Chemistry of Life: Atoms, Bonds, and Macromolecules
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Matter
Anything occupying space and having mass.
States of Matter
Three physical forms: solid, liquid, gas.
Elements
Substances that cannot be chemically broken down.
Molecules
Substances of two or more elements combined.
Atoms
Smallest unit retaining chemical properties of an element.
Atomic Structure
Nucleus contains protons and neutrons; electrons orbit.
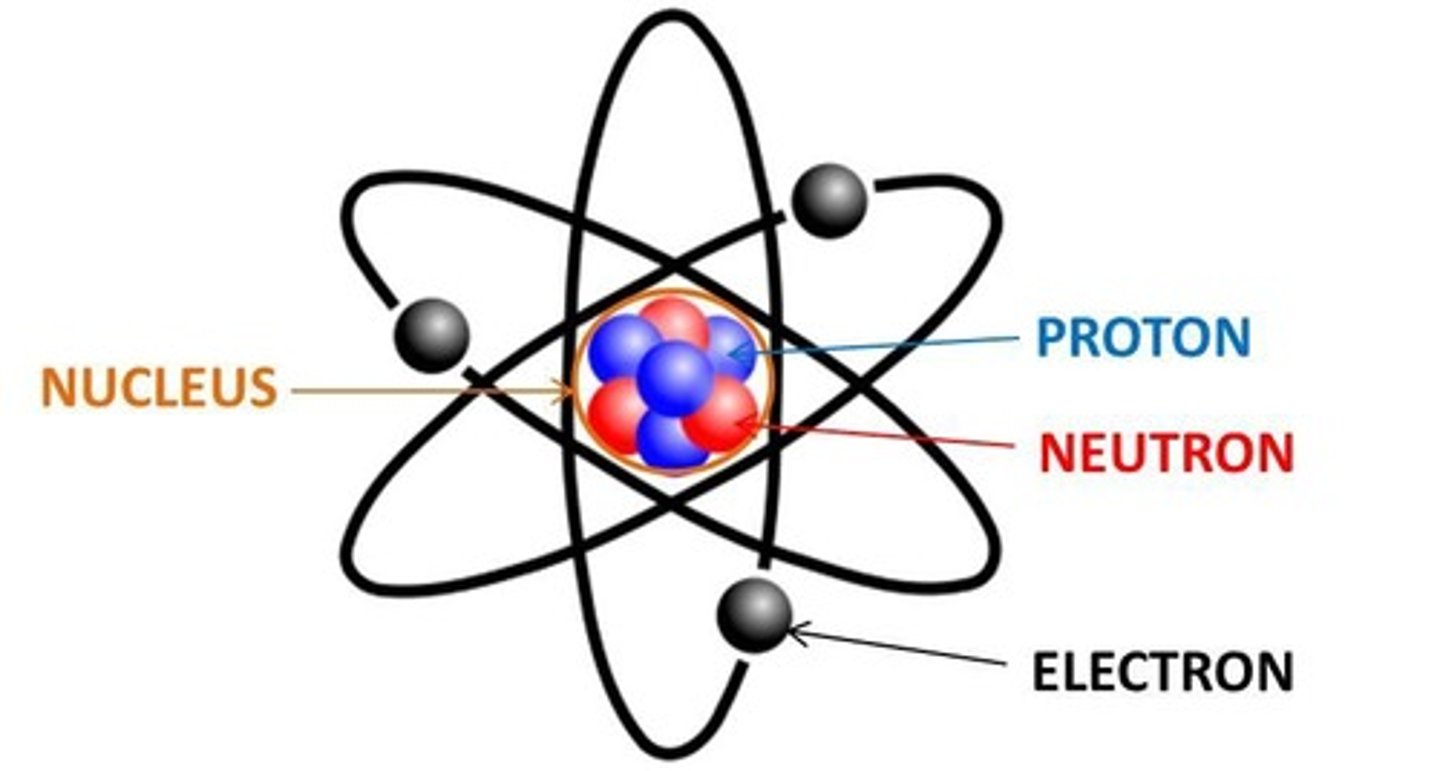
Protons
Positively charged particles in an atom's nucleus.
Neutrons
Neutral particles in an atom's nucleus.
Electrons
Negatively charged particles in electron shells.
Valence Electrons
Outer electrons determining chemical behavior.
Atomic Number
Number of protons defining an element.

Mass Number
Sum of protons and neutrons in nucleus.
Isotopes
Variants of elements with different neutron counts.
Carbon-14
Isotope used for dating up to 50,000 years.
Essential Elements of Life
25 elements found in the human body.
Top 10 Elements
Oxygen, Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Calcium, Phosphorus, Potassium, Sulfur, Sodium, Chlorine.
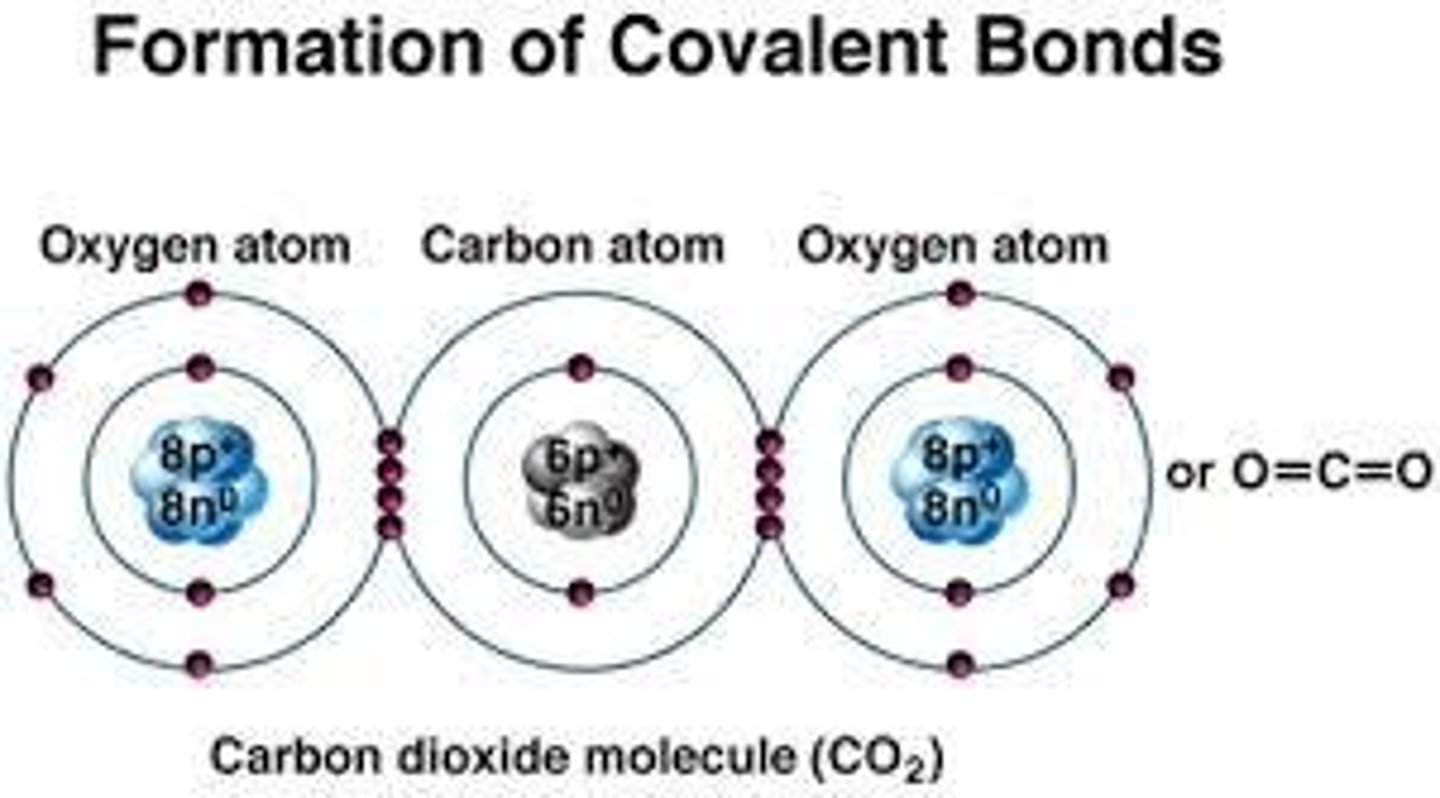
Covalent Bonds
Atoms share pairs of valence electrons.
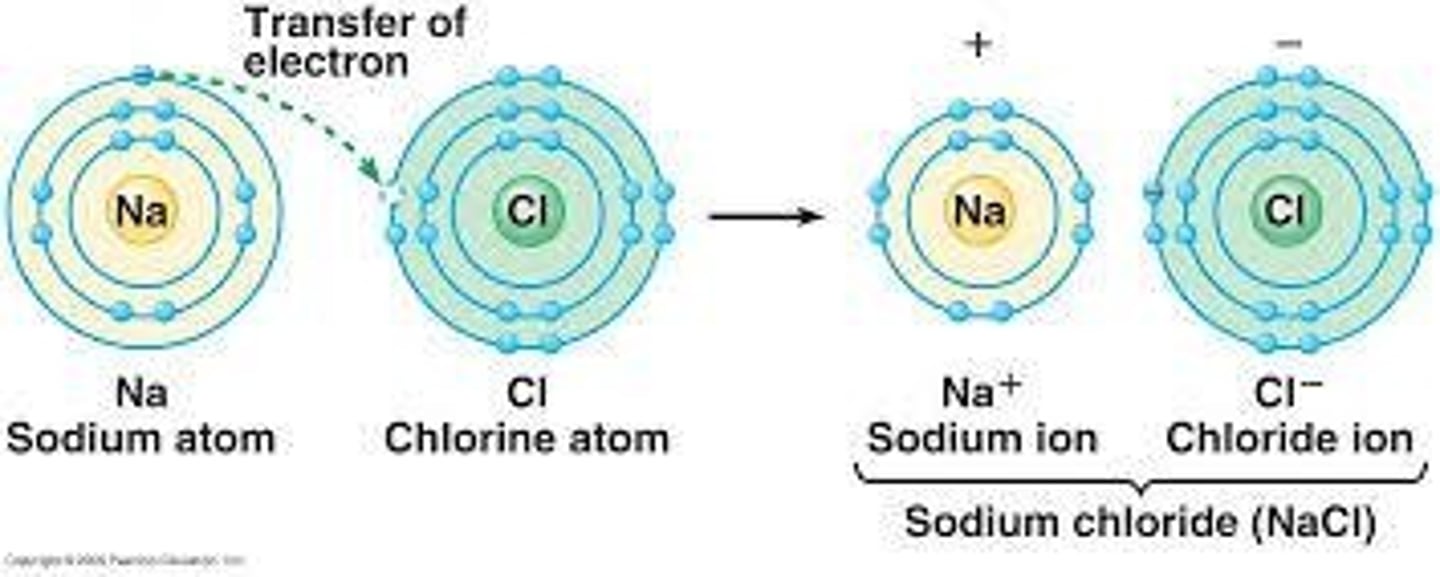
Ionic Bonds
Attraction between oppositely charged ions.
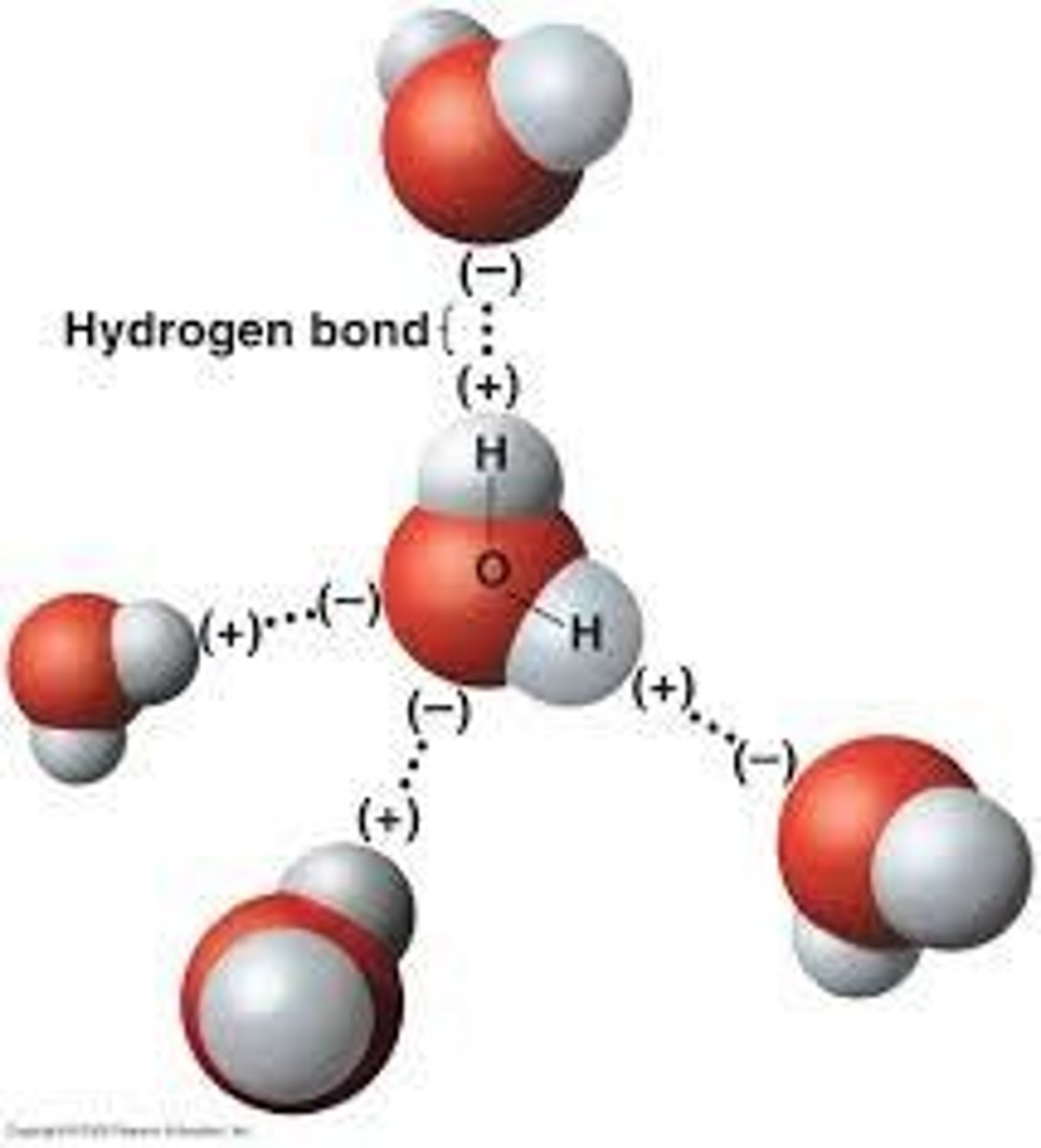
Hydrogen Bonds
Weak attraction between neighboring charged molecules.
Monosaccharides
Single sugar molecules, simplest carbohydrates.
Disaccharides
Two monosaccharides linked together.
Polysaccharides
More than two monosaccharides linked.
Triglycerides
Fat molecules with glycerol and fatty acid tails.
Phospholipids
Molecules forming cellular membranes.
Proteins
Large molecules made of amino acid chains.
Amino Acids
Building blocks of proteins, 20 types exist.
Enzymes
Proteins that catalyze biochemical reactions.
Competitive Inhibition
Inhibitor competes with substrate for active site.
Non-competitive Inhibition
Inhibitor alters enzyme shape, preventing substrate binding.