Carbohydrate Metabolism and Exercise Performance EXAM 3
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
129 Terms
Glycogenolysis
Breakdown of glycogen to glucose.
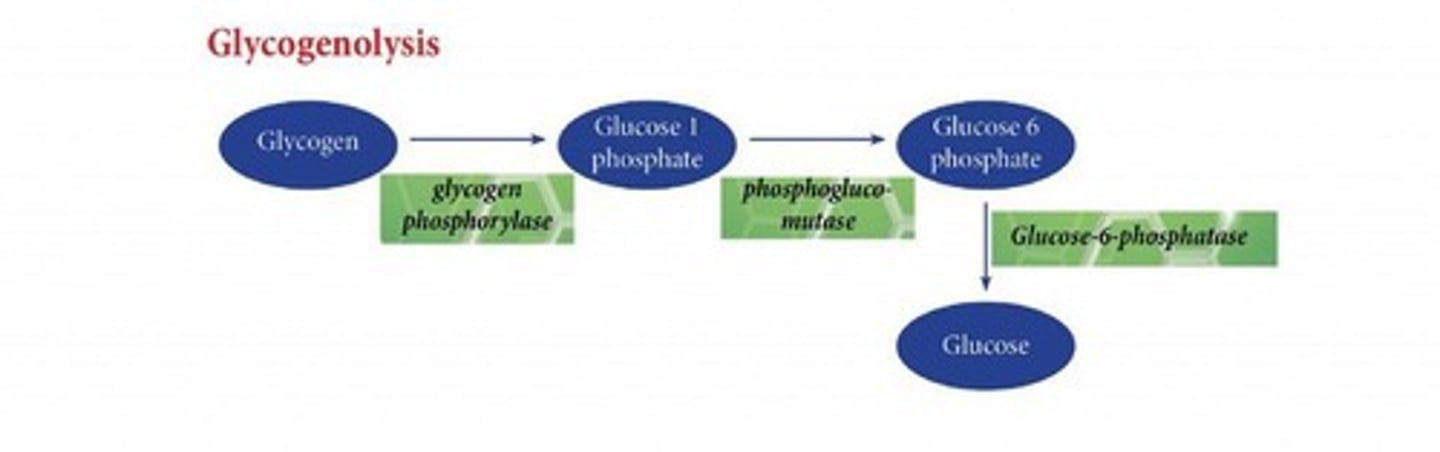
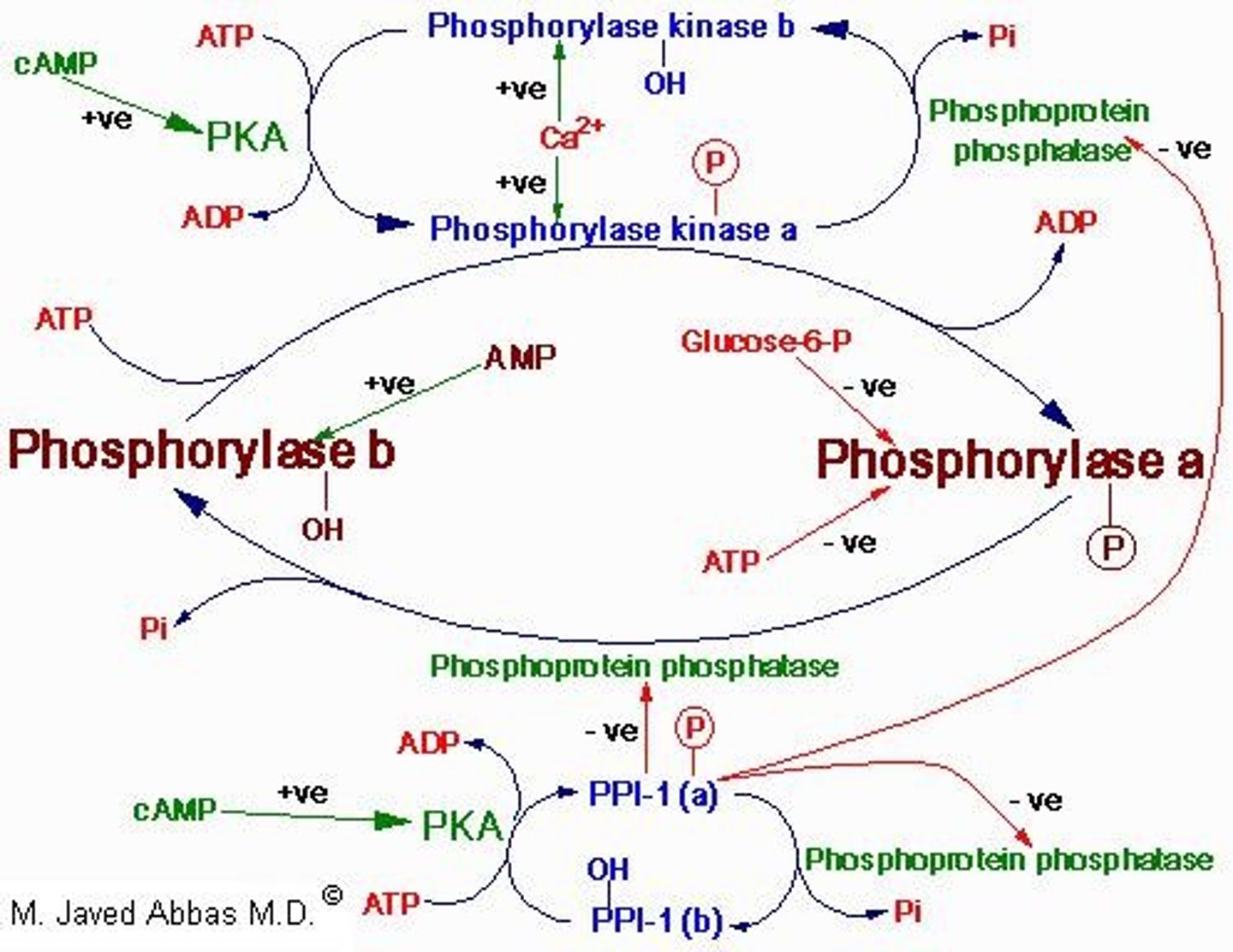
Phosphorylase
Enzyme converting glycogen to glucose.
Phosphorylase a
Active form of phosphorylase enzyme.
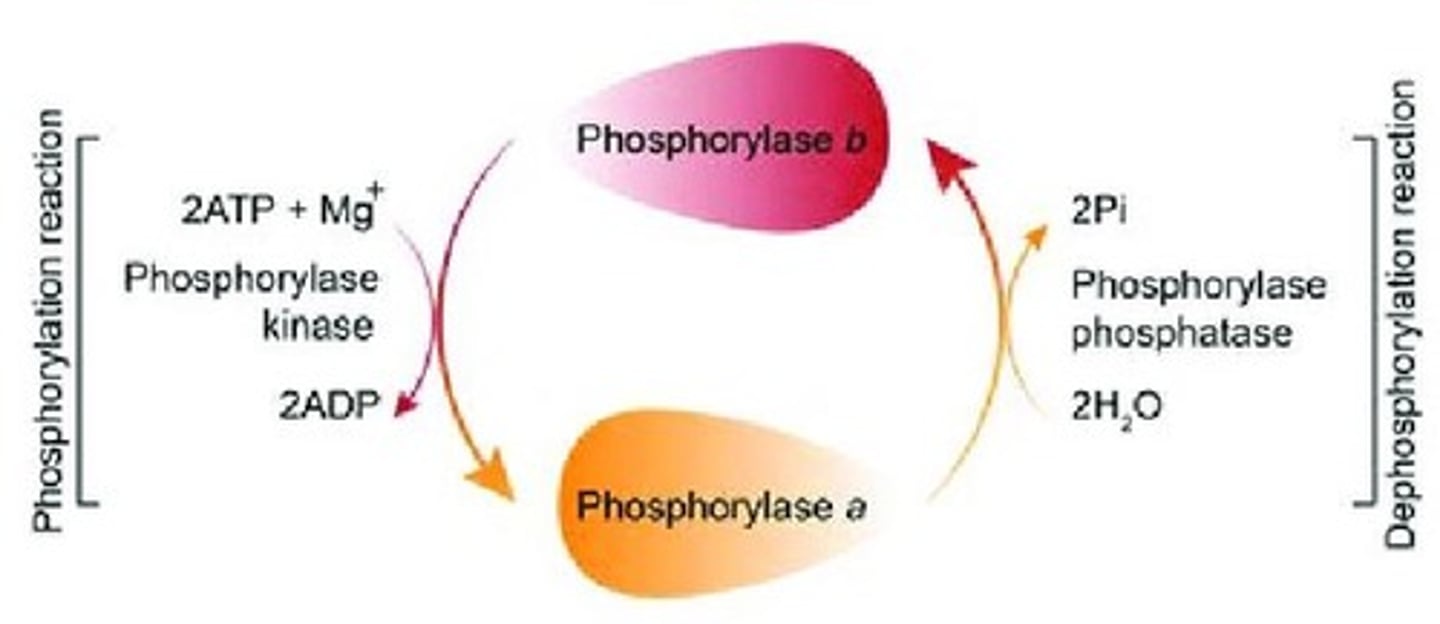
Phosphorylase b
Inactive form of phosphorylase enzyme.
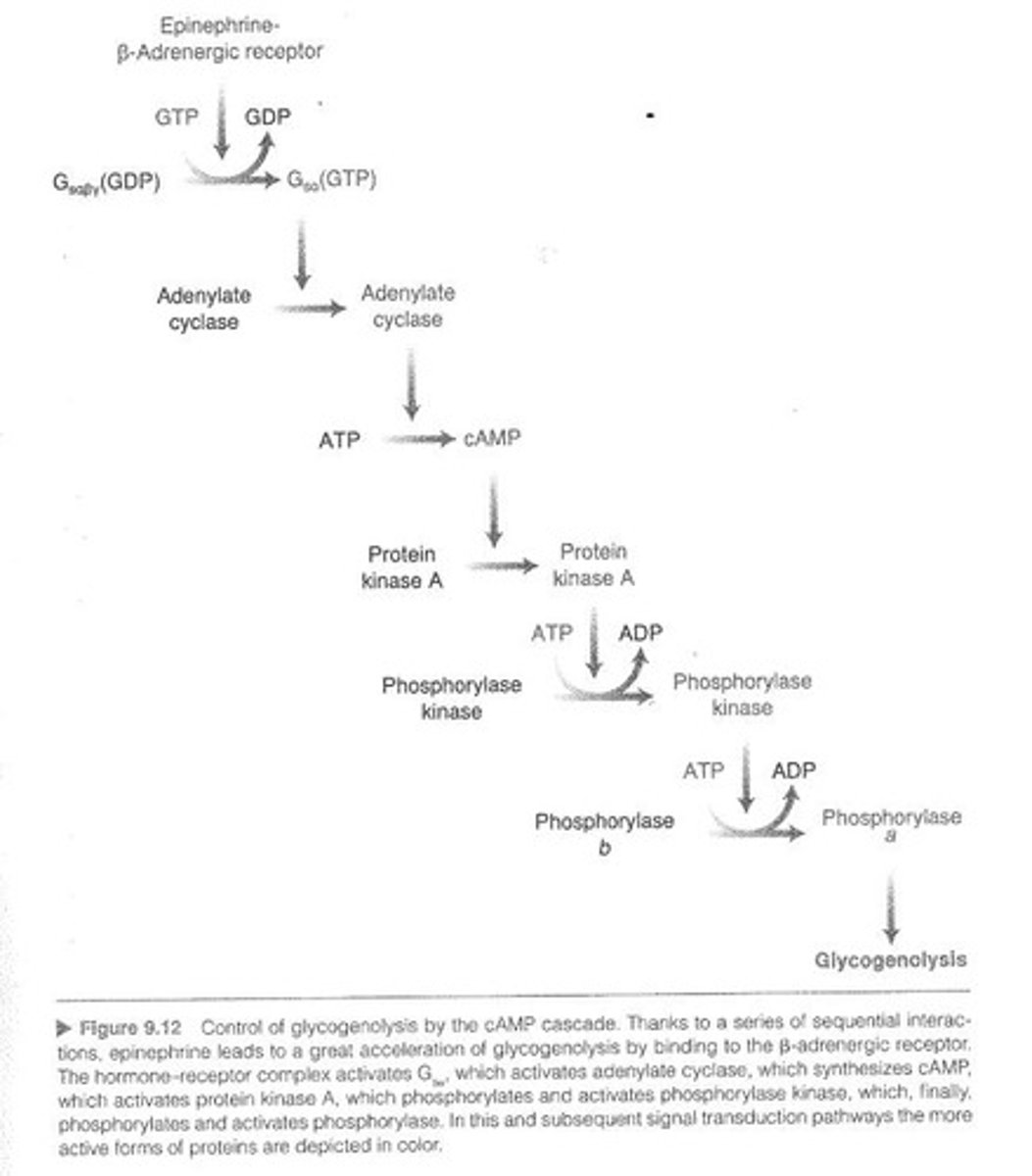
Cyclic-AMP Cascade
Hormonal signaling pathway activating phosphorylase.
Glycogen Synthase
Enzyme responsible for glycogen synthesis.
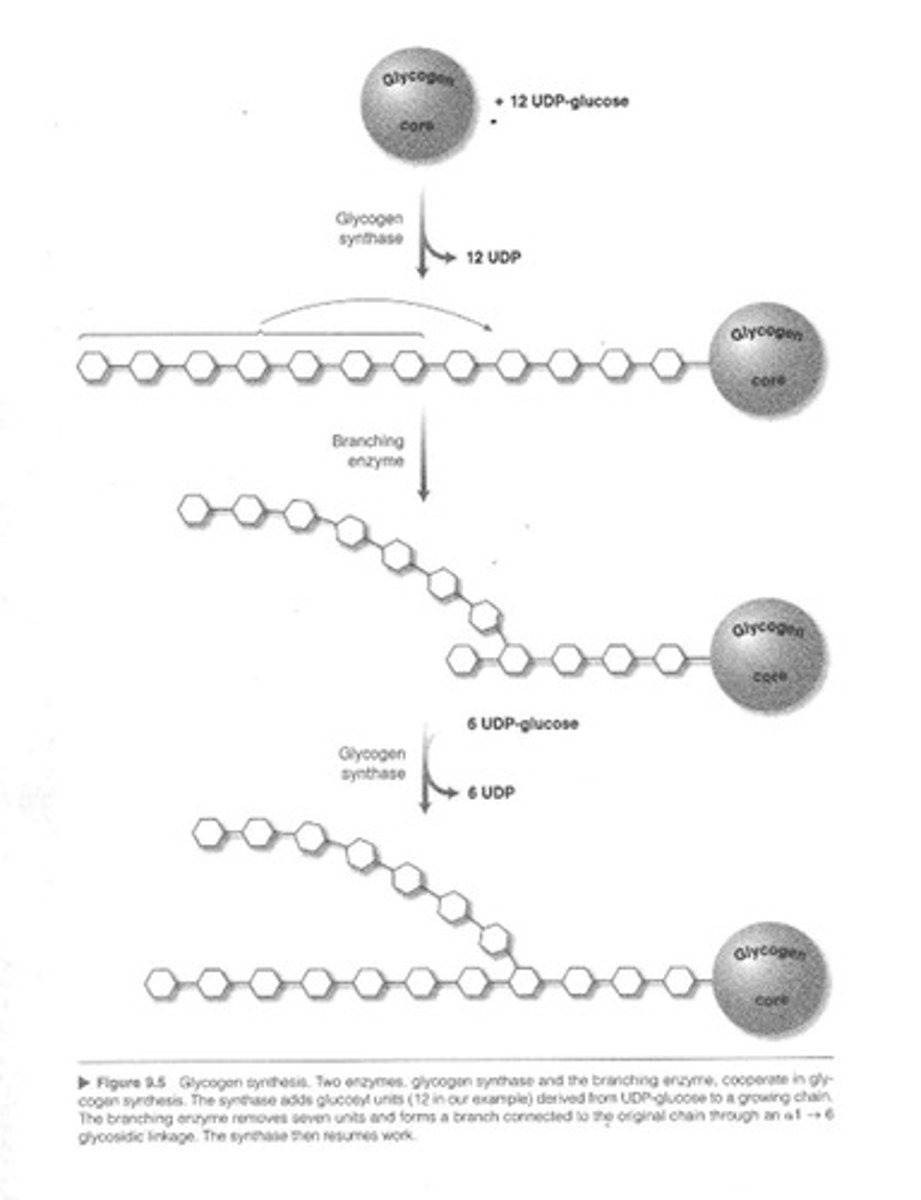
UDP-Glucose
Activated glucose form for glycogen synthesis.
Calmodulin
Calcium-binding protein activating phosphorylase kinase.
Epinephrine
Hormone increasing glycogen breakdown during exercise.
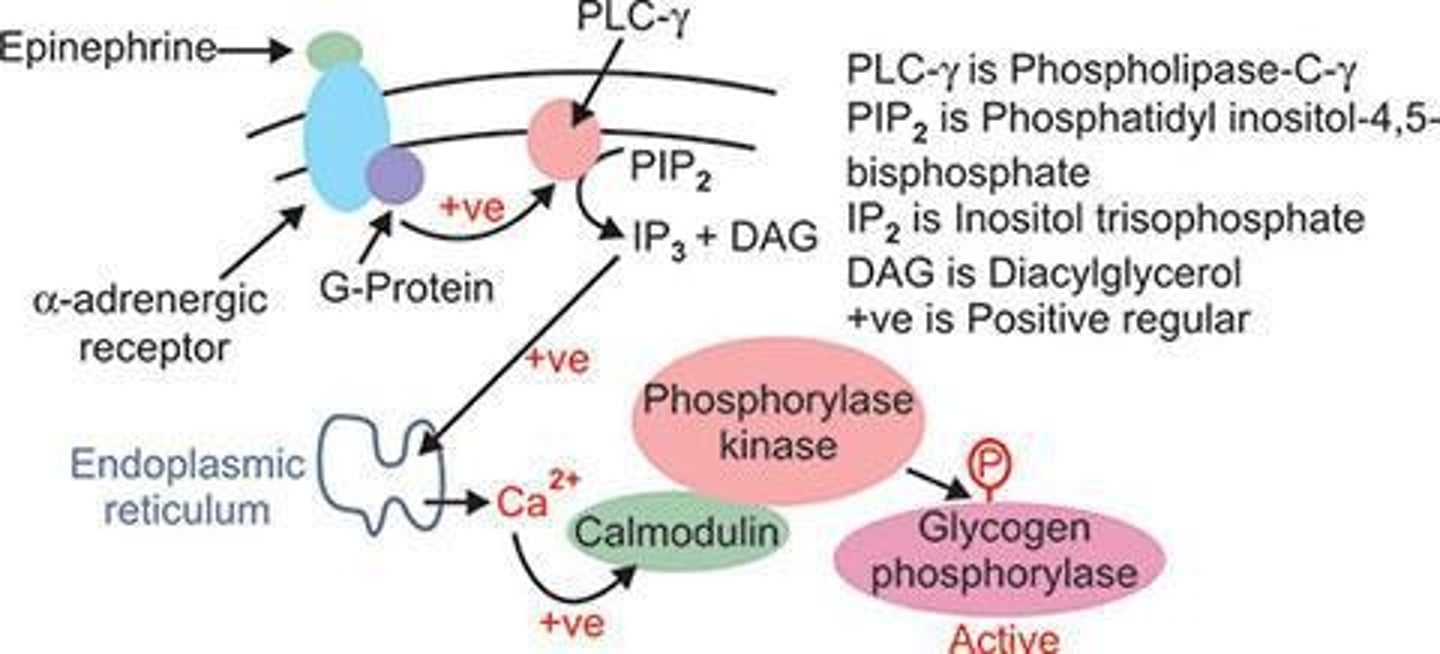
Calcium Increase
Elevated calcium levels activating phosphorylase kinase.
AMP Increase
Stimulates phosphorylase b activation during exercise.
ATP Decrease
Inhibits phosphorylase activation when levels are high.
IMP Increase
Enhances phosphorylase b activation during intense exercise.
Glycogen Loading
Carbohydrate intake strategy for enhancing performance.
Carbohydrate Intake Timing
Optimal consumption before and during exercise.
Chain Elongation
Process of adding glucosyl units to glycogen.
Hepatic Glycogen
Glycogen stored in the liver from carbohydrates.
Muscle Glycogen
Glycogen stored in muscle tissues for energy.
Exercise Intensity
Level of effort affecting carbohydrate needs.
Feeding Schedule
Plan for carbohydrate intake during exercise.
Glycogen Recovery
Restoration of glycogen levels post-exercise.
Epinephrine
A catecholamine acting primarily as a hormone.
Norepinephrine
A catecholamine acting primarily as a neurotransmitter.
Catecholamines
Compounds derived from the amino acid tyrosine.
Adrenal Medulla
Source of epinephrine and norepinephrine secretion.
Sympathetic Nervous System
Part of autonomic system releasing norepinephrine.
Plasma Concentration
Norepinephrine levels exceed epinephrine in blood.
Adrenergic Receptors
Receptors binding catecholamines like epinephrine.
β-Adrenergic Receptor
Receptor type involved in cyclic-AMP cascade.
Adenylate Cyclase
Enzyme activated by β-adrenergic receptor binding.
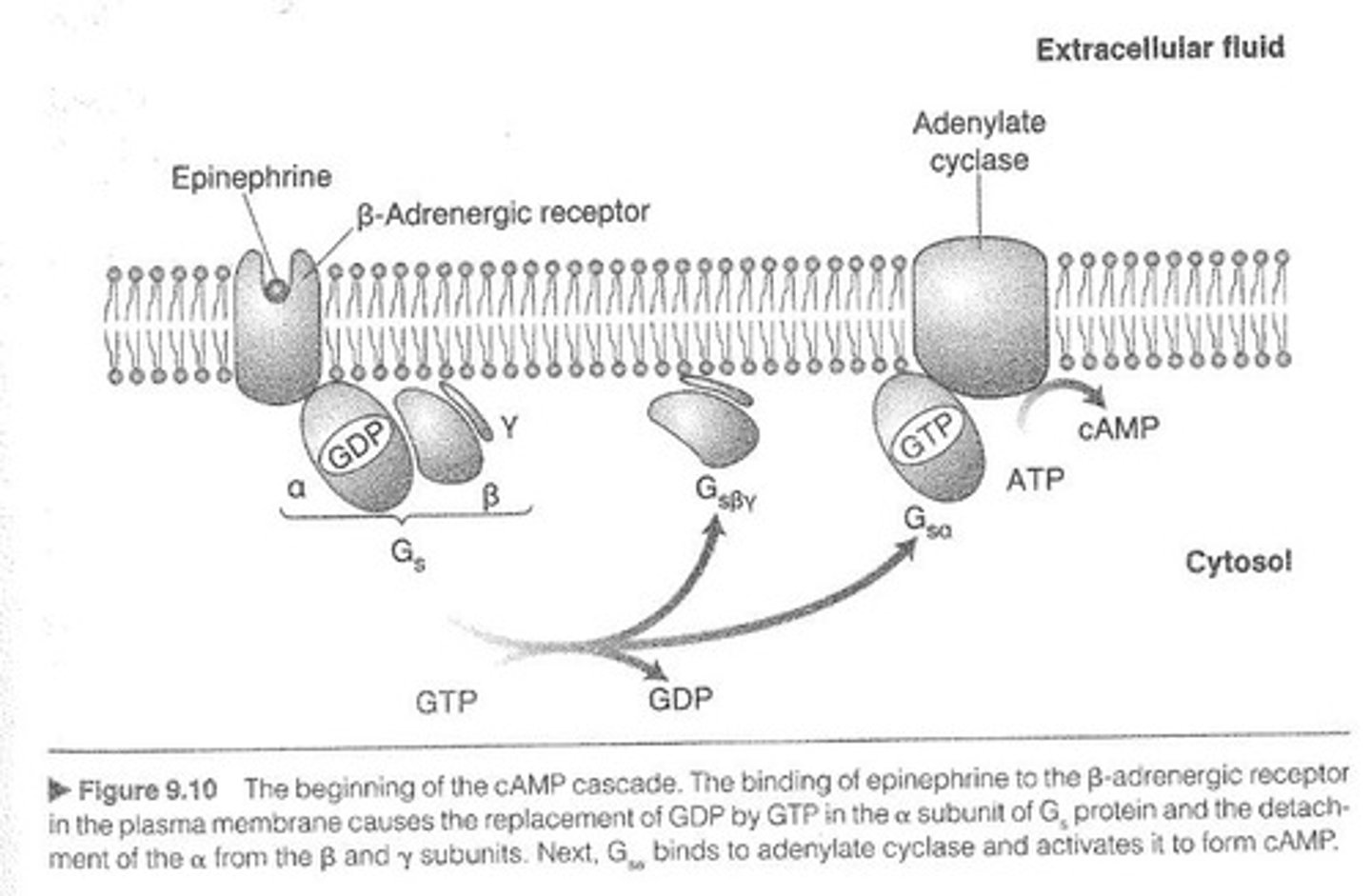
Cyclic AMP (cAMP)
Second messenger synthesized by adenylate cyclase.
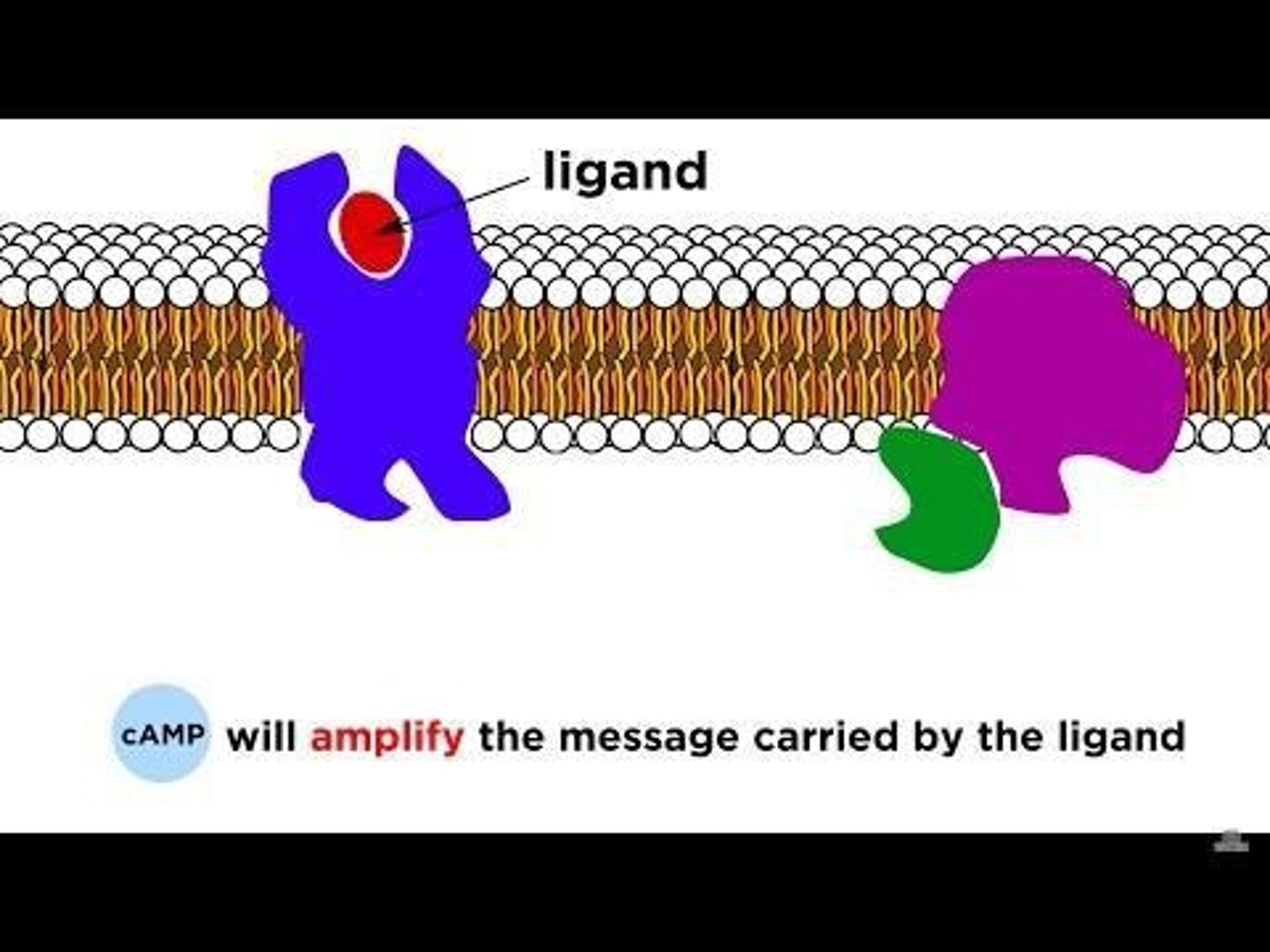
G Protein
Mediates receptor activation of adenylate cyclase.
Gs Protein
Stimulatory G protein activating adenylate cyclase.
GTP
Nucleotide replacing GDP to activate Gsα.
Phosphorylase Kinase
Activated by PKA to enhance glycogenolysis.
Glycogenolysis
Process of breaking down glycogen to glucose.
Glycolytic Rate
Increased significantly during exercise in muscles.
Glucose 6-Phosphate
Product of glycogenolysis, increasing during exercise.
Blood Flow
Enhanced to active muscles, increasing glucose delivery.
GLUT Transporters
Integral proteins facilitating glucose uptake in cells.
GLUT4
Most abundant glucose transporter, not always present.
Exercise Intensity
Higher intensity correlates with increased catecholamine secretion.
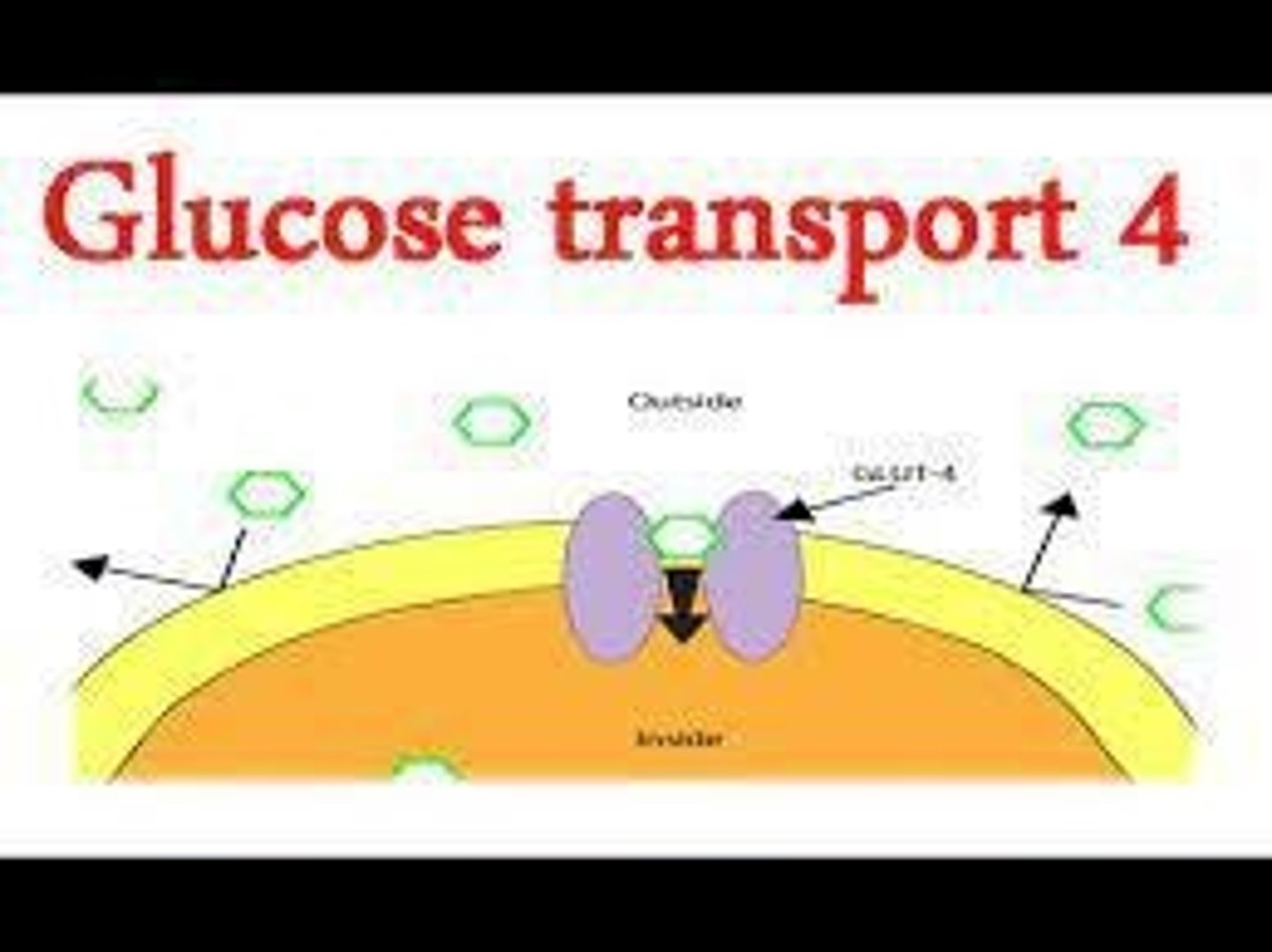
GLUT4
Transporter that facilitates glucose entry into cells.
Intracellular Vesicles
Membrane-bound compartments within cells.
Sarcolemma
Muscle cell membrane surrounding muscle fibers.
Transverse Tubule Membrane
Extensions of muscle cell membrane into fibers.
Calcium Release
Triggered by muscle activation, influences various processes.
Phosphofructokinase (PFK)
Key enzyme regulating glycolysis in muscle cells.
ATP Inhibition
PFK activity decreases when ATP levels are high.
PCr Inhibition
Phosphocreatine also inhibits PFK activity.
AMP Stimulation
Increased AMP activates PFK during low energy.
Acidic pH Inhibition
Low pH inhibits PFK, affecting glycolysis rate.
Glycolytic Rate Decrease
PFK inhibition prevents hazardous pH drops.
Pyruvate Kinase
Enzyme catalyzing final step of glycolysis.
ADP Activation
ADP enhances pyruvate kinase activity.
Carbohydrate Intake
Essential for replenishing muscle glycogen stores.
Supercompensation Protocol
Strategy to increase muscle glycogen before competition.
Glycogen Depletion
Intensive training reduces glycogen for supercompensation.
Hypoglycemia Risk
Low carbohydrate intake can lead to low blood sugar.
Gastrointestinal Problems
Digestive issues may arise from extreme diets.
Carbohydrate Loading
Increases glycogen stores, enhancing endurance performance.
Time to Exhaustion
Carbohydrate loading increases endurance by 20%.
Task Completion Time
Carbohydrate intake reduces task completion time by 2-3%.
Carbohydrate Loading
Effective for events lasting over 90 minutes.
Sprint Performance
Carbohydrate loading ineffective for sprints under 30 minutes.
Supercompensation
Effective but not always applicable in all sports.
Consecutive Competitions
Events occurring within 1-5 days affect loading efficacy.
Water Storage
Each gram of carbohydrate stores 3 grams of water.
Body Mass Increase
500g carbohydrate storage increases mass by 2 kg.
Weight Making Sports
Increased body mass may be undesirable in these sports.
Pre-Exercise Meal Timing
Last large meal should be 3-5 hours before competition.
Importance of Breakfast
Critical after overnight fast for glycogen replenishment.
Muscle Glycogen Incorporation
Carbohydrates consumed pre-exercise enhance muscle glycogen.
Carbohydrate Amount
140-330g recommended before exercise for performance.
Liver Glycogen Importance
Liver glycogen levels drop significantly after fasting.
Blood Glucose Maintenance
Carbohydrate ingestion supports blood glucose during exercise.
Plasma Glucose Return
Glucose and insulin return to baseline in 30-60 minutes.
Pre-Exercise Carbohydrate Effects
Includes glucose drop, increased oxidation, fat mobilization blunting.
Carbohydrate Availability
Enhanced by 200-300g intake 3-4 hours before exercise.
Pre-Exercise Carbohydrate Ingestion
Causes rapid rise in plasma glucose and insulin.
Blood Glucose Fall
Occurs rapidly with exercise onset due to insulin effects.
Hyperinsulinemia
Stimulates glucose uptake during exercise.
Fat Oxidation Reduction
Lower fatty acid availability due to pre-exercise carbohydrate.
Glycemic Index Foods
Focus on low glycemic index for carbohydrate ingestion.
Glycemic response
Blood sugar reaction to carbohydrate intake.
Insulin
Hormone that promotes glucose uptake in muscles.
Catecholamines
Hormones that increase liver glucose output.
Intestinal absorption
Process of glucose entering bloodstream post-ingestion.
Pre-exercise carbohydrate ingestion
Carbohydrate consumed before physical activity.
High GI food
Foods that rapidly increase blood glucose levels.
Endurance capacity
Ability to sustain prolonged physical activity.
Glycogen sparing
Conserving stored glycogen during exercise.
Motor skills improvement
Enhanced physical coordination and performance.
Central nervous system (CNS)
Brain and spinal cord; major glucose consumer.
Exogenous substrates
Nutrients sourced from outside the body.
Endogenous substrates
Nutrients stored within the body.
Exogenous carbohydrate oxidation
Breakdown of external carbohydrates for energy.
Oxidation rates
Speed at which carbohydrates are metabolized.
Feeding schedule
Timing of carbohydrate consumption during exercise.
Optimal carbohydrate intake
Amount needed for peak performance without issues.