Exam 2 A and P
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
What is the pH of urine
ranges from 4.5 to 8.2
usually 6.0 (acidic) → normal
What is the normal pH for blood
7.4
What does the urinary system consist of
6 organs:
2 kidneys
2 ureters
urinary bladder
urethra
what affects lymphatic return?
EXERCISING
significantly increases lymphatic return
(movement/hydration/diet)
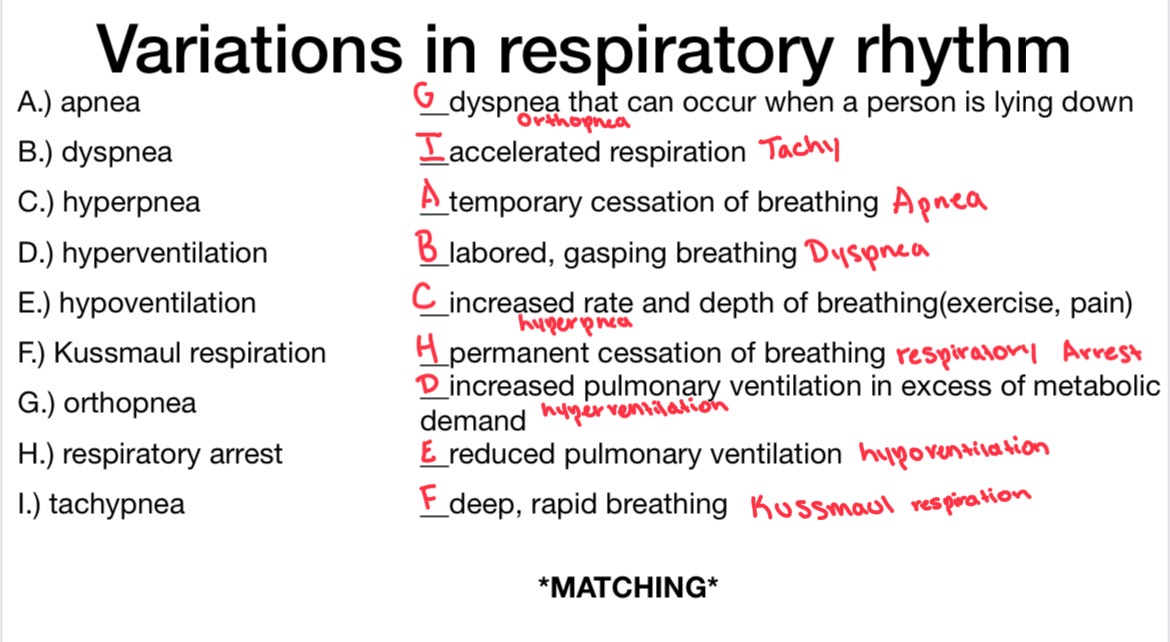
Eupnea
relaxed quiet breathing
apnea
temporary cessation (stoppage) of breathing
Dyspnea
labored, gasping breathing; shortness of breath
hyperpnea
increased rate and depth of breathing due to pain, exercising, etc.
hyperventilation
increased pulmonary ventilation in excess of metabolic demand
hypoventilation
reduced pulmonary ventilation
Kussmaul respiration
deep, rapid breathing often induced by acidosis
Orthopnea
dyspnea that occurs when a person is laying down
Respiratory Arrest
permanent cessation of breathing
Tachypnea
accelerated respiration
What does COPD stand for?
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
What are some examples of COPD’s?
chronic bronchitis and emphysema
What are 3 types of lung cancer
squamous-cell carcinoma
small-cell (oat cell) carcinoma
adenocarcinoma
What lung cancer is the most common
squamous-cell carcinoma
which lung cancer is the least common?
small-cell (oat cell) carcinoma
which lung cancer is the most dangerous?
small-cell (oat cell) carcinoma
What are the 3 R’s of immunity
recognize, react, remember
What do the words “autoimmune diseases” mean?
failures of self-tolerance
immune system fails to distinguish self-antigens from foreign ones
How many classes of antibodies are there?
Name them.
5 classes
IgA
IgD
IgE
IgG
IgM
Name the types of immunity? How many are there?
4 types:
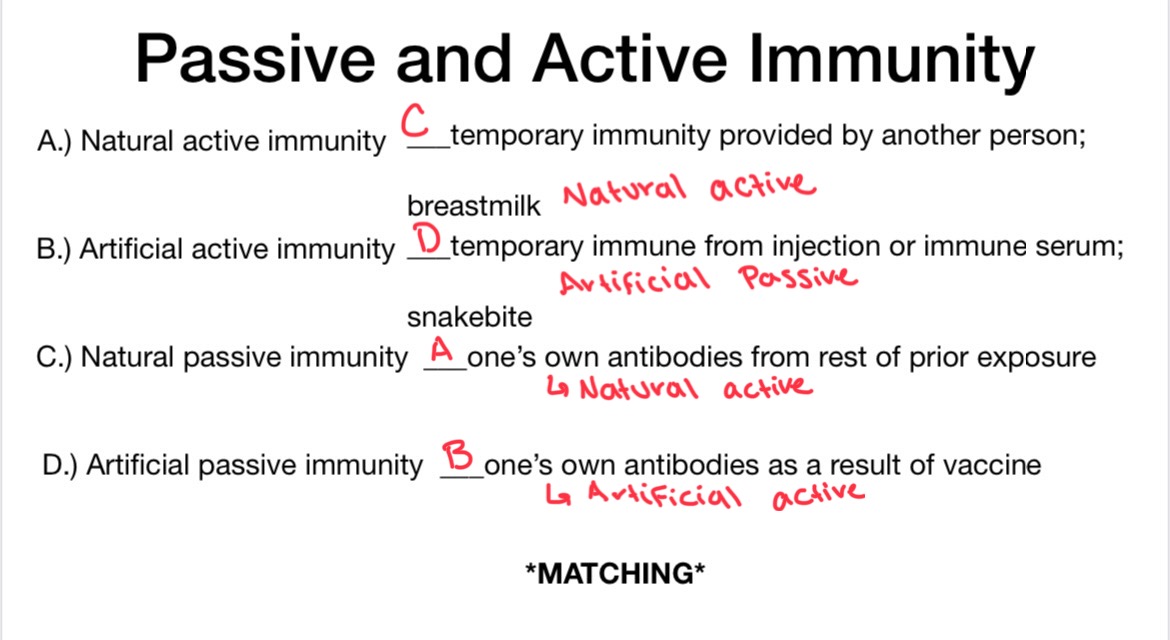
Natural active immunity
Artificial active immunity
Natural Passive immunity
Artificial Passive immunity
describe natural active immunity
producing of ones own antibodies as a result of infection or natural exposure to antigen
describe artificial active immunity
production of one’s own antibodies as a result of vaccination/booster shot against disease
describe natural passive immunity
temporary immunity that results from antibodies produced from another person
fetus acquires antibodies from mother through milk, placenta
describe artificial passive immunity
temporary immunity that results from the injection of antibodies of another person or animal
treatment for snakebite
How many parts are there in renal tubules?
Name them.
4 distinct regions
Proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)
nephron loop
Distal convoluted tubule
collecting duct
Name the start of nephrons.
Name the end of nephrons.
Name the order.
Start: Glomerular capsule
End: Collecting duct
Glomerular capsule → proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) → nephron loop → distal convoluted tubule → collecting duct
Describe the flow of filtrate (fluid)
glomerulus capsule → proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) → nephron loop → distal convoluted tubule → collecting duct → papillary duct → minor calyx → major calyx → renal pelvis → ureter → urinary bladder → urethra
The right lung has how many:
lobes?
fissures?
lobar (secondary) bronchi?
segmental (tertiary) bronchi
the right lung has:
3 lobes
1 horizontal fissure, 1 oblique fissure
3 lobar bronchi
10 segmental bronchi
The left lung has how many:
lobes?
fissures?
lobar (secondary) bronchi?
segmental (tertiary) bronchi
the left lung has:
2 lobes
1 oblique fissure
2 lobar bronchi
8 segmental bronchi
What are the parts of the pharynx
nasopharynx
oropharynx
laryngopharynx
What makes up the framework of the larynx?
Which ones are paired?
which ones are singular?
9 cartilages
Paired:
arytenoid cartilage (2)
corniculate cartilage (2)
cuneiform cartilage (2)
Singular:
epiglottic cartilage
thyroid cartilage
cricoid cartilage
what is vital capacity?
what is its volume?
total amount of air that can be inhaled and exhaled with maximum effort (4700mL)
what is inspiratory capacity?
what is its volume?
maximum amount of air that can be inhaled after a normal expiration (3500mL)
what is functional residual capacity?
what is its volume
the amount of air in lungs that is left over after a normal tidal expansion (2500mL)
what is total lung capacity?
what is its volume?
the total amount of air that can be contained in lung (6000mL)
the measurement of pulmonary function is called
disorders that reduce pulmonary compliance are called
disorders that interfere with airflow by narrowing or blocking airway are called
spirometer
restrictive disorders
obstructive disorders
what is forced expiration volume (FEV)
percentage of vital capacity that can be exhaled in a given time interval
the maximum speed of expiration is called
peak flow
what is minute respiratory volume (MRV)
amount of air that can be inhaled per minute
what is maximum voluntary ventilation
MRV (minute respiratory volume) during heavy exercise
Cortical nephrons:
_ % of all nephrons
___ nephron loops
efferent arterioles branch into ___
85% of all nephrons
short nephron loops
efferent arterioles branch into peritubular capillaries
juxtamedullary nephrons:
_ % of all nephrons
__ nephron loops
efferent arterioles branch into the _
15% of all nephrons
Very Long nephron loops
branch into the vasa recta
The vasa recta is surrounded by what nephron?
the peritubular capillaries are surrounded by what nephron?
vasa recta= juxtamedullary nephrons
peritubular capillaries = cortical nephrons
How many types of white blood cells are there?
Name them.
5
Neutrophil
Basophil
Eosinophil
Monocyte
Lymphocyte
function of Neutrophil
wander in connective tissue killing bacteria
create a killing zone
function of Basophils
secrete chemicals (histamine and heparin) to aid in mobility and action of other leukocytes
function of eosinophils
stand guard against parasites, allergens, etc
function of monocytes
transform into macrophages; actively seeking pathogens
function of lymphocytes
circulating blood contains T cells (80%), B cells (15%) and NK cells (5%)


what does nonspecific resistance mean
Give some examples
immunity that is effective against a broad range of pathogens
Ex: skin, fever, leukocytes, macrophages, inflammation
How many sets of tonsils do we have?
Name them.
3 sets
Palatine tonsil
Lingual tonsil
Pharyngeal tonsil
What organs are included in the lymphatic system. Which ones are primary? Which one are secondary?
primary lymphatic organs:
red bone marrow
thymus
secondary lymphatic organs
spleen
lymph nodes
tonsils
in which type of lymphatic organ are T and B cells becoming immunocompetent (ability to recognize and respond to antigens)
primary lymphatic organs
red bone marrow and thymus
What is the most numerous lymphatic organ?
lymph nodes
What is the body largest lymphatic organ
spleen
What are the types of specific immunity
cellular immunity (cell-mediated)
humoral immunity (antibody-mediated)
describe cellular immunity (cell-mediated)
is it T or B cell?
does it directly attack pathogens?
T cells
-yes, does directly attack pathogens
describe humoral immunity (antibody mediated)
is it T or B cell?
does it directly attack pathogens?
B cells
No, does not directly attack pathogens
both cellular and humoral immunity occur in _ stages. What are they?
3 stages
recognize
react
remember
(the 3 R’s of immunity)
List the lymphatic cells
6
Natural killer (NK) cells
T cells
B cells
Macrophages
Dendritic cells
Reticular cells
describe natural killer cells
responsible for immune surveillance
attack and destroy bacteria
describe T cells
mature in thymus
describe B cells
activation causes plasma cells to produce antibodies
describe Macrophages
large phagocytic cell
phagocytize foreign matter
antigen presenting cell (APC)
describe dendritic cells
branched cells that alert immune system about a pathogen that has breached the surface
describe reticular cells
branched stationary cell that contribute to the storm of a lymphatic organ. Acts as APC in thymus
the phenomenon in which a cancerous cells breaks free from the original primary site, travels to other sites in body and establishes new tumors is called
metastasis
autonomic breathing is controlled by __ pairs of respiratory centers in the reticular form of the __ and the _ .
autonomic breathing is controlled by 3 pairs of respiratory center; in the medulla oblongata and the pons
name the respiratory groups found in the medulla oblongata
name the respiratory groups found in the pons
in the medulla
ventral respiratory group (VRG)
produces 12 breaths per minute
generator of respiratory rhythm
Dorsal respiratory group (DRG)
modifies rate and depth of breathing
in the pons
Pontine respiratory group (PRG)
adapts breathing to special circumstances like sleep, exercise
Path of airflow
nasal cavity → pharynx → larynx → trachea → main bronchus → lobar bronchus → segmental bronchus → bronchiole → terminal bronchiole
how many type of alveolar cells are there? Name them.
3 types
Squamous alveolar cells (type I)
Great alveolar cells (type II)
Alveolar macrophages (dust cells)
(T/F): Squamous alveolar cells, great alveolar cells and alveolar macrophages are the 3 types of cells in the alveolar
True
Name the muscles of respiration
diaphragm
external and internal intercostal muscles
scalenes
what is the prime mover of respiration
the diaphragm
what muscle accounts for two-thirds of airflow
what muscle adds 1/3 of airflow
what muscle is synergist to diaphragm and holds rib 1 and 2 stationary during quiet breathing
diaphragm
internal and external intercostal muscle
scalenes
What are the stages of urine formation (when kidneys blood plasma to urine)
3 stages:
Glomerular filtration
tubular reabsorption and secretion
water conservation
What portion/structure concentrated the urine?
collecting duct
What are the four cardinal signs of inflammation
redness (rubor)
swelling (tumor)
heat (calor)
pain (dolor
If you inhale something into the lung, which lung would it go into? Why?
aspirated (inhaled) foreign objects lodge ____ bronchus more often the ____
RIGHT. It’s more vertical
right; left
What structures consist of the upper respiratory tract? (superior to inferior)
(nose → larynx )
nasal cavity, pharynx, and larynx
What structures consist of the lower respiratory tract (superior to inferior)
(trachea → lungs)
trachea → bronchi → alveolar