Anatomy & Physiology Exam
1/37
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
What provides a basic energy source for speech?
respiration is the force behind speech production and provides energy for oral communication
air pressure
lungs/diaphragm
Muscles are contractile by nature: T/F?
True - muscular tissue is contractile
What’s the most important function of the larynx?
protects us from foreign objects
coughing
throat cleaning
abdominal fixation
What are the different kinds of tissue?
epithelial - outer layer, covers surfaces of the body/cavities/pathways ex: esophagus, vocal cords
connective - binding, binds/supports tissues + organs
areolar - loose supportive tissue ex: lymphoid
fibrous - tendons + ligaments
cartilage - firm + flexible, smooth + elastic types ex: pinna, epiglottis
blood - plasma, blood cells
bone - compact or spongy
muscular - contractile; skeletal/voluntary, smooth/involuntary (ex: lower esophagus), cardiac
nervous - communication highway, consists of neurons or nerve cells; transfers info between neurons, muscles
anatomical position
the body is erect, palms, arms, and hands face forward
axis
midline from which other structures arise; a pivoting point
axial skeleton
spinal cord is axis —> head and trunk pivot around the spinal cord
coronal
divides the body front to back
transverse
divides the body from upper and lower
median/sagittal
divides the body from right and left
superior
above or father from the ground
inferior
closer to the ground
prone
on the belly
supine
on the back
lateral
related to the side
midline
toward the middle
What are the two divisions of the nervous system?
central nervous system - brain, brain stem, spinal cord
peripheral nervous system - nerves coming from the spinal cord
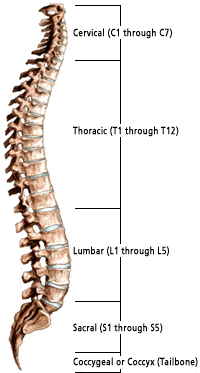
How many lumbar, thoracic, sacral, coccyx?
Cervical: 1-7
Thoracic: 1-12
Lumbar: 1-5
Sacral: 1-5 (5th fused)
Coccyx: 1-4 (4th fused)
Total: 33
What muscle elevates the sternum, clavicle, and helps with head rotation?
sternocleidomastoid muscle
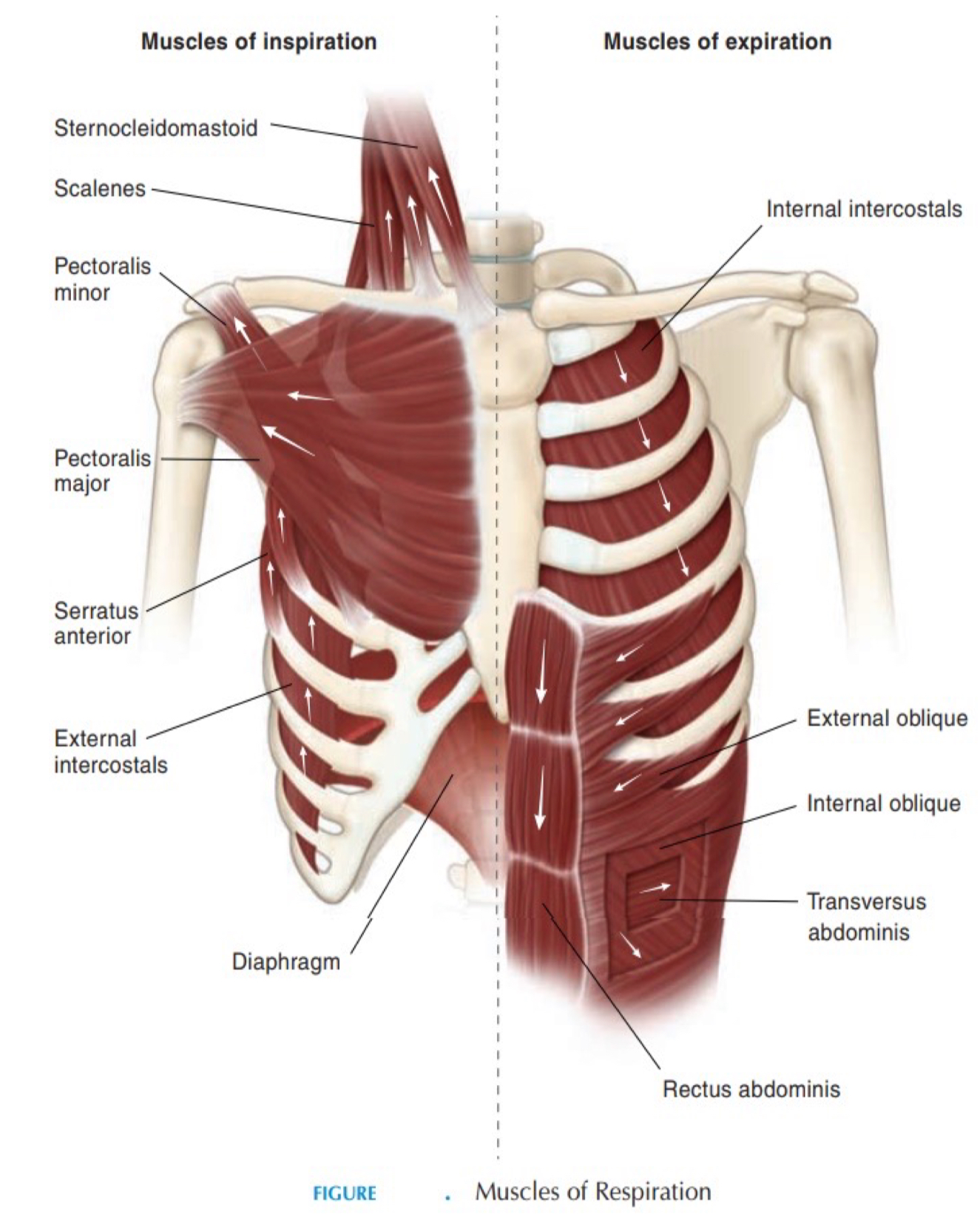
What does the diaphragm do during inhalation and exhalation?
Inhalation: contracts - diaphragm pulled down by central tendon to create space for the lungs
Exhalation: relaxes - diaphragm reverts back to its original position while the lungs deflate
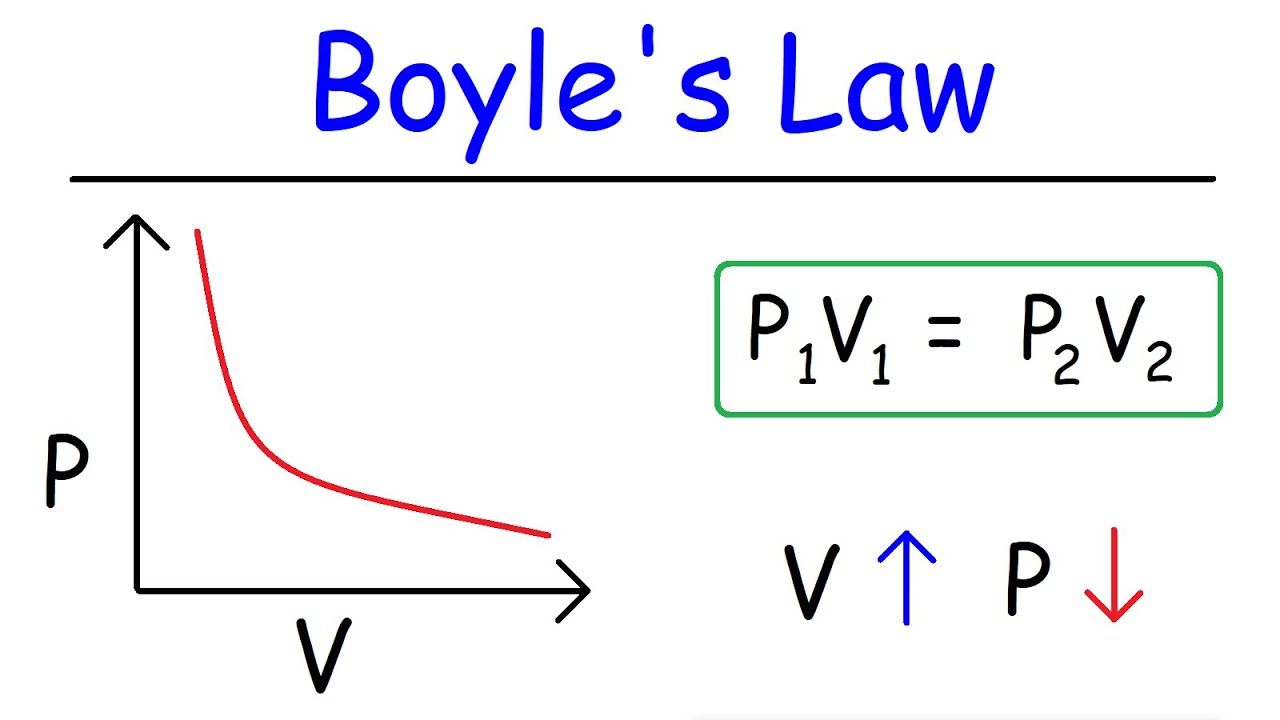
What is Boyle’s Law?
As pressure increases, volume decreases and vice versa; P and V have an inverse relationship
What is the channel through which the spinal cord passes?
vertebral foramen; vertebral canal
What is the flexible tube that forms the first passage way to the lungs?
trachea: bifurcates into the main stem brochi to serve lungs at the carina
What is the relationship between the esophagus and trachea?
Both are part of the respiratory passageway; the esophagus is posterior and parallel to the trachea
both are part of the visceral thorax that connects the lungs with the external environment
In terms of the pressure in the lungs, what happens when the diaphragm relaxes and contracts?
Inhalation: contracts - Pressure decreases due to lungs expanding; increase in volume to the point of negative pressure in the lungs
Exhalation: relaxes - Pressure increases due to loss of volume by deflation of lungs and pushes air out of lungs
What is the basic function of the neuron?
specialized tissue for communicating information; dendrites receive, soma/axon send out
Which cartilage articulates with the thyroid cortical?
cricoid cartilage
What bone articulates with the thyroid cortical?
hyoid bone: loosely articulates with the superior cornu of the thyroid bone
What is the shape and function of the epiglottis?
leaf-like cartilage; protective structure during swallowing by blocking airway to prevent foreign items from entering windpipe/lungs
What is plasticity?
the ability of the brain to re-wire and re-shape itself
What is the time it takes to complete one cycle of vibrations?
period
How do we measure sound?
decibels (dB); intensity/amplitude of the wave
How many decibels is the normal range of hearing?
0 - 120/130 dB; hearing loss starts at ~20 dB
What’s needed to sustain phonation?
vocal folds held in a fixed position in the air stream maintenance of a laryngeal posture through tonic (sustained) contraction of the musculature
7-10 cm of water pressure (3-5 for vocal fold movement)
maintenance of pressure
flow
vocal fold approximation
sufficient air pressure
What is an attack?
the start of phonation; adducting the vocal folds to move them into the air stream
What is the difference between ABduction and ADduction?
ABducted - moving away
ADducted - moving toward
Arytenoids move in what directions?
rock back + forth in 3 dimensions: rotating, rocking, and gliding
What are the different types of attacks?
simultaneous vocal attack - adduction and onset of respiration at the same time (voiced consonants)
breathy vocal attack - start significant airflow before adducting the vocal folds (voiceless consonants)
glottal attack - adduction of the vocal folds prior to airflow