MLT 111 Exam 3 (Ch. 7)
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
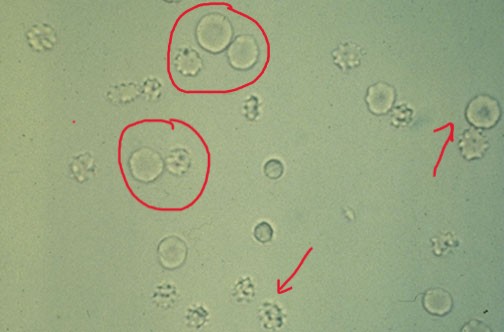
What do you see in this image?
RBC’s (some are crenated)
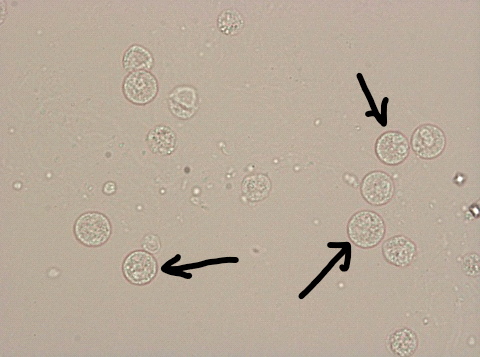
What do you see in this image?
White Blood Cells (neutrophils)
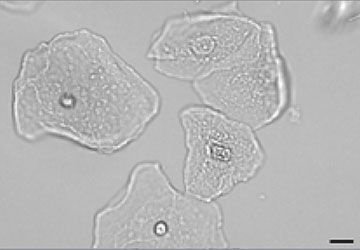
What do you see in this image?
Squamous — Epithelial cell
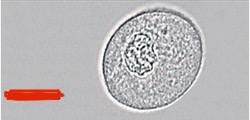
What do you see in this image? Location of origin?
Transitional Epithelial Cells — (lining of renal/bladder)
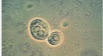
What do you see in this image? Indication?
RTE - Renal Tubular Epithelial — (renal tubule issues)
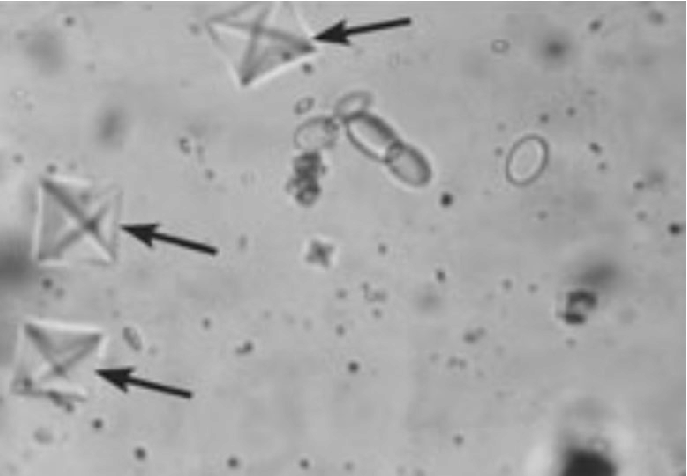
What do you see in this image? What can it indicate?
Calcium Oxalate (dihydrate) — kidney stones
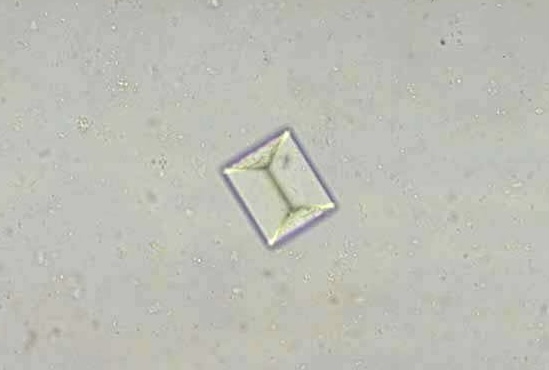
What do you see in this image? Indication?
Triple Phosphate — UTI or kidney stones
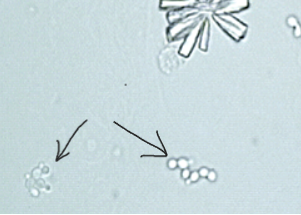
What does the arrow point out in urine? What may it indicate?
Yeast (indicates UTI or contamination)
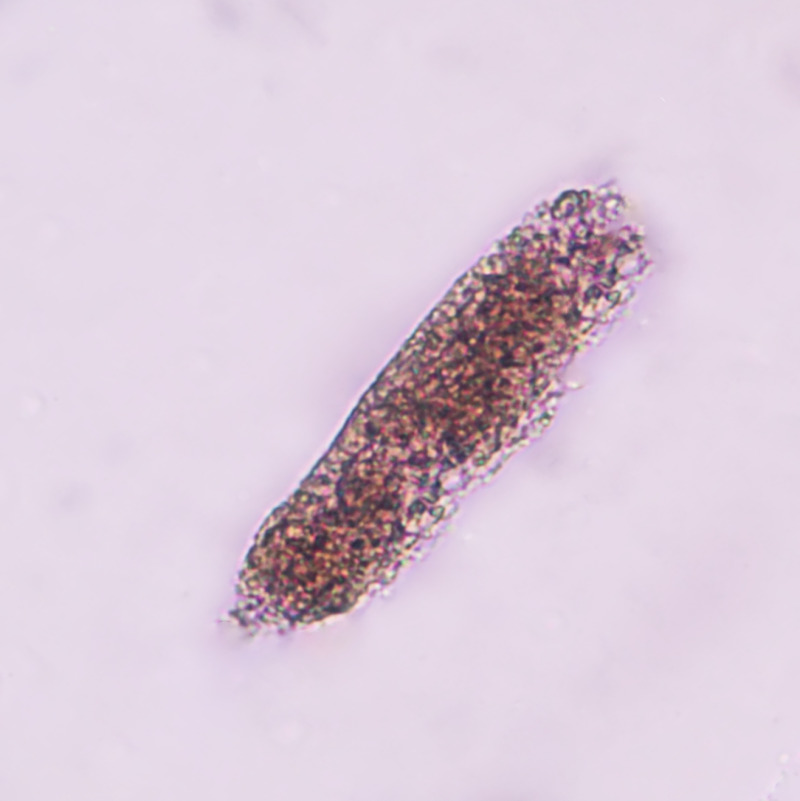
What do you see in this image? Indication?
RBC Cast
Indicator of glomerular damage
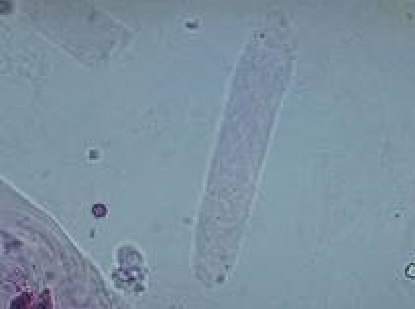
What do you see in this image? Is it normal or abnormal?
Hyaline Cast, Normal
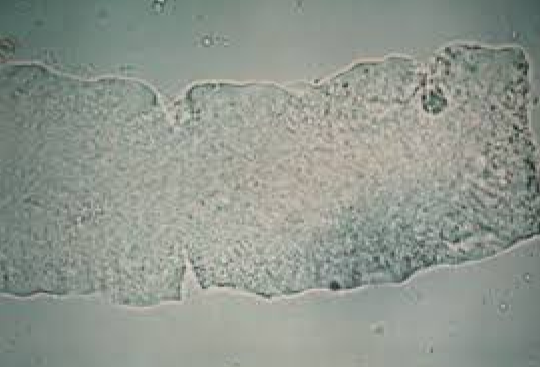
What do you see in this image?
Is it clinically significant (normal or abnormal)?
What can it indicate?
Waxy Cast — ‘Skyrim whips wrappings’
Abnormal, renal failure

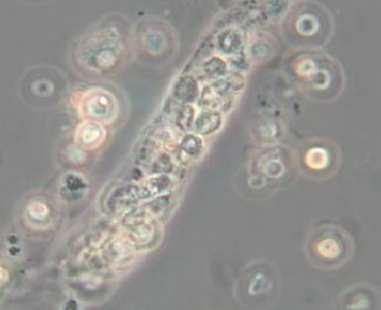
What do you see in this image? Abnormal or normal?
WBC Cast — abnormal
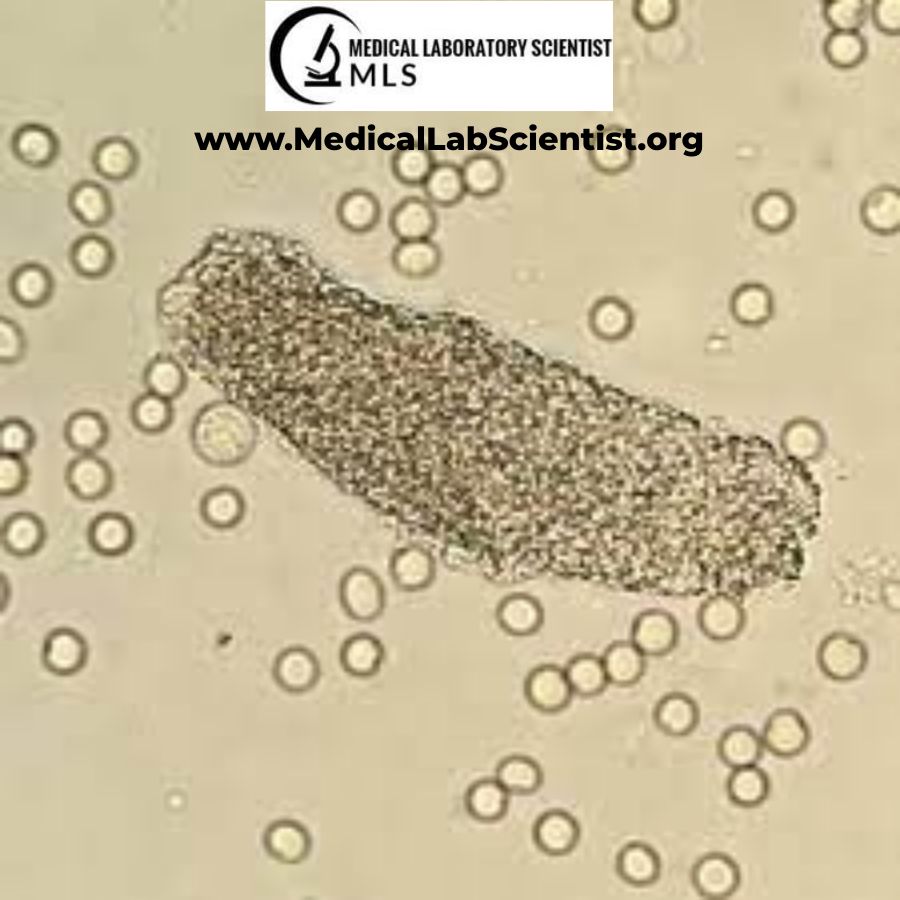
What do you see in this image? What does it indicate?
Granular Cast — Indicates Renal Disease
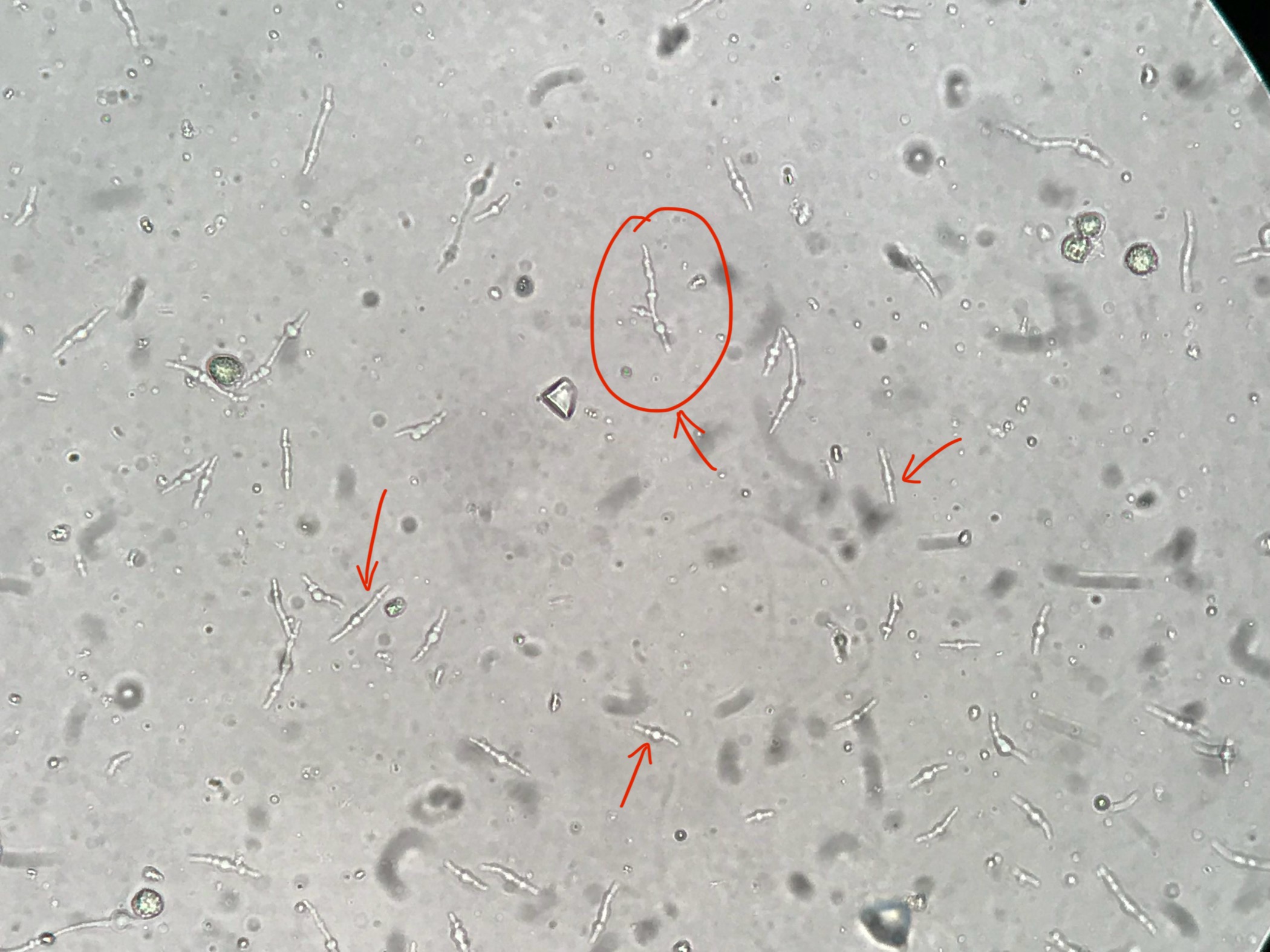
What do you see in this image?
Bacteria (indicated by reduced nitrates)
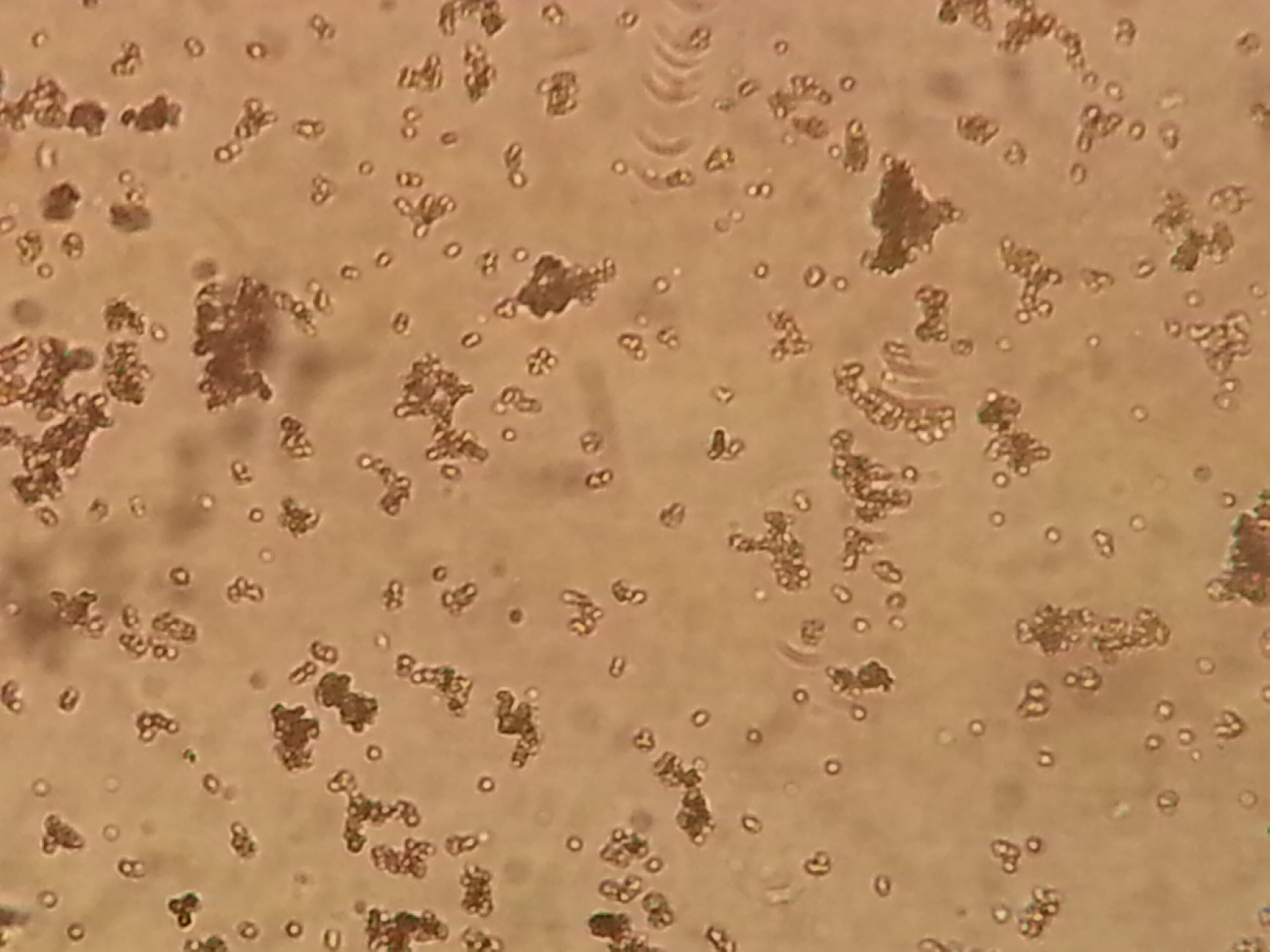
What sediment is in the image?
Amorphous Urates ; Acidic ; Normal
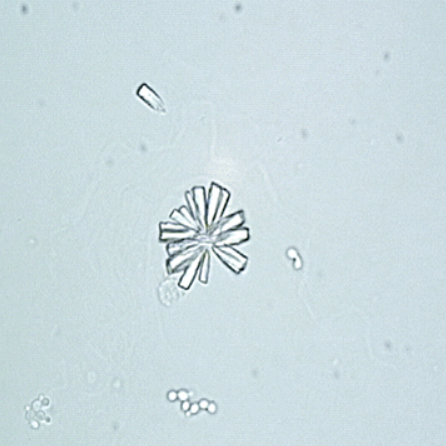
What do you see in this image? What can it indicate?
Calcium phosphate ; Kidney Disease
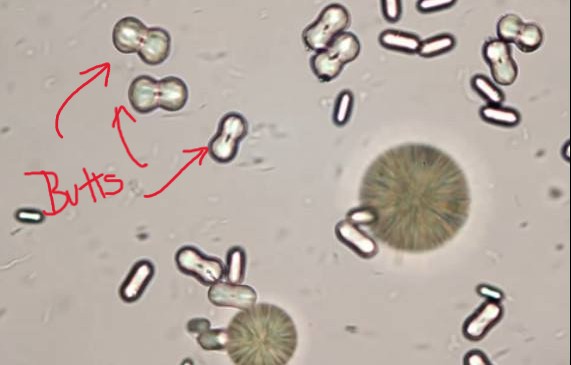
What do you see in this image? Is it clinically significant?
Calcium Carbonate ; Normal

What do you see in this image? What can it indicate?
Cystine — Metabolic disorder
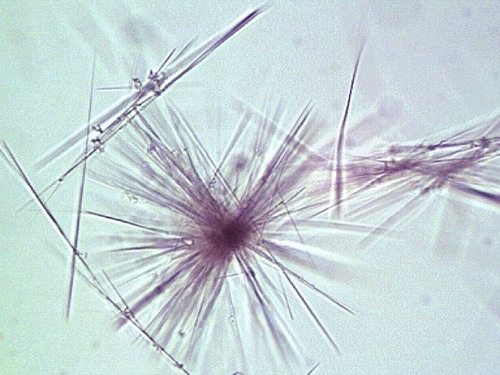
What do you see in this image? What can it indicate?
Tyrosine — Amino acid metabolic disorder
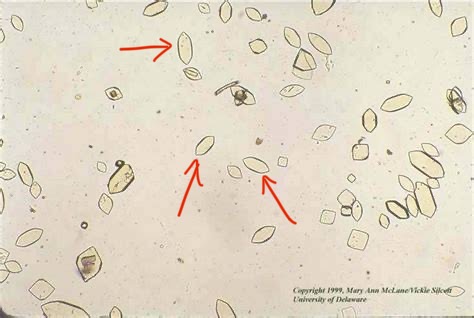
What do you see in this image?
Is it clinically significant?
Acidic or Alkaline?
What can it indicate?
Uric Acid
Acidic
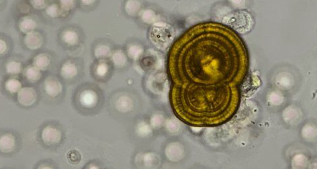
What do you see in this image?
Is it clinically significant?
Acidic or Alkaline?
What can it indicate?
Leucine
Significant
Acidic
Hepatic disorder
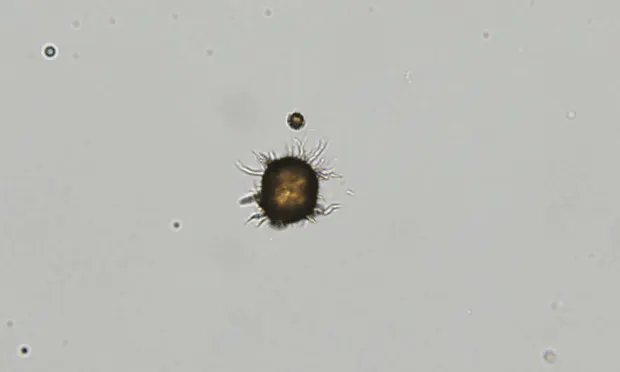
What do you see in this image?
Is it clinically significant?
Acidic or Alkaline?
What can it indicate?
Starch Crystals
What do you see in this image?
Is it clinically significant?
Acidic or Alkaline?
What can it indicate?
Ammonium Biurate
Insignificant
Alkaline
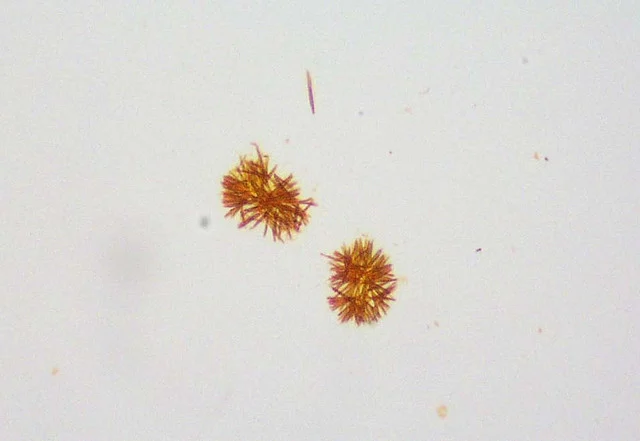
What do you see in this image?
Is it clinically significant?
Acidic or Alkaline?
What can it indicate?
Bilirubin
Significant
Acidic
Metabolic disorder
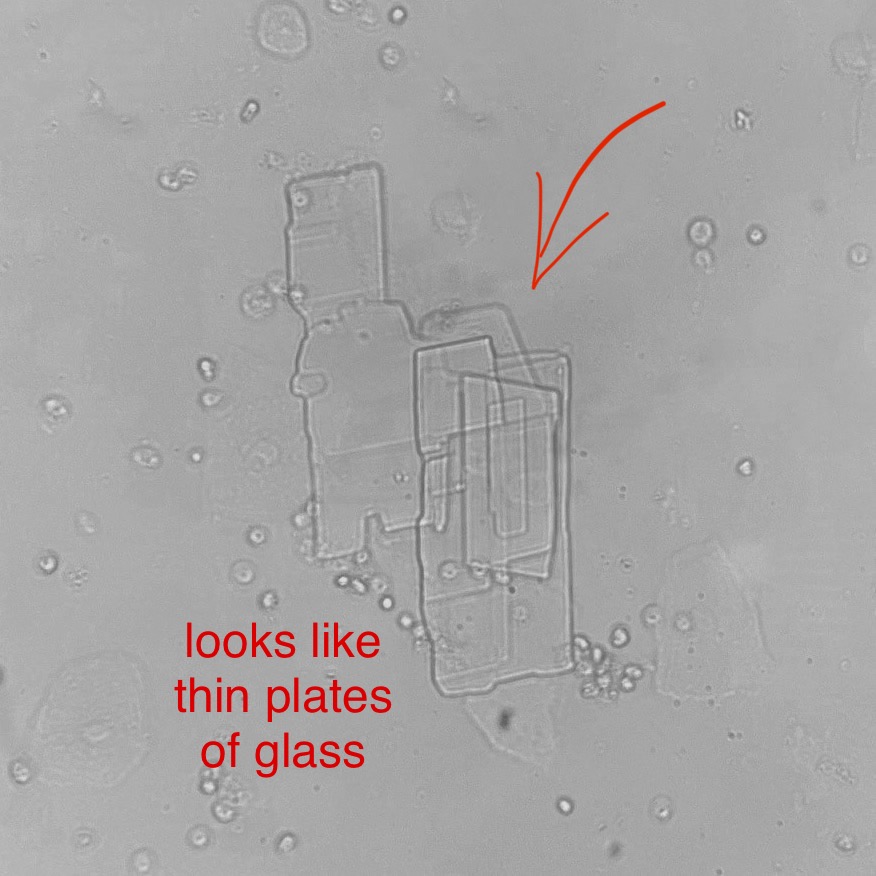

What do you see in this image?
Is it clinically significant?
Acidic or Alkaline?
What can it indicate?
Cholesterol
Significant
Acidic
Nephrotic Syndrome
Calcium carbonate
Alkaline ; normal
Calcium phosphate
Alkaline ; normal
Ammonium Biurate
Alkaline ; normal
Triple phosphate
Alkaline ; abnormal
Amorphous phosphates
Alkaline ; abnormal
Amorphous urates
Acidic ; normal
Uric acid
Acidic ; normal
Calcium oxalate
Acidic ; abnormal
Cystine
Acidic ; abnormal
Cholesterol
Acidic ; Abnormal
Tyrosine
Acidic ; abnormal
Bilirubin
Acidic ; abnormal
Leucine
Acidic ; abnormal
carbonate, biurate, phosphates are…
alkaline
urates and oxalates are…
acidic
A medical laboratory technician (MLT) student consistently obtains lower RBC counts than the instructor. A possible reason for this might be:
Failure to completely resuspend the sediment specimen
Using too much stain
Reading the same cells twice
Counting all crenated cells twice
Failure to completely resuspend the sediment specimen
What’s the needed volume of urine to put in a conical tube for centrifugal spinning for urine sediment?
12 mL (milliliters)
A urine specimen refrigerated overnight is cloudy and has a pH of 6. The turbidity is probably due to:
Triple phosphate crystals
Amorphous urates
Calcium oxalate crystals
Amorphous phosphates
Amorphous urates
Centrifugation of less than the recommended 12 mL of urine for the microscopic examination will:
Produce a false-negative sulfosalicylic acid (SSA)
Increase the number of cellular elements
Produce a false-positive SSA
Decrease the number of cellular elements
Decrease the number of cellular elements
Collection of a midstream clean-catch specimen will alleviate contamination by:
Transitional epithelial cells
RBCs
Squamous epithelial cells
Renal tubular epithelial cells
Squamous epithelial cells
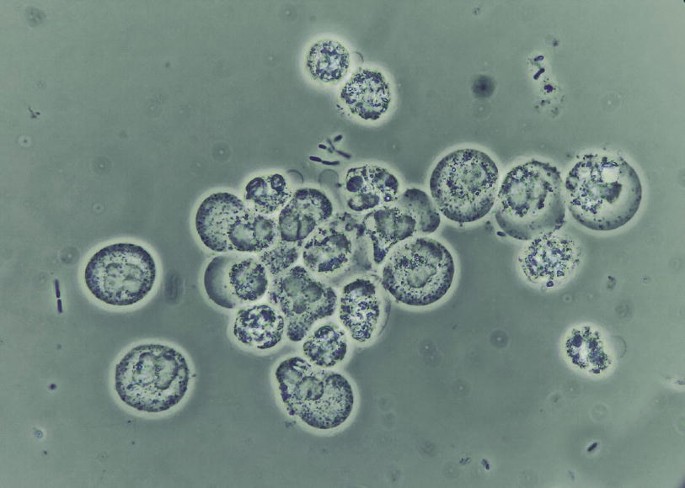
Glitter cell is a term used to describe a specific type of cell that associates with a bacterial infection:
Ketone body
Oval fat body
Renal tubular epithelial cell
Neutrophil
Neutrophil
Initial microscopic focusing on the urinary sediment is frequently performed by referencing:
Mucus
Squamous epithelial cells
Hyaline casts
RBCs
Squamous epithelial cells
Oval fat bodies are:
WBCs that have phagocytized lipids
Squamous epithelial cells that contain lipids
Renal tubular epithelial cells that contain lipids
People who fail to work out regularly
Renal tubular epithelial cells that contain lipids
The major constituent of urinary casts is:
Amino acids
Bence Jones protein
Uromodulin protein
Lipoprotein
Uromodulin protein
The organisms attached to a clue cell are:
Escherichia coli
Gardnerella vaginalis
Candida albicans
Trichomonas vaginalis
Gardnerella vaginalis
The primary factor that favors the formation of urinary casts is:
Positive blood
Low specific gravity
Urinary stasis
High pH
Urinary stasis
The recommended centrifugation setting for preparation of the urine sediment is:
400 RPM for 10 minutes
1,000 RCF for 10 minutes
1,000 RPM for 5 minutes
400 RCF for 5 minutes
400 RCF for 5 minutes
The type of cells that line the bladder and ureters are called:
Basal
Renal tubular
Transitional
Squamous
Transitional
Urinary casts are formed in the:
Proximal tubules and loops of Henle
Distal tubules and loops of Henle
Distal and collecting tubules
Proximal and distal tubules
Distal and collecting tubules
Urine sediment artifacts frequently differ from true sediment constituents by their:
Appearance
Number present
Refractility
Location in the specimen
Refractility
Waxy casts are most easily differentiated from hyaline casts by their:
Refractivity
Color
Granules
Size
Refractivity
Which crystal appears as a thorny apple?
Triple phosphate
Ammonium biurate
Cystine
Calcium carbonate
Ammonium biurate
Which crystal appears to have notched corners?
Cystine
Triple phosphate
Cholesterol
Ammonium biurate
Cholesterol
Which of the following are reported as the quantity per low-power field?
Bacteria
White blood cells
Casts
Red blood cells
Casts
Which of the following does not affect the formation of crystals?
Urine pH
Urine specific gravity
Urinary casts
Urine Temperature
Urinary casts
Which would not help differentiation among RBCs, yeast, and oil droplets?
Observation of budding in yeast cells
Lysis of yeast cells by acetic acid
Increased refractivity of oil droplets
Lysis of RBCs by acetic acid
Lysis of yeast cells by acetic acid
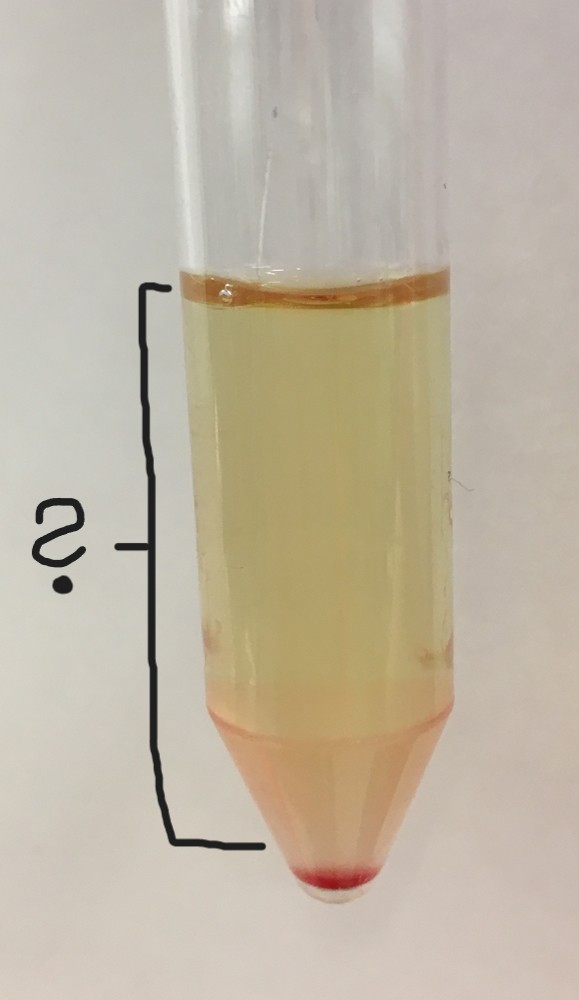

What is this section of this centrifuged urine sample?
supernatant
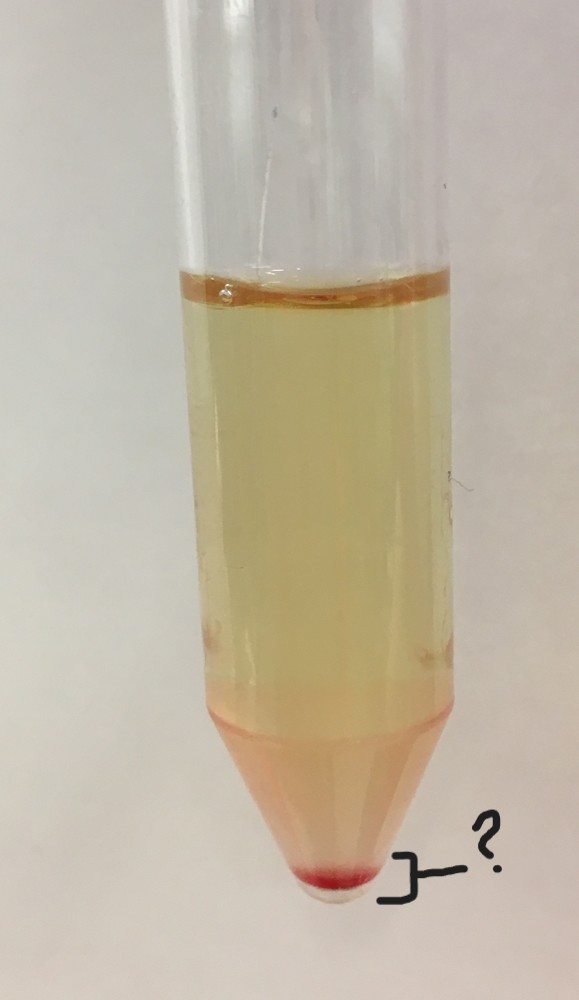

What is this section of this centrifuged urine sample?
sediment
A urine of a patient who has been diagnosed with diabetes mellitus will have a high specific gravity and low volume.
False
A urine from a patient who has liver damage will have what color urine?
Amber
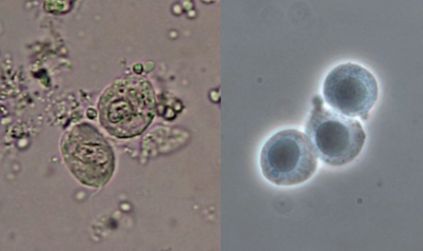
Name the cell.
transitional epithelial
If a cast is seen in a urine microscopic, you would expect what chemical test on the dipstick to be positive?
protein
RBC casts are seen in patients with glomerular nephritis.
True
Which crystal in a urine microscopic would have a hexagonal shape?
cystine
A glitter cell is a specific term used to describe a:
neutrophil
Amorphous urates come from a urine that has been refrigerated with a pH of 6.0 (acidic).
True
When you first look at your urine microscopic what element is recommended to focus on first?
squamous epithelial cell
Waxy cast are often seen in nephrotic syndrome patients?
True
What are oval fat bodies?
renal tubular epithelial cell that contain lipids
Solute content in is higher outside the cells vs inside…
hypertonic (urine)
Solute content is higher inside the cell vs outside of the cell…
hypotonic (urine)