inflation 2.1.2 - measure of economic performance macro economics
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
what is inflation ?
this the general and sustained increase in price, measured by a change in a weighted index of prices such as CPI
why is index numbers used to represent inflation changes ?
this is because percentages changes can be shown more easily making it as an effective comparison as possible
What is deflation
A fall in the general level of price i.e. negative inflation.
will reduce firms from wanting to invest in a country from abroad as the value of output will fall. why buy expensive consumer items when you can buy later when the prices are going to fall.
What is disinflation ?
a fall in the rate of inflation i.e. the prices are rising at a slower rate
this can be a sign that inflation is coming under control but could also mean investment and confidence are low
what does CPI meausre
it measures the price levels not the level of inflation
how can CPI be used to measure the rate of inflation ?
2 survey would need to be undertakes
1)survey on expenditure involves the collection of information about what people buy, - done annually to determine the contents of a basket of goods and services that a household spend their money on , and the proportion spent on each
collects information from a sample of around 7,000 households in the UK using self reported diaries
households spend more on some items than others so weights are attached to the items in price indices = weights reflect the relative importance of each item i.e. 10% of income spent on bread = bread weighing 10%
the second survey us of prices - the price survey is undertaken by civil servants who collect data once a month about changes in the price of 750 of the most commonly used goods and services in a variety of supermarket finding the average price in each good by gathering 120,000 prices all together.
inflation is measured from this by calculating the percentage change in index over consecutive years
what is one major problem with using CPI to measure inflation especially for home/rent owners
monthly mortgage payments often form a large amount of households spending and is a cost of living for almost 10 million households with an average of mortgage payments costing 15%-20% of income %
therefore if the CPI rises by only 2% and inflation seems to be under control, a rise in interest rates will mean that many households experience higher mortgage costs and increase in costs of living.
to wage rises that are linked to CPI exclude a significant change in living costs
what are the other issues with using CPI as a measure for the rate of inflation
only measures the cost of living for the average household does not take into account the top and bottom 4% income brackets. pensioners are not included in this
sampling methods issue -2017 less than 50% of households responded to the survey - lack of accura
ths list of items change only once a year but taste and fashion change more quickly - doesn’t take into account buy one get one free deals that might change people’s habits
ppl with aytypical spending patterns i.e. vegetarian + non-drivers the CPI=unrepresentative i.e. ppl who buy ticket may experience more than 2% inflation with the increase in train ticket
What is CPIH ?
this is CPI with owner owner occupying costs added to it.
includes residential rents across the UK
it does not take into account the changing values of uk homes but more specifically it estimates the amount it will cots all homeowners to rent their houses
unlike CPI - CPIH also includes council tax in it’s calculations
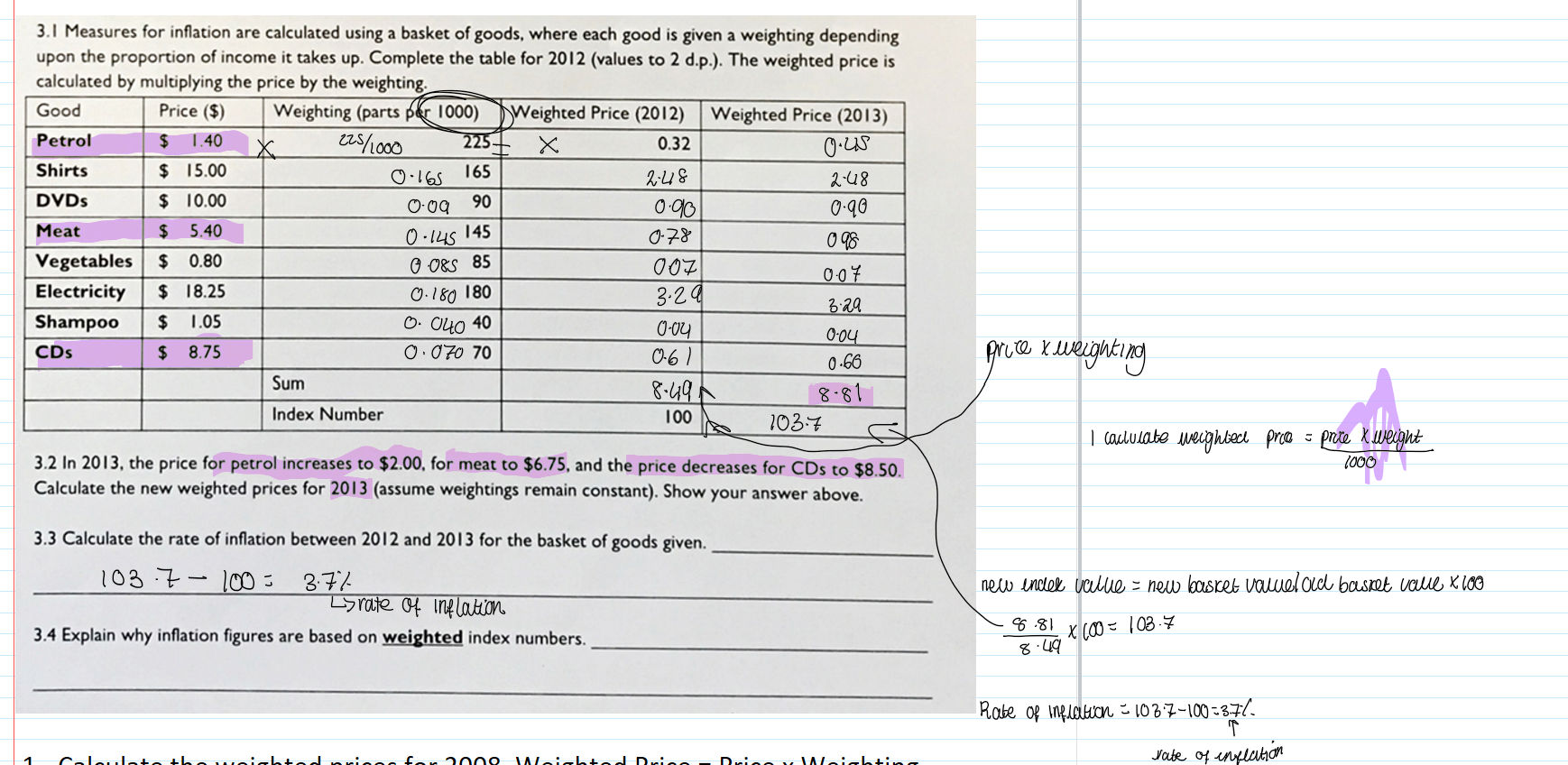
How inflation is calculated
learn it
What is RPI ?
an index used to measure inflation that includes housing costs such as mortgage interest repayments .
It is also used as an appropriate measure for wage increase as cpi fails to take into account a large part of household expenditure = housing costs
WHat are some of the disadvantages of RPI
it is not as reliable for international comparison
the statistical method of basing the data is unique to the uk
when interest rates are raised so does cost of mortgage repayment - so a rise in interest rates to help curb inflation will make inflation appear worse = making policy markers look incompetent
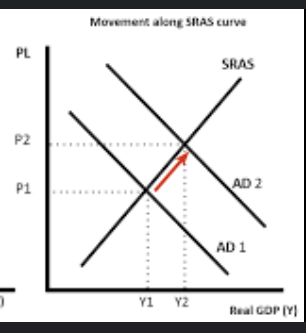
What is demand pull inflation ?
this is associated with a rightward shift in the AD curve.
It may be caused by an increase in any of the components of AD i.e. consumption, government, spending or net exports
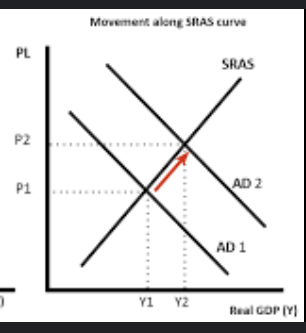
how is does demand pull inflation occur
an increase in the average price is caused by an increase in demand.
this can be caused by higher incomes = increased consumption
higher confidence = causes business to invest more
increase in government spending i.e. more welfare given out = more people are able to consume goods and services
net exports
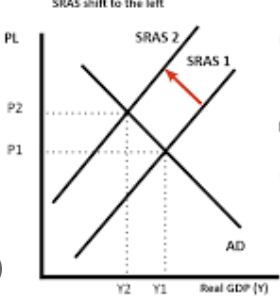
what is cost push inflation ?
an increase in the general level of prices caused by increased production costs
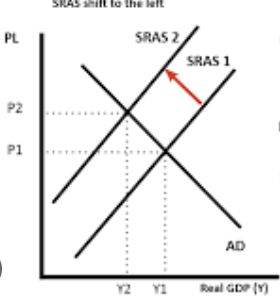
what could cause cost push inflation to occur
a fall in exchange rates = causes goods overseas to be more expensive = imports are more expensive
higher corporation tax
scarcity of capital goods = prices of capital goods to increase
increase in wages = causes cost of production to increase
how can an increase money supply also cause inflation
an increase in the money supply can cause inflation because it reduces the purchasing power of money
how does inflation effect the value of saving for consumers
if the rate of inflation is higher than the rate of interest that people are receiving from their savings then the real value of their savings falls.
inflation makes saving even less attractive to an already significantly under-saving population of working age
how does inflation effect the purchasing power of consumer on fixed incomes
pensioners who rely on annual income will find their living standards decline.
prices have increased by their pension has not
how will inflation affect debt
those with high levels of personal debt will benefit from increased inflation because the real value of debt will fall.
the value of mortgage loans relative to income is likely to fall when the general level of price rises
how does inflation affect firms
increased uncertainty = curbs investment
loss of international competitiveness
investment abroad might decrease -why buy into a falling currency
increased price = firms can make more profit
wage differential can be changed - ppl will accept wage rises below the rate of inflation but will never expect wage cuts
how does inflatioin effect the government ?
they will need to redistribute income on those with fixed incomes
inflation reduces the real interest rate so cost of borrowing falls = gov debt falls
inflation provides a cushion again deflation - which would be a vicious cycle of underinvestment and reduced spending
what are the two main causes of deflation
malignant deflation
benign deflation
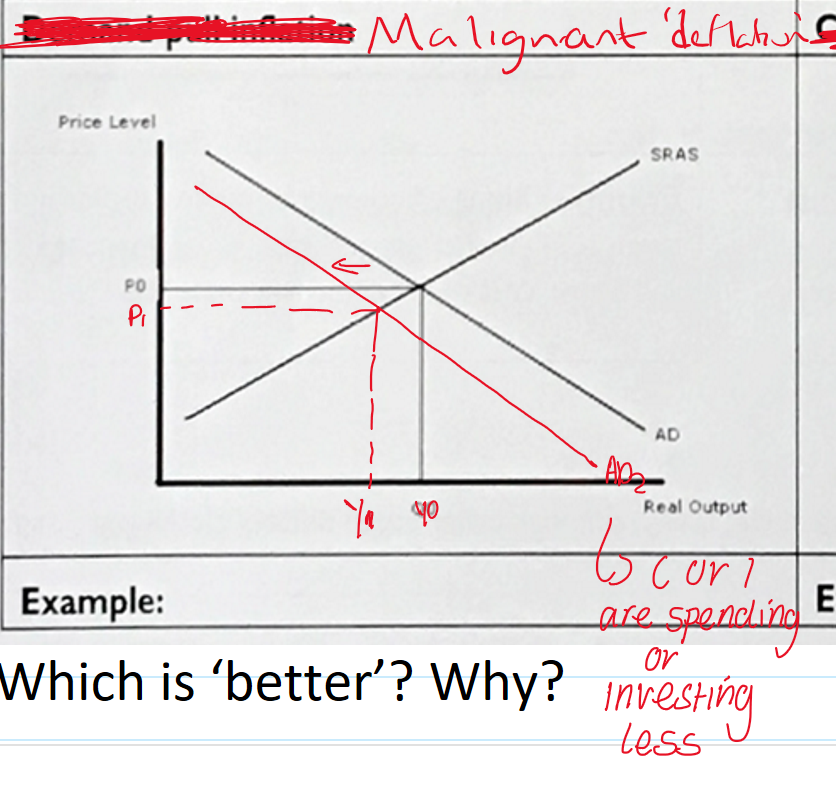
what is malignant deflation ?
A persistent fall in the general price level, output and employment brought about by a steep fall in and then persistently low levels of aggregate demand.
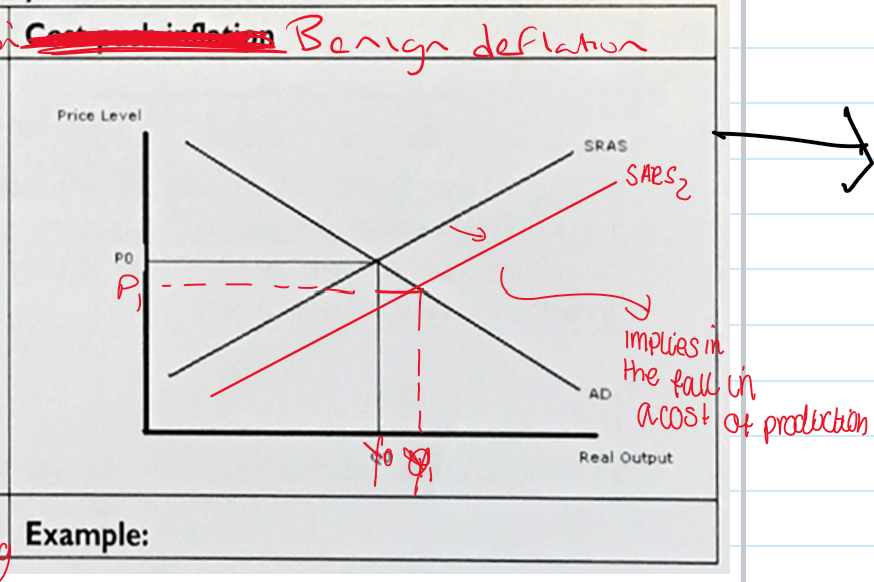
what is benign deflation
this is deflation brought about by the outward shift in the SRAS curve.
which causes a fall in the general price level. This is caused by lower unit costs of supply
give an example of when benign inflation might occur ? i
if consumers are so lacking in confidence that they wont borrow even if it is free.
this causes the government to print more money = causes an increase in the supply of money - leads to hyper inflation
causes a fall in the cots of production for firms
how could the government try to incentives people to spend money during deflation ?
could introduce negative interest rates - so the government charges people to save money which would incentives them to spend
why is RPI used
wage increases - usually linked to inflation.
if the CPI measure is used, wage increases will fail to take into account a larger part of household expenditure in the form of housing costs - so wont be able to accurately raise their wages to reflect the housing cost increase this is why RPI is used
how does inflation effect workers ?
this might mean that some workers expect an increase in their wages but firms do not feel confident about paying higher costs. - this is especially true if firms cannot pass on the higher cost in the form of prices
there is a trade off between wage inflation and unemployment - this means that if their is high wage inflation it is easier for people to find work because firms are rising wages only because they cannot choose other workers at lower prices