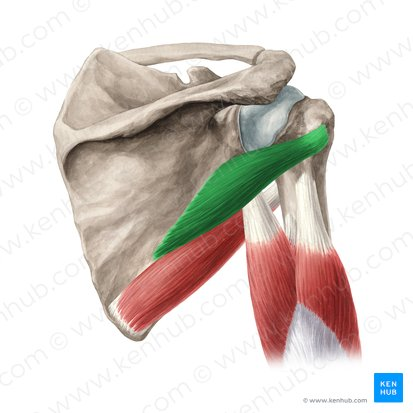
Origin, Insertion, Function
Subscapularis is a rotator cuff muscle that originates from the subscapular fossa of the scapula and inserts on the lesser tubercle of the humerus. It functions to internally rotate the arm and stabilize the shoulder joint.
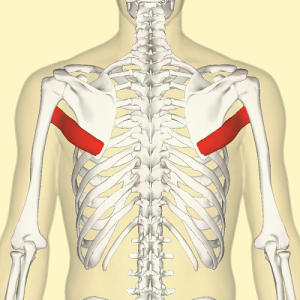
Teres major
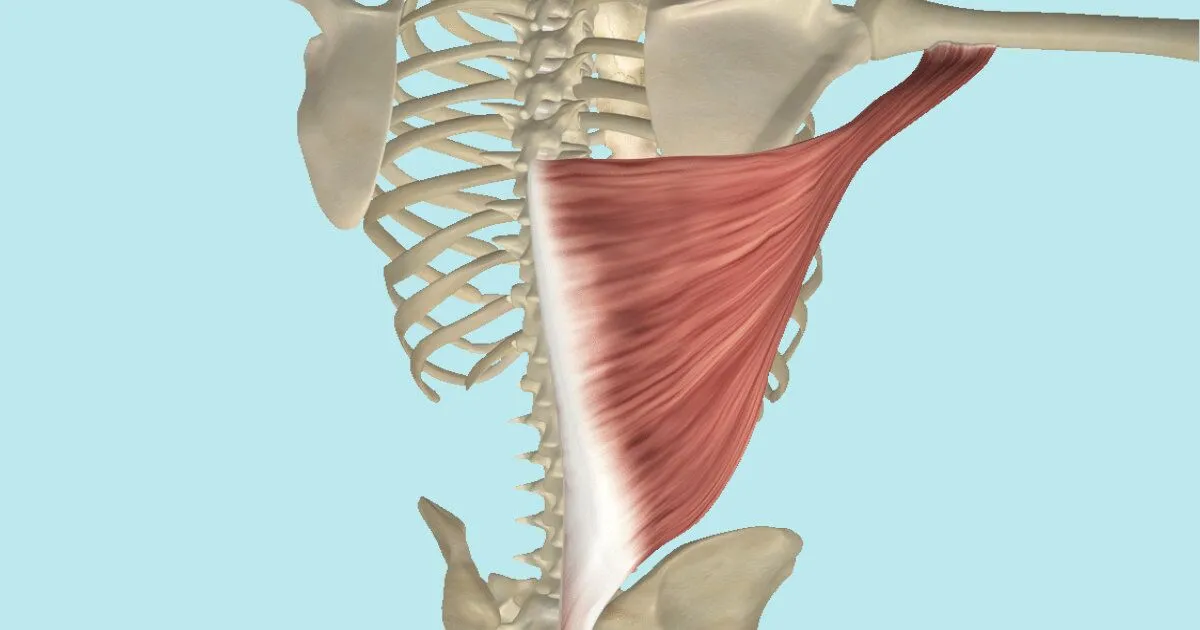
Origin, Insertion, Function
Latissimus dorsi
origin T7-L5, scapula, iliac crest
insertion bicipetal groove
function medial rotation of shoulder joint
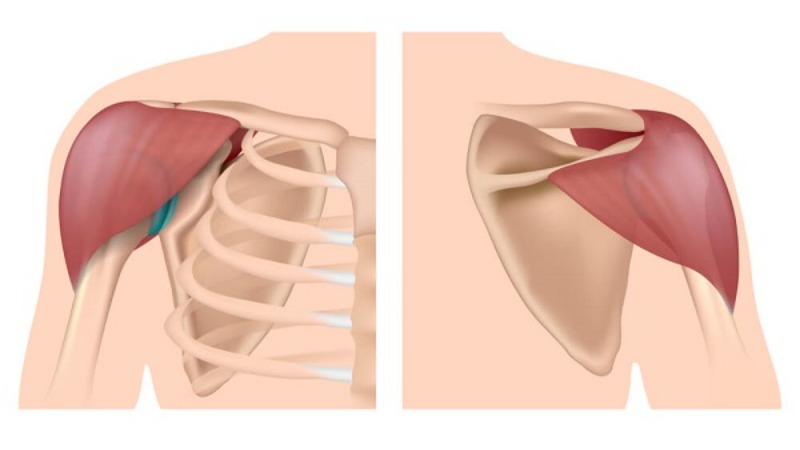
Origin, Insertion, Function
Deltoids
origin clavicle and scapula
insertion deltoid tuberosity on the humerus
function stabilization of shoulder abduction of shoulder
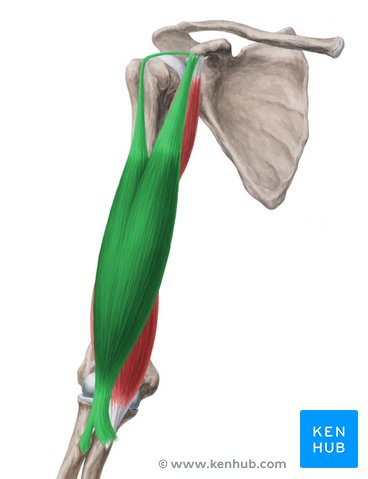
Origin, Insertion, Function
biceps brachii
origin Short head - Apex of the Coracoid process of the scapula
Long head - Supraglenoid tubercle of the scapula
Mnemonic: 'You walk Shorter to a street Corner. You ride Longer on a Superhighway'
insertion Radial tuberosity of the radius
function Flexion and supination of the forearm at the elbow joint
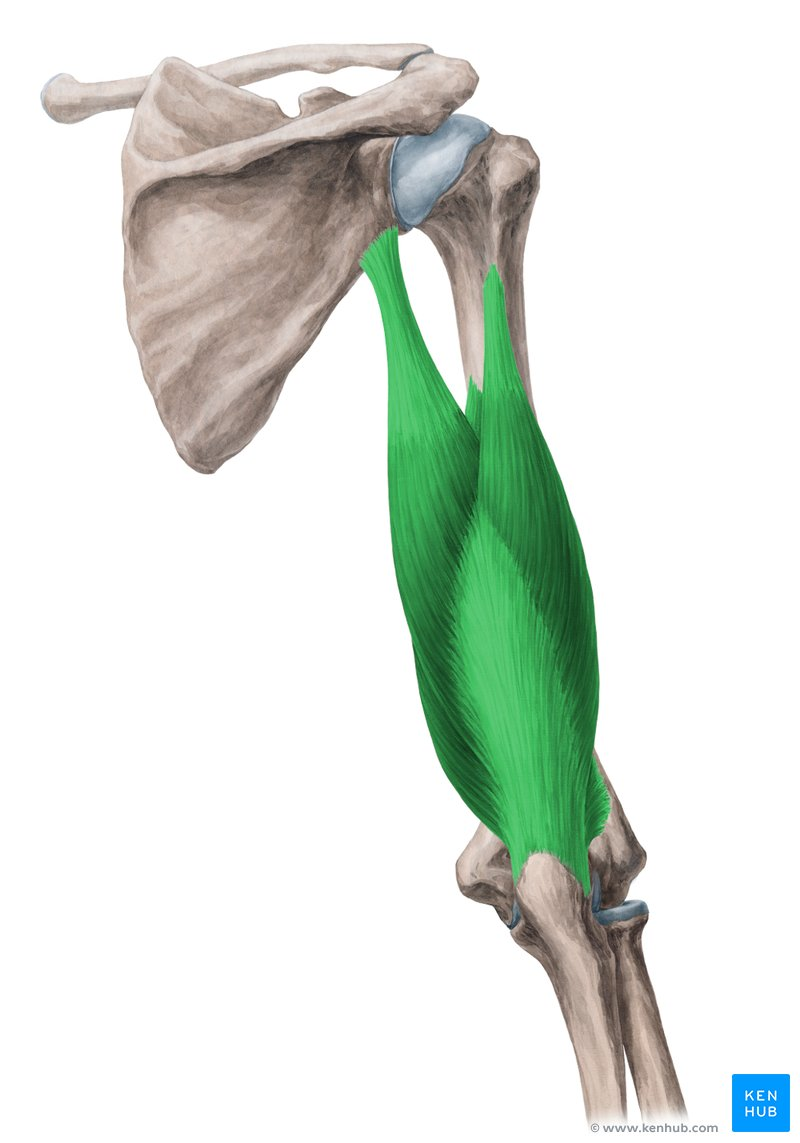
Origin, Insertion, Function
triceps brachii
origin scapula and humerus
insertion Olecranon of ulna and fascia of forearm
function extension of the elbow
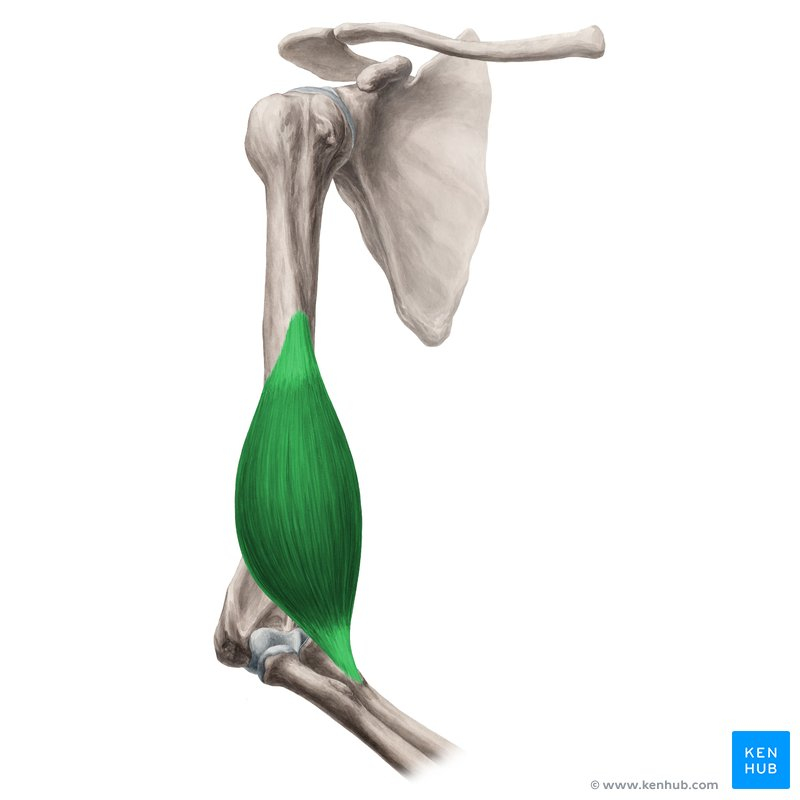
Origin, Insertion, Function
Brachialis
origin humerus
insertion ulna
function strong flexion of forearm at the elbow joint
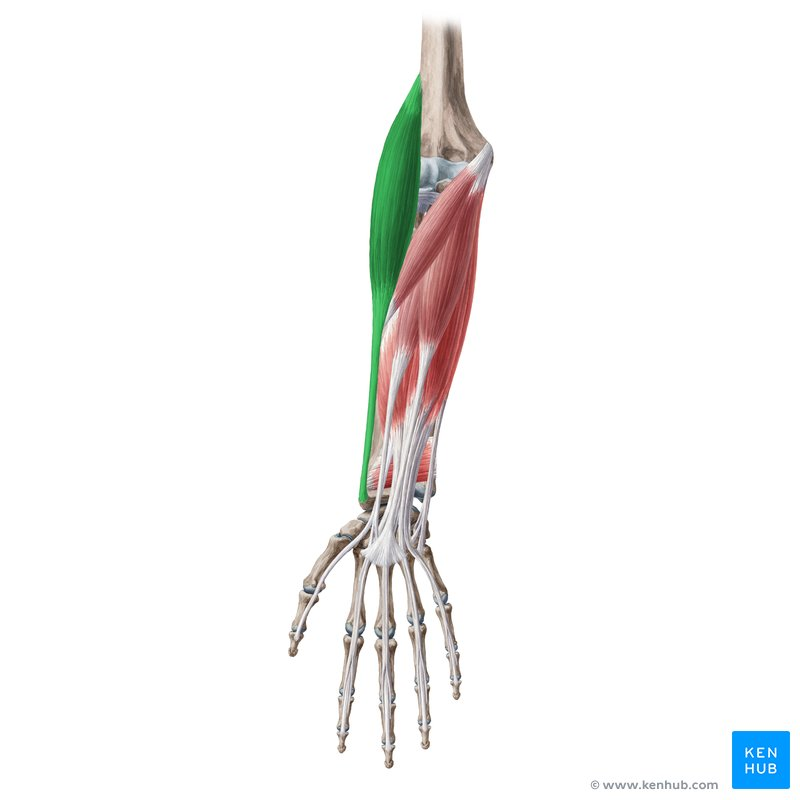
Origin, Insertion, Function
Brachioradialis
origin humerus
insertion radius
function Forearm flexion (when semi pronated)
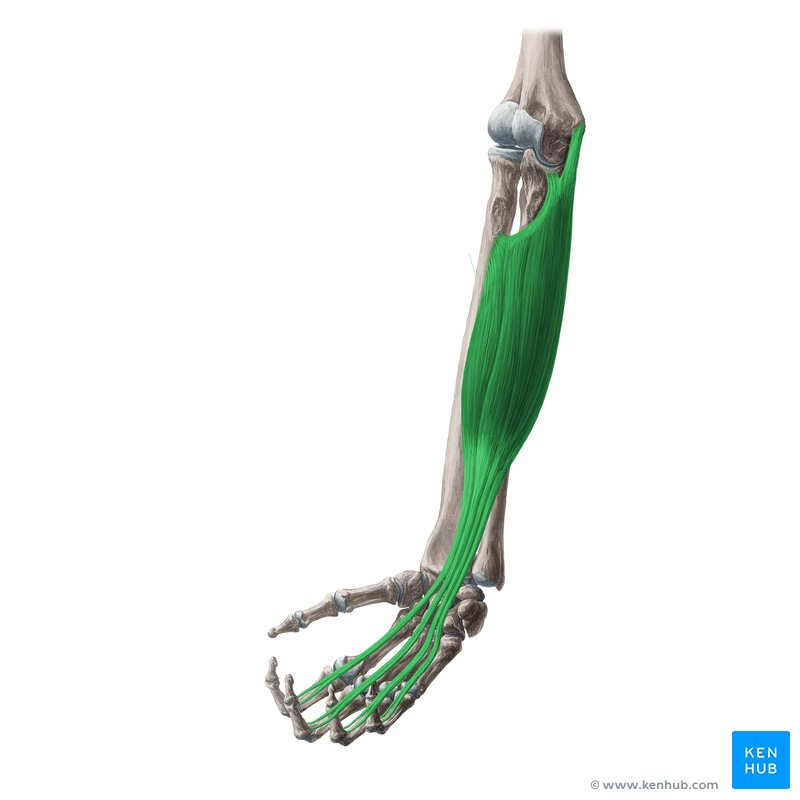
Origin, Insertion, Function
Flexor digitorum superficialis
origin Medial epicondyle of humerus, coronoid process of ulna, and radial head
insertion Sides of middle phalanges of digits 2-5
function finger flexion
Origin, Insertion, Function
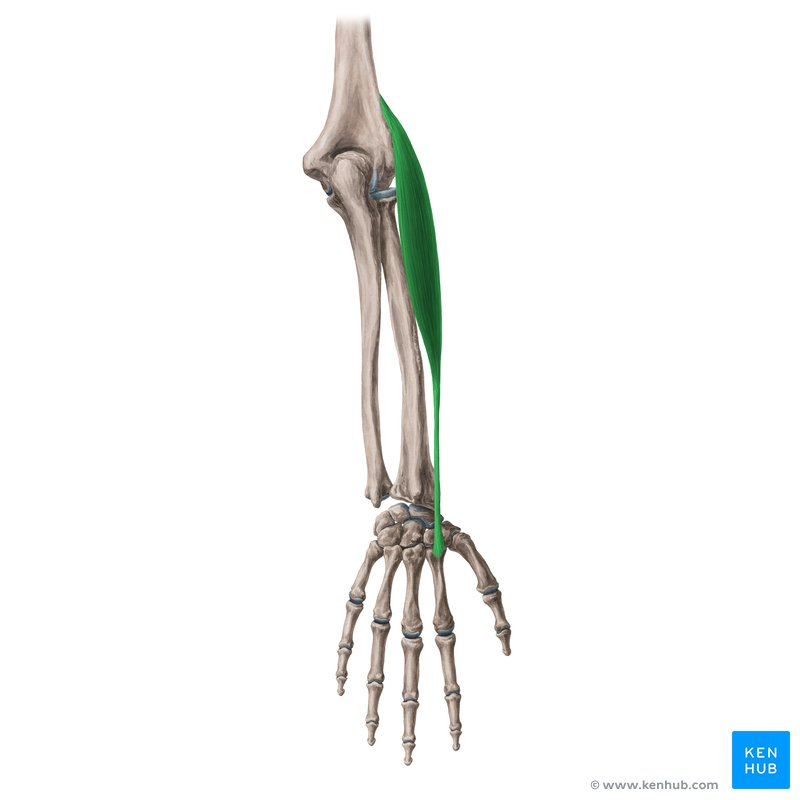
extensor carpi radialis longus
origin humerus
insertion Posterior aspect of base of metacarpal bone 2
function hand extension
Origin, Insertion, Function
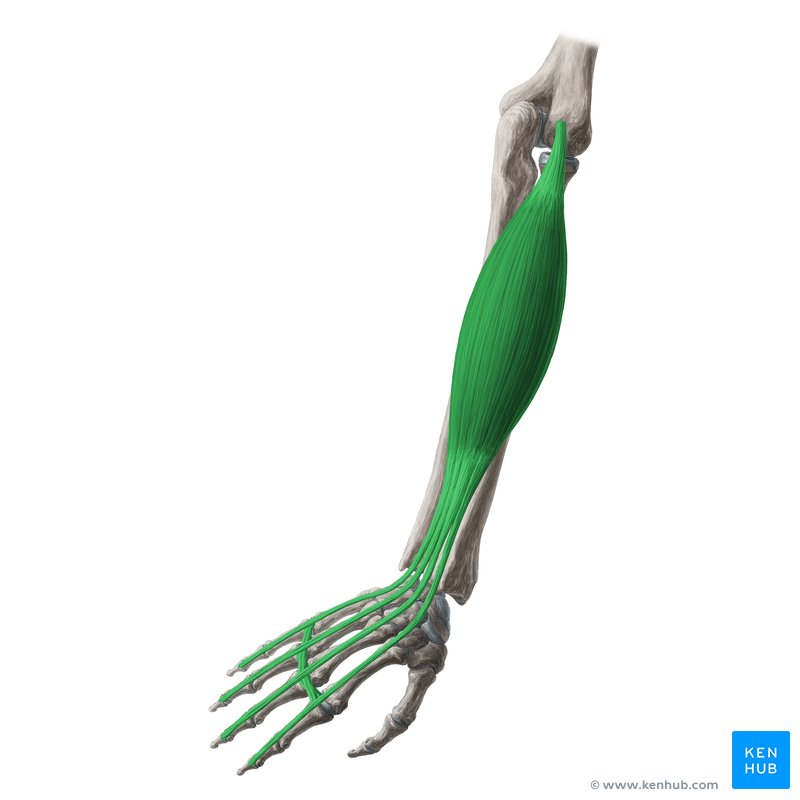
Extensor digitorum
origin humerus
insertion digits 2-5
function finger extension
Origin, Insertion, Function
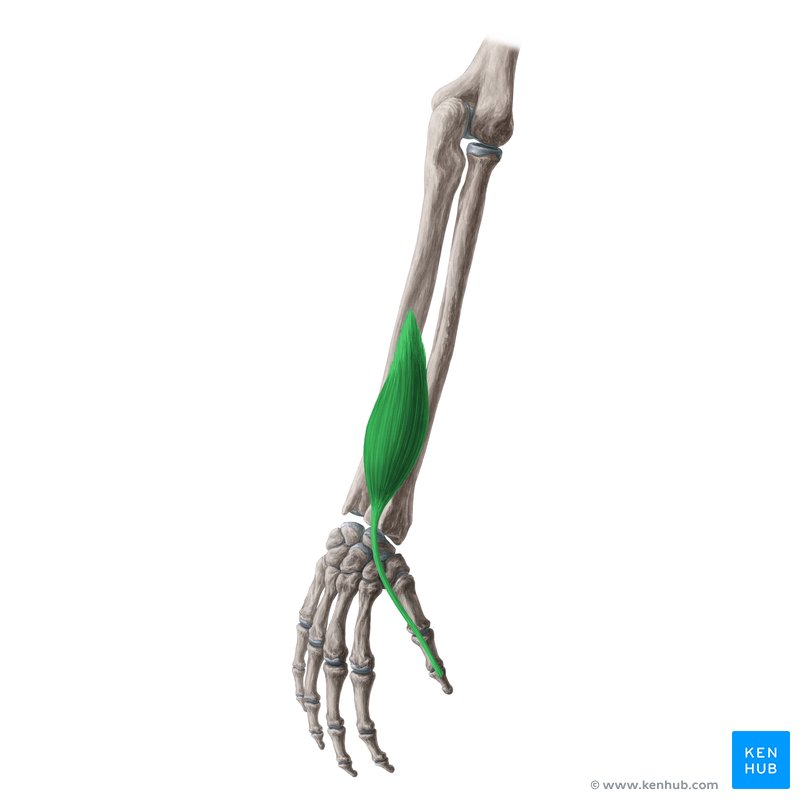
Extensor pollicus longus
origin ulna
insertion distal phalanx of thumb
function thumb extension