Chapter 4: Cells
1/83
Earn XP
Description and Tags
finished chapter in lecture 9/6. Finished flashcards 9/8
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
Cell theory
All living things are made of cells that share some common characteristics (basic shape, internal content, dna chromosomes, metabolic capabilities)
What cells are present in animals, plants, fungi, and protists?
eukaryotic cells
What cells are present in bacteria and archaea?
Prokaryotic cells
Describe the difference between light microscopes and electron microscopes.
Light microscopes use light to illuminate the specimen. Electron microscopes use electrons to illuminate the specimen
cell size is limited by
surface area to volume ratio
fluid mosaic model
phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins
Cytoplasm, cytosol, cytoskeleton
cytoplasm is between the plasma membrane and the central region, contains the cytosol and cytoskeleton.
cytosol is an aqueous solution containing ions, organic molecules, and organelles
cytoskeleton maintains cell shape and plays key roles in cell division
Nucleus in prokaryotic vs eukaryotic cells
eukaryotic cells have a true nucleus separated from the surrounding cytoplasm by membranes.
prokaryotic cells have a nucleoid region without a boundary membrane
DNA in prokaryotic cells
Typically a single circular molecule
Bacterial arrangements is dependent on
pattern of division and how cells remain attached after division
Plasma membrane in prokaryotic cells is surrounded with
Surrounded by a rigid cell wall coated with polysaccharides (glycocalyx)
Functions of the glycocalyx
protect cells from dehydration and nutrient loss
inhibit killing by white blood cells by phagocytosis
attachment (formations of biofilms)
What is the cell envelope?
External covering outside the cytoplasm, containing two basic layers: cell wall and cell membrane.
It maintains cell integrity
Peptidoglycan
determines cell chape and prevents lysis due to changing osmotic pressures, linked by polypeptides. forms a mesh-like surrounding to bacteria
Gram-positive cell wall
thick homogeneous sheath of peptidoglycan, includes teichoic acid and lipoteichoic acid. May have a periplasmic space between the cell membrane and cell wall
Gram negative cell wall
a thin layer of peptidoglycan between the outer and inner membrane of a cell
flagella are anchored in
the cell wall
How do flagella move
rotates 360 degrees
Prokaryotic genetic material
chromosome - usually single, circular double stranded DNA molecule that contains all the genetic info required by a cell (clumped in nucleoid)
Plasmids (extra-chromosomal DNA) possible. may encode antibiotic resistance and other toxins, not essential to bacterial function
Ribosomes made of 60% ___ and 40% ___
ribosomal RNA, protein
Ribosomal subunits
Large and small. Prokaryotic and eukaryotic ribosomes differ in size and number of proteins
Ribosome function
protein synthesis
A coating or layer of molecules external to the cell wall. It serves protective, adhesive, and receptor functions. It may fit tightly or be very loose and diffuse.
Glycocalyx
composed of condensed DNA molecules. DNA directs all genetics and heredity of the cell and codes for all proteins.
Bacterial chromosome or nucleoid
Double-stranded DNA circle containing extra genes
Plasmid
An elongate, hollow appendage used in transfers of DNA to other cells
Pilus
Tiny particles composed of protein and RNA that are the sites of protein synthesis
Ribosomes
Long fibers of proteins that encircle the cell just inside the cell membrane and contribute to the shape of the cell
Actin cytoskeleton
Specialized appendage attached to the cell by a basal body that holds a long, rotating filament. The movement pushes the cell forward and provides motility.
Flagellum
Fine, hairlike bristles extending from the cell surface that help in adhesion to other cells and surfaces
Fimbriae
Stored nutrients such as fat, phosphate, or glycogen deposited in dense crystals or particles that can be tapped into when needed.
Inclusion/Granule
A semirigid casing that provides structural support and shape for the cell
Cell wall
A thin sheet of lipid and protein that surrounds the cytoplasm and controls the flow of materials into and out of the cell pool
Cell (cytoplasmic) membrane
Extra membrane similar to cell membrane but also containing lipopoly saccharide. Controls flow of materials and portions of it are toxic to mammals when released.
Outer membrane
Dormant body formed within some bacteria that allows for their survival in adverse conditions
Endospore
Water-based solution filling the entire cell
cytoplasm
What are Archaea?
Prokaryote, similar to bacteria - circular DNA genome in a nucleoid region with no nuclear envelope. No membrane-bound organelles.
Also shared features with eukaryotes - may share a common ancestral line with eukaryotes.
Phylogenetic Tree of Life
Shows the branches of each type of cell in three domains: bacteria, archaea, eukarya
Endosymbiotic theory
eukaryotes evolved from prokaryotic organisms (and organelled originated from trapped prokaryotic cells)
Which organelles are present in animal cells but not plant cells?
Centrioles, lysosomes, cilia
Organelle for energy metabolism
Mitochondrion
Membrane-bound organelle containing enzymes for digestion of many complex molecules
Lysosome
Cytoskeleton component consisting of tubulin; anchor various organelles and provide tracks for vesicle movement
Microtubules
Membraneless organelle near the nucleus where microtubules are formed and radiate outward; contains a pair of centrioles
Centrosome
Small membrane-bound compartments that transfer substances between various membranous sacs in the cell, such as the endoplasmic reticulum and golgi complex
Vesicle
Responsible for modification, distribution of protiens
Golgi complex
Aqueous solution of cytoplasm containing ions and organic molecules
Cytosol
Lipid bilayer membrane that bounds the cell; contains embedded proteins for transport of substances into and out of cell, and for receiving cellular signals
Plasma membrane
A cytoskeleton component consisting of actin; involved in a number of structural and locomotory functions
Microfilaments
Synthesis, modification, and transport of proteins
Rough ER
Synthesis of proteins
Ribosomes
What are the two locations of ribosomes in the cell?
Attached to the rough ER
Free in cytosol
Synthesis of lipids for membranes
Smooth ER
Membrane-enclosed region of DNA; hereditary control
Nucleus
Controls exchange of material between nucleus and cytoplasm
Nuclear pore complex
Double lipid bilayer membrane that separates nucleus from cytoplasm
Nuclear envelope
Complex of DNA hereditary material and protein
Chromatin
Formed around rRNA genes; rRNA synthesis and ribosome assembly
Nucleolus
Organelles present in plant cells but not animal cells
Cell wall (with plasmodesmata)
Chloroplasts
Central vacuole
Central vacuole membrane, present only in plant cells.
Tonoplast
Cell growth, support, and storage; contains enzymes for digestion of many complex molecules. present only in plant cells.
central vacuole
Photosynthesis; some starch storage
Chloroplasts
Channels through cell wall. Present only in plant cells
Plasmodesmata
Protection, structural support in plant cells
Cell wall
proteins to be imported into the nucleus have a special, short amino acid sequence called a
nuclear localization signal
Liquid within the nucleus is called
nucleoplasm
DNA in eukaryotes
linear
Eukaryotic cells have an ____ that divides the cell into functional and structural compartments
endomembrane system
The endomembrane system includes the nuclear envelope, plasma membrane, and which organelles? (4)
endoplasmic reticulum, golgi complex, lysosomes, vesicles
Describe the path of a protein
proteins synthesized either on the ER or in free ribosomes → enter ER membranes
proteins modified in ER → vesicles bud from ER membrane and transport to Golgi
vesicles from ER bind to cis end of Golgi → modification and sorting → vesicles bud from trans end
Secretory vesicles can take proteins from Golgi to the plasma membrane for release. Lysosomes can digest damaged organelles or contents of vesicles.
The breaking down of bacteria or other cellular debris in lysosomes
Phagocytosis
pH in lysosomes is (basic/acidic)
acidic
Cellular respiration occurs in
mitochondria
The process by which energy-rich food molecules are broken down to water and CO2 , and energy is captured in ATP
cellular respiration
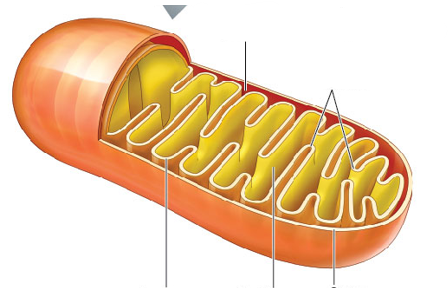
Parts of the mitochondria
Outer mitochondrial membrane covers the organelle
Inner mitochondrial membrane is expanded by folds called cristae
The innermost compartment = mitochondrial matrix (contains DNA, ribosomes, and other components)
Where in mitochondria do ATP generation reactions occur?
In the cristae and matrix
How do eukaryotic flagella and cilia move?
They whip back and forth
colorless plastids that store starch in plant cells
Amyloplasts
Parts of a chloroplast
inner and outer boundary membrane around the stroma (fluid interior).
Within the stroma is a third membrane system of flattened, closed sacs (thylakoids)
when thylakoids are stacked → grana
Chlorophyll stored in thylakoid membranes
cell adhesion molecules
bind cells together
cell junctions
seal the spaces between cells and provide direct communication between cells
Extracellular matrix
supports and protects cells and provides mechanical linkages between tissues
glycoproteins in the plasma membrane that bind to specific molecules on other cells
cell adhesion molecules
__ are the main component of extracellular membrane
Glycoproteins. In animals, collagen