Space Midterm #2
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms

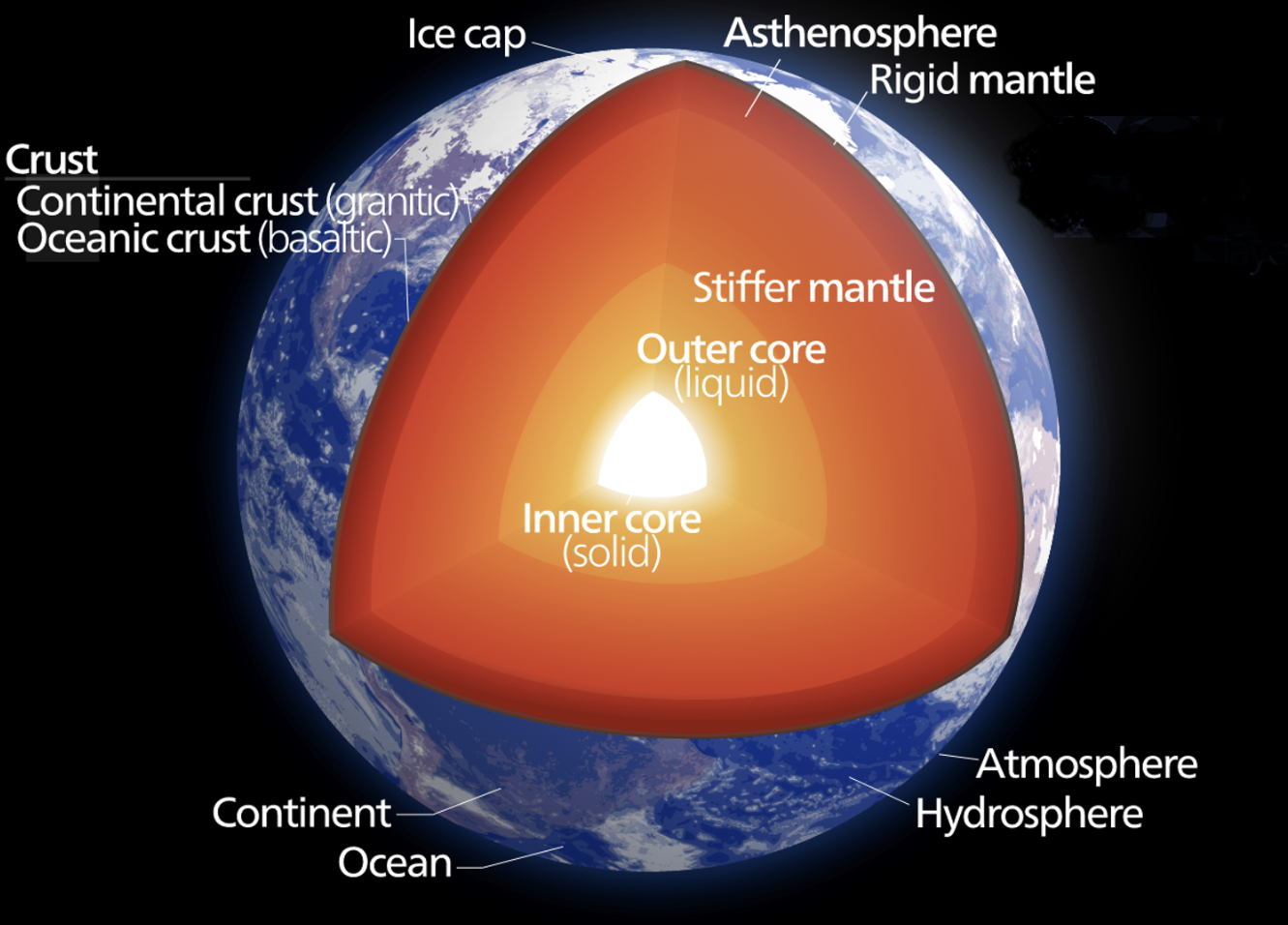
Name the layers of the Earth
Explain Earths magnetic dipole
Tilted dipole that has been
displaced ~500 km from the
center of the Earth toward the northern geographic pole (magnetic center of the Earth). So the southern hemisphere field strength is weaker
What are the possible impacts of rapid
magnetic field change?
Possible impacts include disruptions to navigation systems, increased radiation exposure for satellites and aircraft, and changes in animal migration patterns that rely on Earth's magnetic field.
What are the impacts when the magnetic dipole is horizontal?
When the magnetic dipole is horizontal, it can lead to significant alterations in magnetic field strength and orientation, potentially affecting navigation systems, geological formations, and ecological behaviors of species that rely on magnetoreception.
How does Solar Wind affect the dayside and nightside
It compresses the day side and drags the nightside creating a bullet like shape for the earth
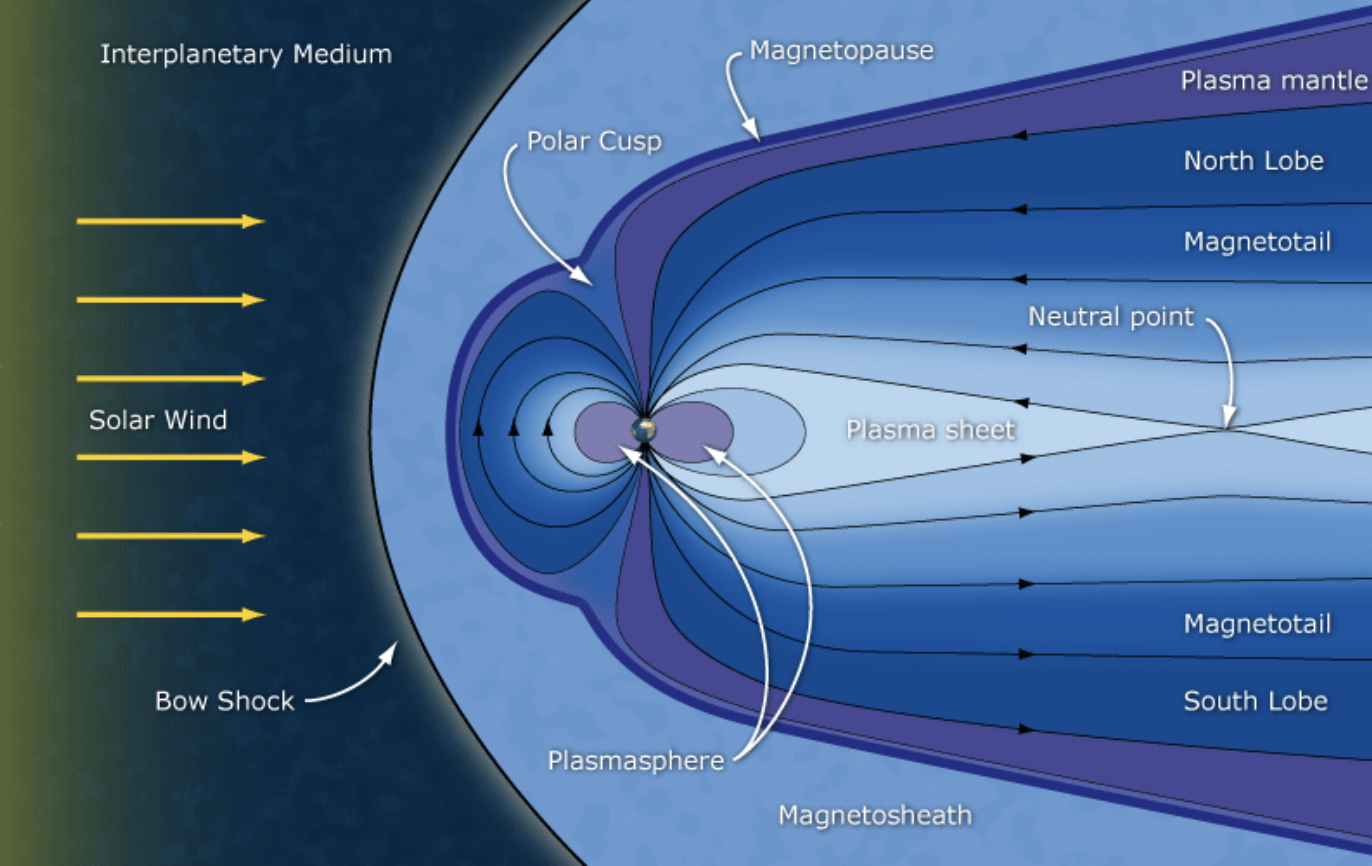
How does the Earths magnetic field act as a shield
Protects us from direct impact of solar particle
radiation
How does the Earths magnetic field act as a accelerator
Time varying magnetic field can create energetic particle radiation, such as magnetic reconnection
Magnetic reconnection
A physical process in highly conducting plasma in which the magnetic topology is rearranged and magnetic energy is converted to kinetic energy, thermal energy, and particle acceleration.
Magnetic reconnection plays an essential role in controlling the shape of the magnetosphere.
What three areas is Magnetic reconnection
(a) Earth’s magnetosphere,
(b) in the solar corona (solar flares and CMEs) and throughout the universe (high-energy particle acceleration). Simulations
(c) guide the MMS measurement strategy.
What causes some of the most energetic phenomena in the universe
supernova explosions
What happens after star explosions
After the explosion, the star collapses into a
neutron star and often into a black hole.
Later, any nearby stars can be distorted and
drawn into the black hole through an accretion disk that is magnetically connected through reconnection to the black hole and neutron star
The transfer of angular momentum by the magnetic field to the neutron star results in the ejection of jets of material from the star
NASA Magnetospheric Multiscale
Mission
Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of magnetic reconnection
The Fast Plasma Investigation
observes the fast-moving plasma
It produces a three-dimensional picture of the ion plasma every 150 milliseconds and of the electron plasma every 30 milliseconds
A factor of 100 times faster than what has been accomplished before for electrons.
The magnetic perturbation generated by current is
• Proportional to the intensity
of current density
• Inversely proportional to the
square of the relative
distance (1/r2)
Magnetometer on every satellite
Part of avionics
30 nT resolution: S/N ~ 10
Iridium Constellation for Science
>70 satellites, 6 orbit planes, ~11
satellites/plane
Six orbit planes provide 12 cuts in
local time
9-minute spacing: resampling
cadence
780 km altitude, circular, polar
orbits
Polar orbits guarantee coverage of
auroral zone
Global currents never expand
equatorward of system
What does AMPERE stand for
Continuous Global Birkeland Currents from the:
Active
Magnetosphere and
Planetary
Electrodynamics
Response
Experiment
Why does space weather matter in the Inner Magnetosphere
This is where lots of commercial and military satellites fly.
Even the calm times are full of dynamic processes.
What are the three main plasma populations in the inner magnetosphere
Plasmasphere: contains the mass
Ring current: contains the energy
Radiation belt: contains the “killer” particles
Difference between inner and outer magnetosphere (Magnetic field strength)
slide 29
Why is the plasma sphere important
dominates the mass of the inner magnetosphere
What is the importance of the ring current
Dominates the energy in the inner magnetosphere
Facts about the radiation belts
Inner and outer belt
extremely hot
what is the importance of radiation belts
Dominates the reasons for spacecraft anomalies, damage, and failures
What causes the third radiation belt
During intense geomagnetic storms, wave–particle interactions (especially from ultra-low frequency (ULF) and whistler-mode waves) can strip away parts of the outer belt.
The process sometimes leaves a residual “storage ring” of ultra-relativistic electrons (energies > 2 MeV) trapped in a narrow region.io
What is the karman line
It is the edge of space, just about 100km above sea level
where areodynamic flight becomes impractical
What happens below 100 km thermosphere
Temperature is nearly a constant over a solar
cycle, so the density does not change much.
What happens above 100km thermosphere
Above 100 km, temperature changes
significantly over a solar cycle, so does the density.
What is the correlation between density and temp in the thermosphere
Higher temp Higher density
What are the three regions of the ionosphere
F Region - the peak density region of the ionosphere due to extreme UV
E Region - 95 - 150 km - daytime layer due to soft x-ray photoionization
D region - 75-95 km - relatively weak ionization due to hard X-ray ionization
What is Photonization
is the physical process in which an ion is
formed from the interaction of a photon with an atom or molecule.
What did Sir Edward Appleton discover about the ionosphere
That you could bounce radio waves off of it making long distance communication possible
What is critical frequency
The frequency at which radio waves are perfectly reflected from the ionosphere
What is TEC (Total Electron Content)
The ionosphere causes delay on the GPS
signal, which is proportional to the total number of electrons (TEC) encountered along the signal path. So using the time delay, we can estimate the TEC along each ray path.
TEC is the integral of the electron density within a unit area between a receiver and a satellite.
sudden changes can affect gps
Diffuse Aurora
Typically 100s of eV in energy (maybe up to 1 keV)
Structureless, fills the whole auroral oval
Discrete Aurora
Small but energetic component of the total
Structured
Discrete auroras are the most intense auroral types where field-aligned acceleration play an important role, forming the so-called inverted-V precipitation