Anatomy Exam 2
1/172
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
173 Terms
CNS Structures
brain and spinal cord
PNS structures
cranial nerves, spinal nerves, ganglia
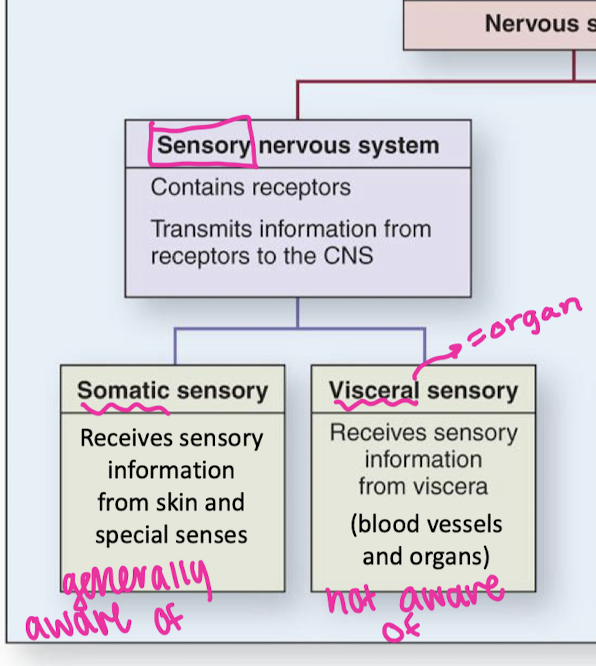
sensory nervous system divisions
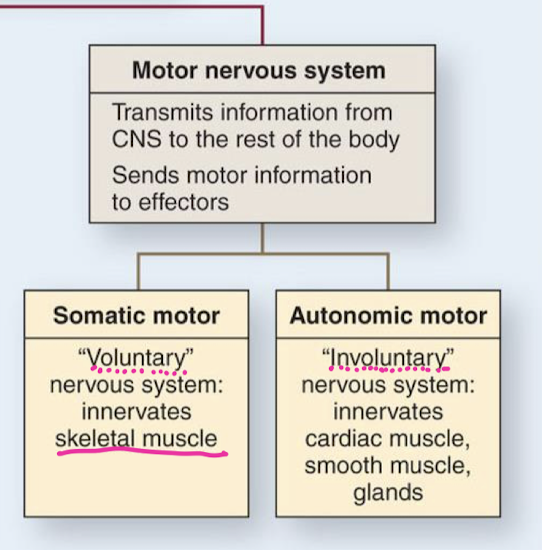
Motor nervous system divisions
neuron characteristics
high metabolic rate, depend on glucose and oxygen
extreme longevity
can change but can’t divide
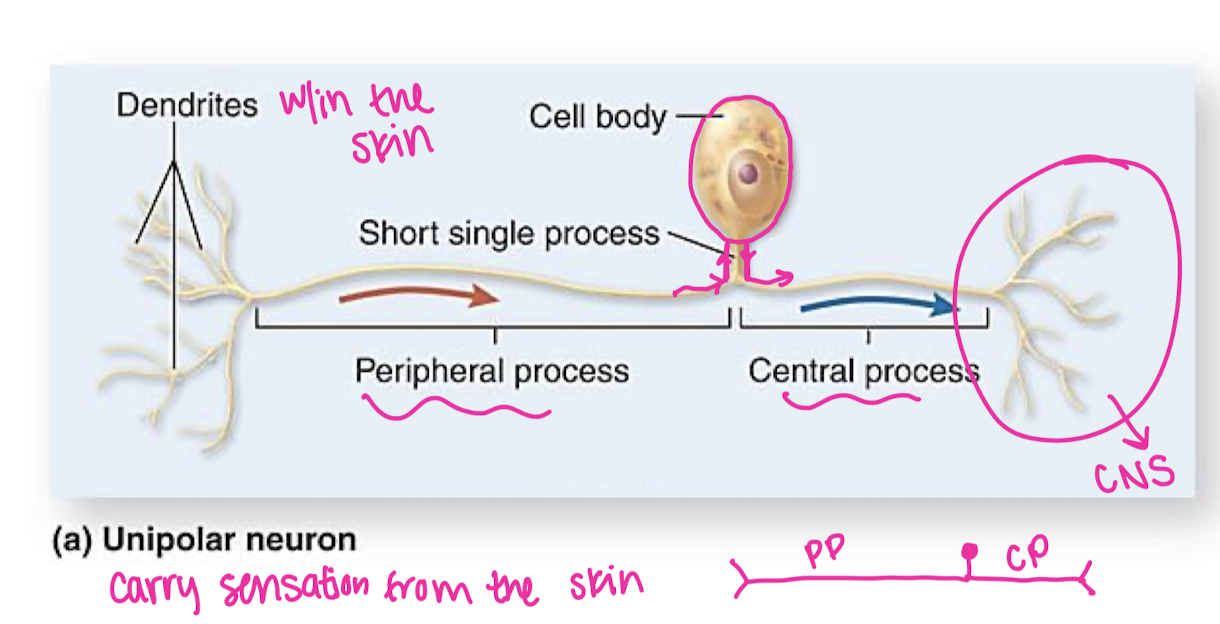
Unipolar neuron digram/parts and function
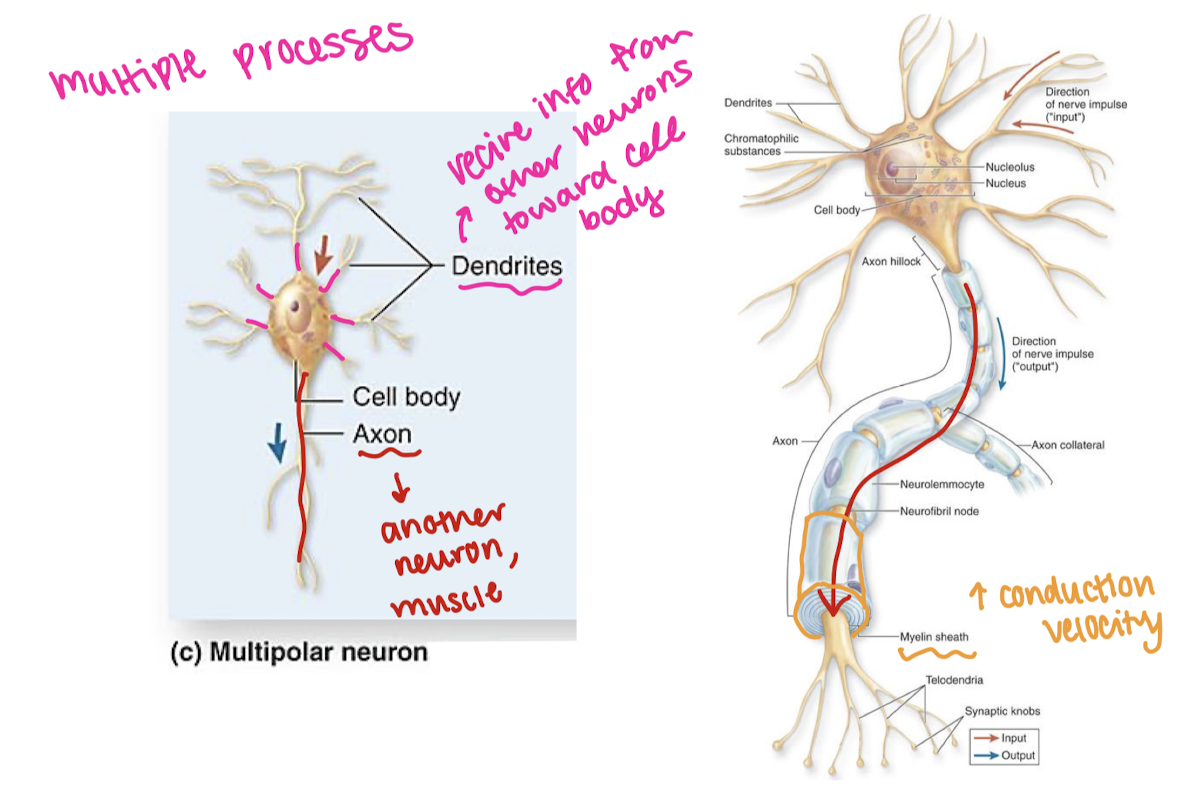
multipolar neuron diagram/parts
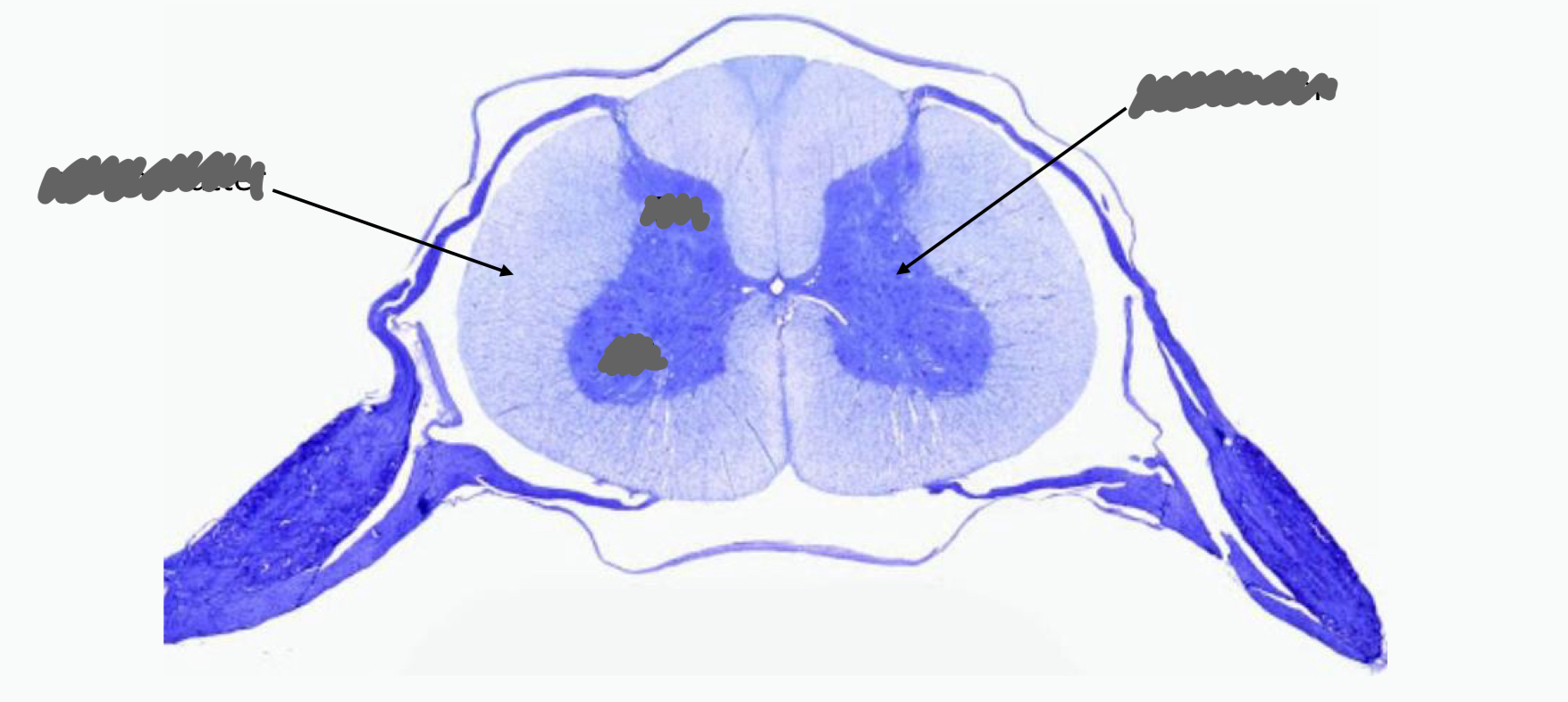
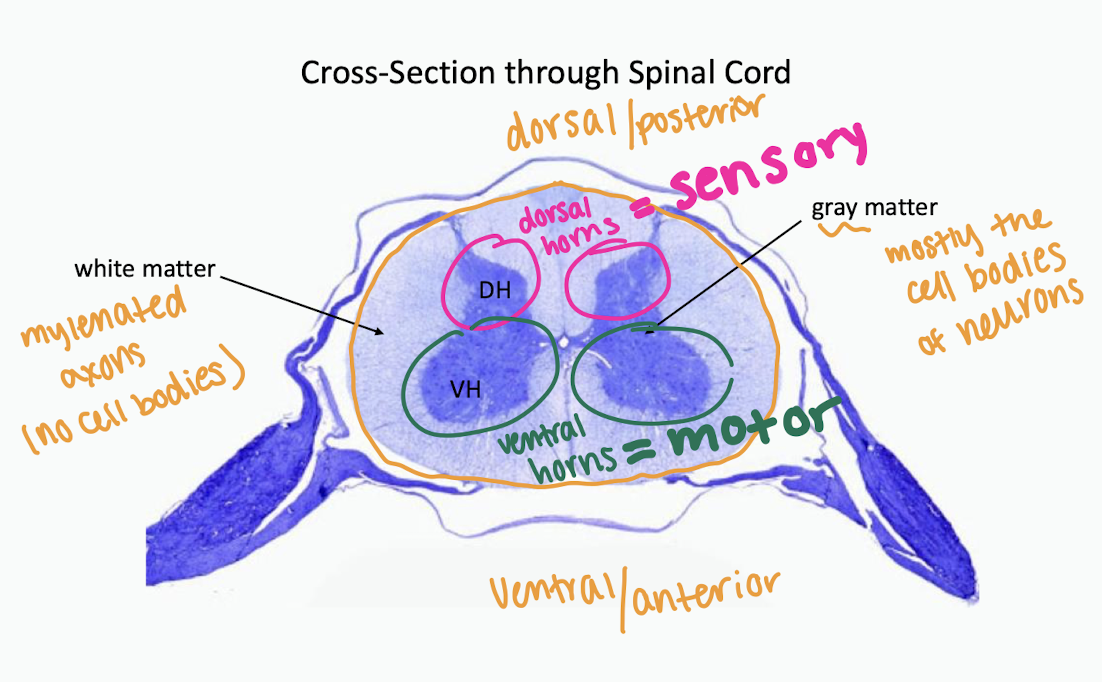
label parts of sc cross section
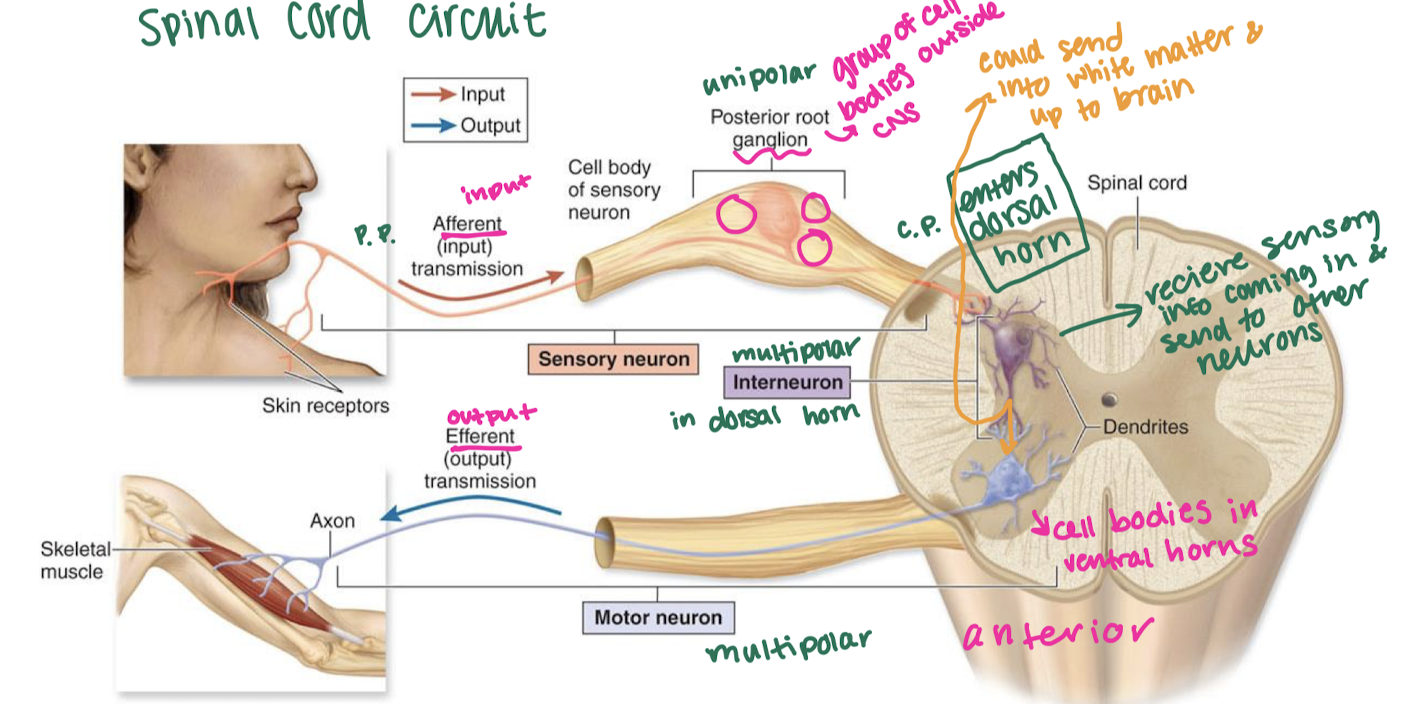
draw a basic spinal cord circuit
unipolar neuron sends info from skin to dorsal horn, multipolar interneuron relays signal w/in sc, multipolar neuron leaves ventral horn and leads to muscle
glial cells
nerve glue, assist neurons, protect, nourish, framework, ½ volume of nervous system, far outnumber neurons
afferent vs efferent
afferent = input
efferent = output
types of glial cells
CNS: astrocytes, ependymal cells, microglia, oligodendrocytes
PNS: schwann cells (neuromlemmocytes) and satellite cells
astrocytes
CNS, fill in space left behind when neurons die → framework, b/w neurons and capillaries of brain (form blood-brain-barrier)
Blood brain barrier
astrocytes: perivascular feet
capillary: tight junctions, continuous basement membrane
choroid plexus
capillaries + ependymal cells
ependymal cells
cns
bring fluid out of capillary and into cavity as CSF
microglia
cns
keeps cns clean of debris through phagocytic activity removing debris of dead neurons
oligodendrocytes
cns
attach to nearby axons and wrap cell membrane around them to form myelin
improve impulse speed
phospholipid bylayer
Neuron Depolarization & myelin
send impulse = depolarization = let Na+ in = make inside of neuron more positive (at rest charge outside is positive)
in myelinated neurons sodium only enters at nodes b/w myelin (faster!)
satellite cells
PNS
lines outside of unipolar neuron cell bodies
regulates delivery of nutrients and removal of waste products
neurolemmocytes (schwann cells)
myelenate peripheral neurons
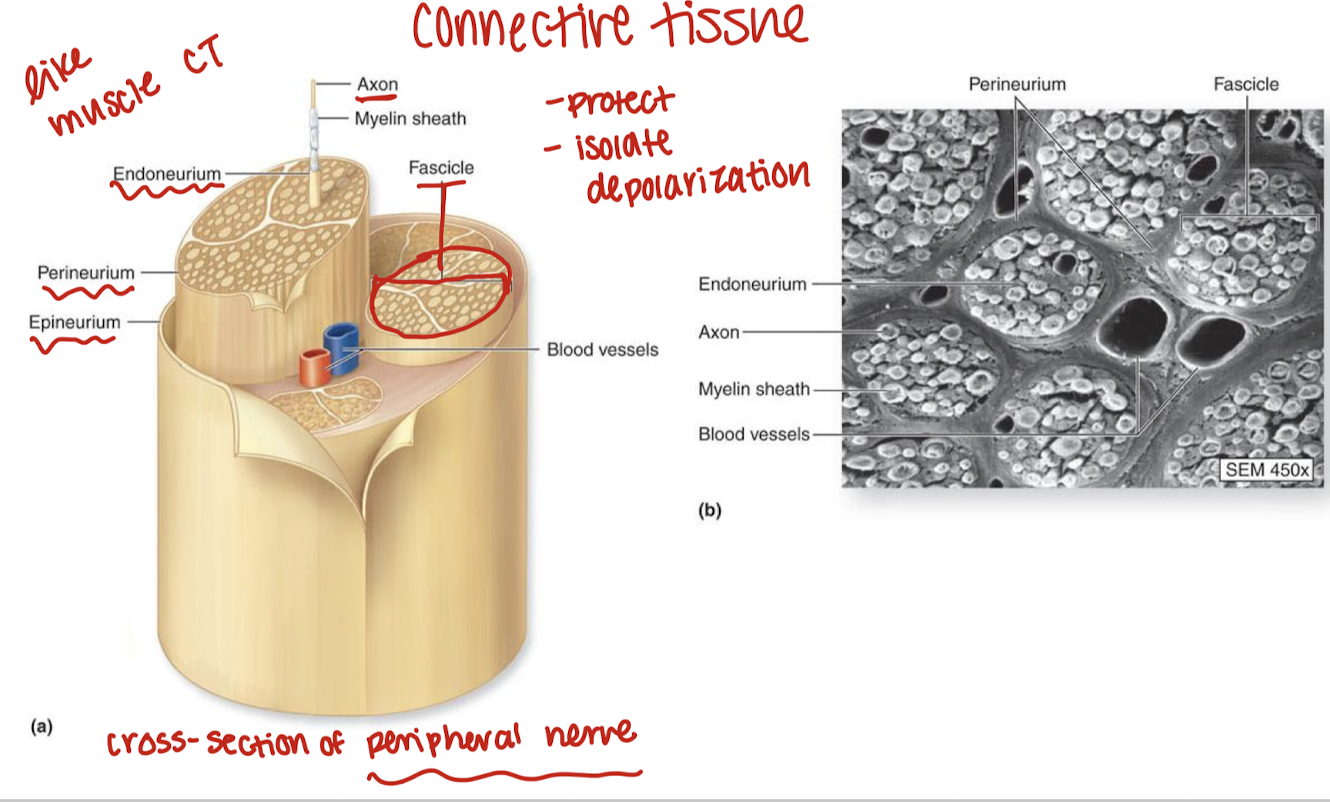
nervous connective tissue
endoneurium: surrounds neurons
perineurium: surrounds fasicles
epineurium: surrounds nerves
Peripheral nerve damage/regrowth
neurolemmocytes form regeneration tube
neurolemmocytes release nerve growth factor
axon regrows 1-3 mm/day
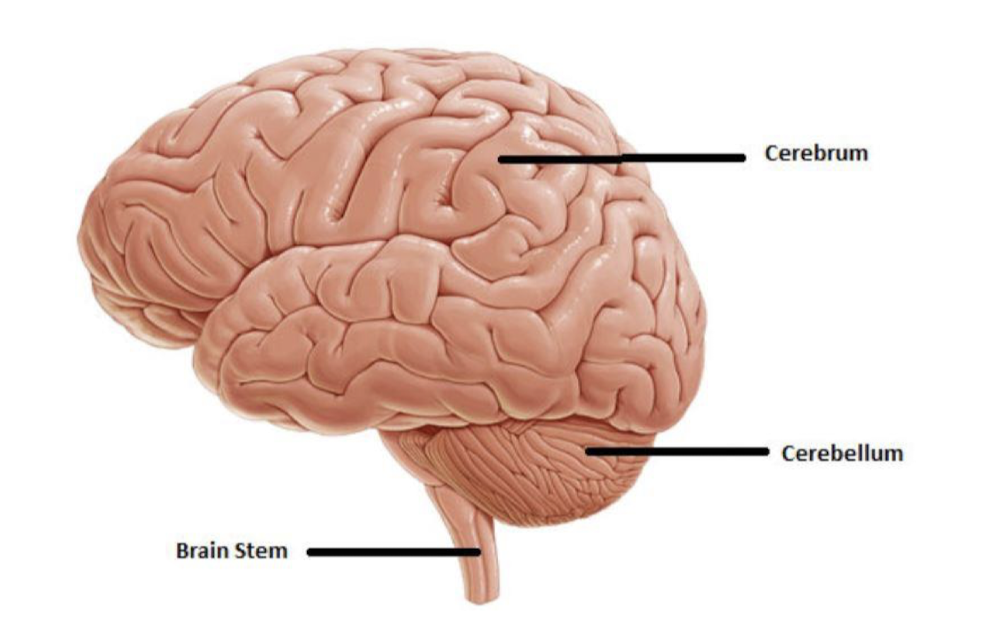
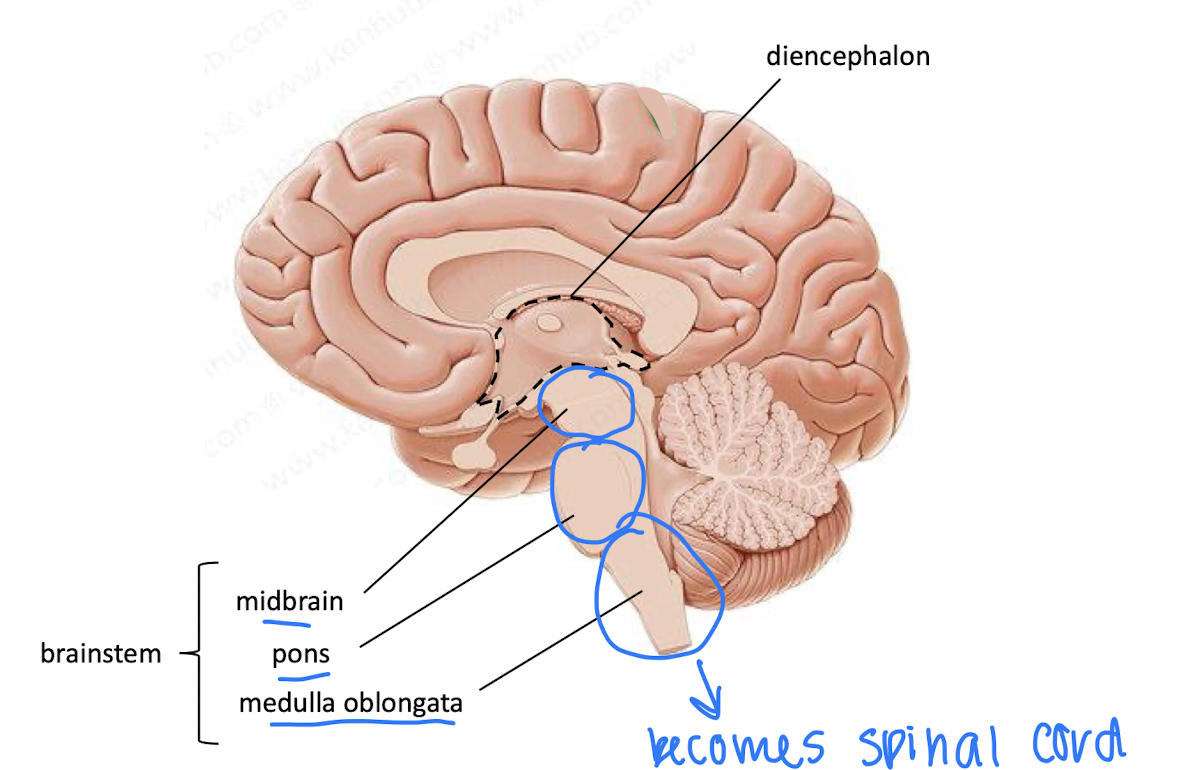
parts of brainstem
Primary vessicles
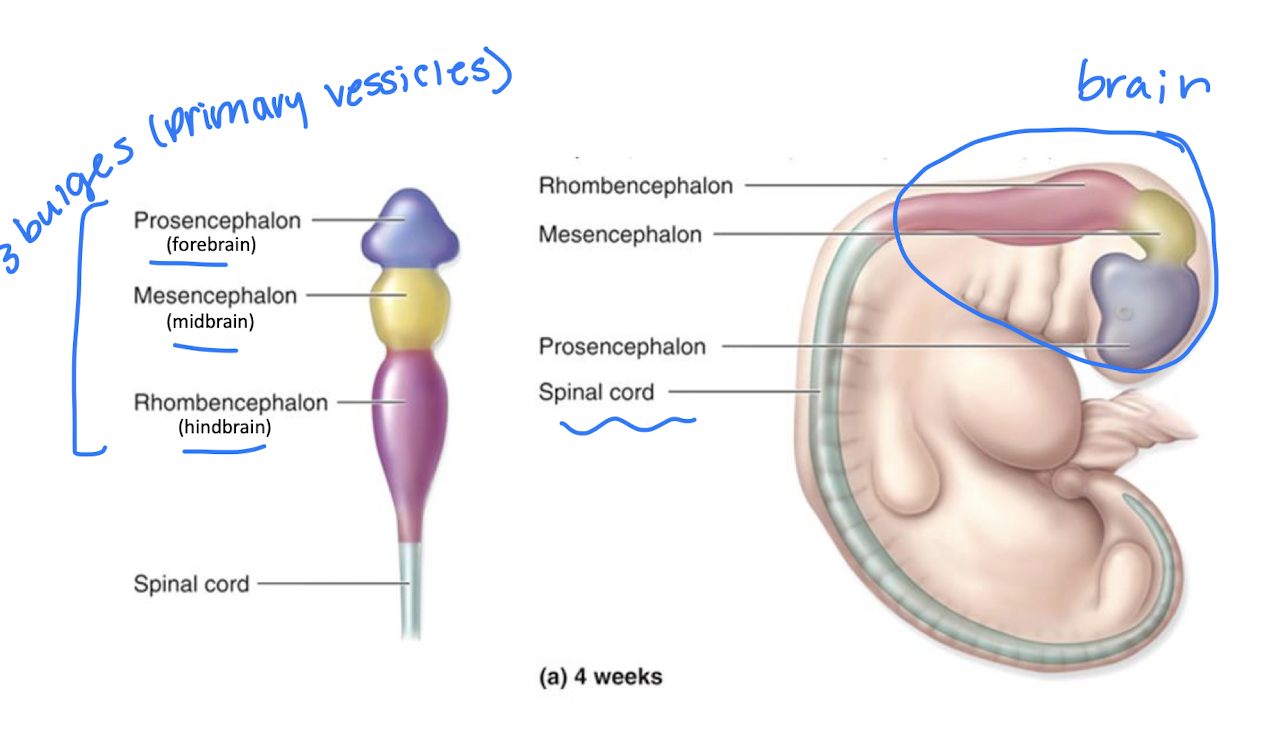
secondary vessicles
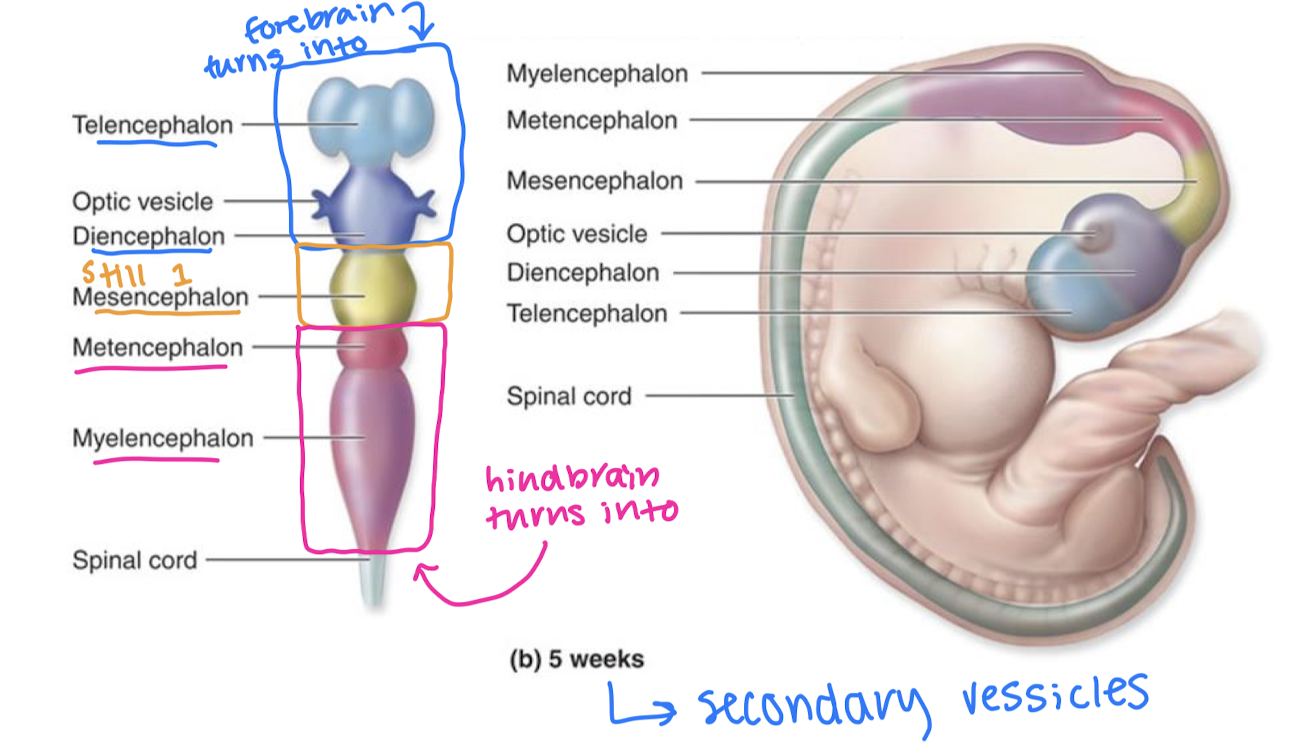
what does the prosecephalon turn into?
→telencephalon→cerebrum
→diencephalon→thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalimus
what does the mesencephalon turn into?
→mesencephalon→midbrain
what does the rhombencephalon turn into?
→metencephalon→pons and cerebellum
→myelencephalon→medulla oblongata
directions when describing the brain
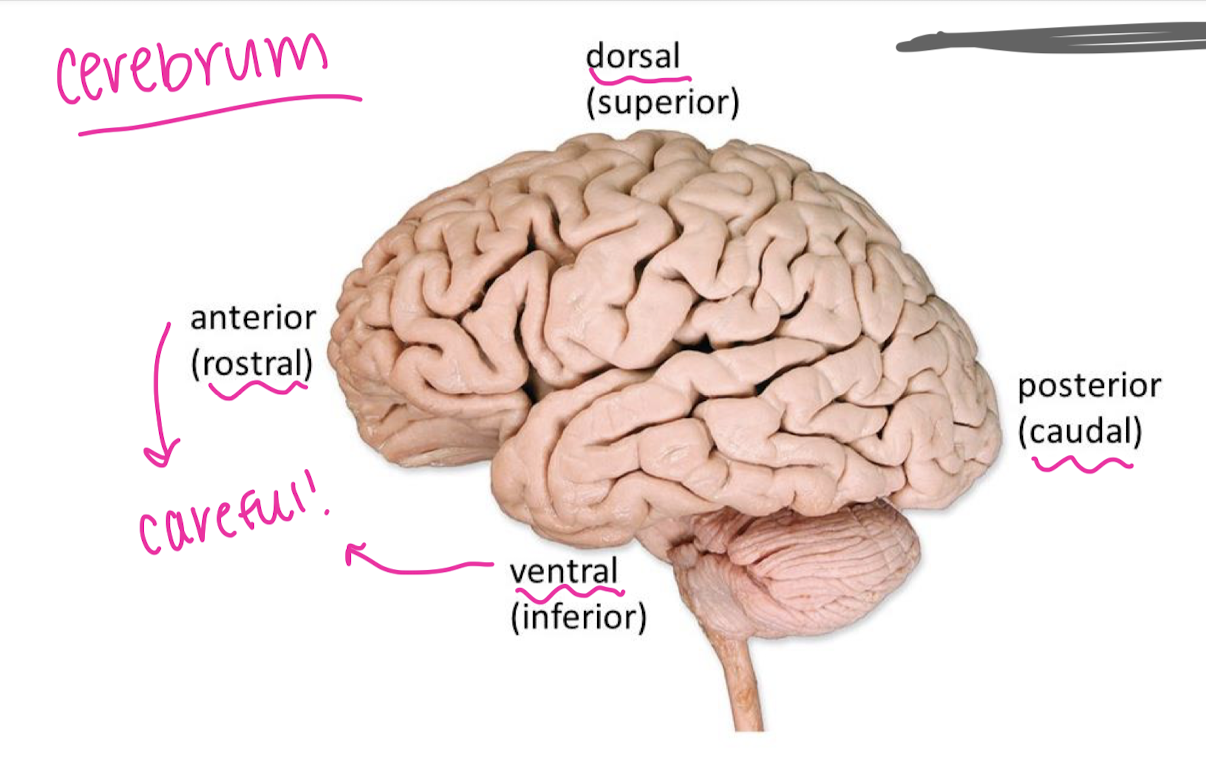
features of the cerebrum
wrinkles are gyri
grooves are sulci
deep grooves are fissures
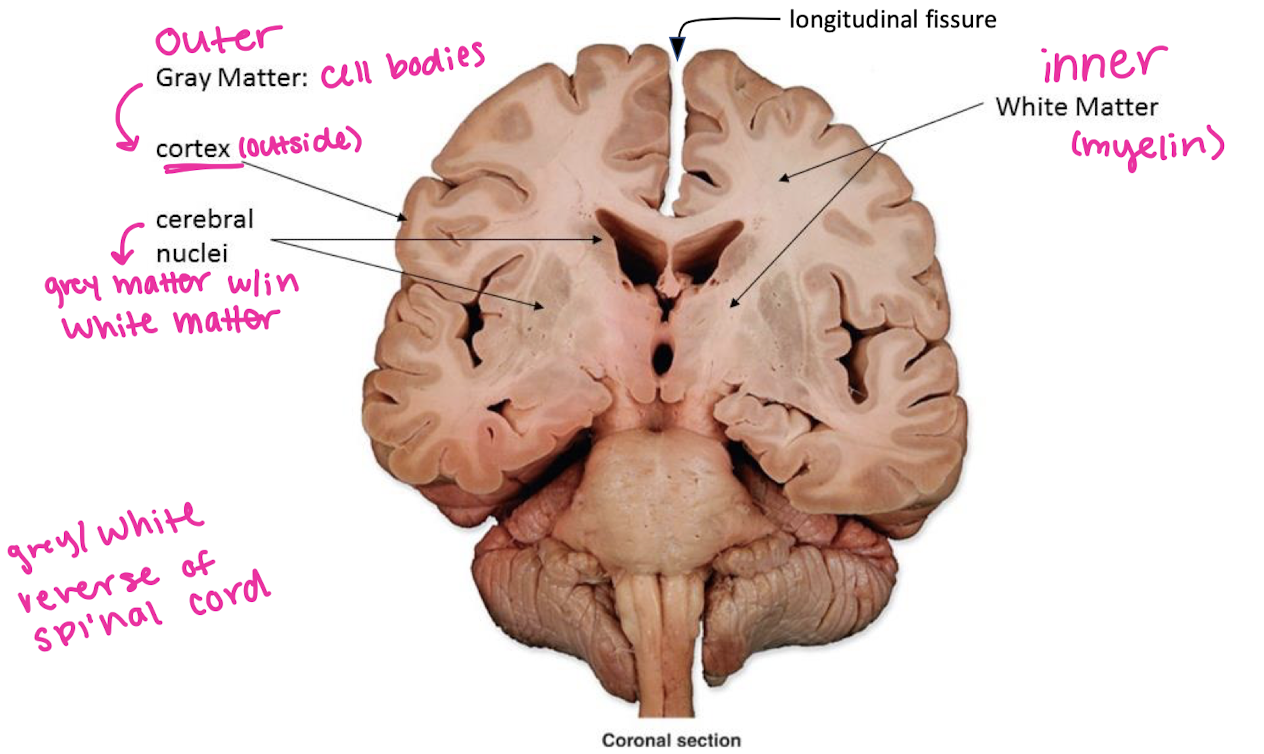
white/grey matter of the brain, cerebral nuclei
pia mater
deepest: adheres to the surface of the brain
arachnoid mater
middle layer: has arachnoid trabeculae, stringlike projections attaching to pia mater
dura mater
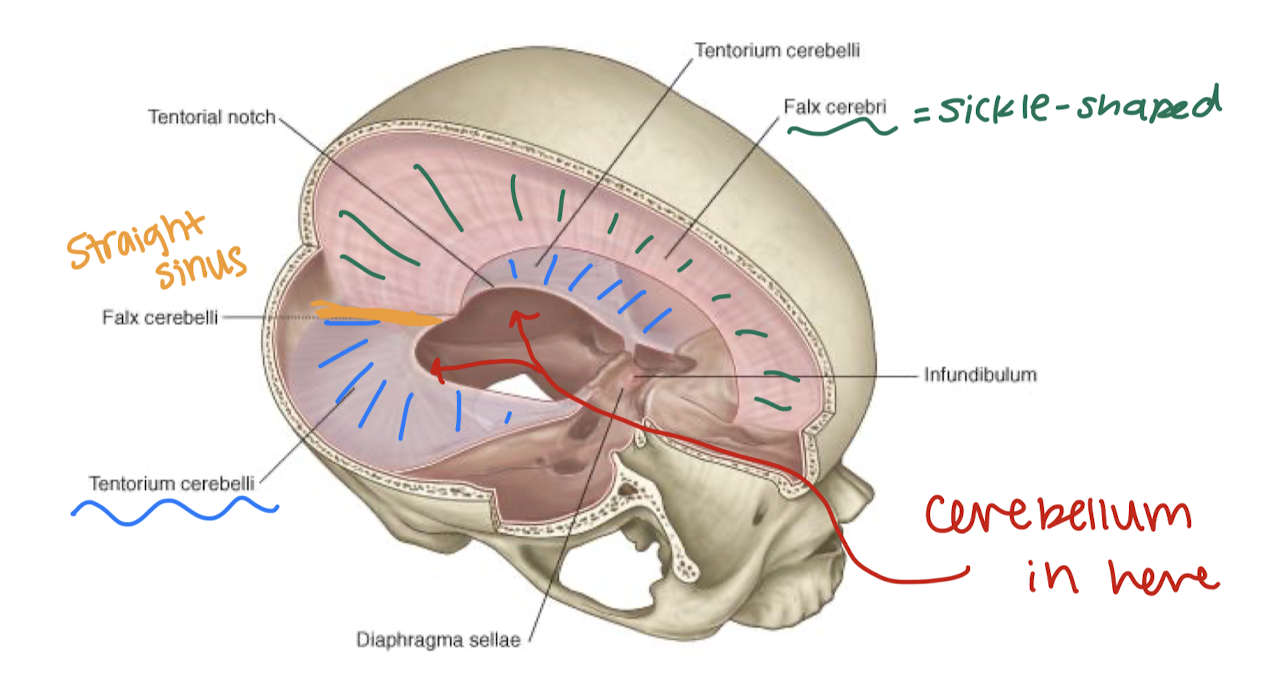
outermost layer, periosteal dura is fused to the inside of the skull, while meningeal dura can peel away from periosteal layer to form structures (fural venous sinuses filled w/ blood)
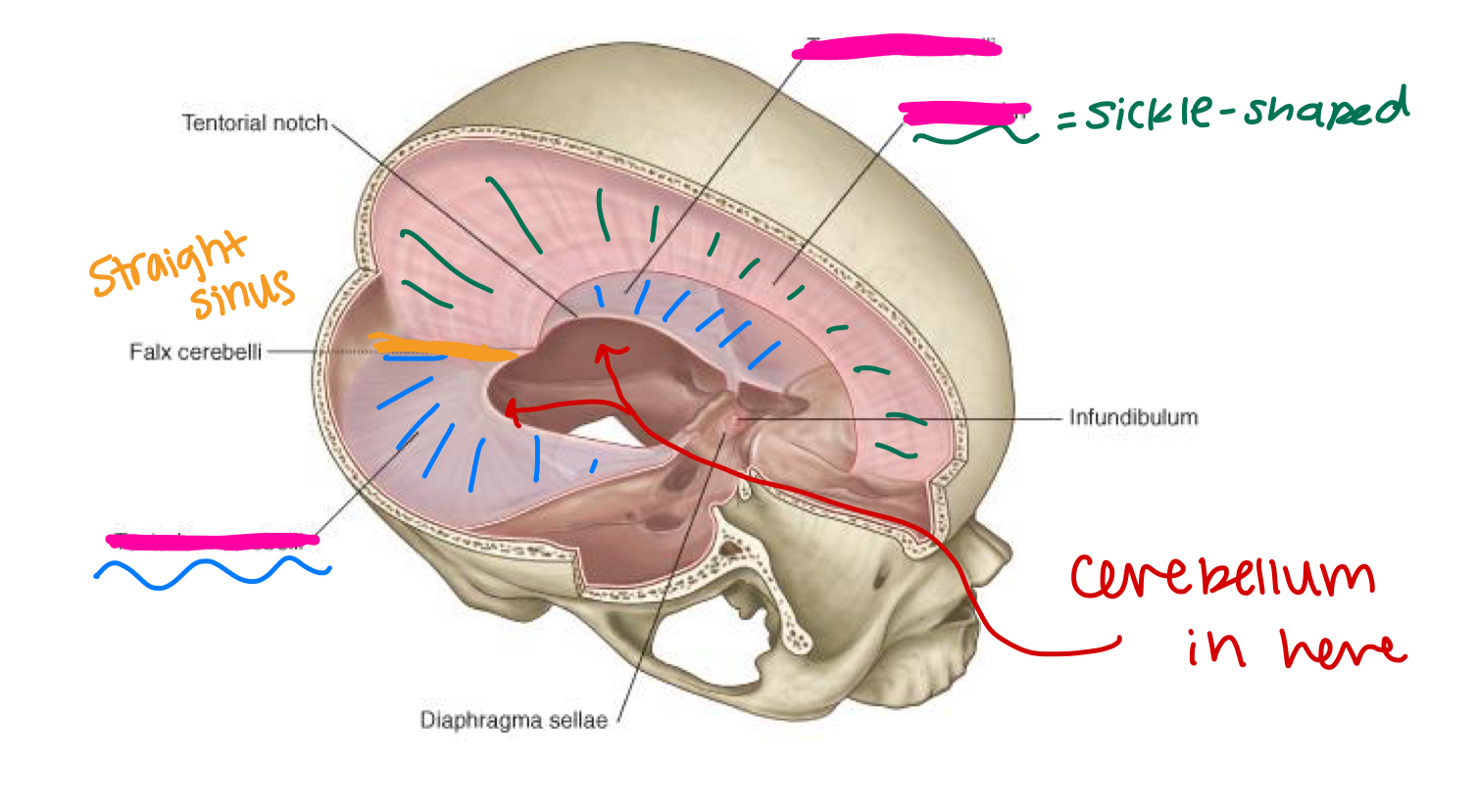
label the missing parts (pink):
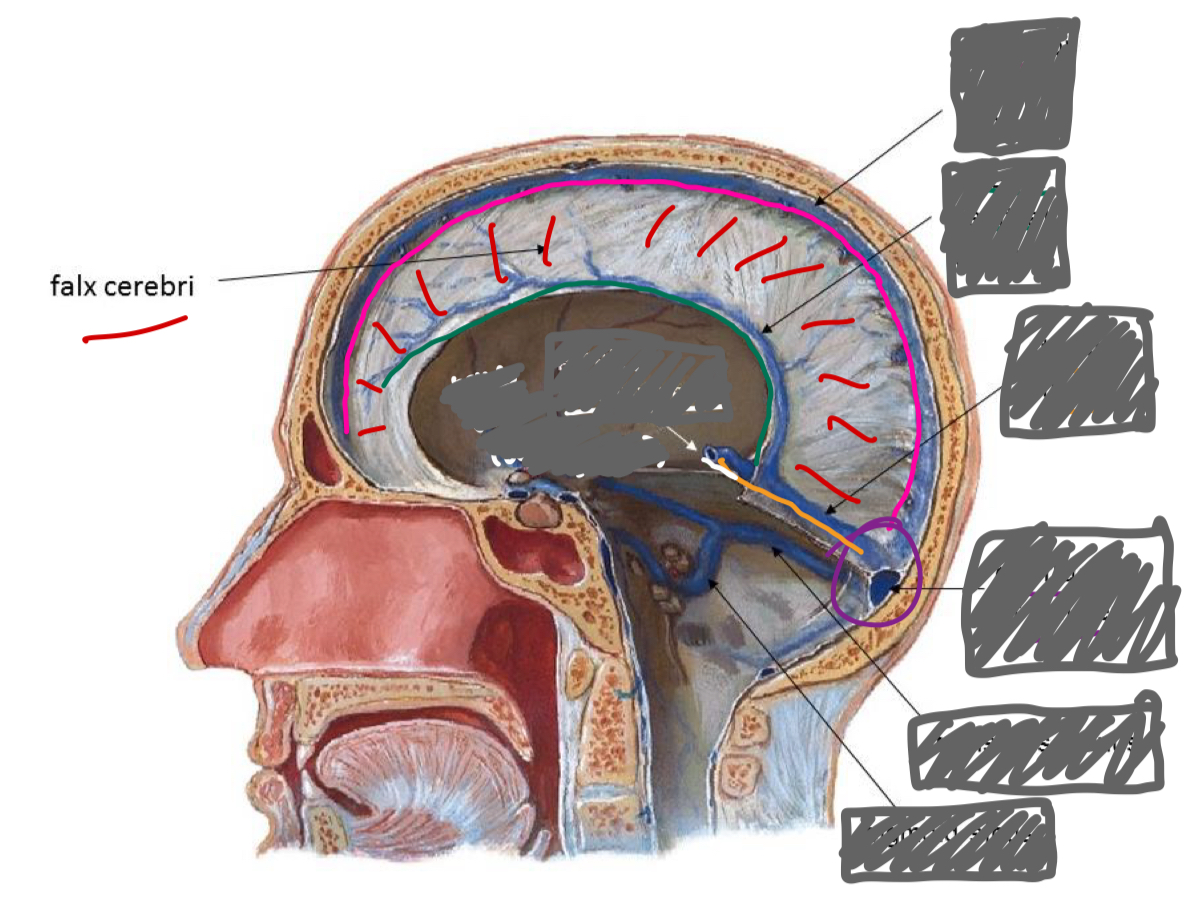
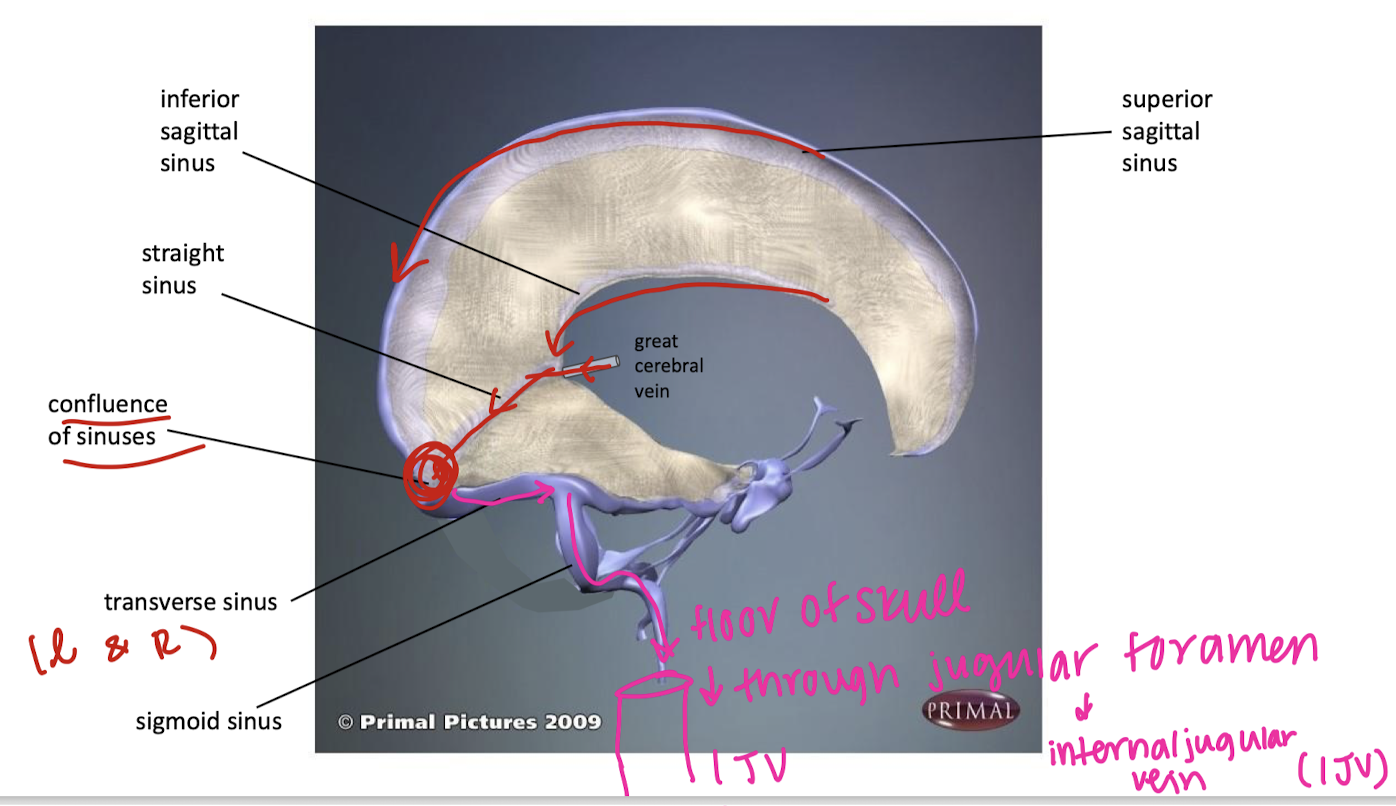
label the sinuses (and vein)
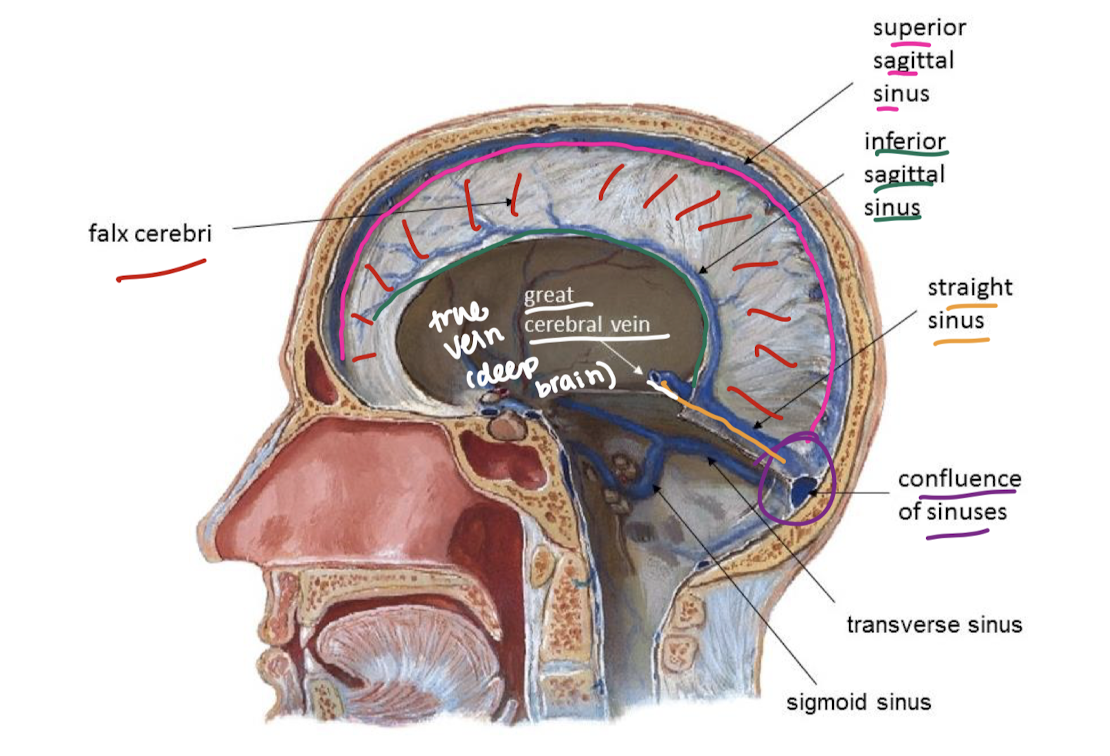
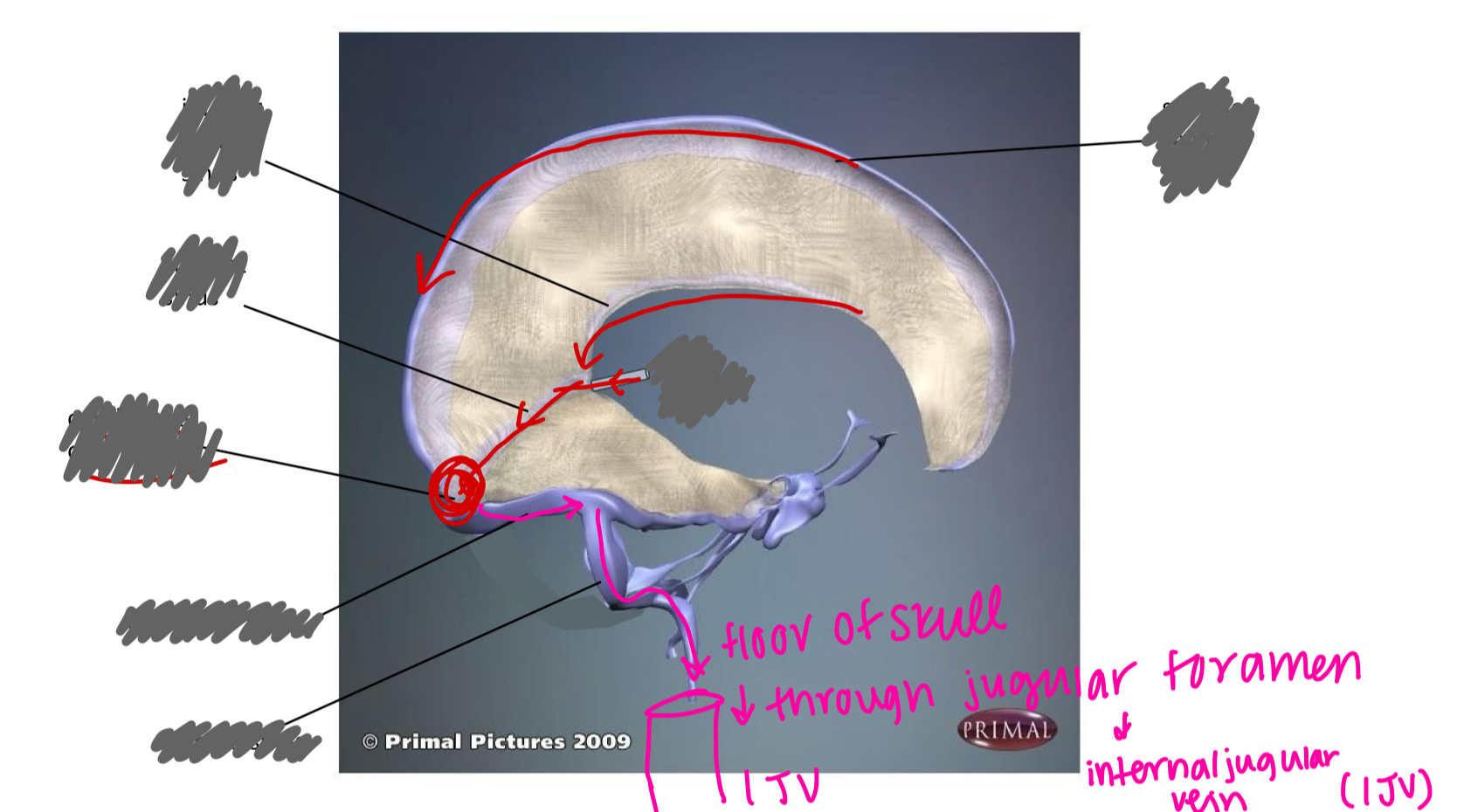
label the sinuses
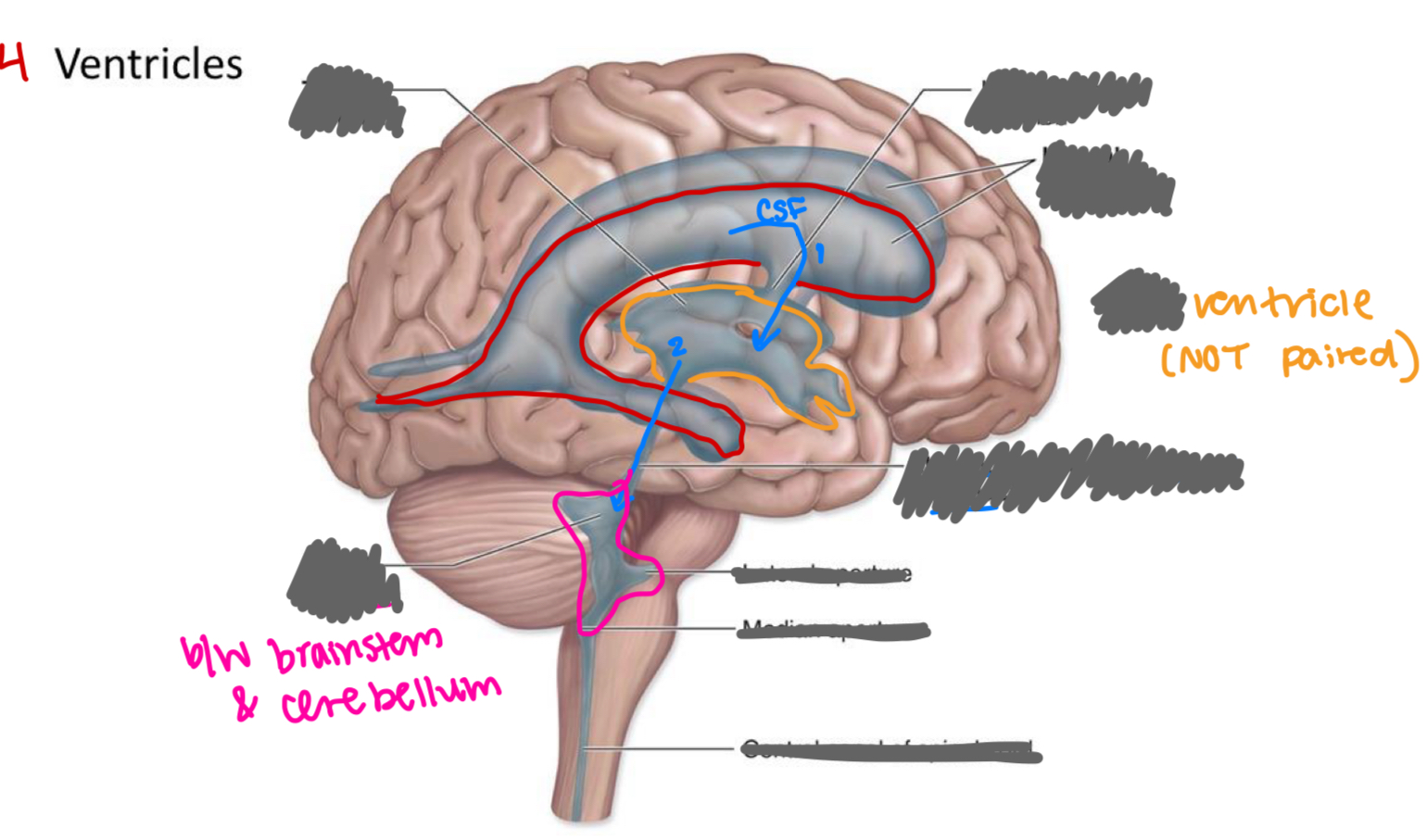
label the ventricles/associated structures
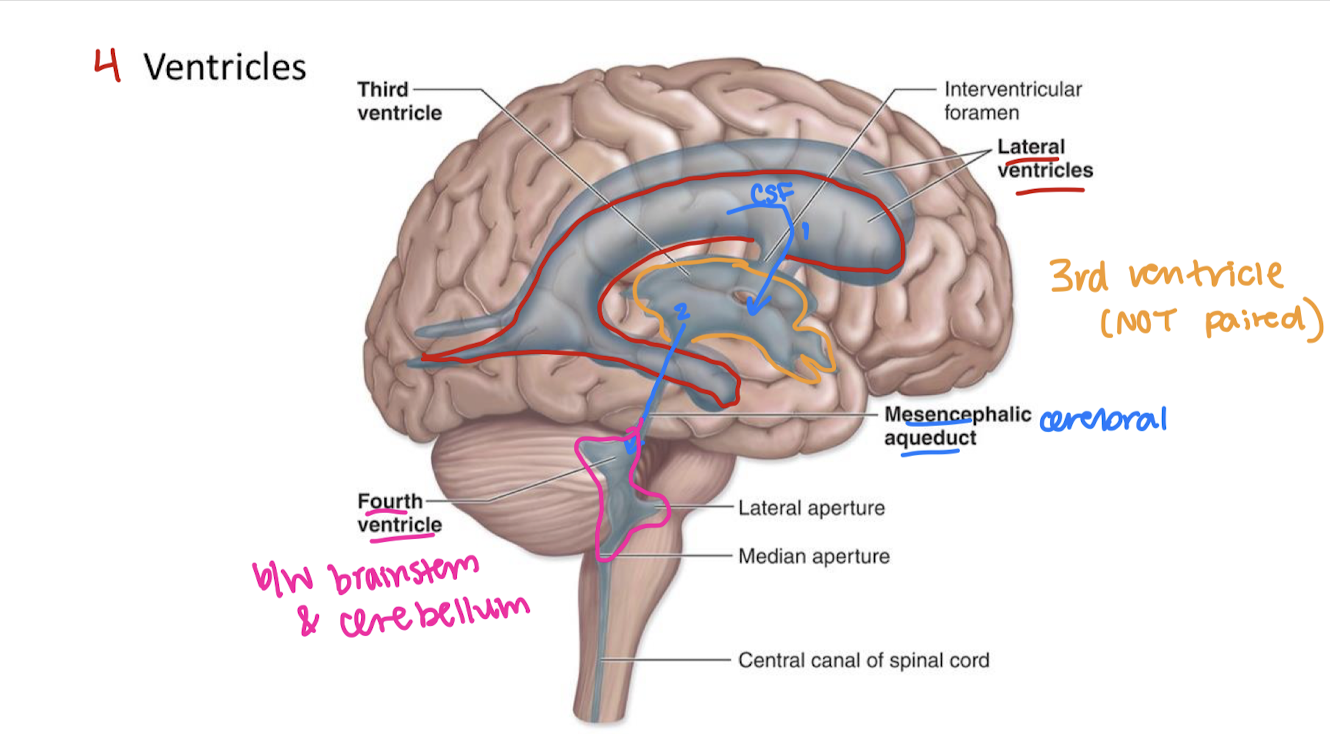
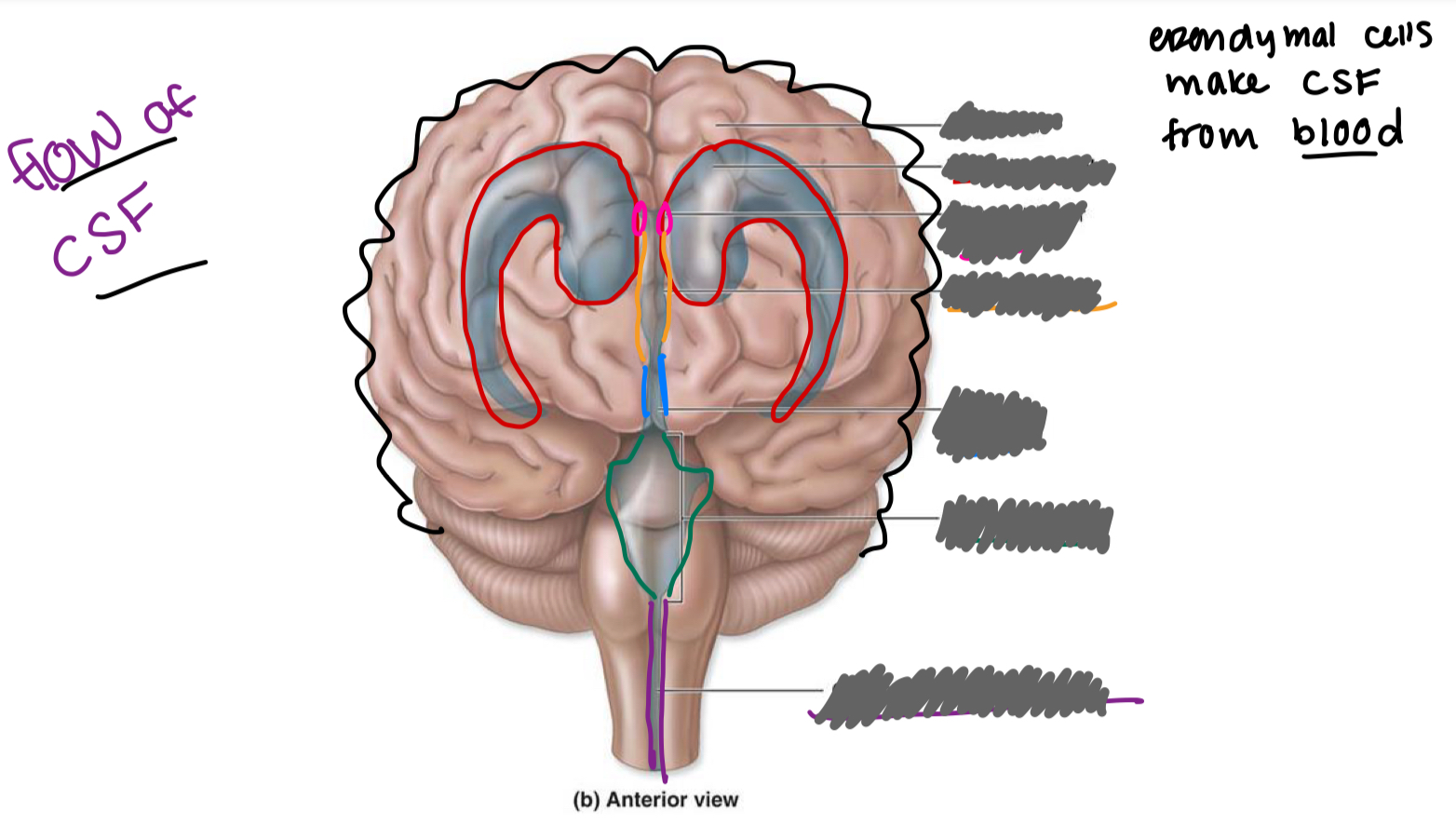
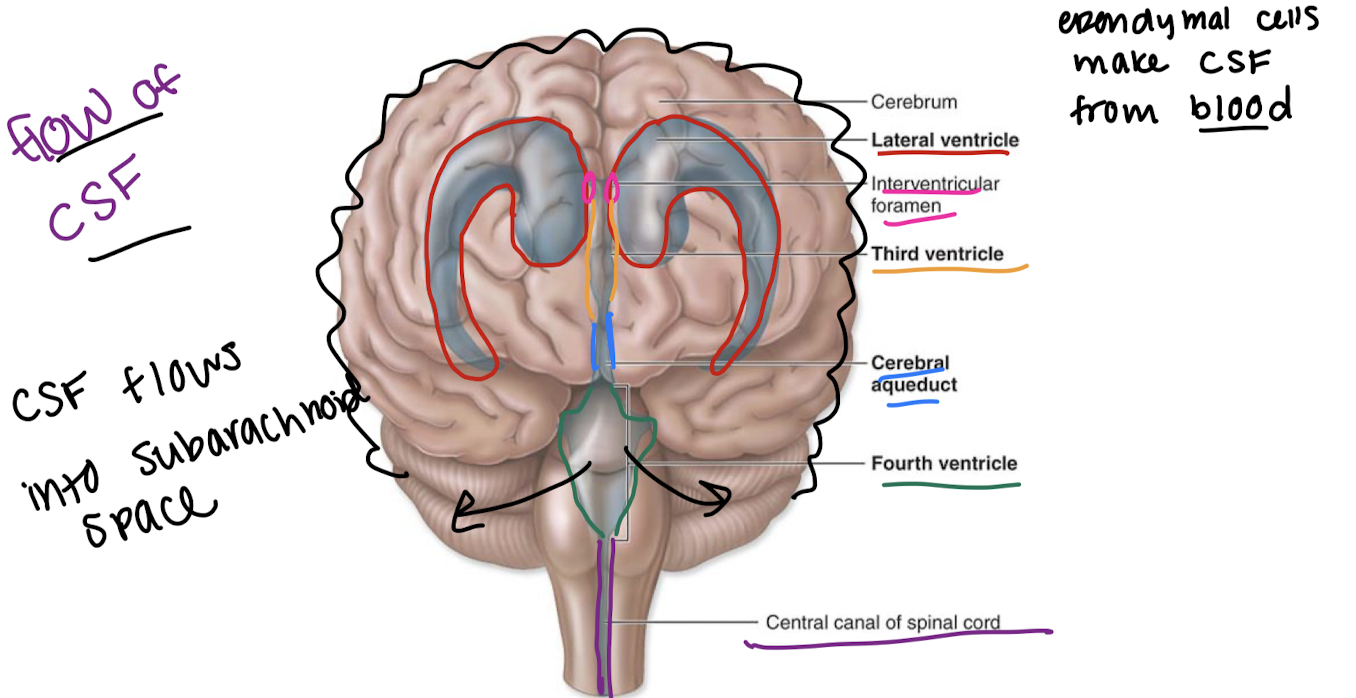
label the ventricles/associated structures and explain the flow of CSF
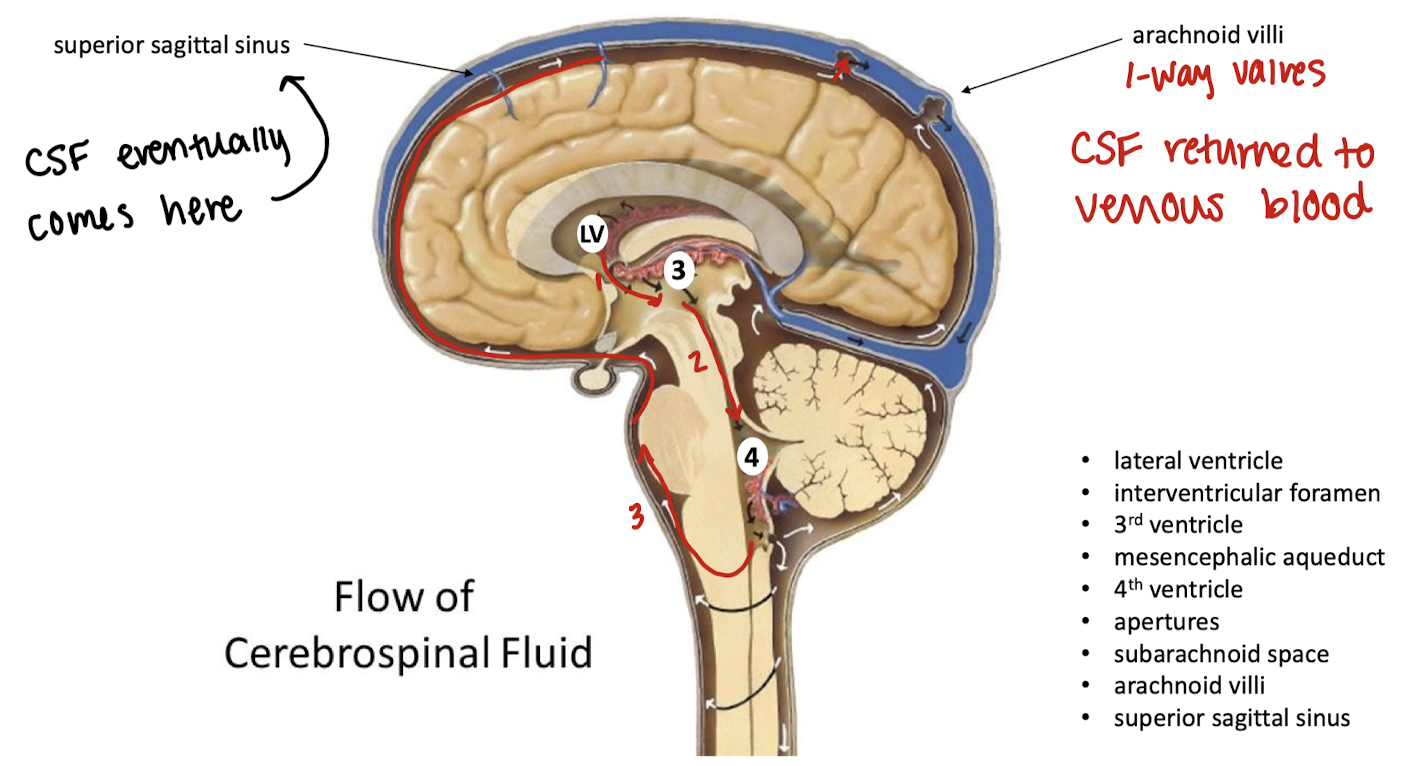
flow of CSF starting point → sinus
name of the groove b/w left and right cerebral hemispheres
longitudinal fissure
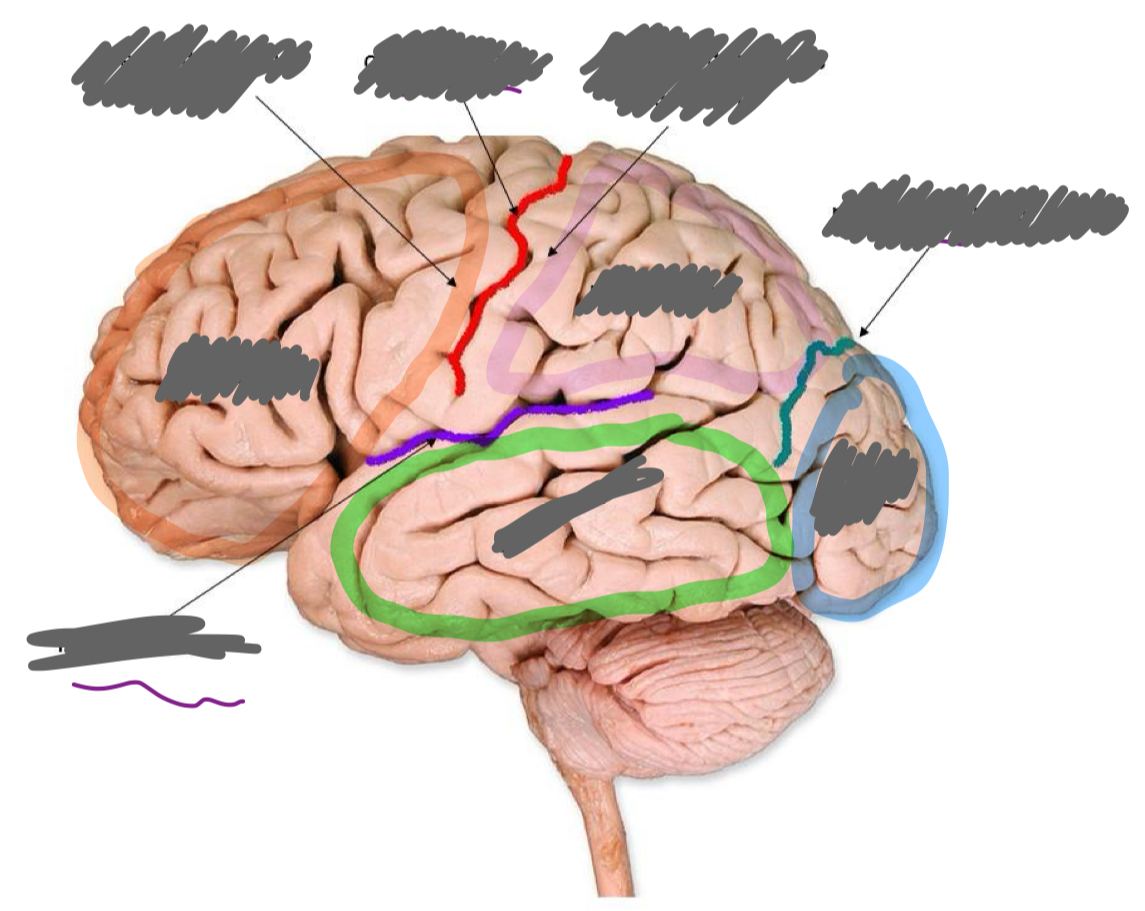
Label the brain parts:
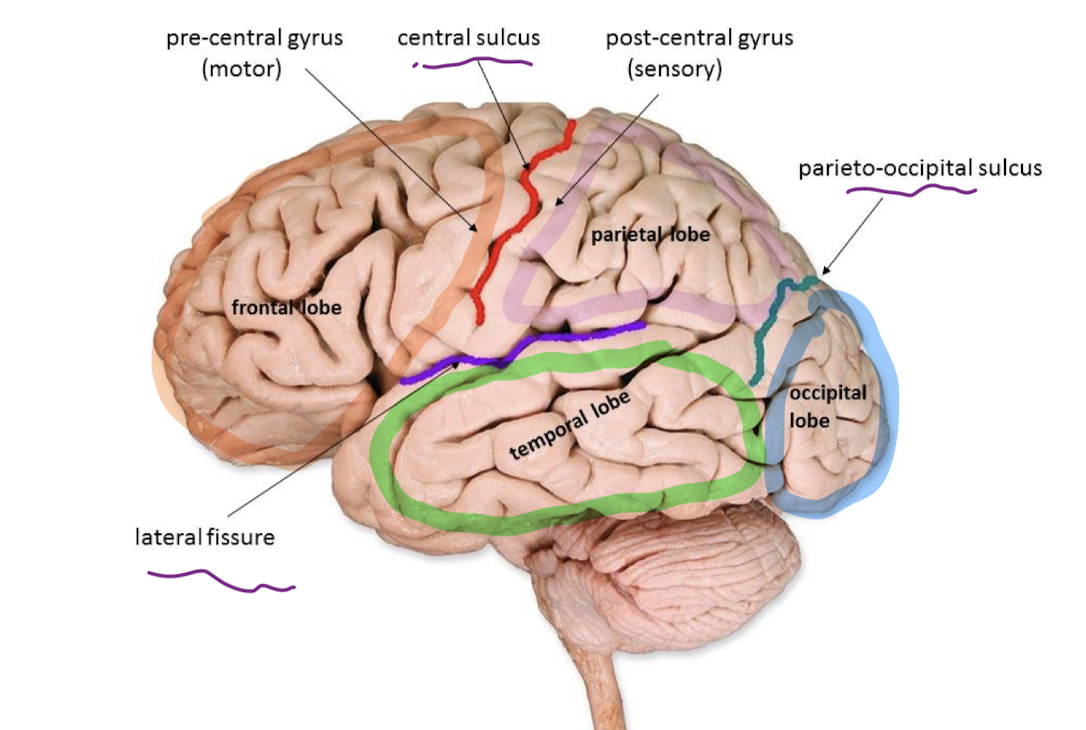
precentral gyrus
controls skeletal muscle on the opposite side of the body
postcentral gyrus
receives sensation from skin on the opposite side of the body
wernicke’s area
in parietal lobe, sensory speech: understand what someone is saying to you
primary visual cortex
at back of occipital lobe, receives info from eyes to allow sight, “projector screen”
primary auditory cortex
mid-superior temporal lobe: hearing
primary olfactory cortex
frontal superior temporal lobe: smell
broca’s area
in frontal lobe, motor speech: speak in a way that makes sense
what separates the frontal and parietal lobes?
central sulcus
what separates parietal and occipital lobes?
parieto-occipital sulcus
what separates frontal/parietal lobes from temporal lobe?
lateral fissure
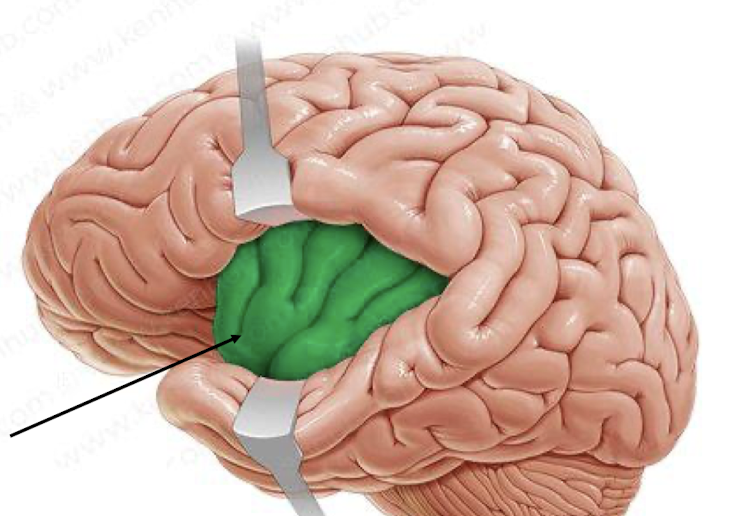
insula: taste, awareness of self, perception of pain
left cerebral hemisphere functions
right side motor control
spoken and written language
numerical and scientific skills
reasoning
right cerebral hemisphere functions
left side motor control
musical/artistic awareness
space and pattern perception
insight
imagination
mental images
tracts
bundles of axons that connect different parts of the brain
association tracts
connect different parts of the same hemisphere
commissural tracts
connect one hemisphere to another (I.e. corpus callosum)
projection tracts
project from cerebral hemispheres down to brainstem and spinal cord
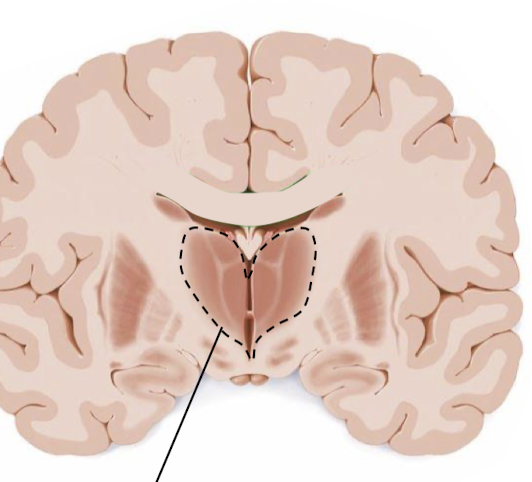
what structure is this?
thalamus
3 major parts of the diencephalon
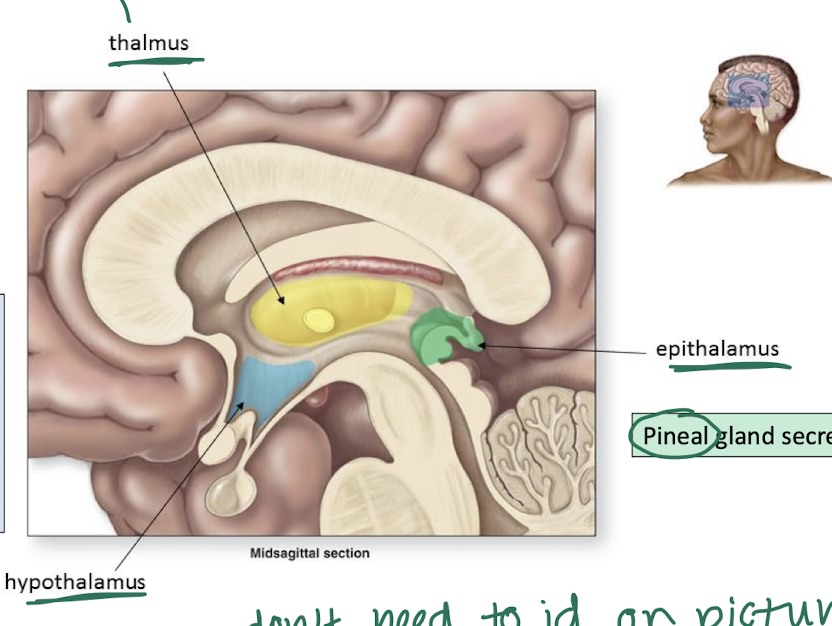
thalamus
relays somatosensation (sensation we are aware of) to proper lobe of cerebral cortex
hypothalamus
controls ANS
controls endocrine system
reg. body temp
controls emotion
thirst & hunger
circadian rhythm
epithalamus
pineal gland secretes melatonin
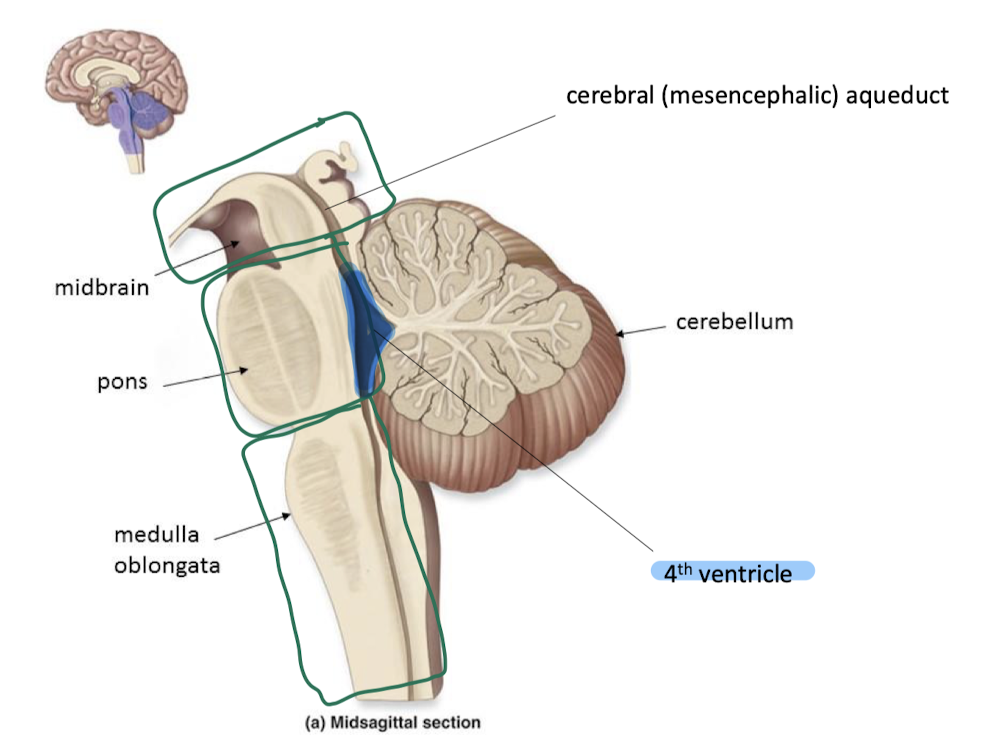
parts of the brainstem
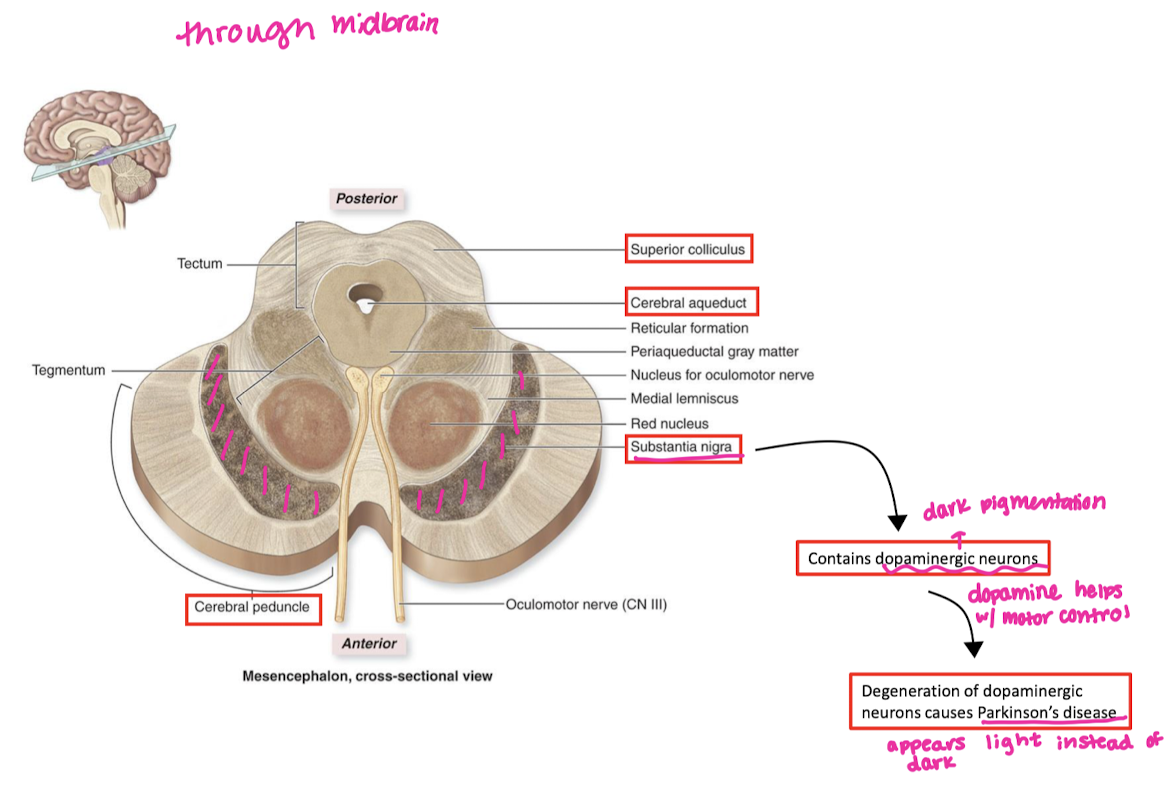
Midbrain features and functions
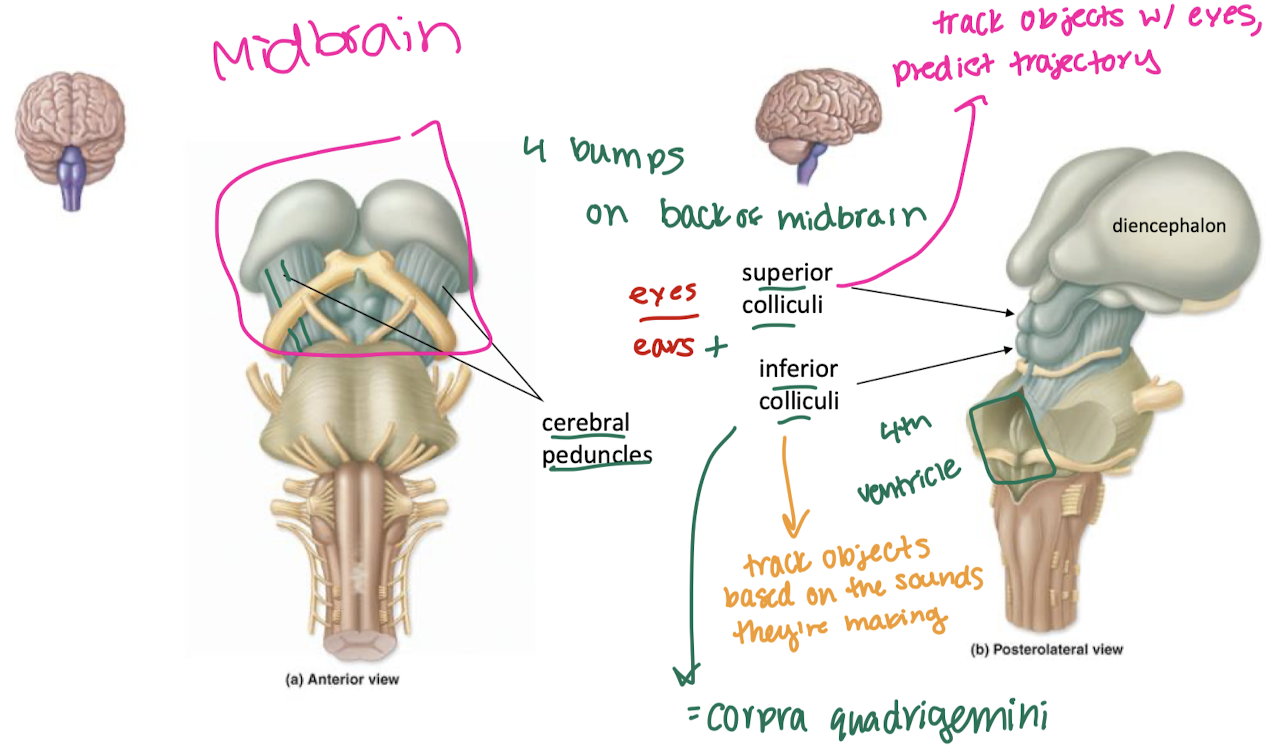
superior colliculi
track objects w/ eyes, predict trajectory
inferior colliculi
track objects based on the sounds they make
substantia nigra
cerebellum
perform actions with great precision
process cerebrum’s signals and smooth them out
damage→ataxia (jerky movement)
pons
(middle of brainstem)
respiratory control
medulla oblongata
(bottom of brainstem) cardiac and respiratory control
Cranial nerve name mnemonic
oh once one takes the anatomy final very good vacations are heavenly

cranial nerve motor, sensory, or both mnemonic
some say marry money but my brother says big business makes money
CN I
olfactory nerve
smell, receptors on roof of nasal cavity
CN I passage through skull
cribiform plate of ethmoid bone
CN II
optic nerve
vision, receptors in retina of eye (info projected to same and opposite side of the brain)
CN II pathway through skull
optic foramen
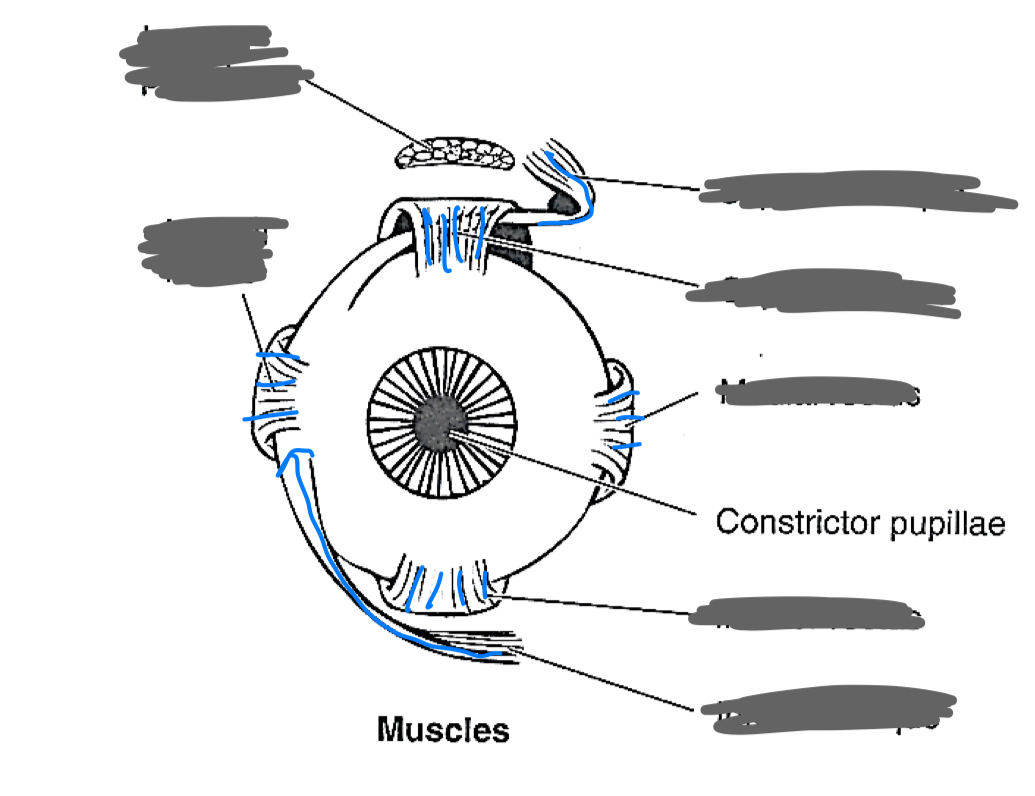
label the eye muscles
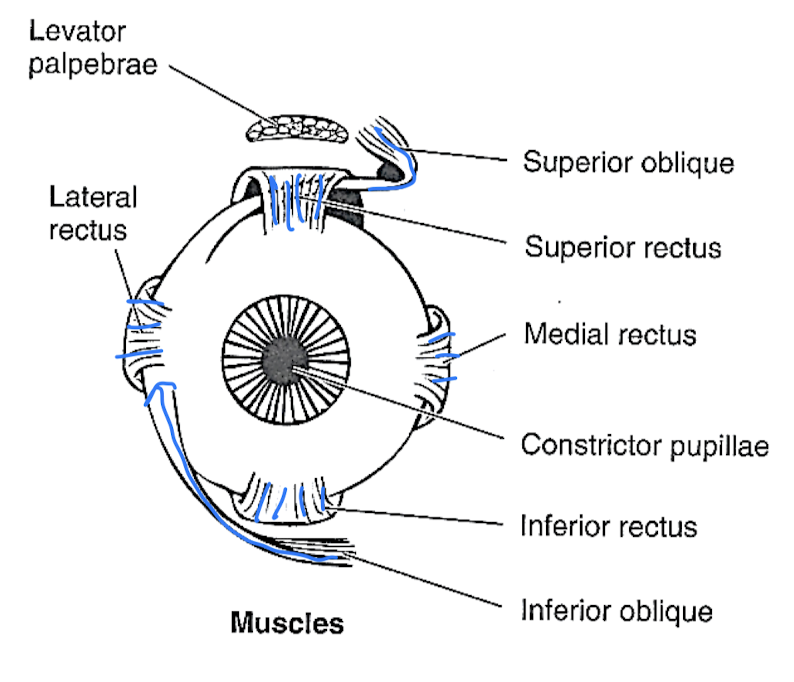
how to remember which cranial nerves control which eye muscles
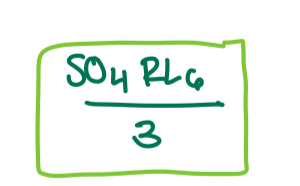
how does the inferior oblique move the eye?
up and out
how does superior rectus move the eye?
up and in
how does the medial rectus move the eye?
inward
how does the inferior rectus move the eye?
down and in
how does the superior oblique move the eye?
down and out
how does the lateral rectus move the eye?
outward
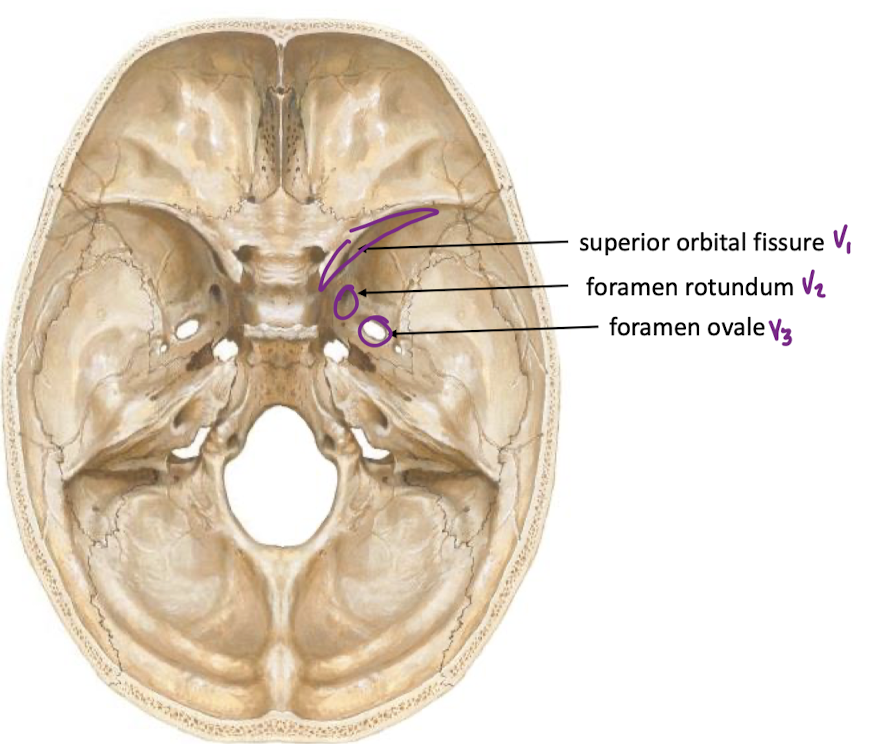
how do cranial nerves III, IV, and VI reach the orbit?
superior orbital fissure
CN III
oculomotor nerve:
superior rectus
levator palpebrae superioris
medial rectus
inferior rectus
inferior oblique
CN IV
trochlear nerve: superior oblique
CN VI
abducens nerve: lateral rectus
CN V-1
opthamalic branch of trigeminal nerve:
forehead and nose skin sensation
cornea sensation
CN v-1 skull pathway
superior orbital fissure
CN V-2
trigeminal - maxillary branch
sensation of skin b/w inferior eyelid and mouth
sensation from upper teeth
CN V-2 Pathway through skull
foramen rotundum
CN V-3
mandibular trigeminal
skin around mandible sensation
sensation from lower teeth
general (touch) and special (taste) sensation from tongue
somatic motor to muscles of mastication
only V-3 has motor!
CN V-3 pathway through skull
foramen ovale
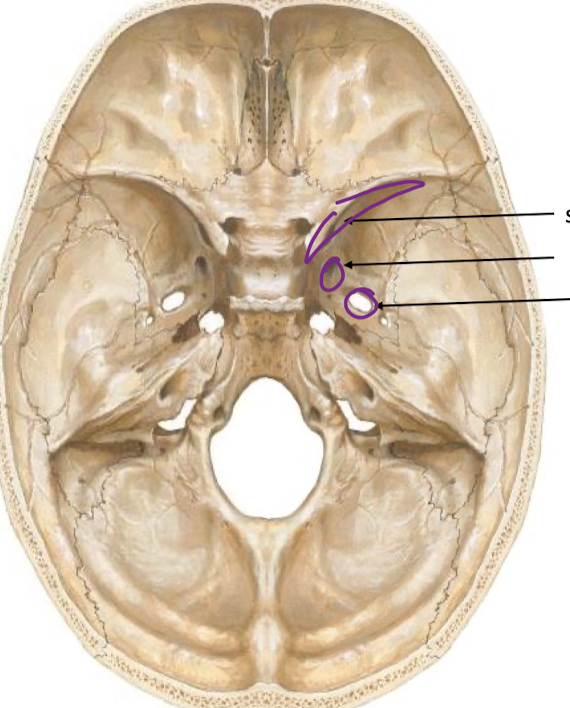
label pathways and which trigeminal branches pass through them
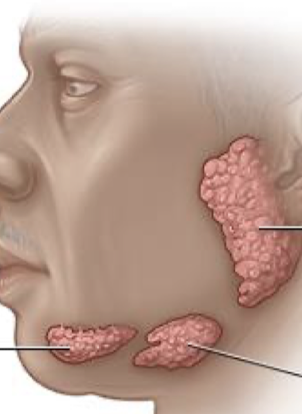
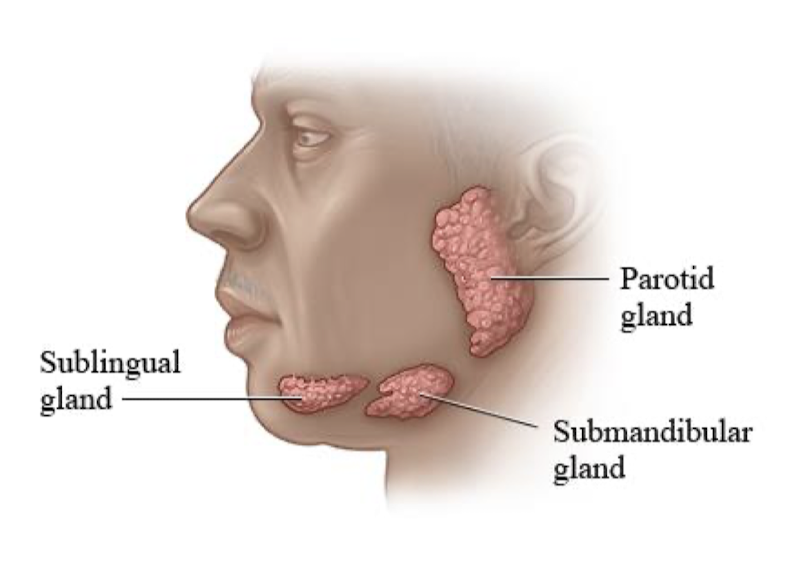
label the salivary glands