Equilibrium
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What does it mean when a reaction is at equilibrium
WHAT
WHAT
What does it mean when a reaction is at equilibrium
Forward and reverse reactions occur at the same time (rates are equal)
[products] and [reactants] remain constant (steady state)
What is the equilibrium constant
K (upercase)
For K
WHAT
Follows WHAT
Describes the effects of the “WHAT” of reaction
WHAT
WHAT
For K
Ration of products to reactants
Follows reaction stoichiometry
Describes the effects of the “thermodynamic conditions” of reaction
Temperature specific
Reaction specific
What is the general reaction for the equilibrium constant
K = [products]^x / [reactants]^n (if nR →← xP)
What is Kc (concentration- in mol/L) given the reaction aA + bB →← cC + dD
Gases or aqueous
Kc = [C]^c [D]^d / [A]^a [B]^b
What is Kp (pressure - in bar) given the reaction aA + bB →← cC + dD
Gases
Kc = PC^c PD^d / PA^a PB^b
K is never in WHAT
Pure liquids or pure solids
What is the reaction between Kc and Kp
Kp = Kc (RT)^Δn
where
R = 0.008314 barL/molK
T = Kalvin
Δn = nProducts (gas) - nReactants (gas)
What are the units for K
Unitless
the larger the value of K the further a reaction has gone in the WHAT direction
the larger the value of K the further a reaction has gone in the FORWARD direction
The equilibrium constant can be used to determine whether the formation of WHAT or WHAT is favoured
The equilibrium constant can be used to determine whether the formation of REACTANTS or PRODUCTS is favoured
Reactions must be occurring at the same WHAT for their WHAT to be compared to each other
Reactions must be occurring at the same TEMPERATURE for their EQUILIBRIUMS to be compared to each other
if K > 1 WHAT is favoured
WHAT does the graph look like
if K > 1 PRODUCTS is favoured
WHAT does the graph look like
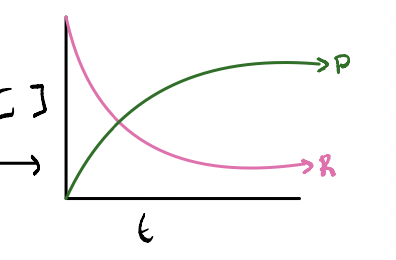
if K < 1 WHAT is favoured
WHAT does the graph look like
if K < 1 REACTANTS is favoured
WHAT does the graph look like
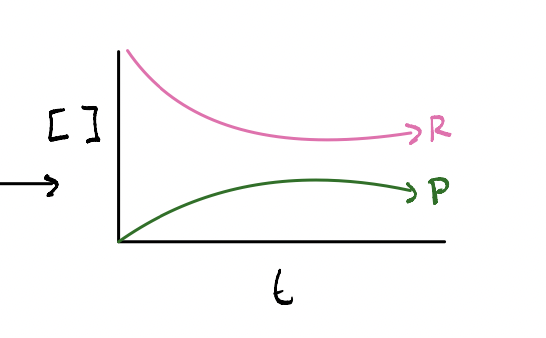
If K1 = [NO] / [N2O2] and reaction 2 reverses the reaction what happens to K1
1 / K1
If K1 = [NO] / [N2O2] and reaction 3 multiplies the reaction by 2 what happens to K1
To the power of the multiple ex: 2 in this instant so (K1)²
Reaction quotient, Q:
The same form as the WHAT
Measured at WHAT during the reaction
Reaction quotient, Q:
The same form as the EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT
Measured at ANYTIME during the reaction
If Q < K, reaction is in the WHAT
Forward direction
If Q = K reaction is WHAT
at equilibrium
If Q > K reaction is in the WHAT direction
Reverse direction
K depends on WHAT between the forward and reverse reactions
Final concentration
What are the steps to determining which direction a reaction will proceed
Calculate Q
Compare Q to K
Le Chatelier’s Principle states that when a system at equilibrium is perturbed, the system will establish a WHAT to WHAT the disturbance
Le Chatelier’s Principle states that when a system at equilibrium is perturbed, the system will establish a NEW EQUILIBRIUM to COUNTERACT the disturbance