Alkali metals
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
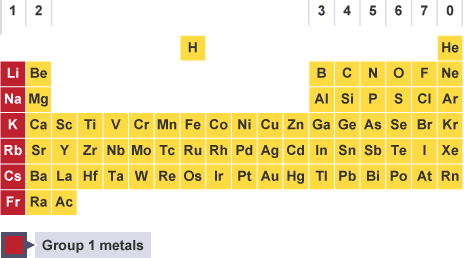
Where are the alkali metals on the periodic table?
in group 1
What are the properties of alkali metals?
- highly reactive
- low melting & boiling points
- soft
- shiny
- low densities
Why do alkali metals have similar properties?
because they all have 1 electron in their outer shell
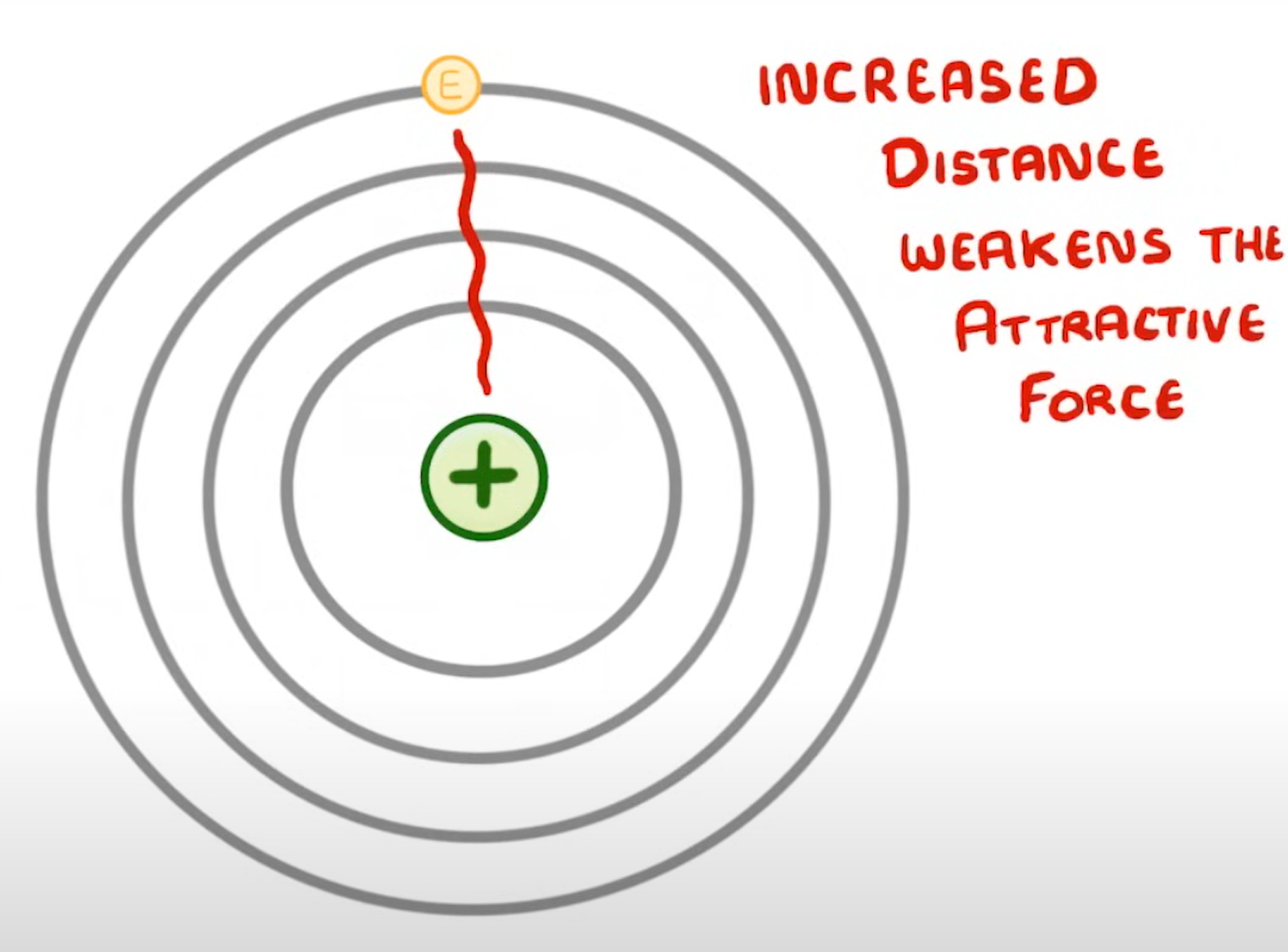
What happens to the reactivity of alkali metals down group 1 & why?
- reactivity increases
- this is because the number of electron shells increases down the group which weakens the electrostatic force of attraction between the nucleus & the outer shell, making it is easier for the electron to be lost
What happens to the melting & boiling points of alkali metals down group 1 & why?
- melting & boiling points decrease
- this is because the atomic size of alkali metals increases down group 1 which means that they form weak metallic bonds. Therefore, it takes less energy to overcome these bonds so only low temperatures are required
What happens when alkali metals react with water?
- it reacts vigorously to produce a metal hydroxide & hydrogen gas
- the metal oxide increases the pH because it is basic
- the metal floats because it is less dense than water
Why can the reaction between alkali metals & water be described as exothermic?
because heat energy is released
What is the reaction of lithium in water?
- fizzes steadily & becomes smaller until it eventually disappears
lithium + water → lithium hydroxide + hydrogen
2Li(s) + 2H2O(l) → 2LiOH(aq) + H2(g)
What is the reaction of sodium in water?
- melts to form a ball that moves around the surface of the water
- fizzes rapidly before it disappears
sodium + water → sodium hydroxide + hydrogen
2Na(s) + 2H2O(l) → 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g)
What is the reaction of potassium in water?
- melts & moves very quickly on the surface of the water
- metal gives off sparks & ignites the hydrogen gas with a lilac flame
potassium + water → potassium hydroxide + hydrogen
2K(s) + 2H2O(l) → 2KOH(aq) + H2(g)
What happens when alkali metals react with oxygen?
they tarnish & produce a metal oxide
What is the reaction of lithium in oxygen?
- tarnishes slowly
lithium + oxygen → lithium oxide
4Li(s) + O2(g) → 2Li2O(s
What is the reaction of sodium in oxygen?
- tarnishes quicker
sodium + oxygen → sodium oxide
4Na(s) + O2(g) → 2Na2O(s)
What is the reaction of potassium in oxygen?
- tarnishes quickest
potassium + oxygen → potassium oxide
4K(s) + O2(g) → 2K2O(s)
What is combustion?
- a reaction where a substance burns in oxygen
- the substance gains oxygen so it is an oxidation
What happens in the combustion of lithium, sodium & potassium?
LITHIUM → least reactive, burns with a red flame
SODIUM → more reactive, burns with an orange-yellow flame
POTASSIUM → most reactive, burns with a lilac flame