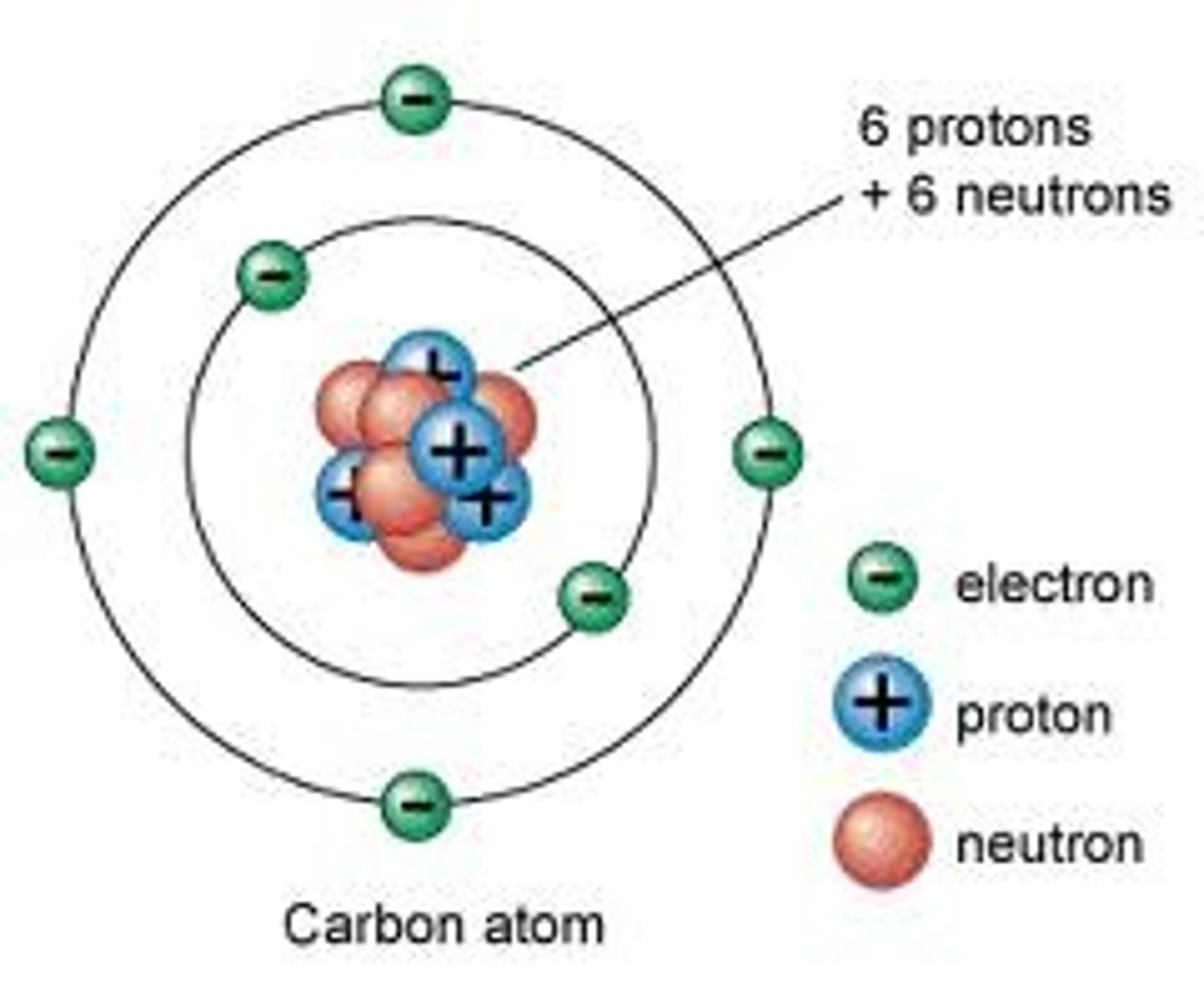
Atomic Structures
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
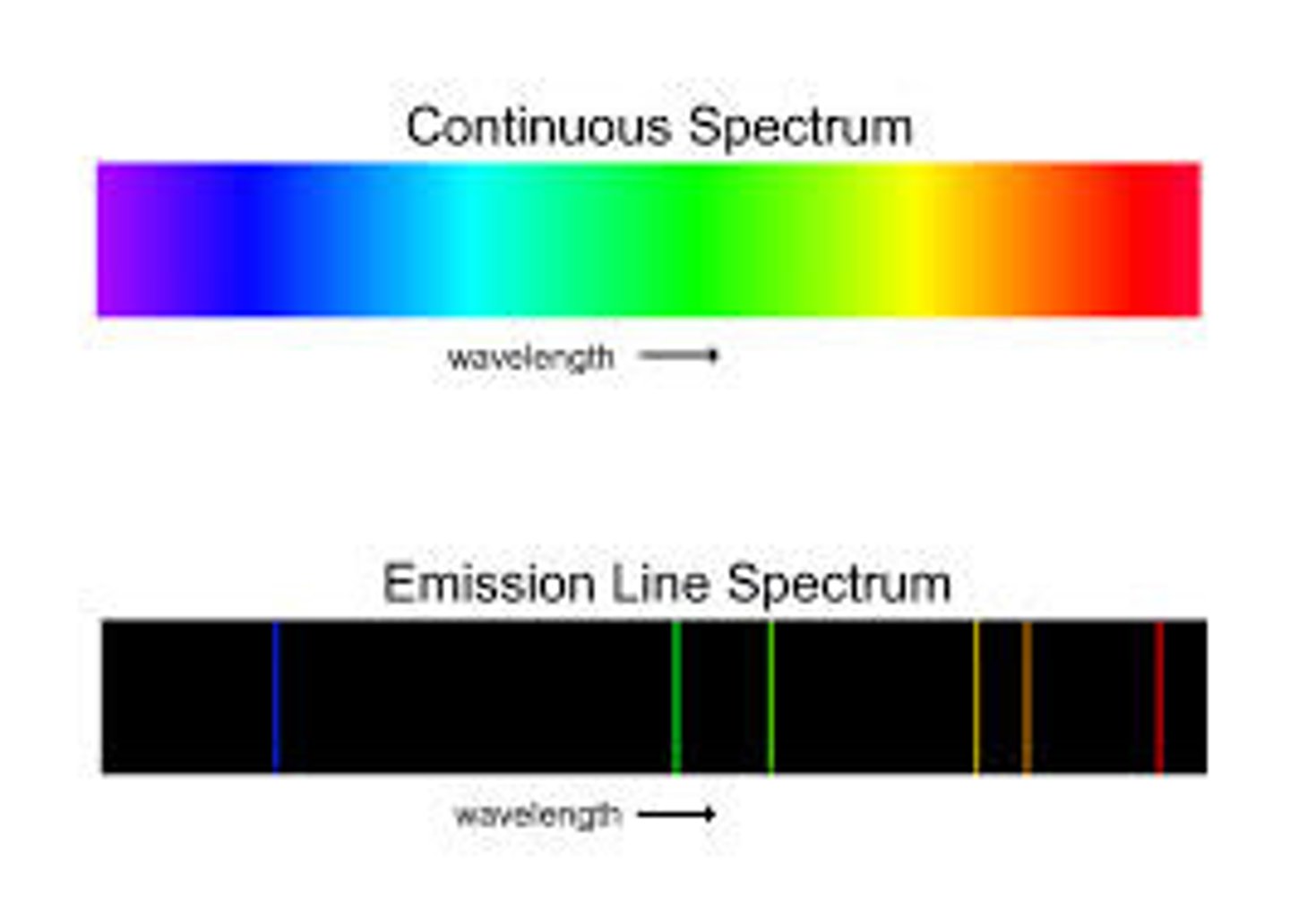
What is the continuous spectrum ?
HydrHydrogen emission spectrumogen emission spectrum
Aristotle
Rejected the concept of the atom because he believed matter could be subdivided into smaller and smaller particles.

John Dalton
He took Democritus's theory and expanded it into a scientific theory, he proved that atoms ARE the smallest particles.
J.J Thomas
Proposed Cathode rays
discovered electrons
created the plum pudding model
What are Cathode rays?
Streams of particles smaller than atoms
What are ELECTRONS ?
Negatively charged subatomic particles
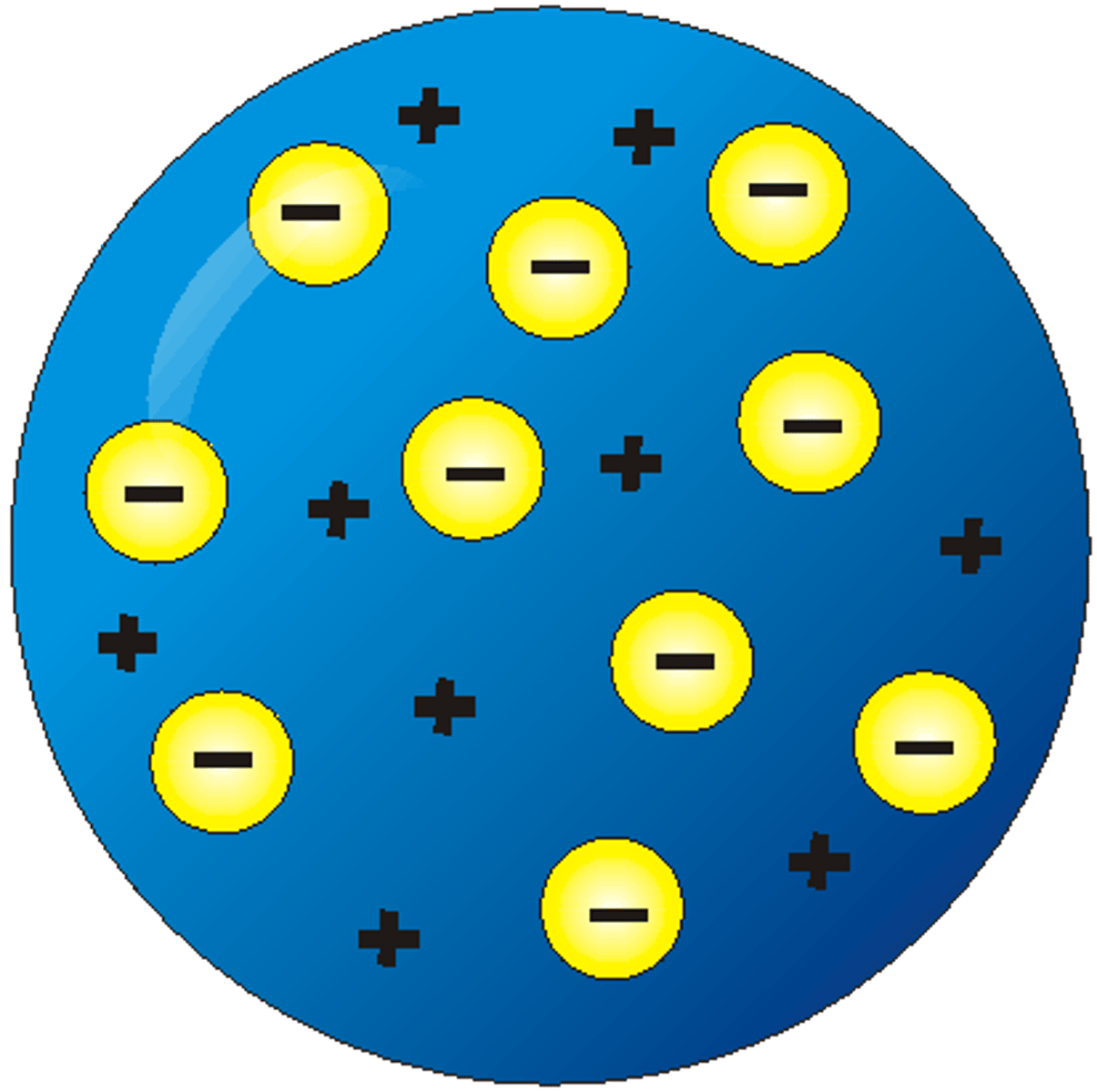
what is the Plum Pudding Model
It is a way of depicting an electron
Importance: proved that Daltons rejection of the electron was incorrect and that subatomic particles exist
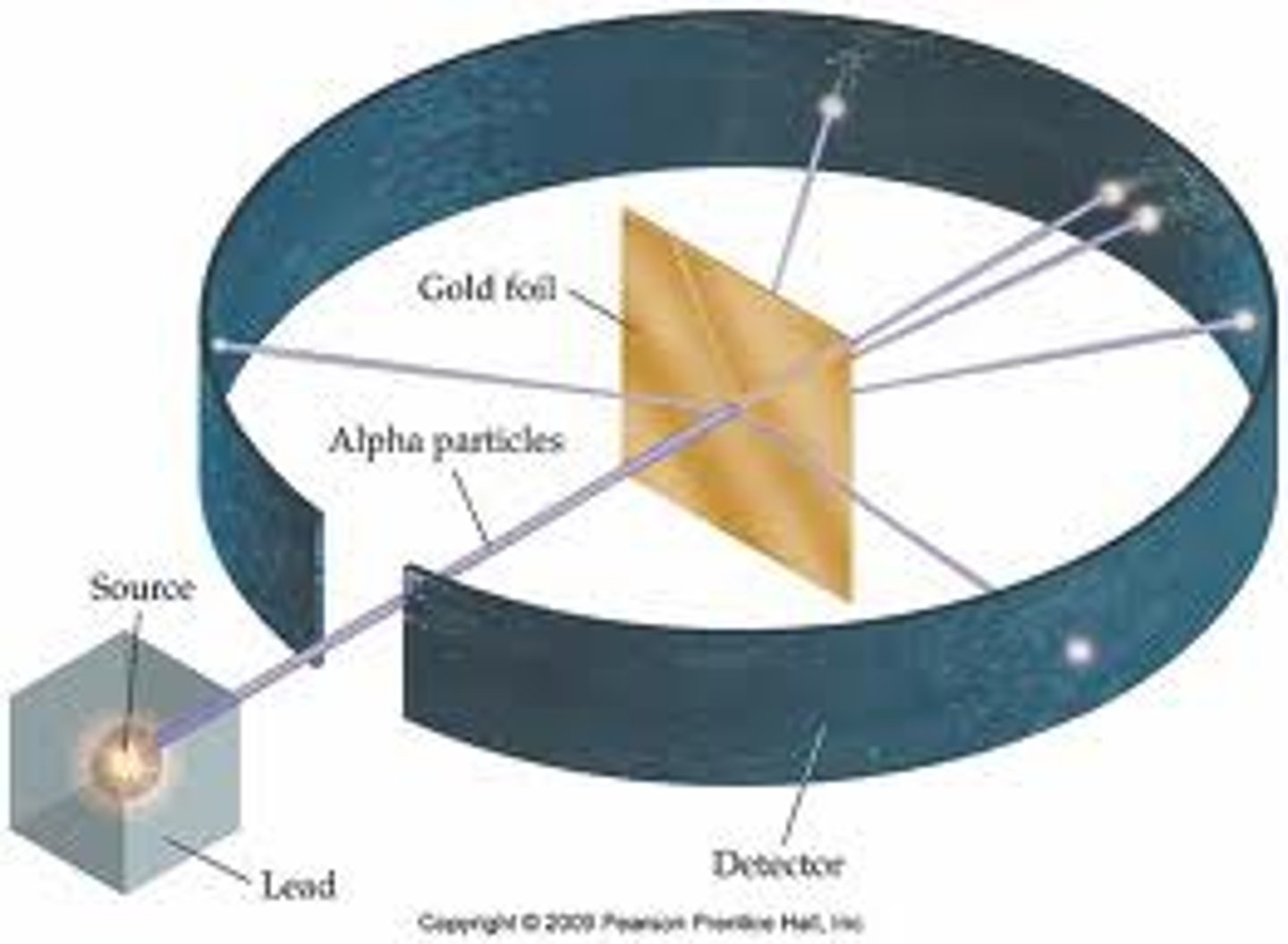
What is significant about Ernest Rutherford's Gold Foil Experiment?
MOST particles pass strait through the gold foil proving that THE ATOM IS MOSTLY MADE UP OF EMPTY SPACE but..
A small amount of particles reflect off the foil at large angles suggesting that there is a denser area inside the atom (Nucleus)
What does Rutherford's Model of the Atom look like?
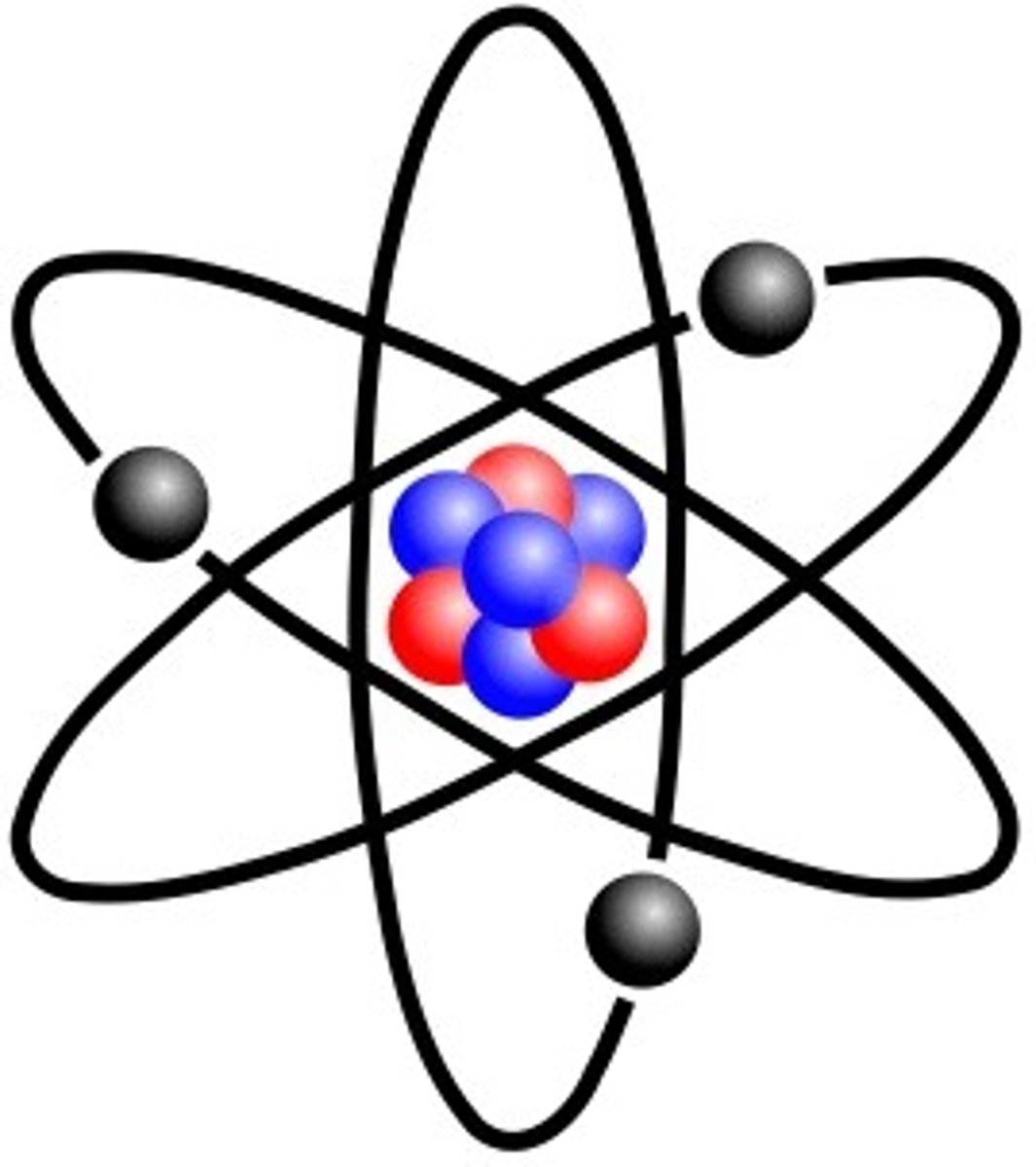
How does Bohr's model of the atom represent the electron?
The orbitals represent energy levels, orbitals contain electrons
orbitals closest to the nucleus contain the least amount of energy and increase in energy as you go out.
As electrons move up in energy level energy is ___________ by the electron
Absorbed
As electrons move up in energy levels energy is _________ by the electron
Emitted
what is Erwin Schrodinger's the wave machine model of the atom
-uses mathematical equations to represent the likelihood of finding an electron in a certain position (density of dots)
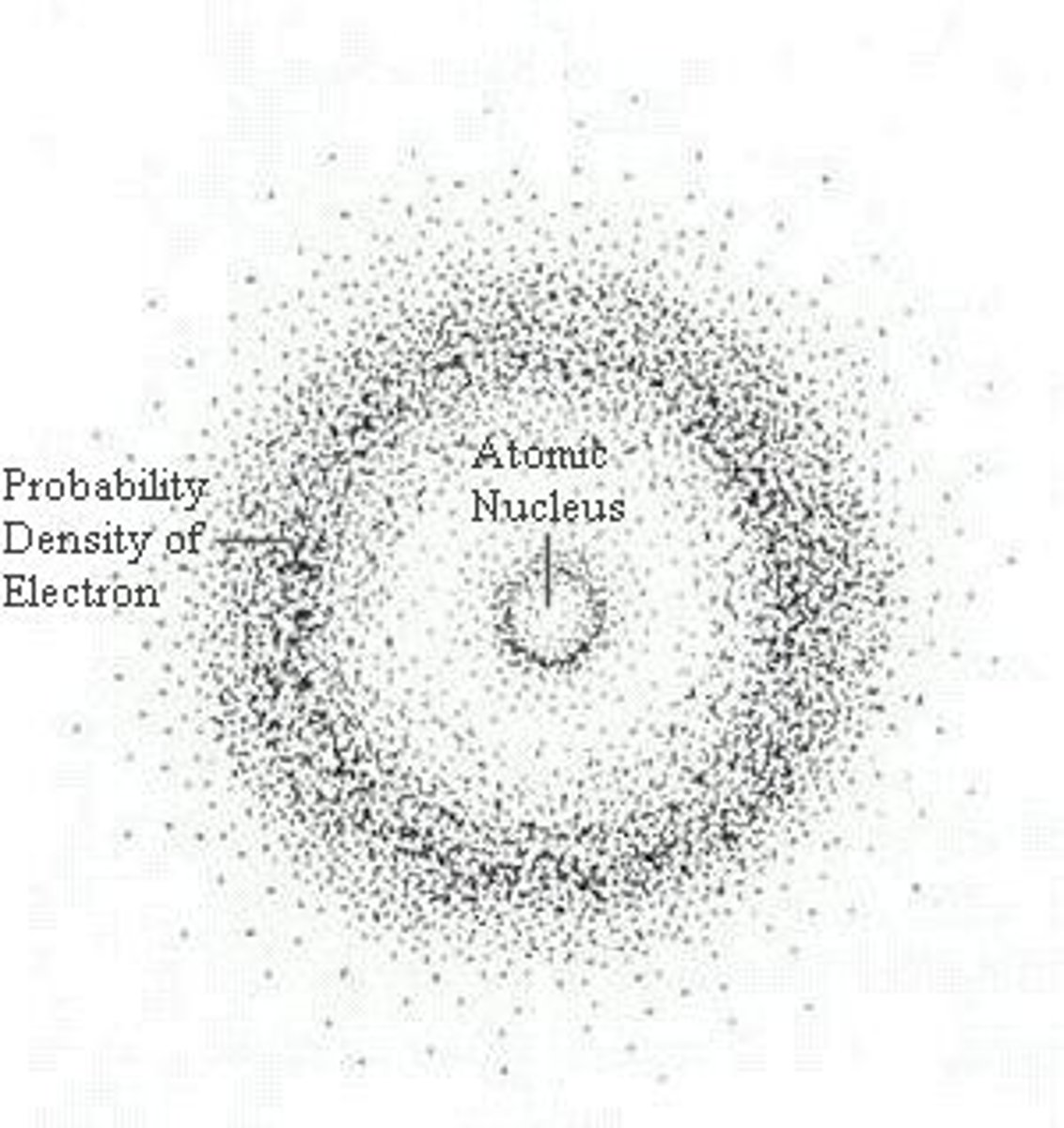
What did James Chadwick discover?
The neutron
Atomic number
Number of Protons
Atomic number=
number of protons = number of electrons
Number of protons =
number of electrons
What is a Isotope
Atoms of the same element with a dif number of neutrons
Mass number =
= number of protons + number of nuetrons
In element notations does the mass number or atomic number go on top
Atomic number goes on the bottom and mass number goes on top
What is an ION?
Formed when an atom gains or looses an e- so that protons and electrons are not even
-has a dif chemical properties than its atom
What is relative atomic mass?
Average mass of an atom taking into account its isotopes and their relative abundance ?
What are Valance electrons?
Electrons in outermost energy levels and determine chemical properties
What are sublevels?
1s
2s 2p
3s 3p 3d
4s 4p 4d 4f
5s 5p 5d 5f
6s 6p 6d
7s 7p
8s

Lewis Dot Diagram
Represents valance electrons
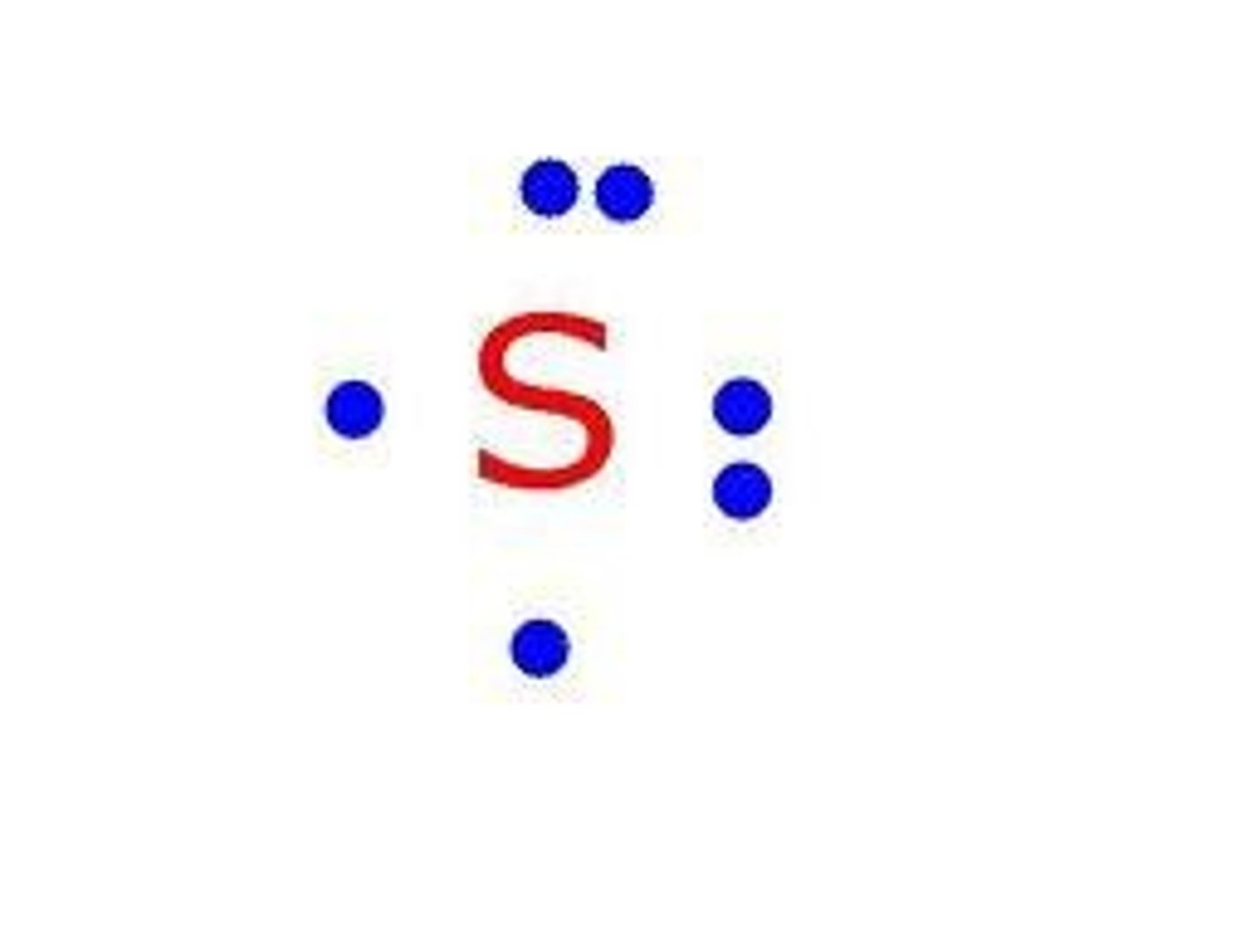
What elements have partially filled 4s sublevels?
Chromium and Copper
Why is 4s filled first in the Chromium and Copper sublevels?
By having 1 electron occupy the sublevel the 3d sublevel will be half full and completely full which is more stable
what experiment can be used to distinguish different elements?
The flame test- elements emit dif wavelenghts produce different lights - dif color flames
As energy and frequency increase wavelength ______
Decreases
What is the continuous line spectrum ?
full light spectrum of light produced by elements
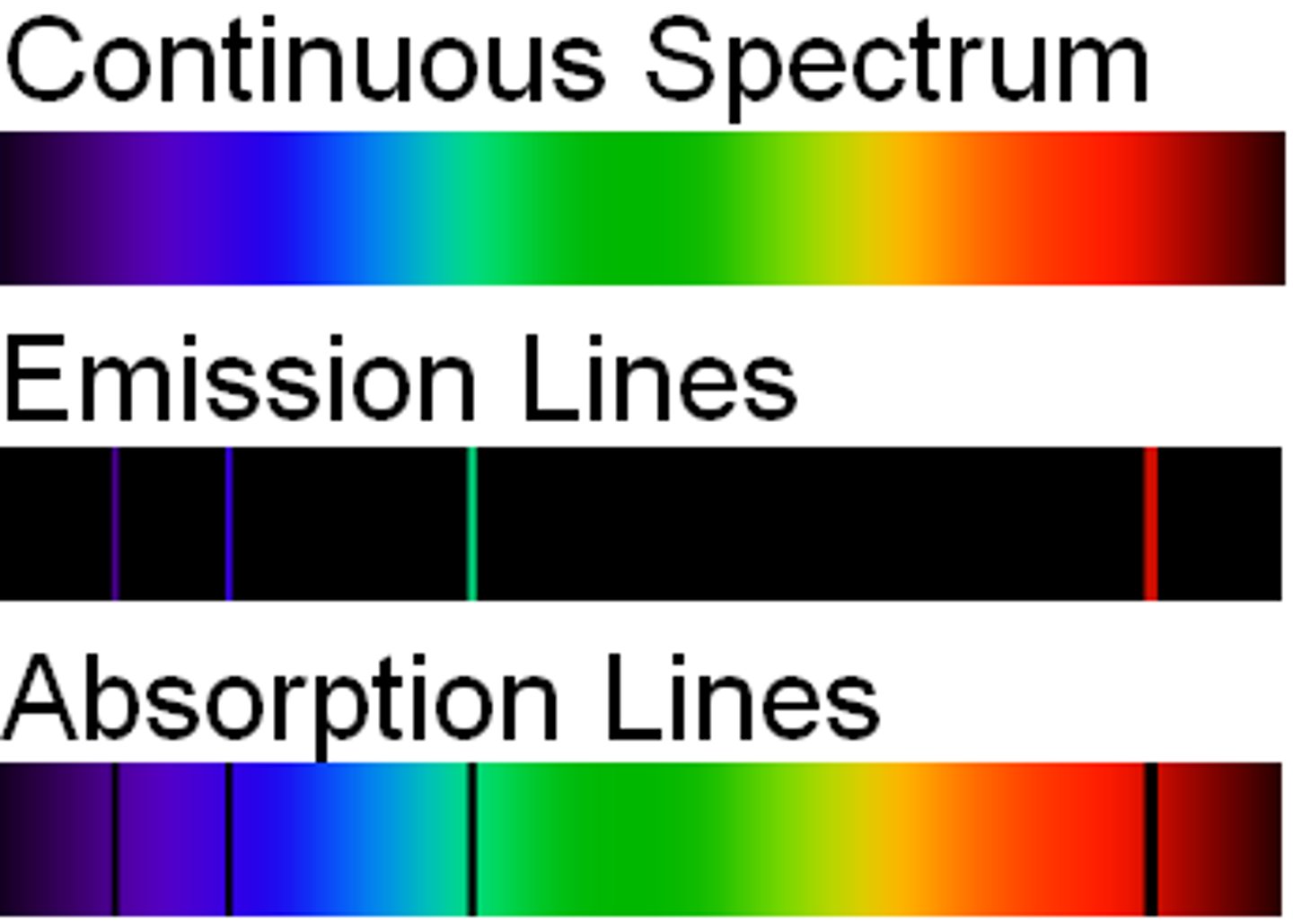
What is the emission spectrum?
A set of bright lines that represent wavelengths of elements, ex: Hydrogen emission spectrum
When energy is supplied to the atom, the electron goes up in energy level this is the __________
excited state
Once the e- falls back down to the ________ it _______________
Ground state, releases energy