Respiratory Week 1 Review
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/109
Last updated 8:51 PM on 2/23/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
1
New cards
BA-pMDI
an aerosol inhaler that is activated by inspiration
2
New cards
pMDI
an aerosol inhaler that uses coordinated administration
3
New cards
DPI
a breath activated inhaler that uses a powder inhalation
4
New cards
SMI
inhaler that creates a slow, fine aerosol (Respimat)
5
New cards
percentage of patients using inhalers with administration errors
50%
6
New cards
MDI administration
shake before administration
slow, prolonged breath timed with actuation
hold breath for 10 seconds
slow, prolonged breath timed with actuation
hold breath for 10 seconds
7
New cards
DPI administration
do NOT shake before administration
quick, steady breath
hold for 10 seconds
(rinse mouth for ICS)
quick, steady breath
hold for 10 seconds
(rinse mouth for ICS)
8
New cards
SMI BUD
60 days from canister assembly
9
New cards
Asthma
chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways
10
New cards
atopic asthma
allergic asthma
11
New cards
nonatopic asthma
nonallergic asthma
12
New cards
mixed asthma
allergic and nonallergic asthma
13
New cards
types of asthma
exercise-induced
occupational
cough variant
glucocotricosteroid-resistant
occupational
cough variant
glucocotricosteroid-resistant
14
New cards
typical asthma symptoms
wheezing, SOB, cough, chest tightness
15
New cards
asthma steps
1. activation of mast cells
2. infiltration of eosinophils
3. increased activated helper T 2 cells
16
New cards
asthma risk factors
airway hyperreactivity
allergen exposure
atopy
early menarche
familial history of asthma
male gender
tobacco exposure
obesity
allergen exposure
atopy
early menarche
familial history of asthma
male gender
tobacco exposure
obesity
17
New cards
asthma presentation
narrowing of airways
hyperresponsiveness of airways
increased bronchial response to stimuli
hyperresponsiveness of airways
increased bronchial response to stimuli
18
New cards
th2 cells
responsible for cytokine production that drive eosinophil attack
19
New cards
Asthma allergen triggers
dust mites
pollens
molds
pet dander
cockroach droppings
pollens
molds
pet dander
cockroach droppings
20
New cards
asthma irritant triggers
cigarette smoke
strong fumes
woodfires/charcoal grills
strong fumes
woodfires/charcoal grills
21
New cards
NSAID induced asthma
asthma caused by inhibition of the COX pathway that pushes arachindonic acid to make leukotrienes (asthma bois) instead of COX
22
New cards
Drugs used for NSAID induced asthma
LT inhibitors, lipooxygenase inhibitor (zileuton)
23
New cards
Bronchodilator classes
Beta-2 agonists, muscarinic antagonists, methylxanthenes
24
New cards
Beta-2 agonist MOA
1. activate beta-2 receptor -> activate adenyl cyclase and increase cAMP -> smooth muscle relaxation
2. prevent mediator release from mast cells
25
New cards
SABAs
albuterol*, levabuterol*, metaproterenol, pirbuterol, terbutaline
26
New cards
LABAs
Formoterol, Salmeterol
27
New cards
Ultra LABAs
Olodaterol*, Indacaterol, Vilanterol*
28
New cards
Methylxanthine MOA
non-selective PDE inhibitor
29
New cards
PDE4 inhibitor
Roflumilast
30
New cards
Roflumilast MOA
inhibits breakdown of cAMP by PDE4
31
New cards
SAMA
Ipratropium
32
New cards
LAMA
tiotropium, aclidinium, umeclidinium
33
New cards
anticholinergics MOA
competitively bind M3 receptors to block ACh binding
34
New cards
antimuscarinic AEs
anti-SLUD (salivation, lacrimation, urination, defecation)
35
New cards
ICSs
beclomethasone*, budesonide*, fluticasone*, mometasone*ciclesonide
36
New cards
corticosteroid conversions
quick mafs (equivalents will be given on exam)
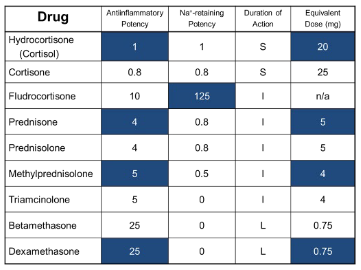
37
New cards
ICS MOA
inhibit inflammation of the airways and modulate cytokine and chemokine production
38
New cards
LT receptor antagonists
Montelukast, zafirlukast
39
New cards
5-Lipoxygenase inhibitor
Zileuton
40
New cards
anti-IgE agent
omalizumab
41
New cards
IL-5 inhibitors
(MR. B)
mepolizumab
reslizumab
benralizumab
mepolizumab
reslizumab
benralizumab
42
New cards
COPD risk factors
cigarette smoking
alpha 1-autitrypsin
alpha 1-autitrypsin
43
New cards
Chemical factors for beta2 selectivity
bulky substituent
proper phenyl ring (resorcinol, salicyl alcohol, N-formamide)
proper phenyl ring (resorcinol, salicyl alcohol, N-formamide)
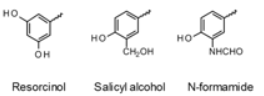
44
New cards
Levalbuterol
(R)-isomer of albuterol
45
New cards
factors determining length of action
longer, bulkier, more lipophilic chains will act longer by resisting COMT and MAO metabolism
46
New cards
active enantiomer of olodaterol
R enantiomer
47
New cards
corticosteroid prodrug tells
Ester @ C-17 or 21
Ketone @ C-11
Ketone @ C-11
48
New cards
methylxanthine base structure
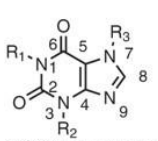
49
New cards
major enzyme in methylxanthene breakdown
xanthine oxidase
50
New cards
active chemical group of zileuton
N-hydroxyl group
51
New cards
LT receptor antagonists SAR
acidic or negative group
at least three aromatic rings (hydrophobic regions)
at least three aromatic rings (hydrophobic regions)
52
New cards
threshold for reversibility of airflow limitation
12% increase
53
New cards
Asthma control assessment
Daytime asthma symptoms more than 2x per week
Nighttime waking due to asthma
Reliever used more than 2x per week
Activity limitations from asthma
(0 = well controlled / 1-2 = partially controlled / 3-4 = uncontrolled)
Nighttime waking due to asthma
Reliever used more than 2x per week
Activity limitations from asthma
(0 = well controlled / 1-2 = partially controlled / 3-4 = uncontrolled)
54
New cards
Constant assessment in asthma patients
INHALER TECHNIQUE
55
New cards
Step up criteria
Uncontrolled asthma or risk of exacerbation
56
New cards
asthma step down criteria
consider when well controlled more than 3 months
57
New cards
PA - Step 1/2 initiation criteria
symptoms
58
New cards
PA/AA - step 3 initiation criteria
symptoms most days OR
Night awakening more than once per week
Night awakening more than once per week
59
New cards
PA/AA - step 4 initiation criteria
Step 3 + low lung fxn (read absolutely fucked)
60
New cards
AA - step 1 initiation criteria
Sx < 2x per month
61
New cards
AA - step 2 initiation criteria
symptoms 2 or more times per month but less than 4-5 times per week
62
New cards
PA - step 1/2 therapy
low dose ICS/formoterol PRN
63
New cards
PA - Step 3 therapy
low dose ICS/formoterol maintenance and PRN
64
New cards
PA - Step 4 therapy
Medium dose ICS/formoterol maintentance and low dose ICS/formoterol PRN
65
New cards
PA - Step 5 therapy
Add LAMA to step 4 therapy
66
New cards
AA - step 1 therapy
SABA + ICS prn
67
New cards
AA - step 2 therapy
Low dose ICS maintenance + SABA PRN
68
New cards
AA - step 3 therapy
Low dose ICS/LABA maintenance + SABA PRN
69
New cards
AA - step 4 therapy
medium/high dose ICS/LABA maintenance + SABA PRN
70
New cards
AA - step 5 therapy
Add LAMA to step 4 therapy (Trelegy only asthma approved triple therapy)
71
New cards
Symbicort low dose
160/4.5 - 1 puff QD or BID
72
New cards
Symbicort medium dose
160/4.5 - 2 puffs BID
73
New cards
Symbicort reliever dose
160/4.5 - 1 puff PRN
74
New cards
Max daily Symbicort dose
12 puffs daily max
75
New cards
Asthma diagnostic criteria
1. history of respiratory symptoms AND
2. variable expiratory airflow limitation
76
New cards
measurement device for airflow
Spirometer
77
New cards
Atopic triad
1. dermatitis
2. allergic rhinitis
3. asthma
78
New cards
ICS Counselling Points
Rinse mouth and spit with maintenance doses to reduce risk of oral candidiasis
may cause hoarseness of voice
2 weeks for clinical effects
may cause hoarseness of voice
2 weeks for clinical effects
79
New cards
syndrome occurring with coadministration of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors and high doses of ICS
Cushing syndrome
80
New cards
LABA BBW
Do NOT use without ICS
* increased asthma related death -- yay!
* increased asthma related death -- yay!
81
New cards
SAMA/SABA asthma indication
only to be used for acute exacerbations in the hospital setting
82
New cards
Only asthma approved single-agent LAMA
Spiriva (tiotropium)
83
New cards
post-injection monitoring time for Omalizumab
first three months -- 2 hours then 30 minutes every visit after
84
New cards
IL-4 antagonist (dupilumab) AE
injection site pain
transient blood eosinophilia
transient blood eosinophilia
85
New cards
Possible LTRA uses
asthma patients with…
1. allergic rhinitis
2. aspirin sensitivity
3. exercise-induced asthma
1. allergic rhinitis
2. aspirin sensitivity
3. exercise-induced asthma
86
New cards
Asthma therapy follow-up
2-6 weeks after initiation of therapy then 3-12 months after controlled
targeting stepdown: every three months
exacerbation: 1 week followup
targeting stepdown: every three months
exacerbation: 1 week followup
87
New cards
pharmaceutical aerosol definition
a pressurized dosage form that is released in a fine dispersion
88
New cards
pharmaceutical aerosol ingredients
1. product concentrate
2. propellant
89
New cards
Propellant pressure range (room temp \[70 F\])
10-15 PSI
90
New cards
Propellant requirements
"propellant should not be noticable in the suspension”
91
New cards
Aerosol propellants
hydrocarbons
hydrochlorofluorocarbons
hydrofluorocarbons
compressed gasses
hydrochlorofluorocarbons
hydrofluorocarbons
compressed gasses
92
New cards
two-phase aerosol system
1. liquid phase
2. product concentrate
93
New cards
three-phase aerosol system
1. water immiscible propellant
2. Aqueous product concentrate
3. Vapor phase
94
New cards
Compressed gas system
Product insoluble in gas
95
New cards
main advantage of inhaled vs systemic corticosteroids
increased bioavailability in lungs/lack of systemic adverse effects.
96
New cards
factors for particle distribution
1. particle size\*
2. velocity of inspiratory flow
97
New cards
ideal particle size
1-5 microns
98
New cards
problem with large particles
fall out of the air quicker / stop upon initial impact (often before the lungs)
99
New cards
problems with small particles
move too easily → get exhaled as if a gas
100
New cards
percentage of medication reaching the lungs
10-20%