GCE O Level Biology: Definitions of Keywords from Nutrition in Humans, Respiration and Excretion
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
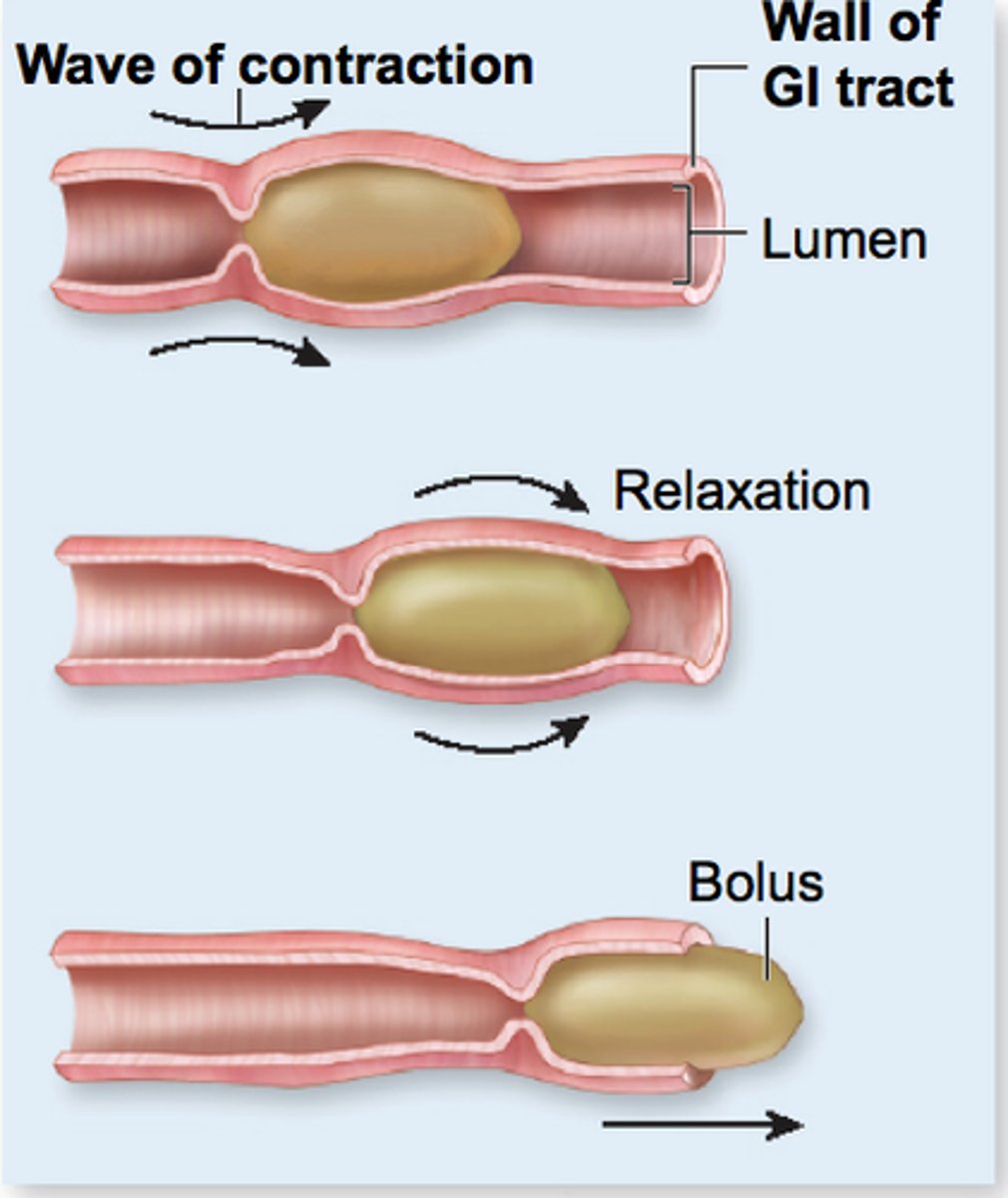
Peristalsis
Rhythmic wave-like contractions of the wall of the gut caused by alternate contractions of the circular and longitudinal muscles in the walls to help push food along the gut
Emulsification of fats
Occurs when bile breaks big blobs of fat into smaller fat droplets
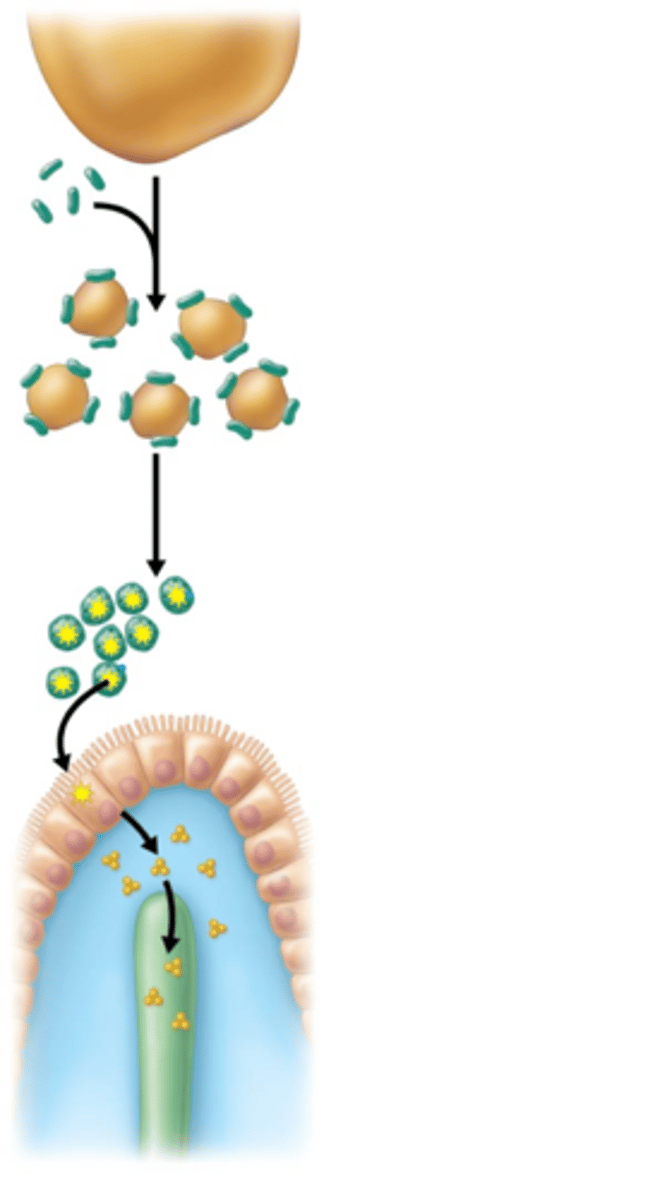
Egestion
Removal of undigested food from the body
Deamination
Process of removing amino groups from excess amino acids and converted to urea, and occurs in the liver
Detoxification
Process of converting harmful substances into harmless substances
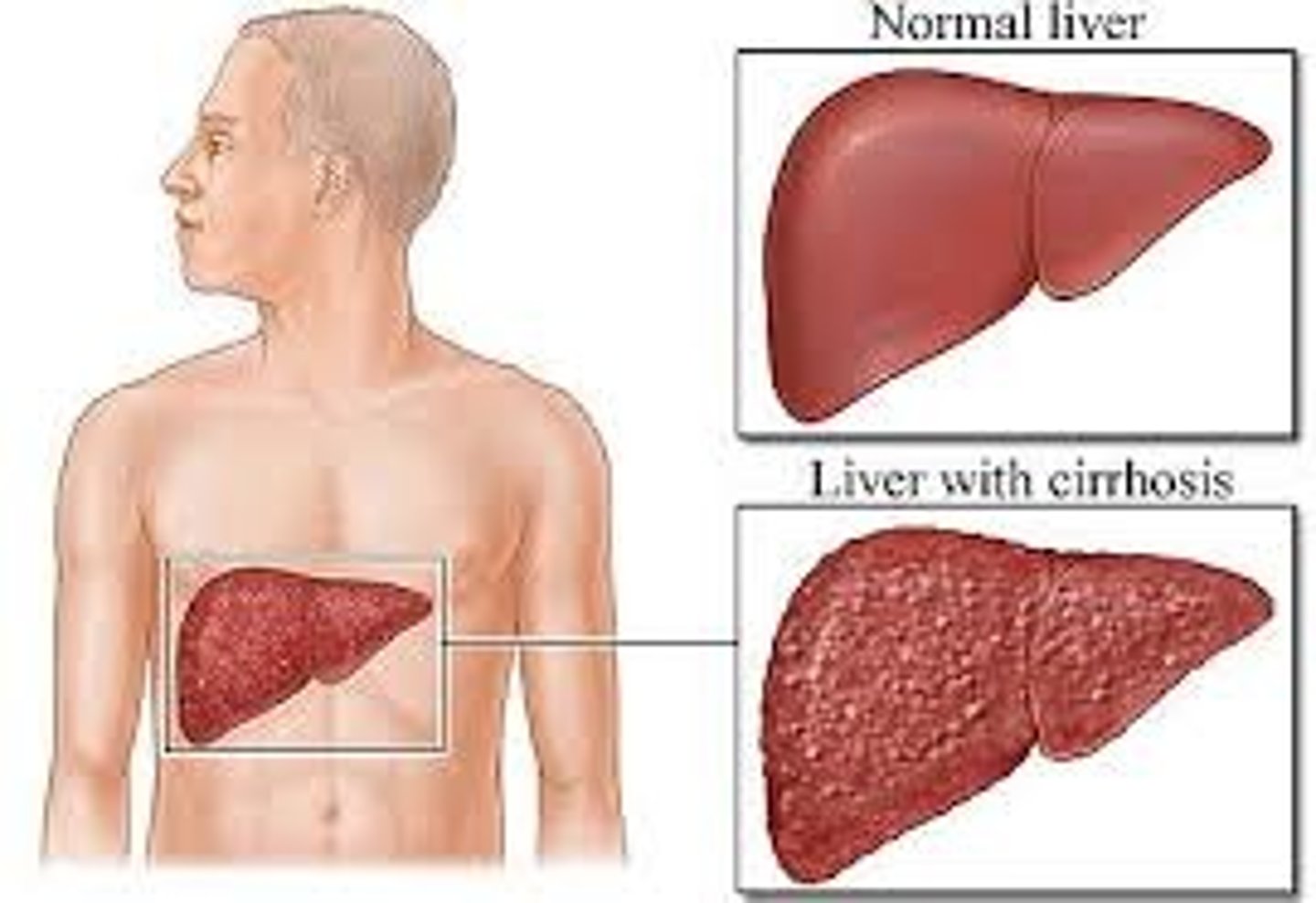
Cirrhosis of the liver
Disease where liver cells are destroyed and are replaced with fibrous tissue
Respiration
Oxidation of food substances with the release of energy in living cells
Aerobic respiration
Oxidation of food substances in living cells, in the presence of oxygen, with the release a large amount of energy. Carbon dioxide and water are released as waste products.

Anaerobic respiration
Breakdown of food substances in the absence of oxygen. Less energy is released than aerobic respiration.
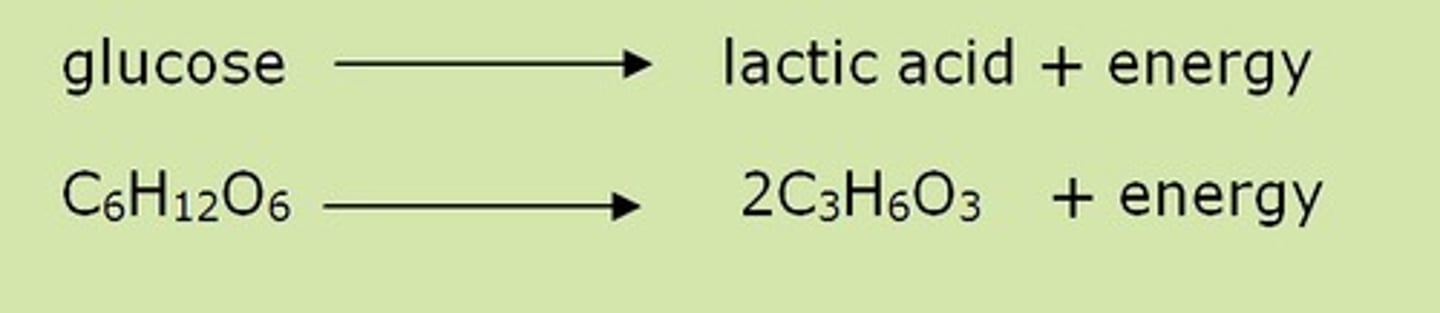
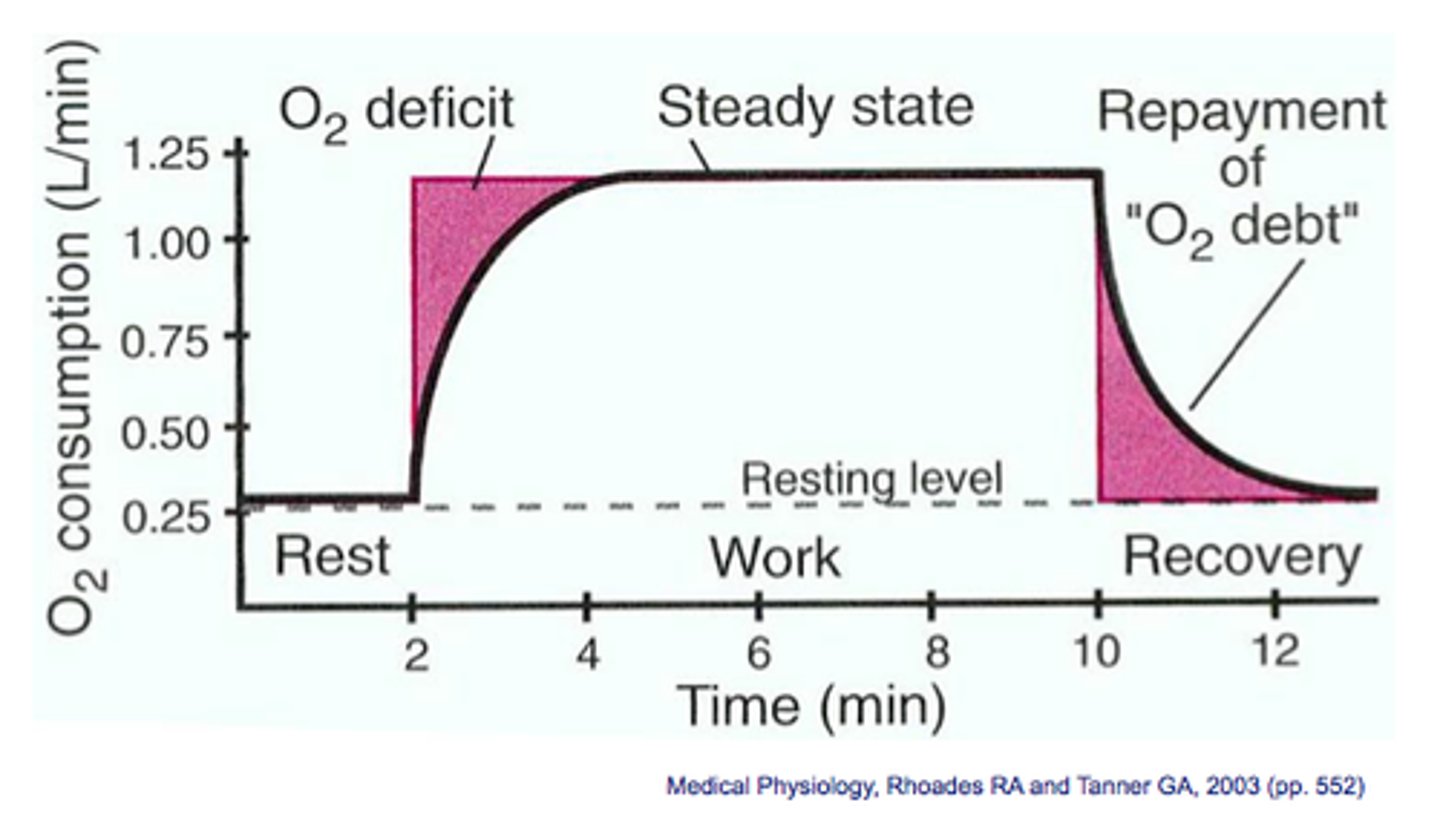
Oxygen debt
Amount of oxygen required to oxidise lactic acid produced in muscles during anaerobic respiration
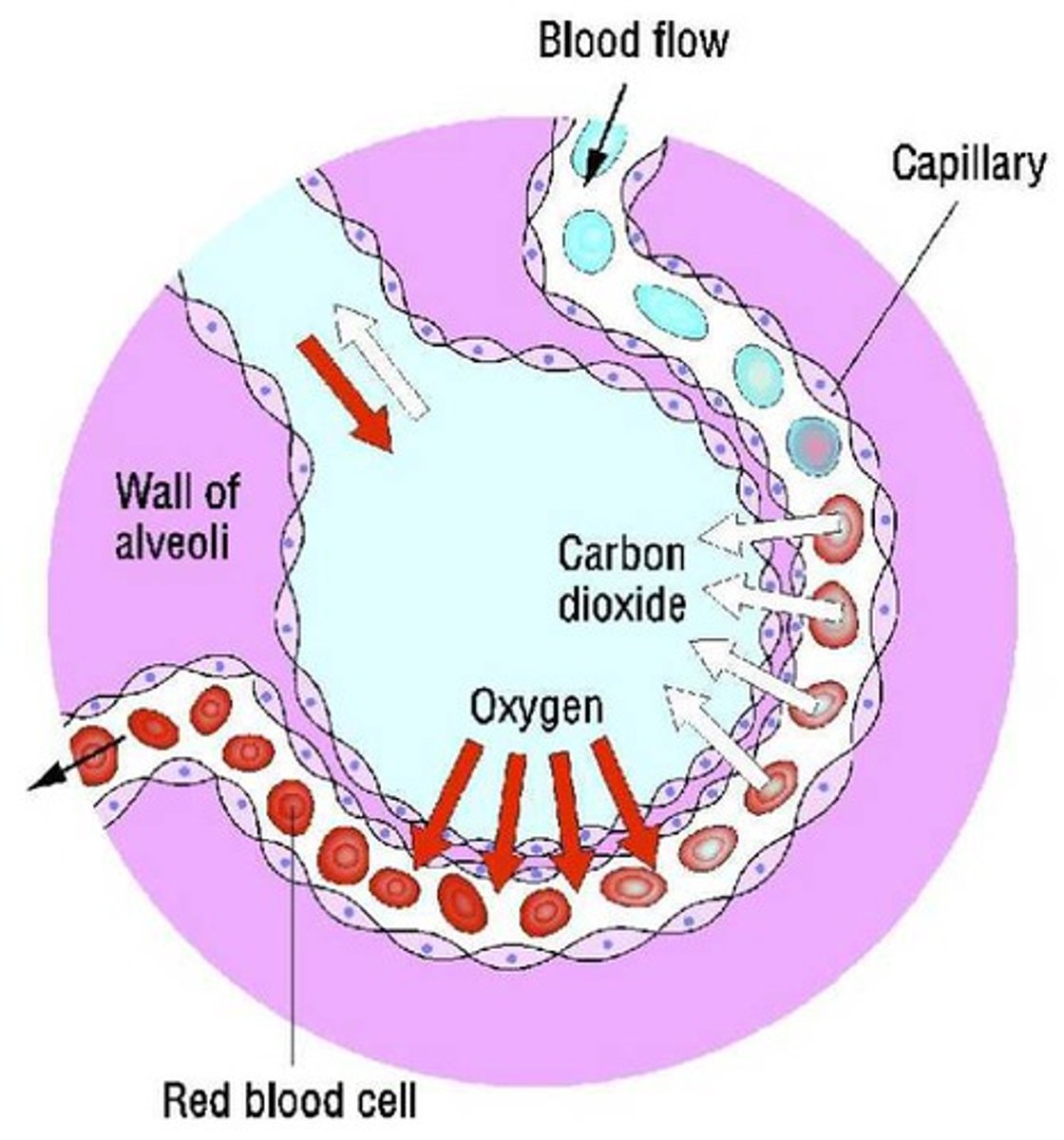
Gaseous exchange
Exchange of gases between an organism and the environment
Inhalation / inspiration
Taking in of air
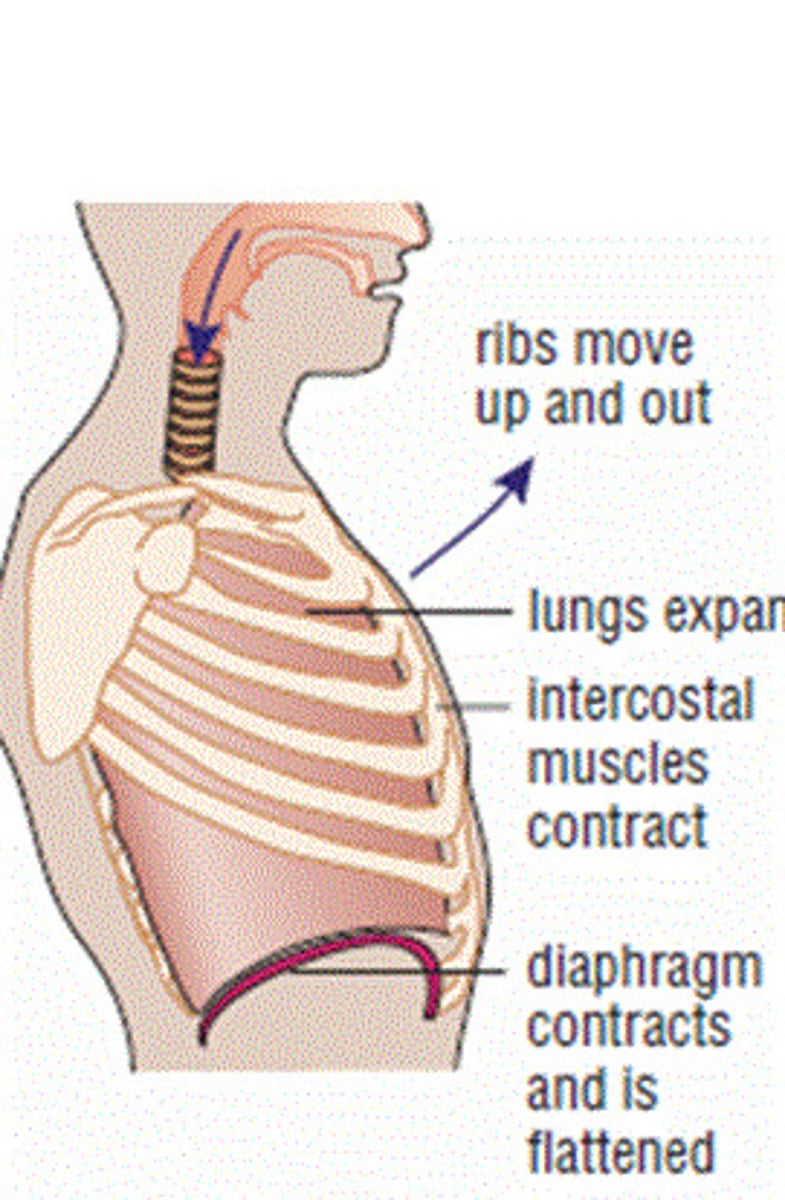
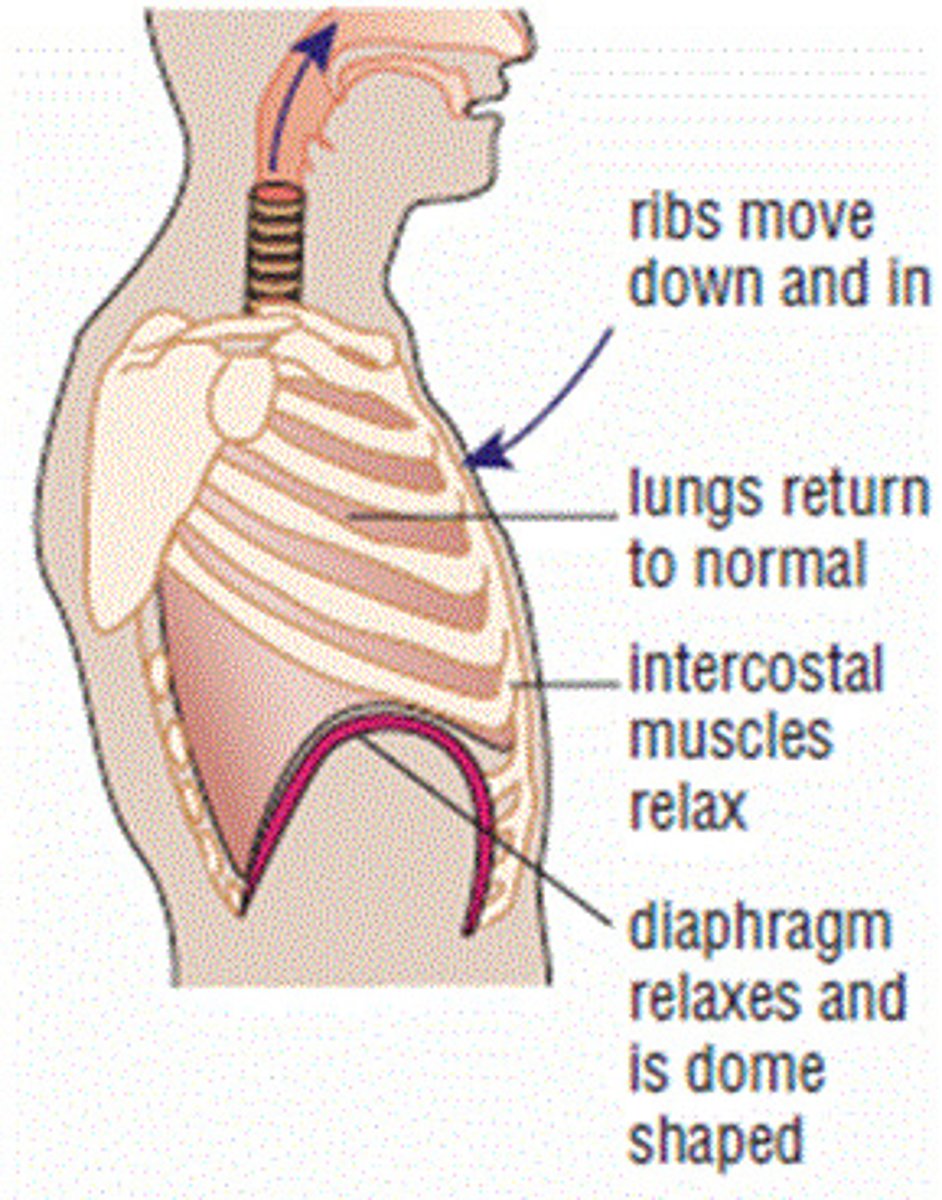
Exhalation / expiration
Giving out of air
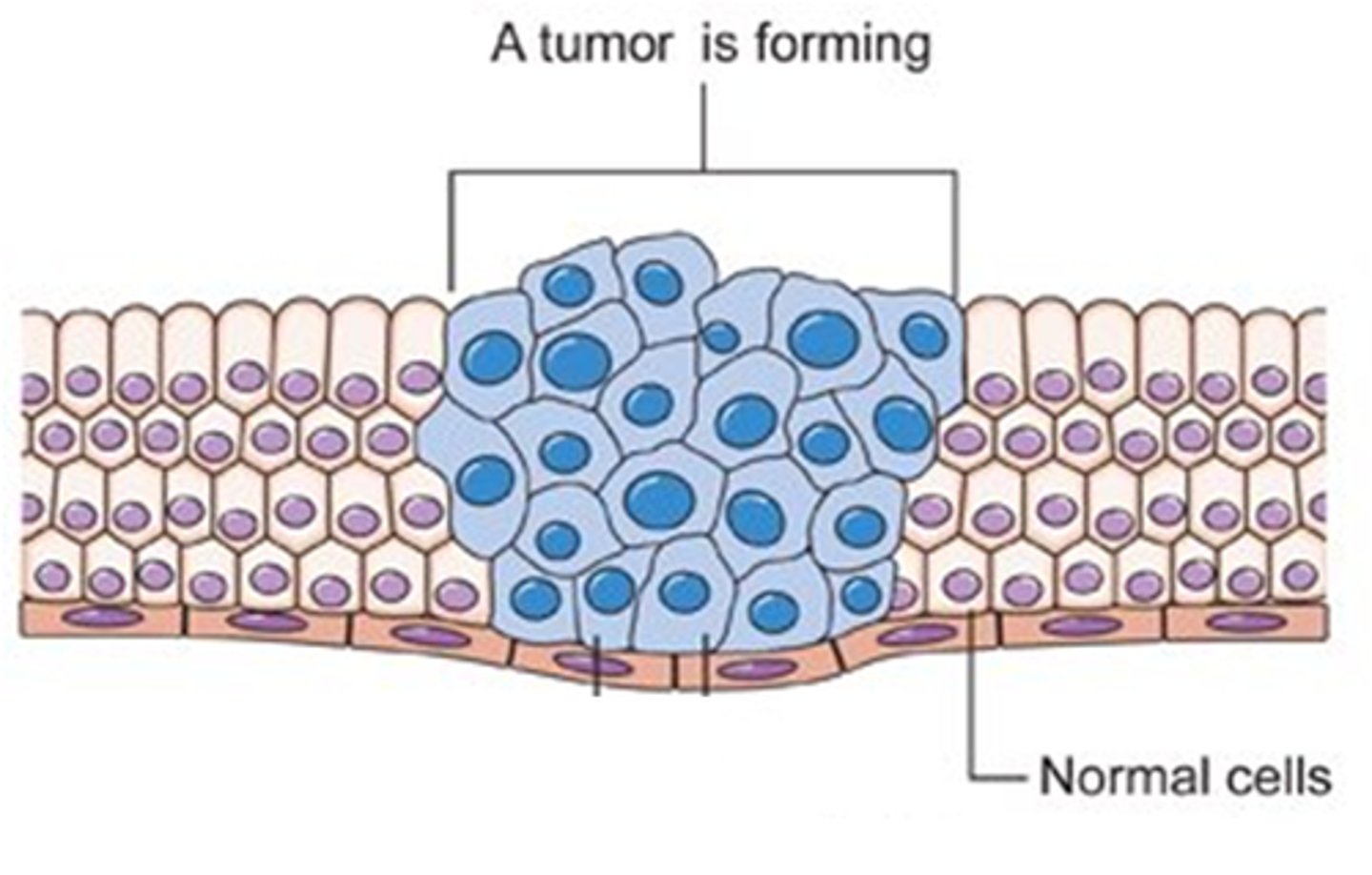
Cancer
An uncontrolled division of cells producing outgrowths or lumps of tissues
Excretion
Process by which metabolic waste products and toxic materials are removed from the body of an organism
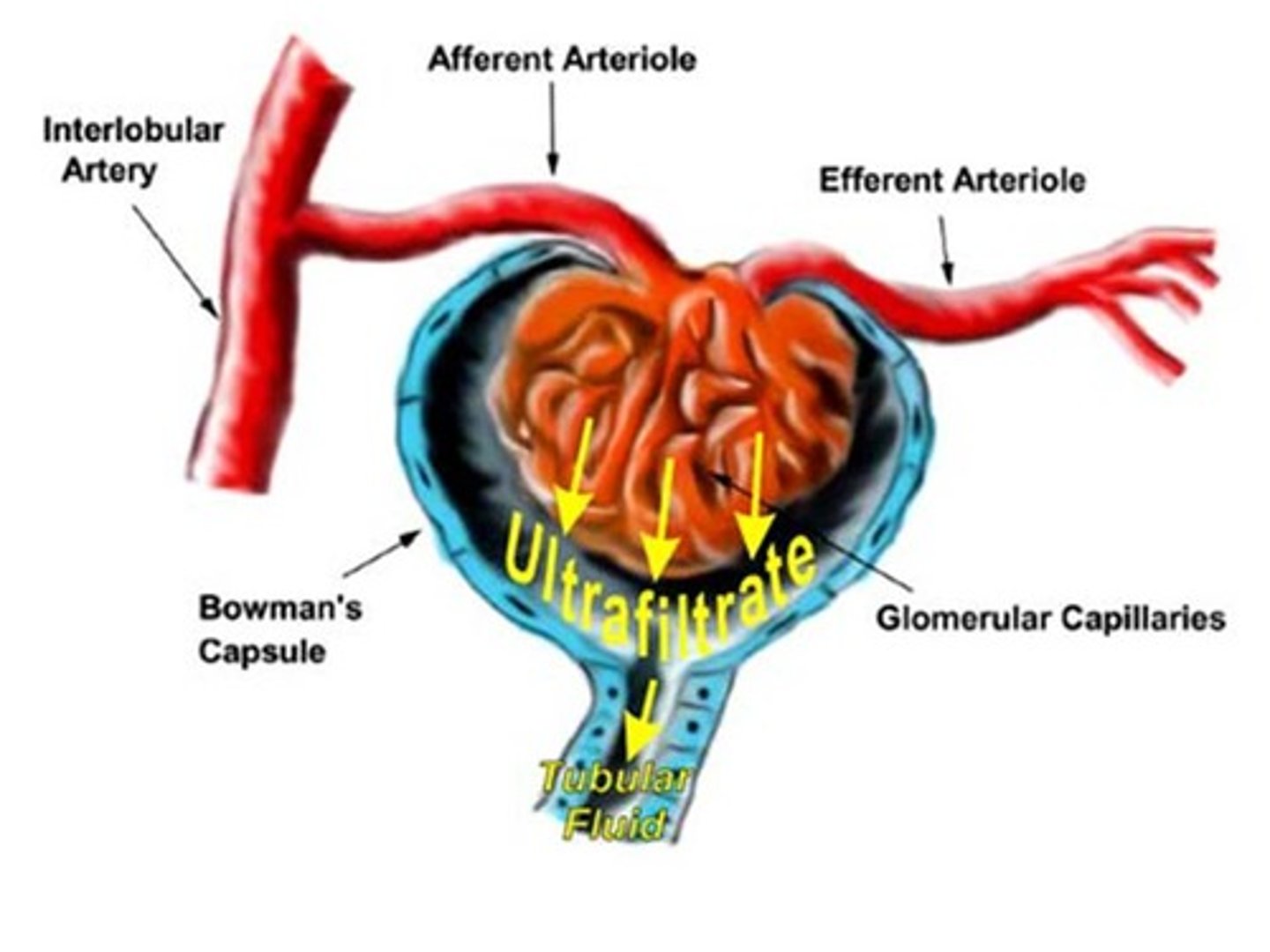
Ultrafiltration
Process in which hydrostatic pressure causes water and small dissolved substances and ions to move across the capillary wall into the nephron tubule
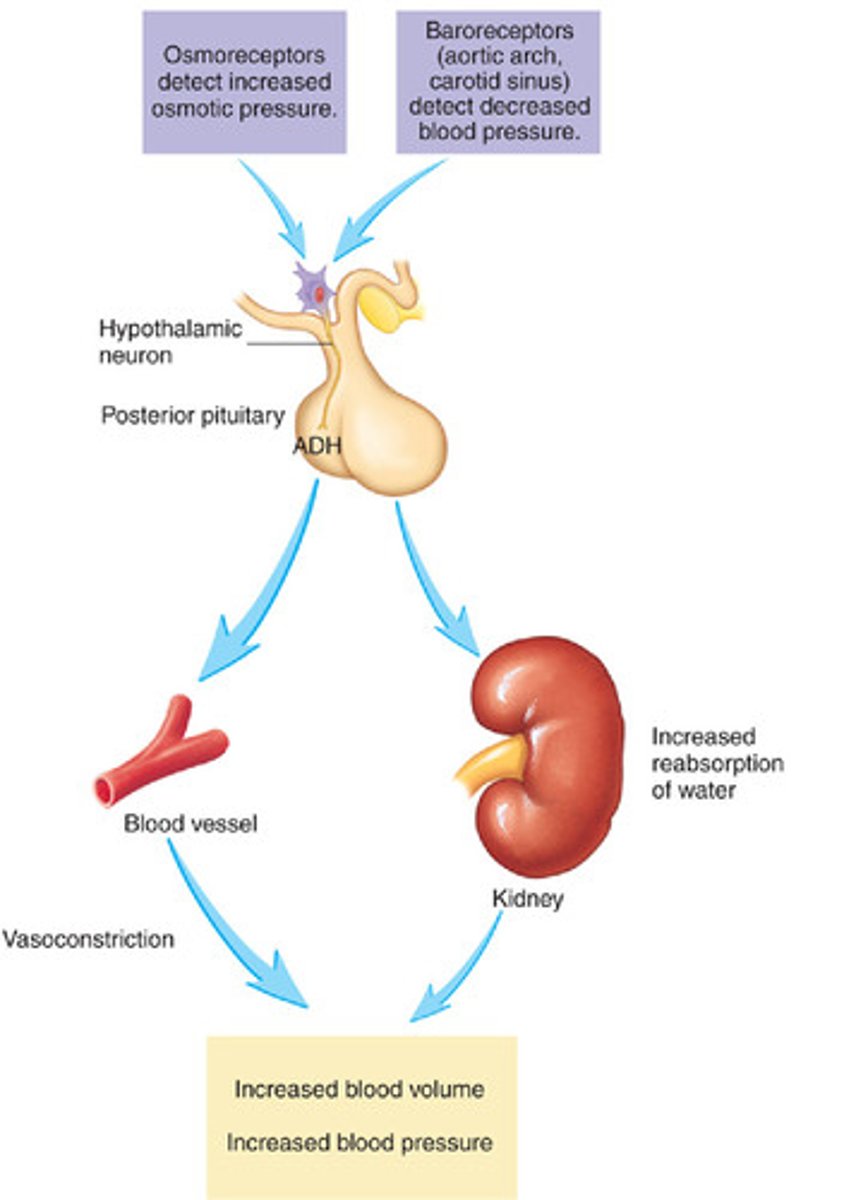
Osmoregulation
Control of water and solute levels in the blood to maintain a constant water potential in the body