Transport across root and xylem
1/26
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What are the two main transport systems in plants?
Xylem and Phloem
What is transported via the Xylem?
Water and mineral salts
What is transported in the Phloem?
Sugars and amino acids
What is the function of root hair cells?
Absorb water from the soil by osmosis
What are the features of root hair cells?
Large surface area for water to enter by osmosis
Cellulose cell wall which is freely permeable to water
Large number of mitochondria to provide ATP for active transport of mineral ions
Large number of protein carriers embedded in membrane fir active transport of mineral ions
Label this root structure
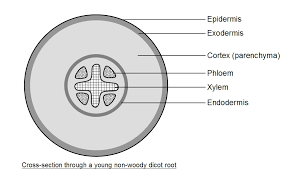
What is the stele/vascular bundle composed of?
Xylem, phloem, and cambium
What is the function of the epidermis in a root?
Outer cell layer containing root hair cells to increase area for water and mineral uptake
What type of tissue is xylem?
Dead tissue that carries water and mineral ions up the plant.
What type of tissue is phloem?
Living tissue that carries dissolved organic materials (sucrose) around the plant.
What is the function of the cortex?
Layer of packing tissue between epidermis and vascular tissue
What is the function of the endodermis?
A layer of cells containing a waterproof casparian strip to control movement of ions into the xylem.
What is the Apoplast pathway?
Water soaks into cellulose fibres of the epidermal and cortical cell wall and seeps across the root from cell to cell without entering the cell cytoplasm.
What is the Symplast pathway?
Water moves into the cytoplasm of a cortical cell by osmosis across the plasma membrane and between adjacent cells via plasmodesmata to the xylem.
What is the Vacuolar pathway?
Water moves via the vacuoles in the cytoplasm, but has to cross plasma membranes, however resistance is high and little water moves by this pathway.
How does nitrogen enter a plant?
As Nitrate ions (NO3 - ) or ammonium ions (NH4 +). They diffuse with water along the apoplast pathway but at the endodermis enter the symplast pathway by active transport against the concentration gradient to bypass the casparian strip.
Why does water enter the root hair cells by osmosis?
Active uptake of mineral ions lowers the solute potential.
Which route does water cross the cortex of the plant mostly?
Apoplast route due to the polar nature of water and cellulose. Water molecules attracted to cellulose by adhesion and to each other by cohesion.
What prevents water from continuing along the apoplast route?
Casparian strip, so it crosses the cytoplasm by the symplast pathway
What happens to the solute potential in the pericycle as minerals are actively transported?
It lowers.
How does the Casparian strip affect water movement?
It blocks the apoplast pathway, forcing water into the symplast pathway.
What is transpiration?
The loss of water vapour from leaves, giving rise to the transpiration stream.
How does light intensity affect transpiration?
Affects the degree of opening and closure of stomata
How does temperature affect transpiration?
Higher temperatures increase the kinetic energy of water molecules and cause them to diffuse more quickly. Warm air also has more kinetic energy so holds more water.
How does humidity affect transpiration?
Dry air outside the leaf creates a steeper diffusion gradient between the internal air spaces and the environment thus increasing the transpiration rate. High humidity reduced rate of transpiration.
How does air movement affect transpiration?
Maintains a diffusion gradient by blowing away humid air around the stomata and replacing it with fresh air that is less saturated with water vapour.
What instrument is used to measure the rate of water absorption?
Potometer