Metallic Bonding
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
What is the structure of metals?
Metals consist of giant structures of atoms arranged in a regular pattern
What is metallic bonding?
The sharing of delocalised electrons in a lattice of positive metal ions.
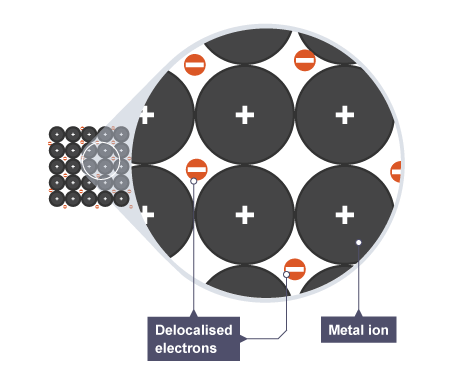
What are delocalised electrons?
Electrons that are not associated with a specific atom and can move freely throughout the metal lattice.
Why are metals excellent conductors of electricity?
delocalised electrons can move freely and carry charge
Why do metals have a high melting and boiling point?
strong attraction between cations & and electrons so requires a large amount of energy to break bonds
Why are metals good conductors of heat?
they are closely packed together so the particles pass on energy easier
What are some of the properties of metals due to metallic bonding?
high density - metal ions closely packed together
high tensile strength (not easily broken) - strong metallic bonding
malleable/ductile - in layers so can easily be pulled apart
hard
lustrous/not reactive
What are alloys?
composed of different metals/non-metals & metals
Examples of alloys
brass - copper & zinc
steel - iron and carbon
Why do we have alloys?
Most pure metals are too soft to use so we can add other metals or elements to make them harder
Why are pure metals soft?
They have a giant metallic structure so when force is applied the layers slide over each other and not much force is needed in a pure metal for that to happen
Why are alloys hard?
In an alloy the atoms are different sizes so the different sized atoms distort the layers in a pure metal so greater force is required for layers to slide over each other