Electrolyte Imbalances and Nursing Considerations
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Electrolyte
Minerals in the body that carry an electric charge and are essential for various bodily functions.
Potassium - K+
An essential electrolyte with a normal range of 3.5-5.0 mEq/L, crucial for muscle contraction, heart rhythm, and nerve impulse.
Hypokalemia
A condition where potassium levels are below 3.5 mEq/L, often monitored with a heart monitor for arrhythmia.
Causes of Hypokalemia
Laxative abuse, GI suction, diuretics, vomiting, and diarrhea.
Signs and Symptoms of Hypokalemia
Heart arrhythmia, GI distention, abdominal pain, depressed ST segment, and prolonged QT interval.
Treatments for Hypokalemia
Mnemonic: "BASIC BAWSSY"
(Think: Be a "basic bossy" potassium pro!)
Each letter stands for a potassium-rich, memory-friendly food:
B – Bananas 🍌
A – Avocados 🥑
S – Spinach 🥬
I – Iceberg’s smarter cousin... sweet potatoes 🍠
C – Coconut water 🥥
B – Beans (white beans especially) 🫘
A – Oranges (aka "A-orange" for the mnemonic's sake) 🍊
W – Water from coconuts again – extra hydration! 💧
S – Salmon 🐟
S – Swiss chard (another leafy green) 🌿
Y – Yogurt 🥣
Hyperkalemia
A condition where potassium levels are above 5.0 mEq/L, associated with renal failure and EKG changes.

Causes of Hyperkalemia
Renal Failure
Treatments for Hyperkalemia
Increase fluid intake, administer insulin, and decrease salt substitutes.
Sodium
An essential electrolyte with a normal range of 135-145 mEq/L, important for central nervous system and neuromuscular function.
Hyponatremia
A condition where sodium levels are below 135 mEq/L, often due to low sodium diets or excessive water intake.
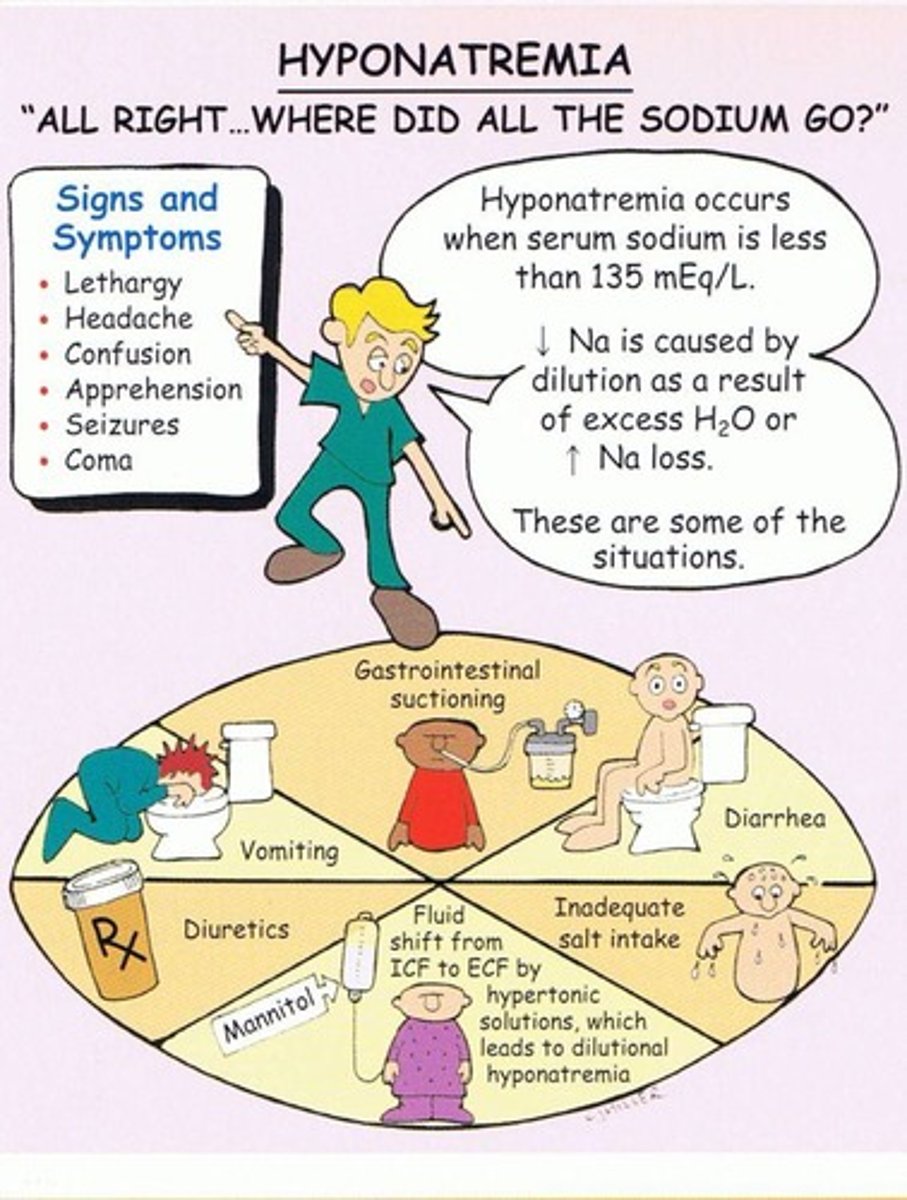
Signs and Symptoms of Hyponatremia
Confusion, seizures, decreased level of consciousness, decreased sensation, and headache.
Treatments for Hyponatremia
Increase sodium in foods, sodium tablets, restrict water intake, and IV fluids with sodium.
Hypernatremia
A condition where sodium levels are above 145 mEq/L, often associated with dehydration and excessive salt intake.

Signs and Symptoms of Hypernatremia
Confusion, flushed skin, increased fluid retention, hypertension, and decreased urine output.
Treatments for Hypernatremia
Increase fluid intake and decrease sodium diet.
Calcium
An essential electrolyte with a normal range of 9-10.5 mg/dL, important for blood coagulation and muscle activity.
Hypocalcemia
A condition where calcium levels are below 9 mg/dL, often resulting from parathyroid surgery or calcium shift into the bone.
Signs and Symptoms of Hypocalcemia
Muscle spasms, tetany, seizures, and positive Chvostek and Trousseau signs.

Treatments for Hypocalcemia
Increase calcium diet and provide supplements 30 minutes prior to meals.
Mnemonic: "Can Some Good Cheese Help Boost Strong Bones?"
Each word represents a calcium-rich food:
C – Canned fish (with bones, like salmon or sardines) 🐟
S – Seeds (chia, sesame, poppy) 🌱
G – Greens (collard greens, kale, spinach) 🥬
C – Cheese 🧀
H – Hard tofu (set with calcium sulfate) 🍱
B – Beans (especially white beans) 🫘
S – Soy products (soy milk, edamame) 🥛
B – Broccoli 🥦
Hypercalcemia
A condition where calcium levels are above 10.5 mg/dL, often due to excessive intake of antacids or bone tumors.

Signs and Symptoms of Hypercalcemia
Polyuria, constipation, fractures, and calculi.
Treatments for Hypercalcemia
Decrease calcium diet and use diuretics for calcium excretion.
Magnesium
An essential electrolyte with a normal range of 1.5-2.5 mEq/L, important for muscle contraction and nerve activity.
Hypomagnesemia
A condition where magnesium levels are below 1.5 mEq/L, often due to malnutrition or chronic diarrhea.
Signs and Symptoms of Hypomagnesemia
Hyperactive reflexes and leg cramps.
Treatments for Hypomagnesemia
Increase dietary magnesium and provide supplements.
Mnemonic: "Some Awesome Nuts & Seeds Help Boost Calm Muscles"
Each part stands for a magnesium-rich food:
S – Spinach 🥬
A – Avocados 🥑
N – Nuts (especially almonds, cashews, peanuts) 🥜
S – Seeds (pumpkin, flax, chia, sunflower) 🌻
H – Halibut (and other fatty fish) 🐟
B – Black beans (also kidney, pinto) 🫘
C – Chocolate (dark, 70%+) 🍫
M – Milk or magnesium-fortified dairy 🥛
✨ Bonus Short Version Mnemonic:
“MAGnesium CHAMPS”
M – Milk / Mackerel
A – Avocado
G – Greens (spinach, chard)
C – Chocolate (dark)
H – Halibut / Haddock
A – Almonds / cashews
M – Magnesium-fortified cereals
P – Pumpkin seeds
S – Soybeans / Sunflower seeds
Hypermagnesemia
A condition where magnesium levels are above 2.5 mEq/L, often due to sea water aspiration or chronic kidney disease.

Phosphorus
An essential element involved in ATP production.
Hypophosphatemia
A condition often caused by vitamin D deficiency or hyperparathyroidism, leading to confusion and seizures.
Hyperphosphatemia
A condition where phosphate levels increase, causing a decrease in calcium levels and potential joint issues.
Chloride
An electrolyte important for acid-base balance, with a normal range of 98-106 mEq/L.