Nucleophilic Substitution
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
What happens in a nucleophilic substitution reaction?
A nucleophile attacks a polar molecule, kicks out a functional group and settles itself down in its place.
What is the general equation for the nucleophilic substitution of an alkane?
CH3CH2X + Nu- → CH3CH2Nu + X-
What is the overall equation for the reaction of a halogenoalkane (R-X) with OH-?
R-X + OH- → ROH + X-
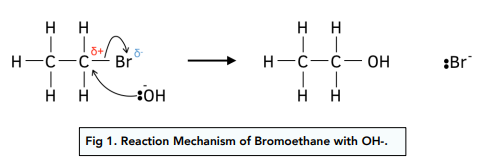
What is the mechanism for the nucleophilic substitution of bromoethane with a hydroxide ion?
The C-Br bond is polar. The partially positive C attracts a lone pair of electrons from the OH- ion.
The OH- ion acts as a nucleophile, attacking the slightly positive carbon atom.
A new bond forms because the C and the OH- ion, making an alcohol.
The C-Br bond breaks. Both the electrons from the bond are taken by the Br.
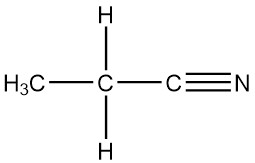
What are nitriles?
Nitriles have CN groups. The carbon atom and nitrogen atom are held together with a triple bond. They are derived from hydrogen cyanide.
What is the reaction of bromoethane with potassium cyanide?
CH3CH2Br + KCN → CH3CH2CN + KBr
The ethanolic potassium cyanide dissociates for form a K+ ion and a CN- ion.
KCN → K+ + CN-
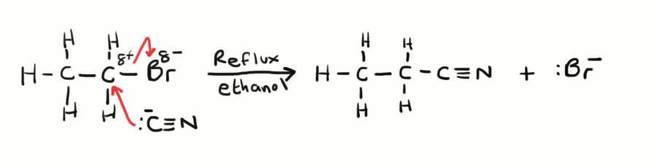
What is the mechanism for the nucleophilic substitution of bromoethane and potassium cyanide under reflux?
The lone pair of electrons on the cyanide ion attacked the partially positive carbon, the C-Br bond breaks and the bromine leaves.
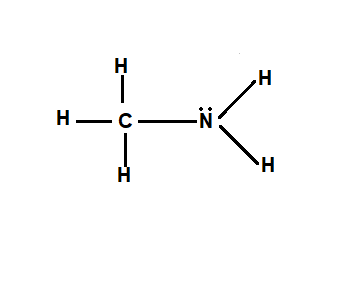
What are amines?
An amine has the structure R3N. The R groups can be hydrogens or another group.
In amines, the nitrogen always has a lone pair
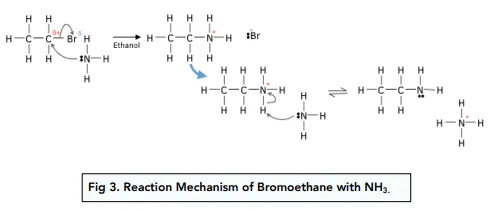
What is the mechanism for the nucleophilic substitution reaction of bromoethane with ethanolic ammonia?
The first step is the same as the other mechanisms. The nitrogen atom donates the lone pair of electrons to the carbon atom to create a bond
The nitrogen atom was neutral to begin with, so nitrogen is left with a positive charge
In the second step another ammonia molecule removes a hydrogen from the NH3 group to form an ammonium ion and an amine
The ammonium ion can react with the bromide ion to form ammonium bromide
How does reactivity differ for different halogenoalkanes?
The carbon-halogen bond strength decides reactivity as for the reaction to occur this bond needs to break
The C-F bond is the strongest so fluoroalkanes undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions more slowly than other halogenoalkanes.
The C-I bond has the lowest bond enthalpy, so it is easier to break. This means iodoalkanes are substituted more quickly.