Aldehydes and ketones
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
When does nucleophilic addition occur?
When there is a reaction of an aldehyde or ketone
Both have carbonyl group c=o
What happens in a nucleophilic addition mechanism and why?
A positive seeking species (nucleophile) joins on to the carbonyl carbon
The carbon in the carbonyl group is partially positive as the O is more electronegative
Nucleophile attacks partially positive carbon
2 examples of nucleophilic addition
Reduction of aldehydes and ketones to form alcohols
Aldehyde→ Primary alcohol
Ketone→ Secondary alcohol
Preparation of hydroxynitriles
What is required in the reduction of aldehydes/ketones to form alcohols?
Aqueous NaBH4 (Sodium borohydride)
Which is the reducing agent
What is required to prepare hydroxynitriles?
KCN (aq)
Dilute acid (for H+)
What is NaBH4
A reducing agent
Ionic compound
When it is dissolved in water, to make an aqueous solution it is a source of H- - hydride ion
Mechanism for the reduction of an aldehyde (ethanal) and explain it
Partially positive carbon attracts the hydride ion
Hydride ion attacks the partially positive carbon and uses its lone pair of electrons to form a new bond between carbon and hydride ion
Bond between C=O partially breaks→ 2 of the 4 electrons are pulled by the O away from the carbon
Negatively charged oxygen uses its lone pair to form a new bond with H+ (which typically comes from the solvent the sodium borohydride was dissolved in)
Producing an alcohol - ethanol

Write the equation for ethanal being reduced to ethanol
2 before the H because the aldehyde (or ketone) will be gaining 2 hydrogens
1 from the nucleophile and 1 from the solvent.
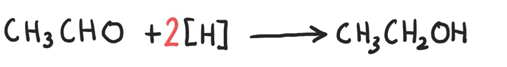
How do you name a hydroxynitrile?
Nitrile functional group takes priority
So carbon attached to the N is always treated as carbon 1
Check notes for further guidance
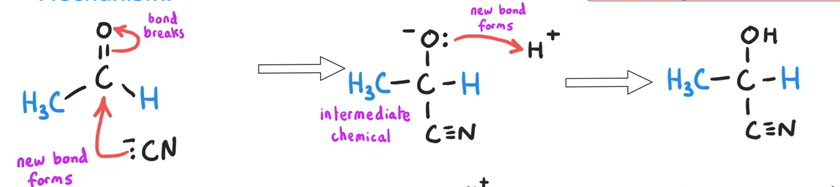
What is KCN and what happens when u make it an aqueous solution?
Ionic compound
When dissolved in a solvent (water) it will fully dissociate into CN- and K+
Draw the mechanism for ethanal being used to make a hydroxynitrile
( H+ Comes from dilute acid)
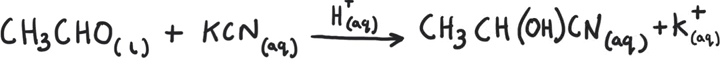
Write the equation of ethanal becoming a hydroxynitrile
(Don’t worry about state symbols)
What does the solubility of organic compounds like ketones and aldehydes depend on?
Molecular size
Larger carbon chain= Less soluble
E.g ethanal has a smaller carbon chain so its likely to be soluble
Risk assessment for producing hydroxynitriles: Hazard is KCN - why is it dangerous and give a control measure?
KCN is toxic and produces HCN which is also toxic
Should be handled and stored carefully
Do the reaction in a fume cupboard to prevent HCN from entering the room
Risk assessment for producing hydroxy nitriles: Organic products are the hazard- why are they dangerous and give a control measure
Flammable
Heat in water bath and don’t expose it to a naked flame (if you wish to speed up the reaction)
What can be used instead of KCN when preparing hydroxynitriles?
HCN
In this case the mechanism will look the same but the reaction equation will be slightly different
Write an equation for ethanol reacting with HCN to produce a hydroxynitrile and explain why the equation is different?
No acid will be added when using HCN as HCN can be the source for both cyanide ion and H+
Because it is weakly acidic and dissociates into H+ and CN -
So in the equation there is not H+ over the arrow and no K+

Why is KCN preferred over HCN?
KCN is an ionic compound so it completely/ readily dissociates in water and produces a higher cyanide ion concentration than HCN
HCN is also a gas so its harder to handle and store.
What happens when you carry out nucleophilic addition(to produce hydroxynitriles) reactions on aldehydes and unsymmetrical ketones?
You produce a mixture of enantiomers
Even though nucleophilic addition produces 2 enantiomers, why is there no optical activity?
The product is a racemate
Meaning there’s equal amounts of the 2 enantiomers
The rotation of the plane polarised light clockwise and anticlockwise will cancel out
Thus no optical activity
Why is the racemic mixture produced?
Molecules with a carbonyl group are planar in the region around the carbonyl carbon
Nucleophile can attack from either side with equal probability
Producing equal amounts of the 2 enantiomers