Chapter 2 Lab Prep Sheet Extended via PPT Additional Info
1/192
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
193 Terms
anatomical position
is a standing position, head facing forward and the arms to the side.
Palms facing forward, fingers extended, thumbs pointing away from body
The feet spaced slightly apart with toes pointing forward
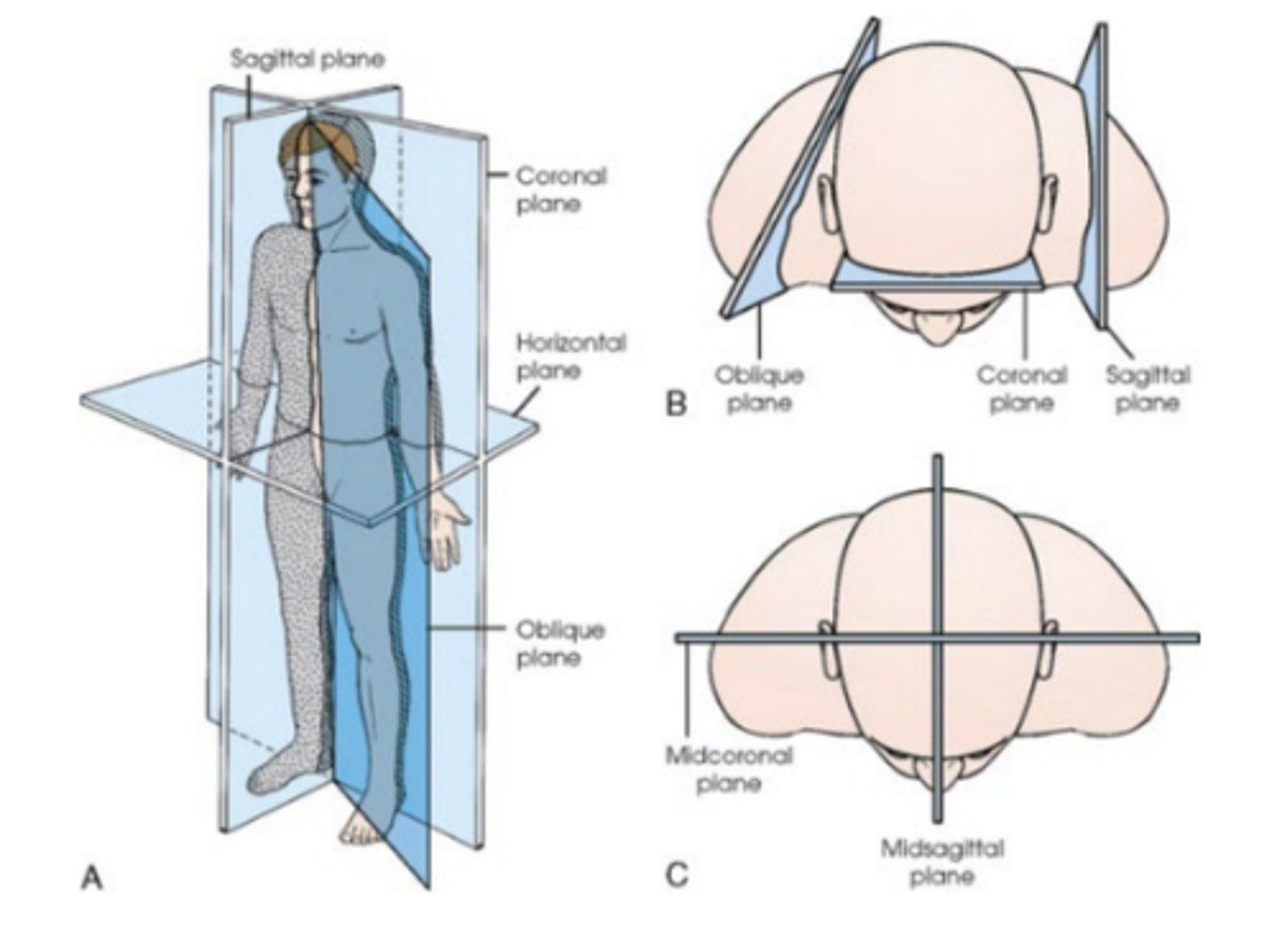
anatomical planes
four imaginary flat surfaces or planes that pass through the body in the anatomical position.
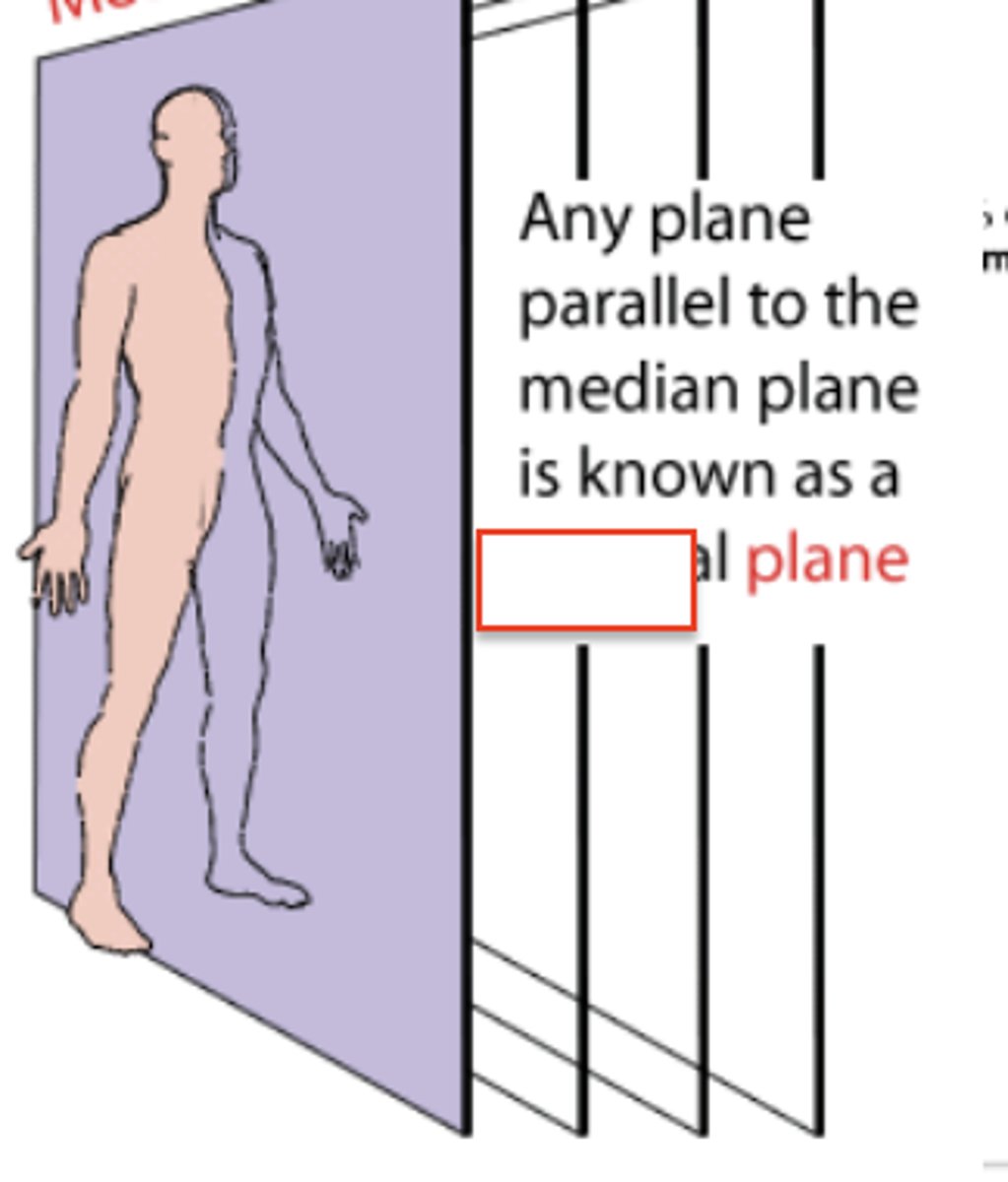
median plane
sagittal planes
coronal (frontal) planes
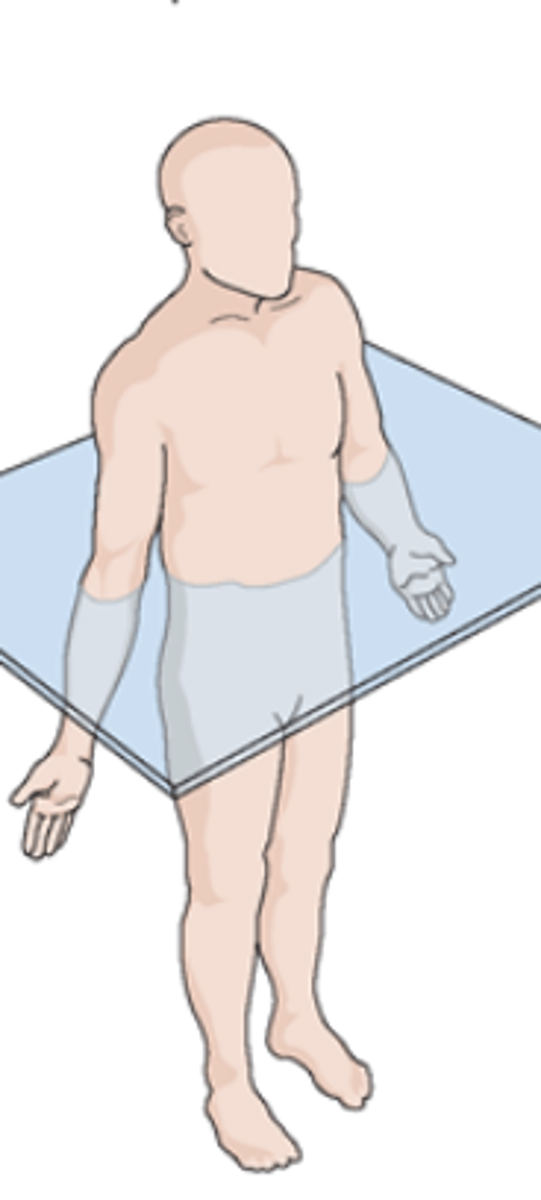
horizontal (transverse) planes
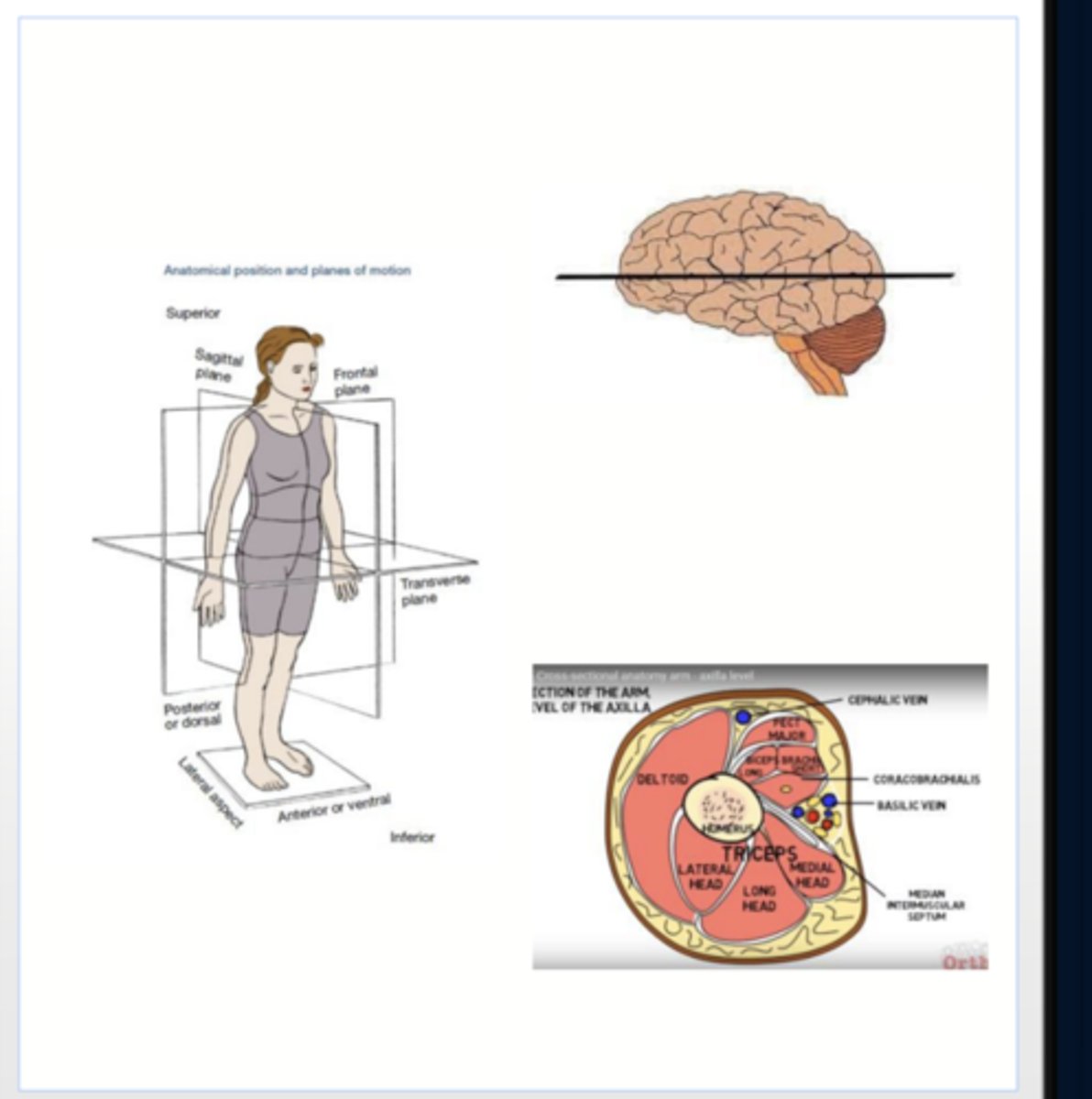
horizontal planes
pass crosswise through the body or body part at right angles to the longitudinal axis
Positioned at right angle to sagittal and coronal planes
divides the body into superior and inferior portions
also called transverse, axial, or cross-sectional planes
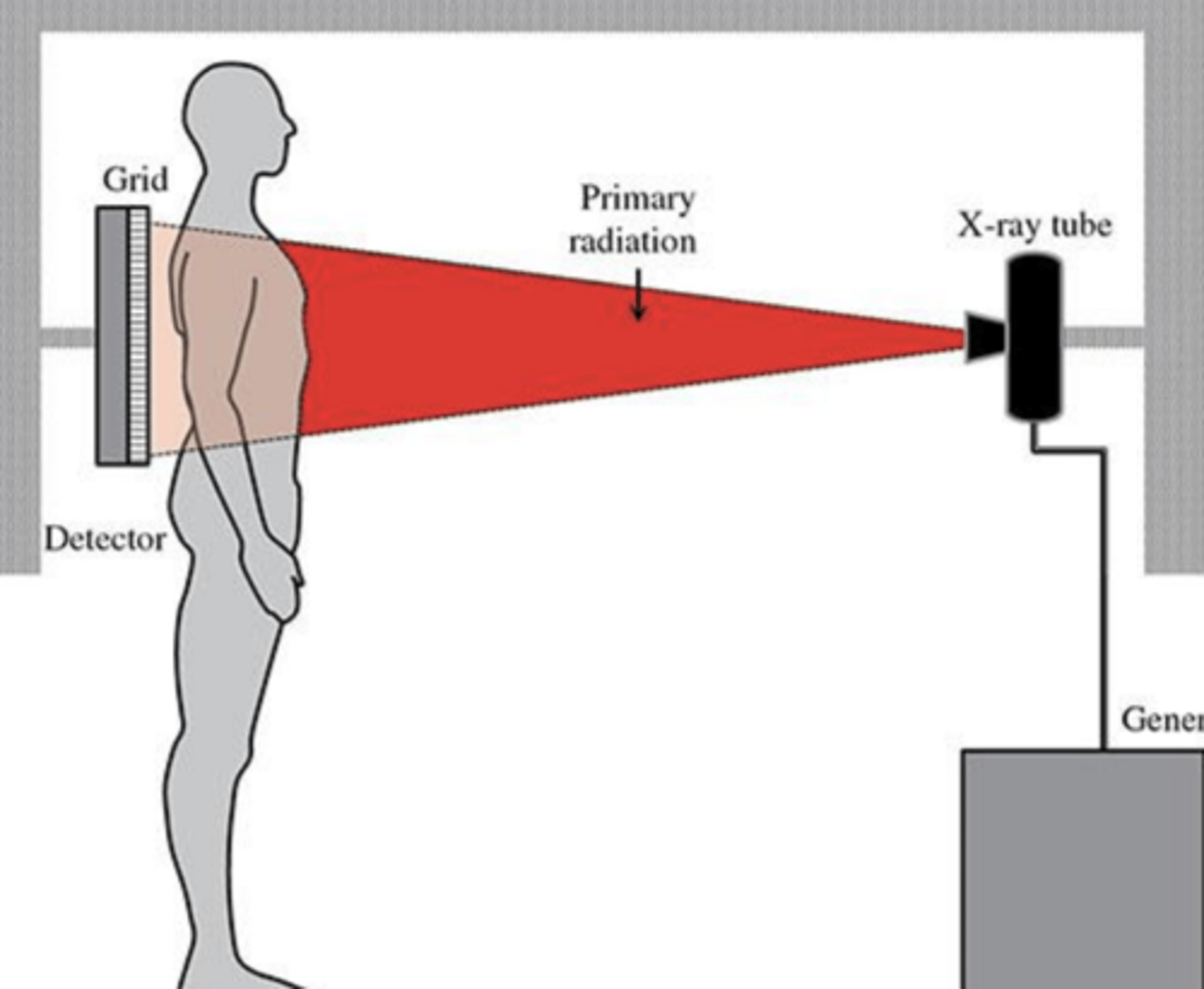
projection
Defined as the path of the Central ray as it exits the xray tube, passing through the patient to the IR
identified by the entrance and exits points of the body
sagittal plane
vertical plane passing through the body, parallel to the median plane. divides the body into right and left parts
coronal (frontal) planes
frontal planes passing through the body dividing it into anterior and posterior portions. these planes are at right angles (90 degrees) the the median and sagittal planes
horizontal (transverse) planes
planes passing through the body, dividing it into superior and inferior parts. these planes are at right angles (90 degrees) to the median, sagittal and coronal planes
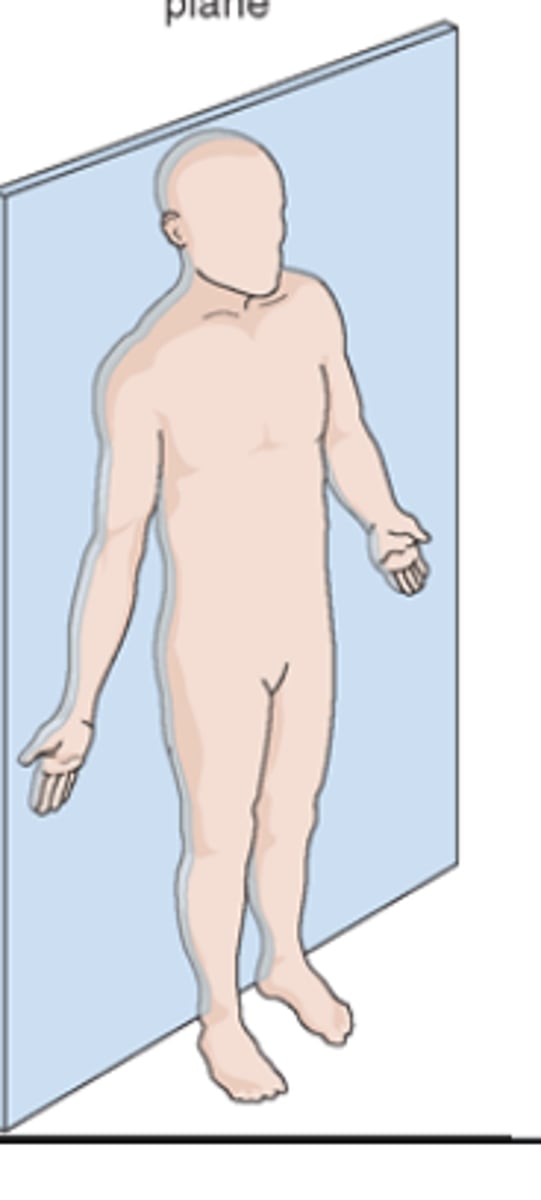
midsagittal or median plane
vertical plane that passes through the body longitudinally, dividing it into right and left halves. it is also defined as the sagittal plane that divides the body into right and left halves
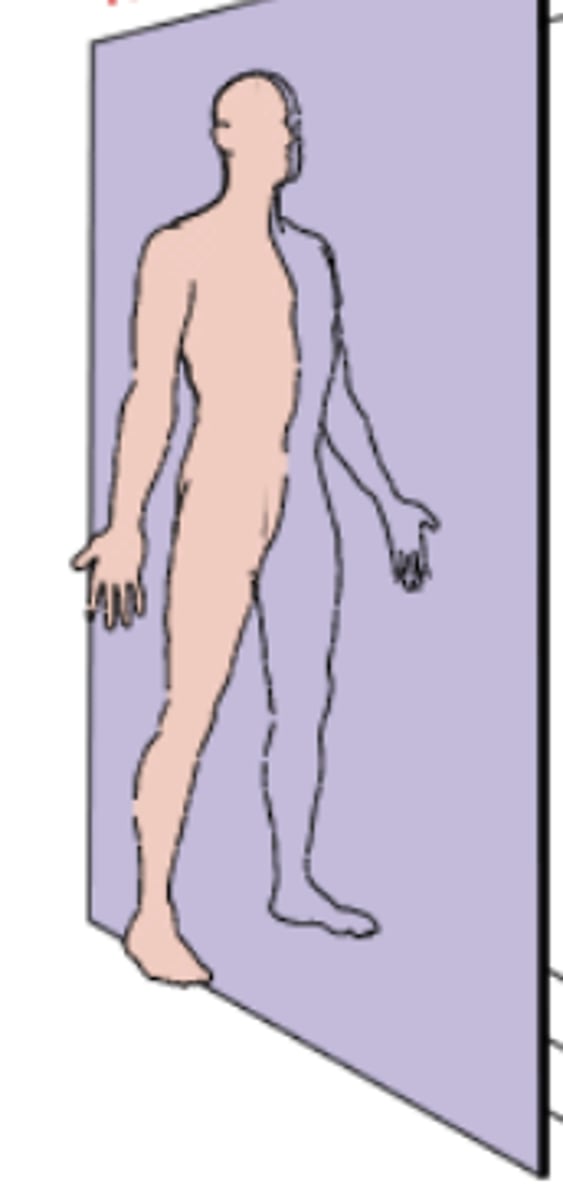
midcoronal plane
plane perfectly divides the body front to back
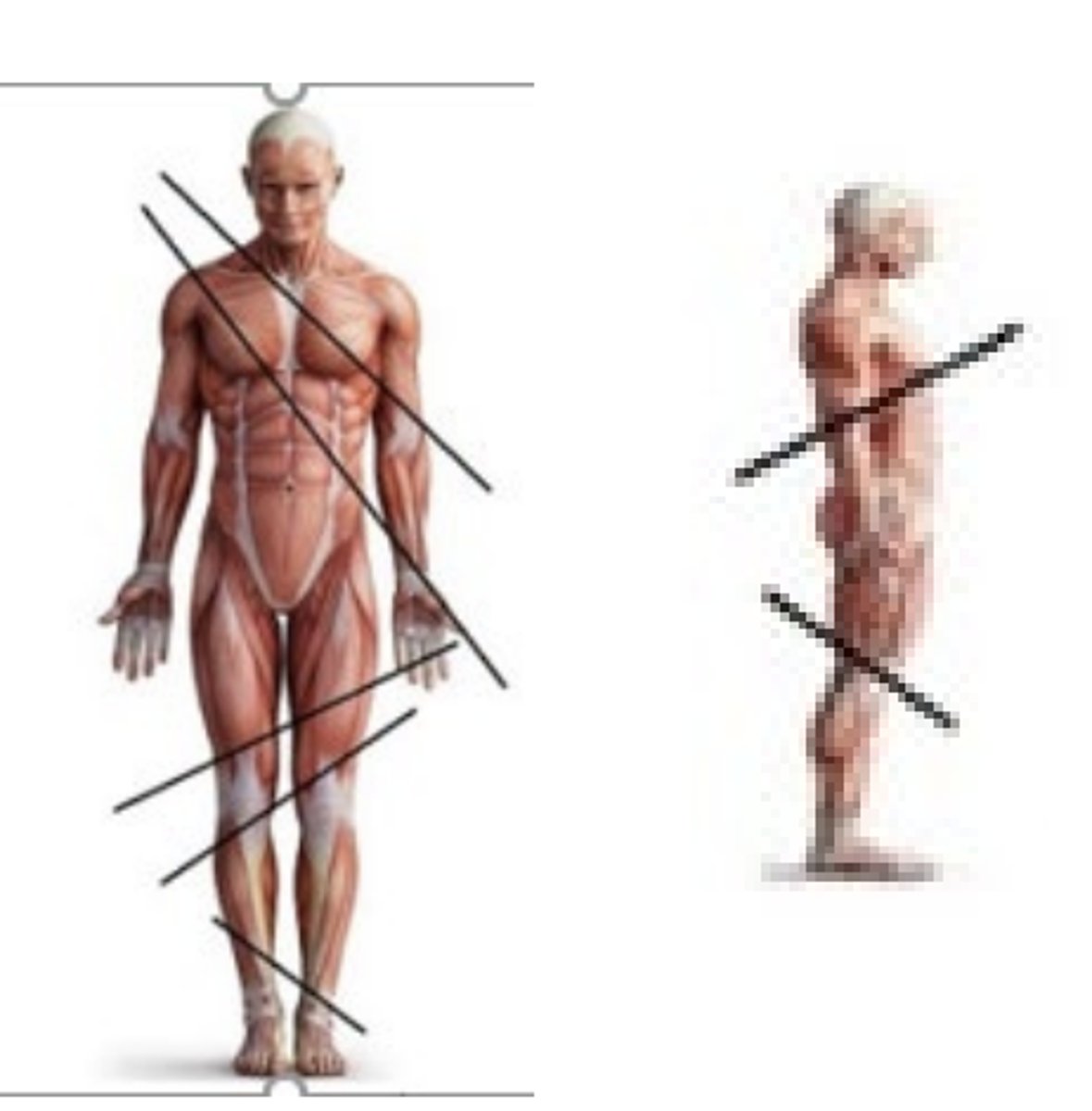
oblique planes
any plane that is any type of angle other than horizontal or vertical
pass through a body part at any angle between the previous three planes
Btwn 0-90 degrees
means something is not parallel or a right angle. OBL is ODD angles
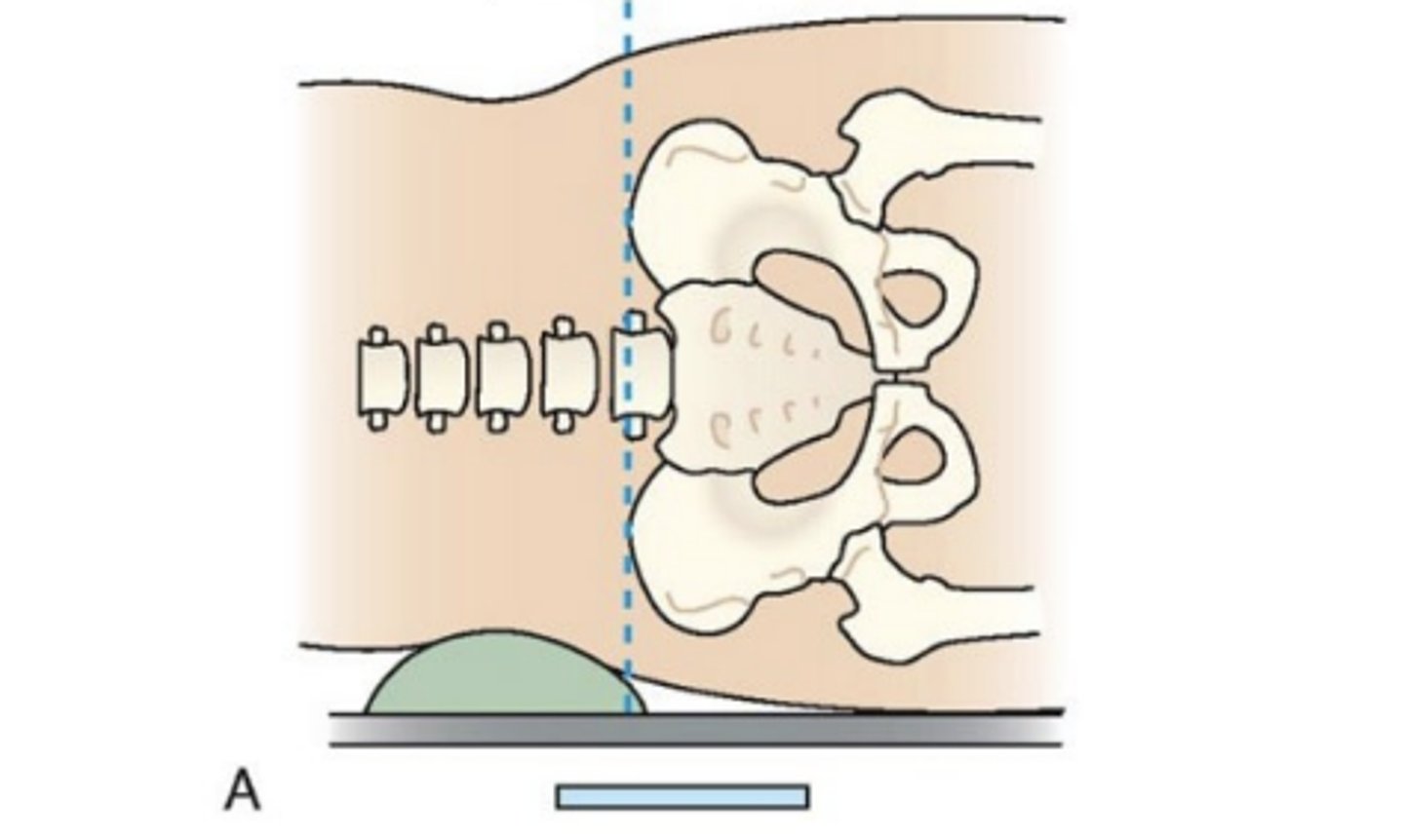
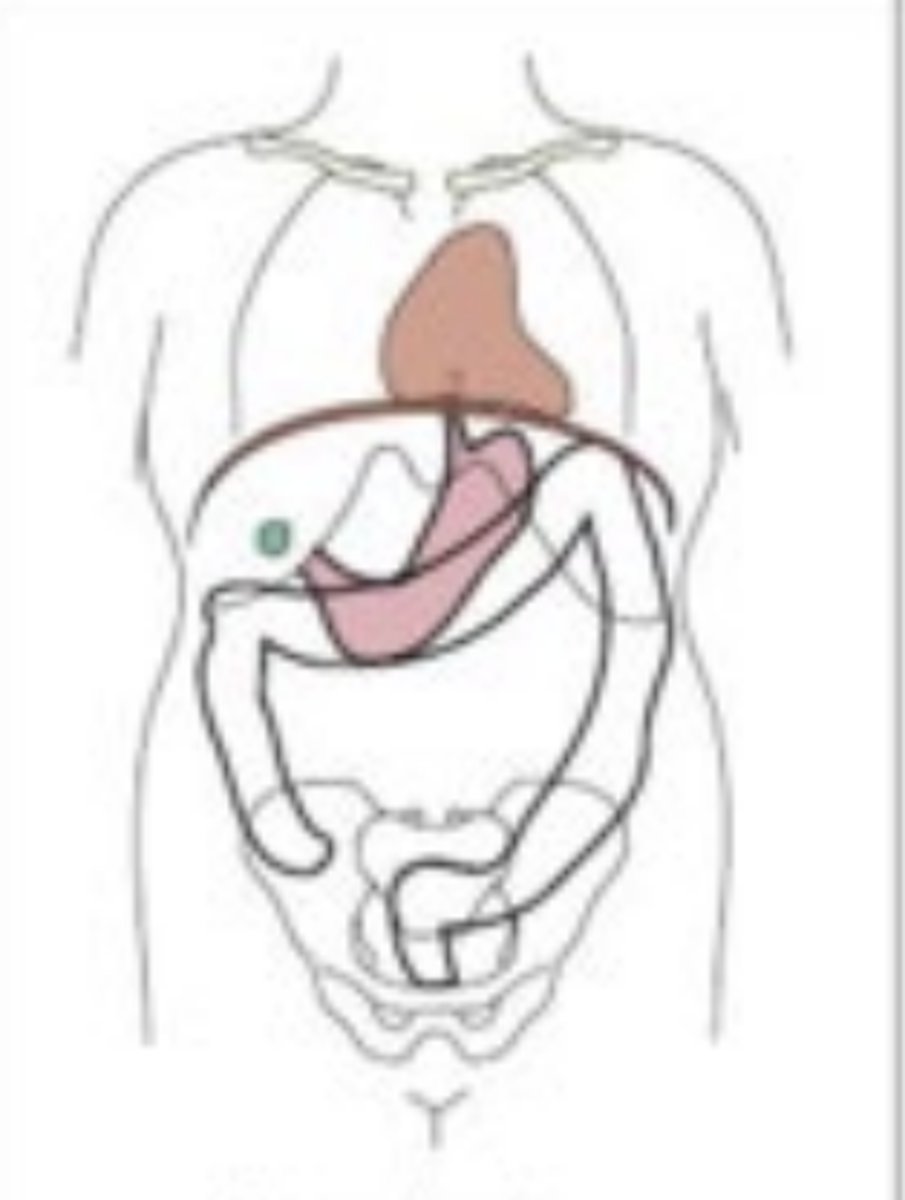
Interiliac plane
transects the pelvis at the top of the iliac crest at the 4th lumbar spinous process (L4). utilized for positioning in the lumbar spine, sacrum, and coccyx
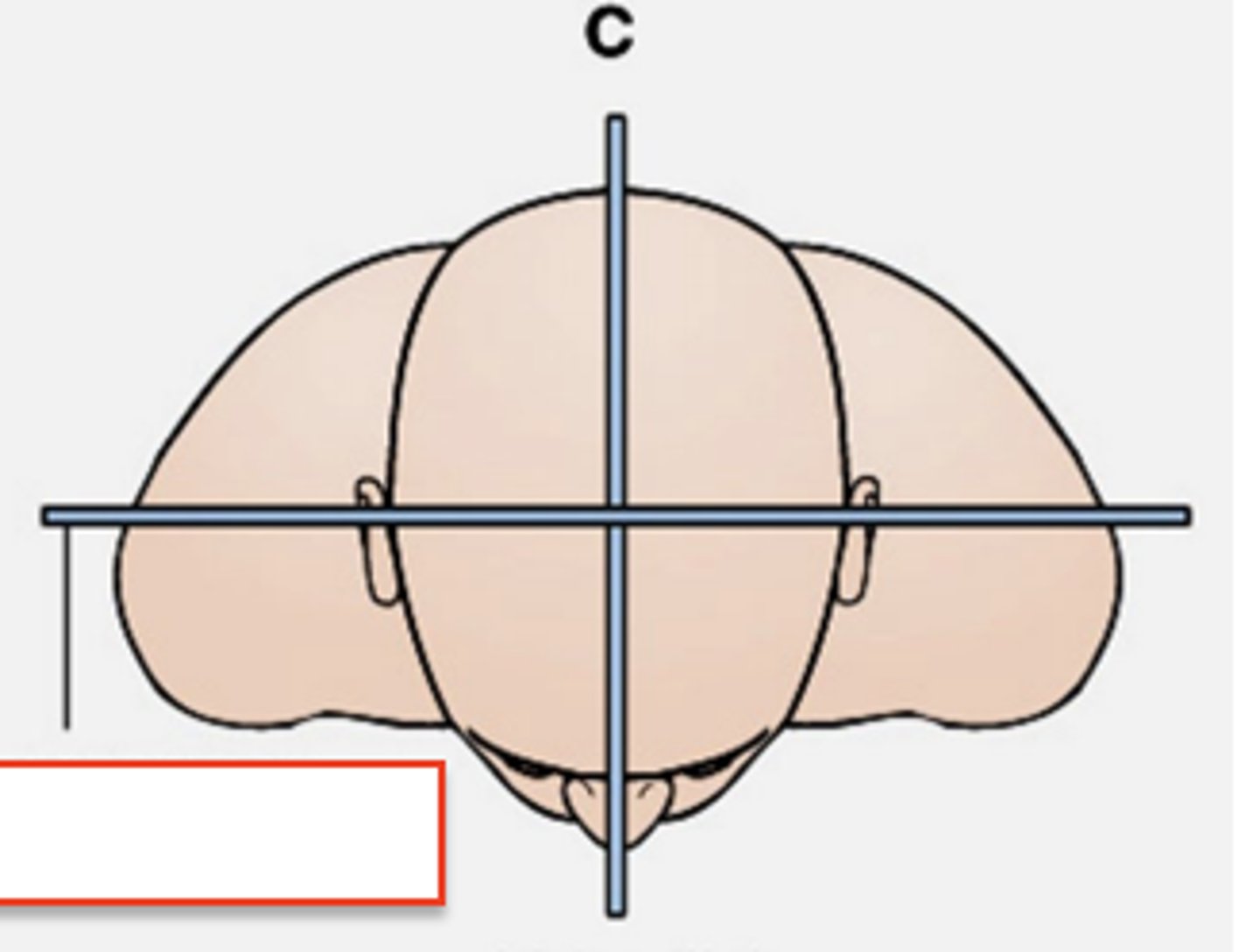
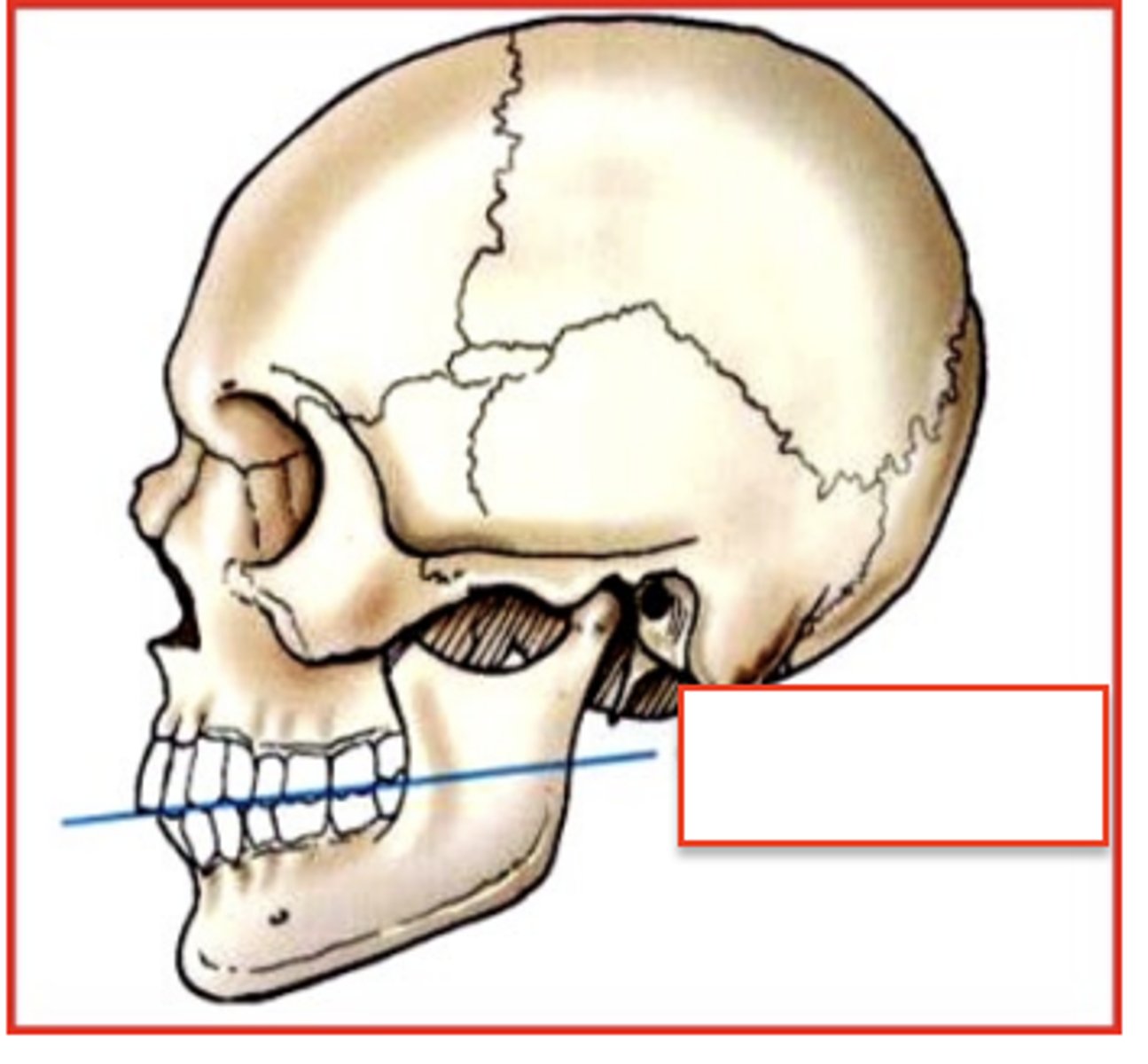
occlusal plane
formed by the biting surfaces of the upper and lower teeth with jaw closed
Sthenic
Type of Body Habitus
Hyposthenic
Type of Body Habitus
Asthenic
Hypersthenic
Medial
towards midline of the body
toward the median plane of the body or toward the middle of a body part
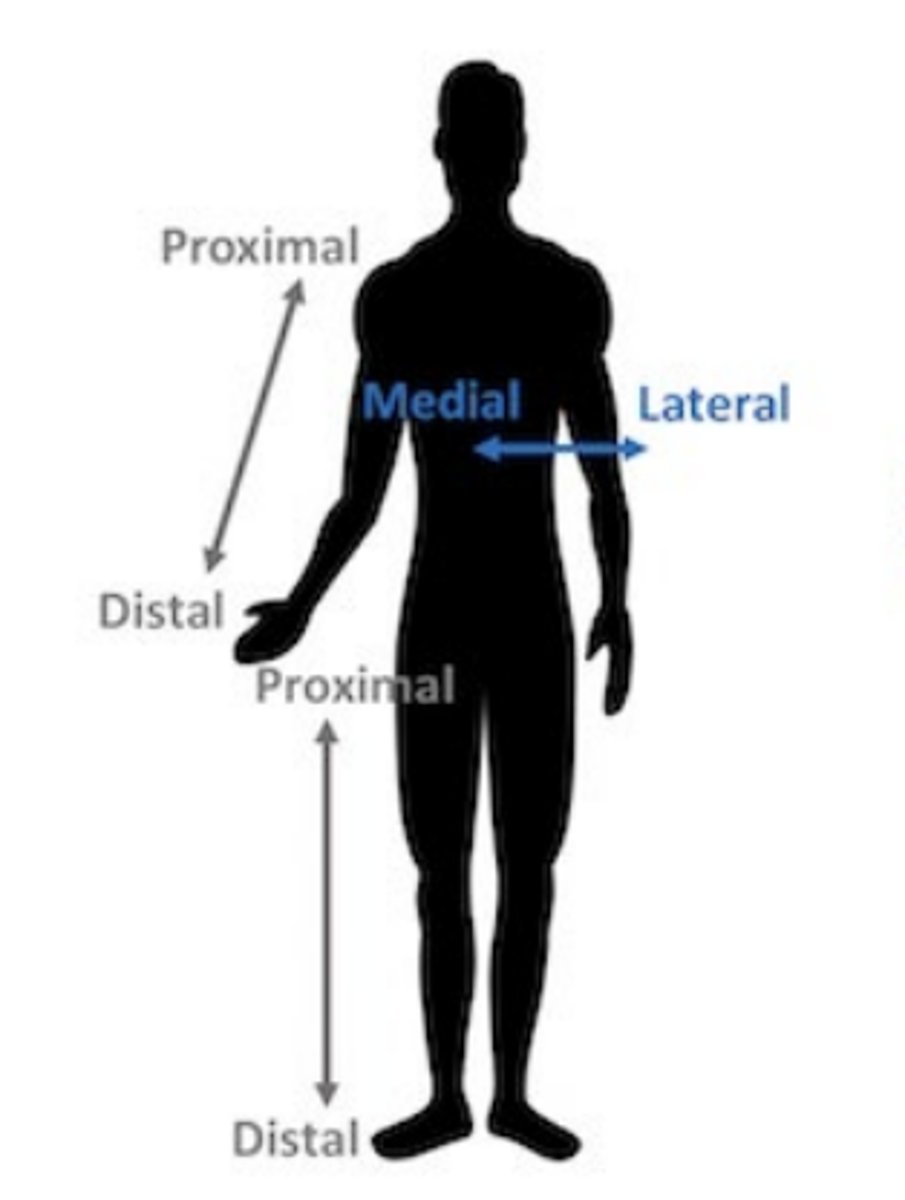
Lateral
away from the midline of the body
away from the median plane or away from the middle of a part
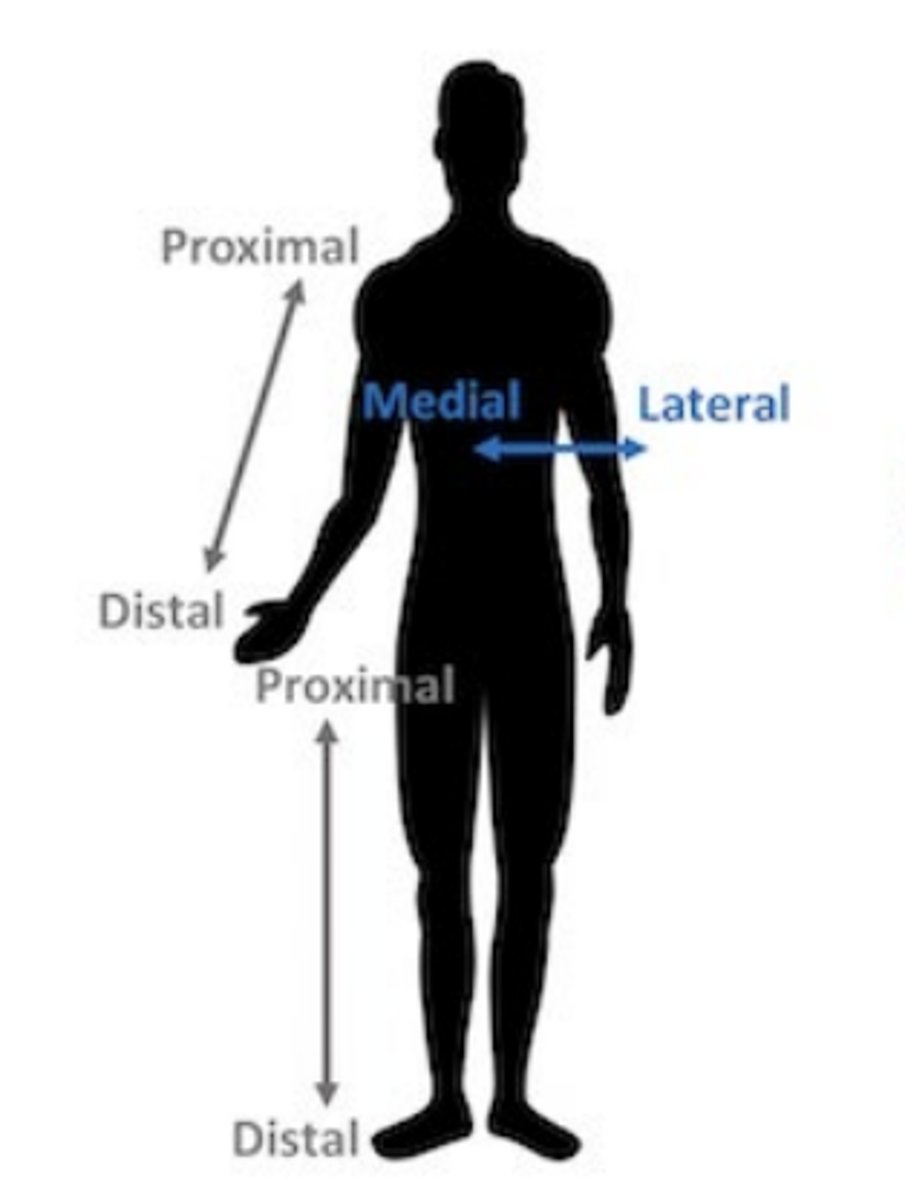
external
outside the body
internal
inside the body
superior (cephalic)
"toward the head end of the body" or "higher/above"
Cephalad - central ray angle
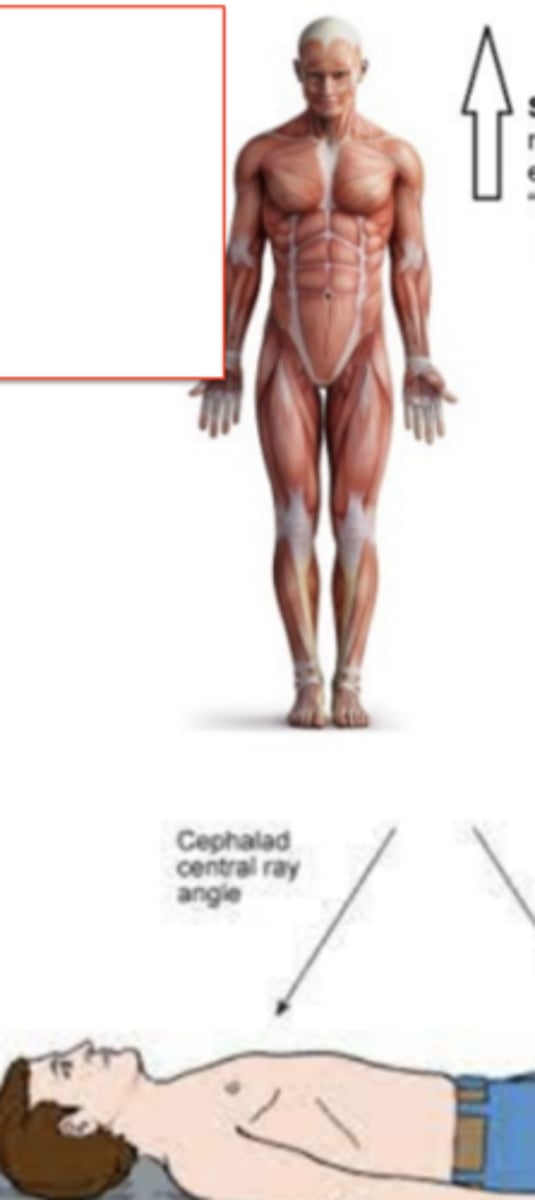
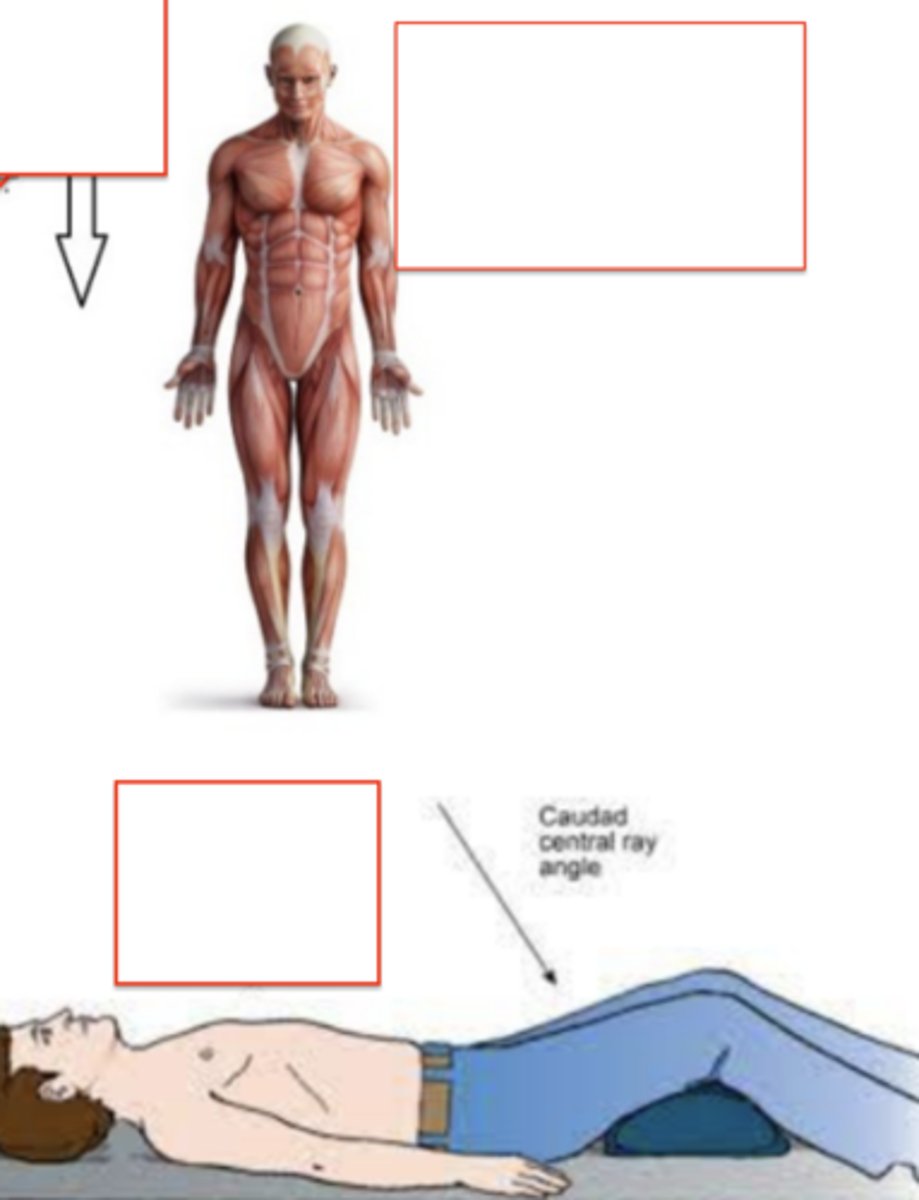
inferior (caudal)
"away from the head" or "lower/under"
Caudad central ray angle
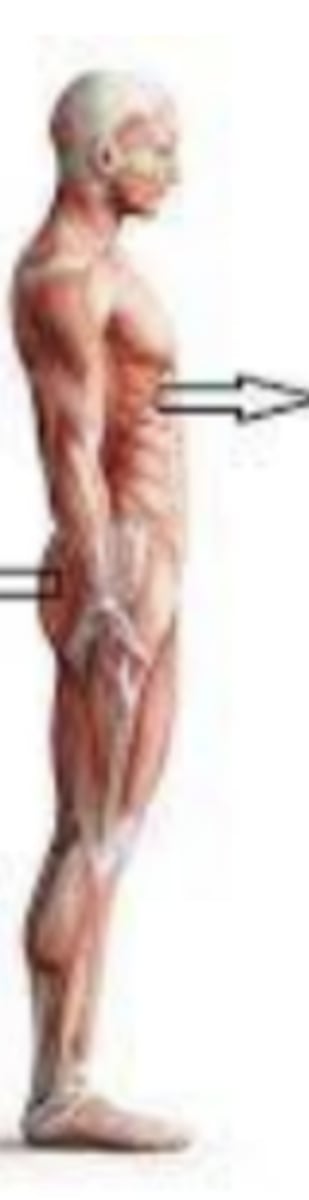
anterior (ventral)
front of / in the front. your abdominal muscles are on the X side of the body
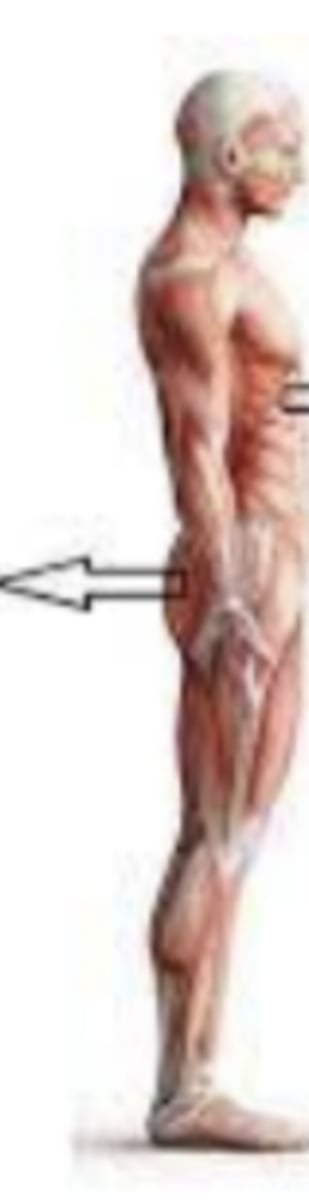
posterior (dorsal)
opposite of the anterior; back of/ behind / on the back
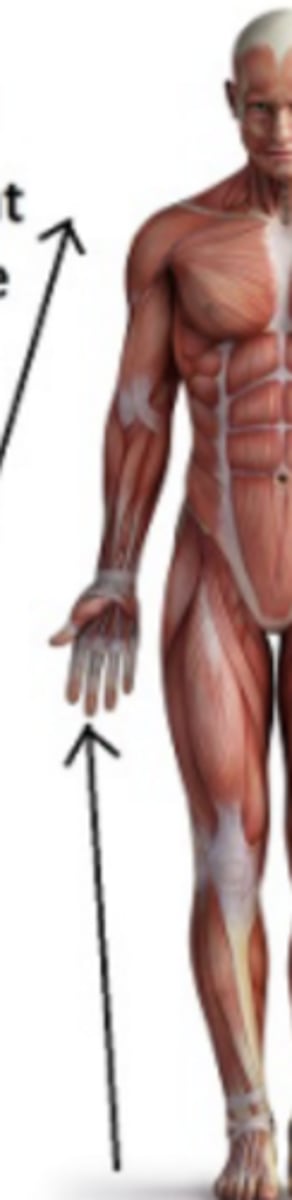
proximal
closer to the trunk as compared to another structure
nearer to the point of attachment or origin
distal
farthest away from attachment or origin; farther from the trunk
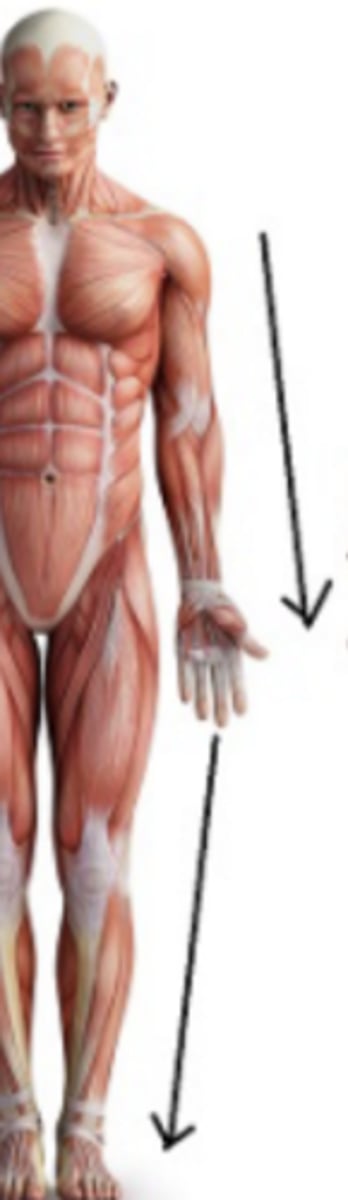
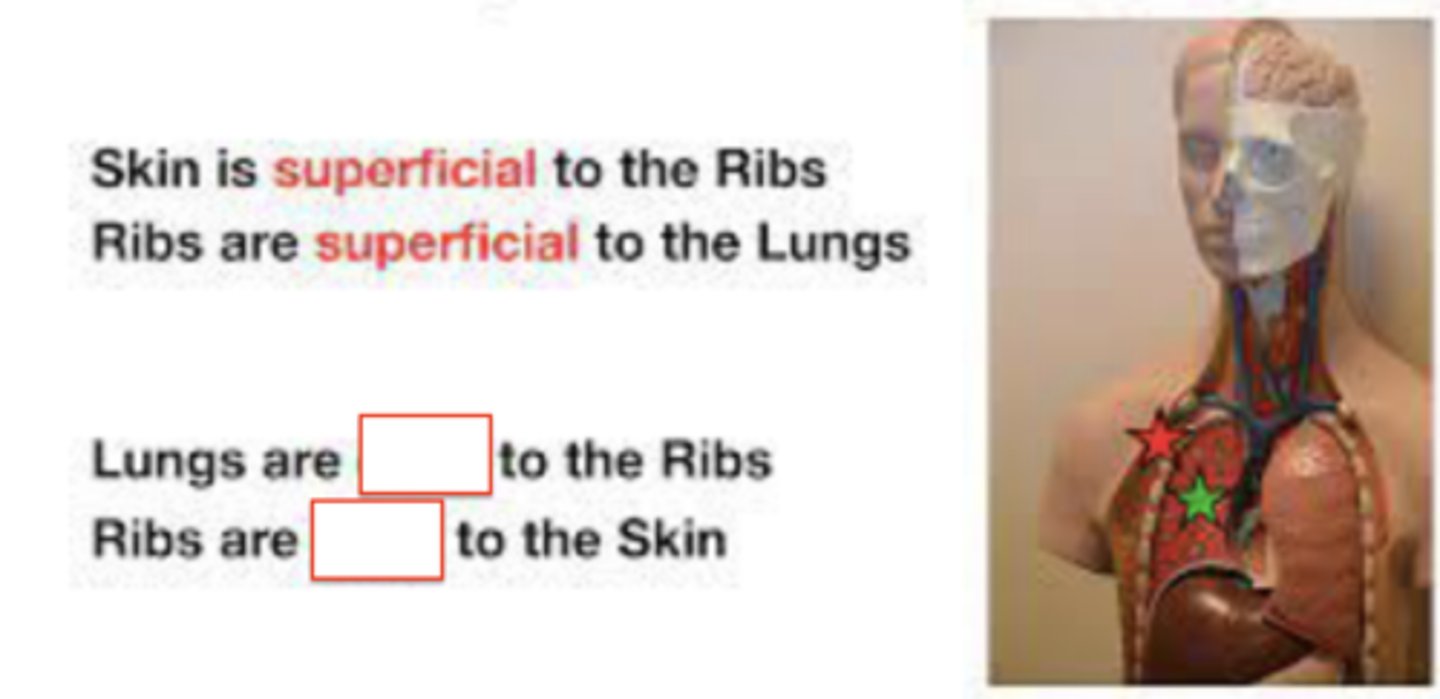
superficial (peripheral)
closer to the surface of the body or towards the edge
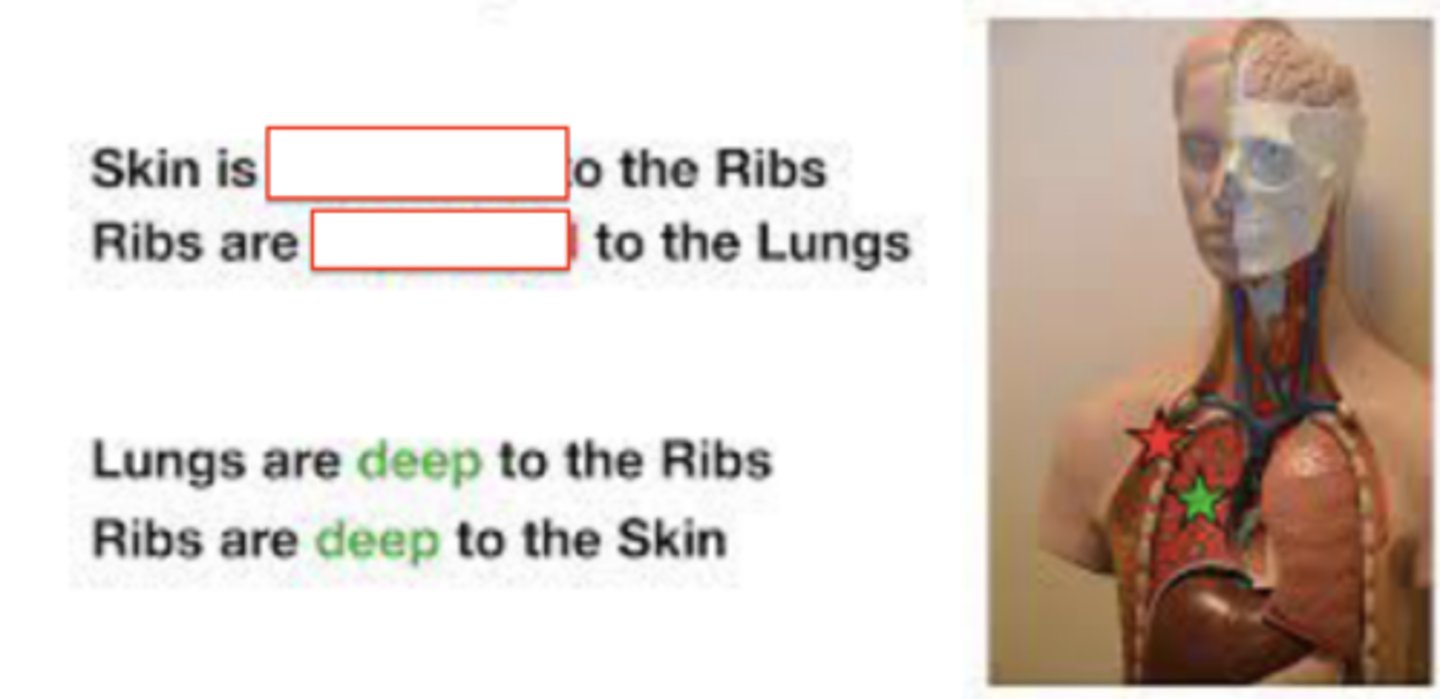
deep (central)
more internal to body
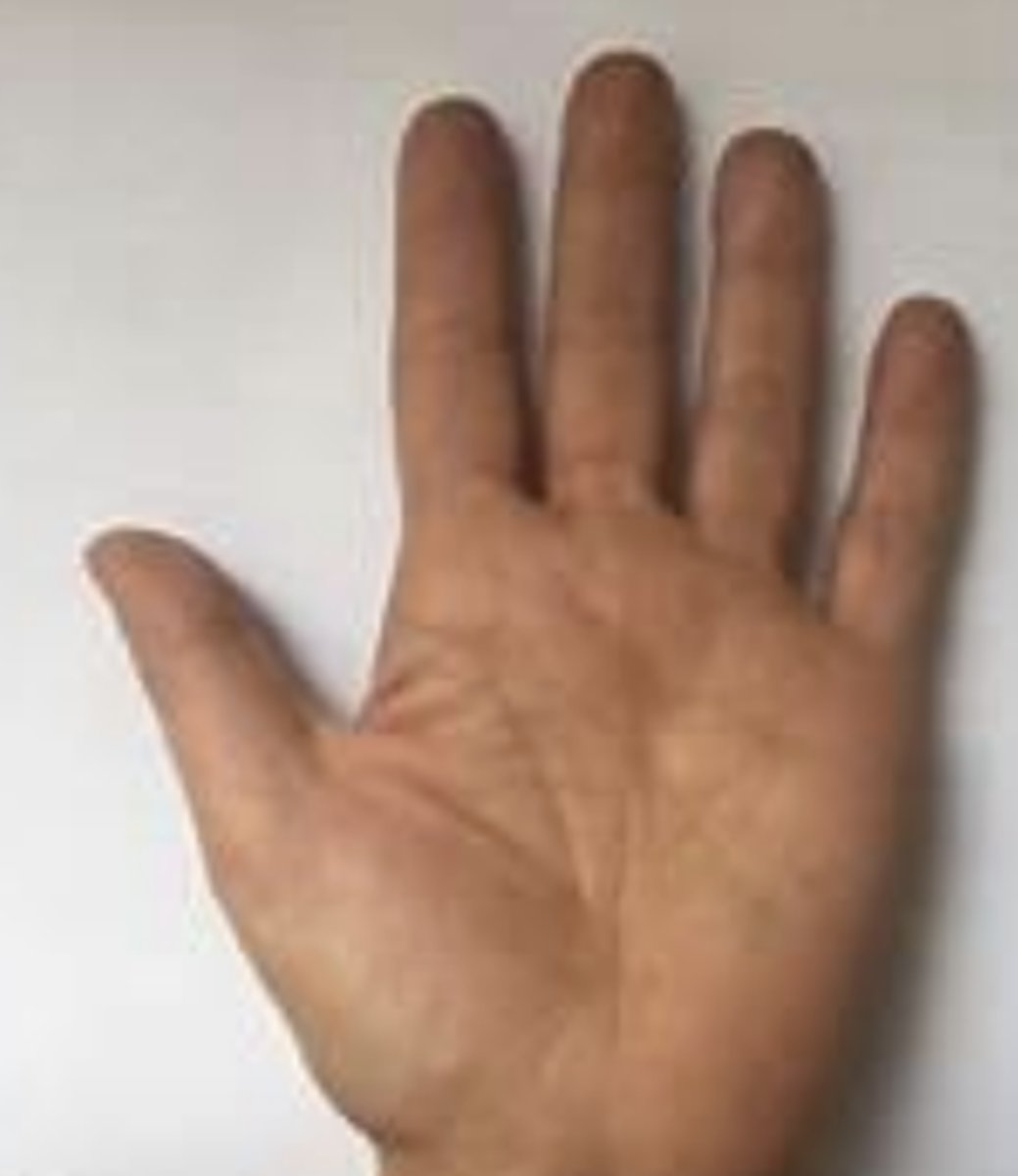
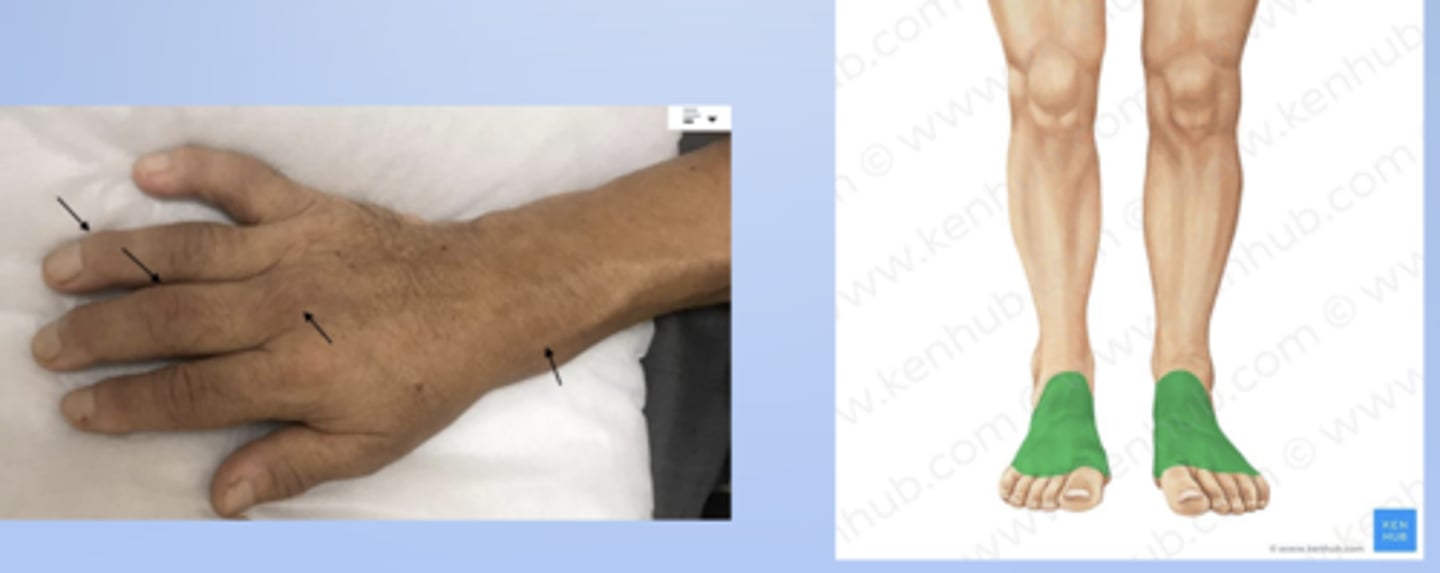
palmar
palm of the hand
hand is supinated
plantar
sole of the foot
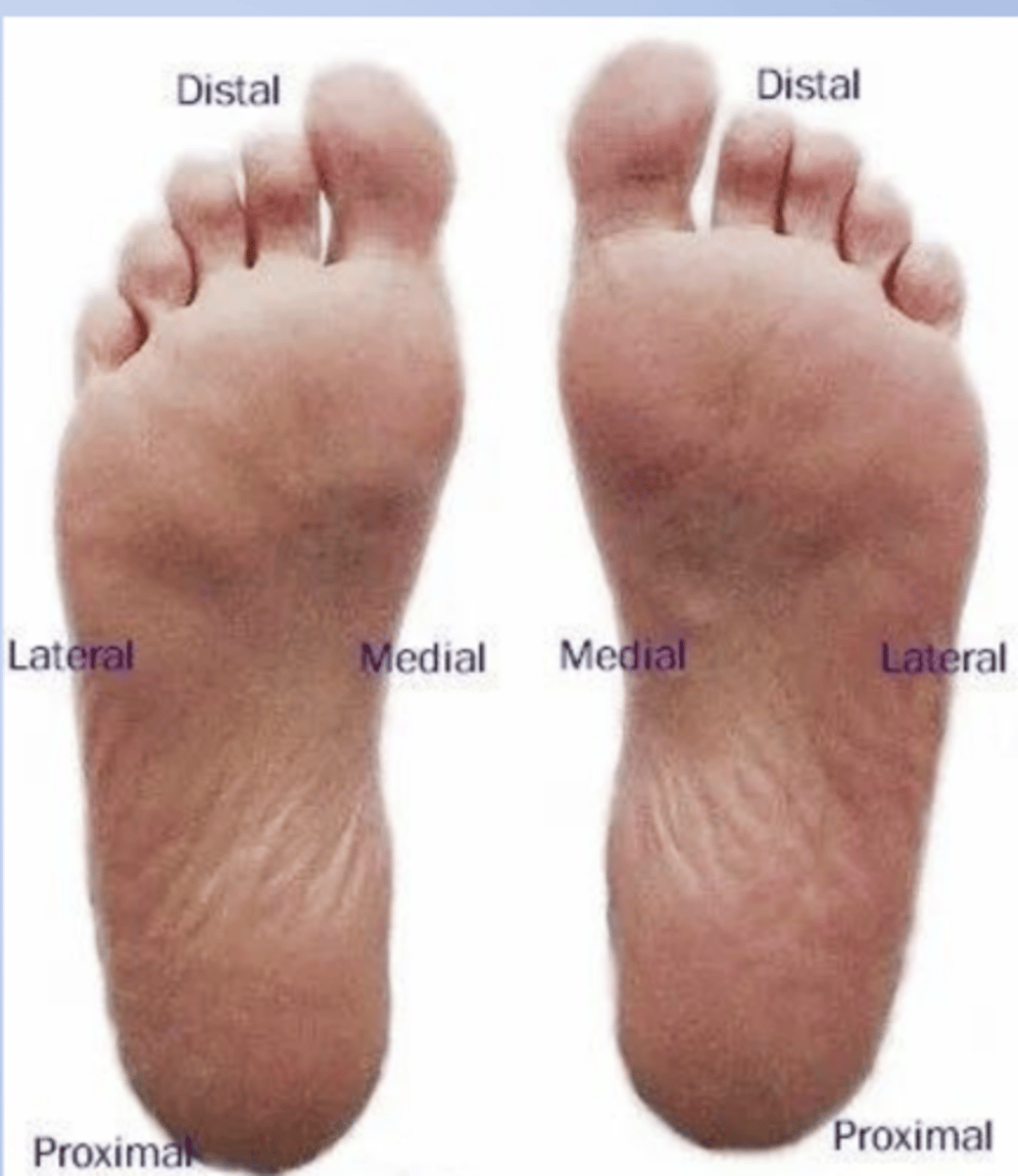
dorsum
anterior or top of the foot or the back of the hand
unilateral
involving one side of the body
"uni" = one
RED
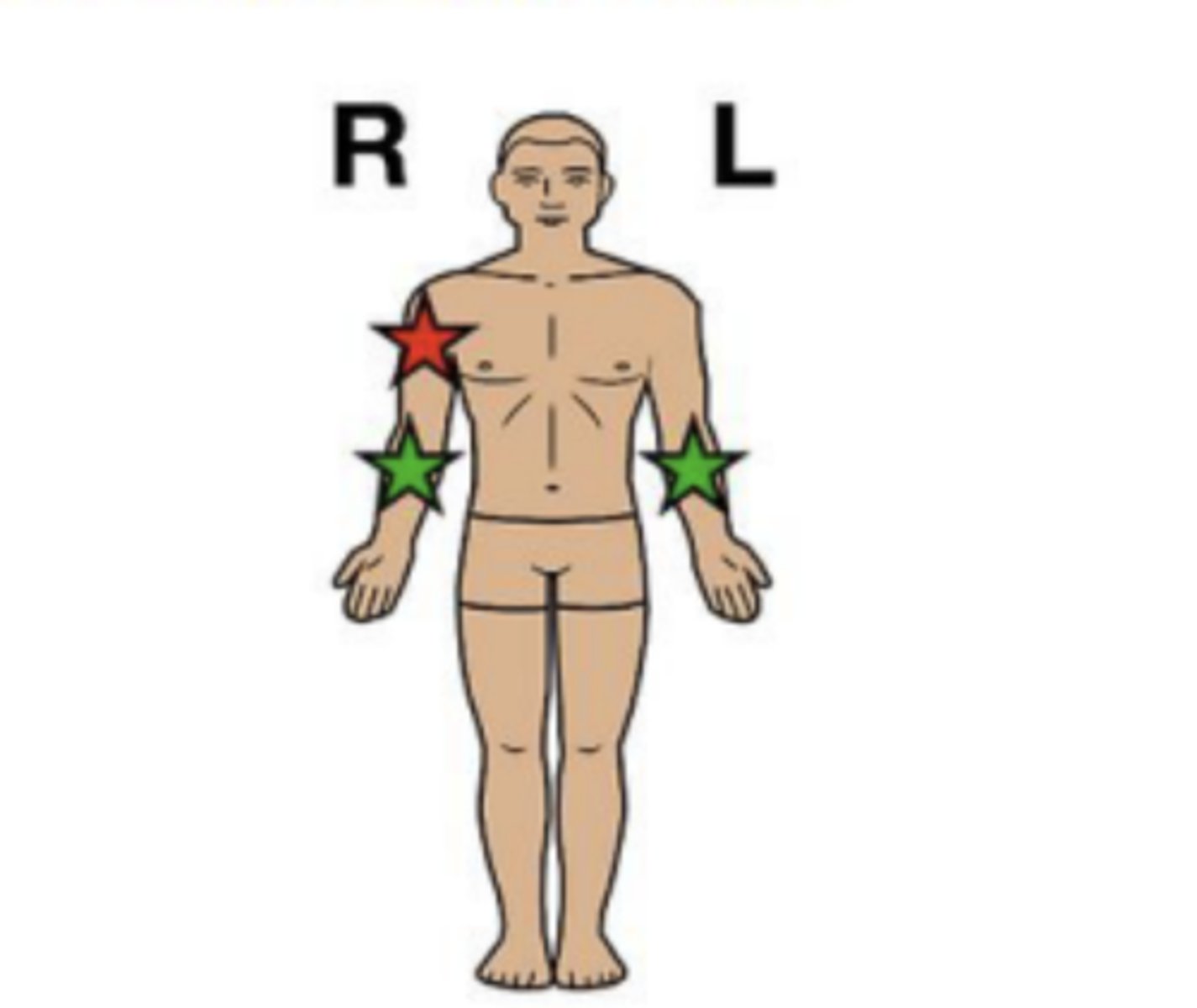
bilateral
involving both sides of the body
"bi" = two
GREEN
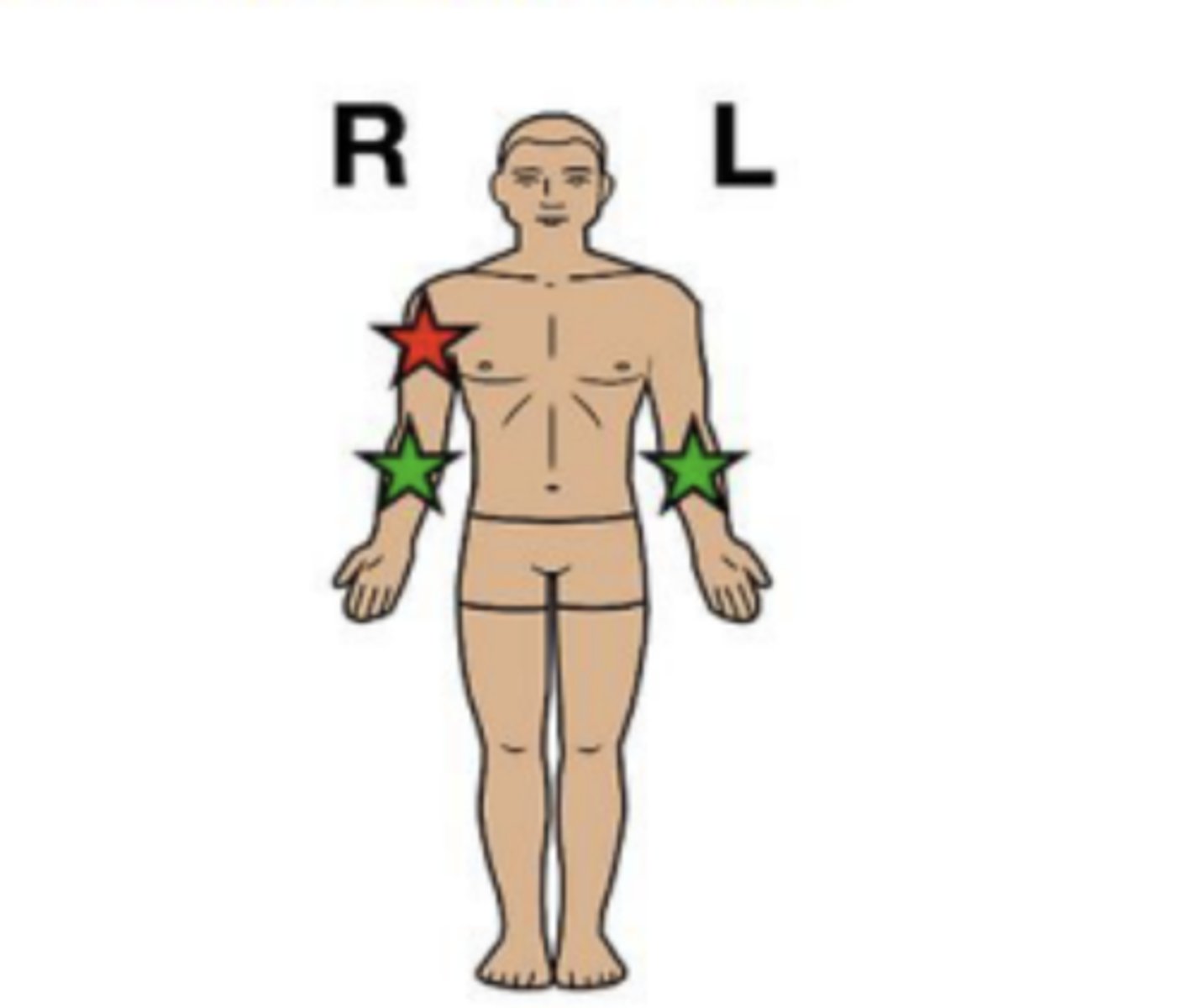
ipsilateral
on the same side of the body
"ipsi" = same
RED
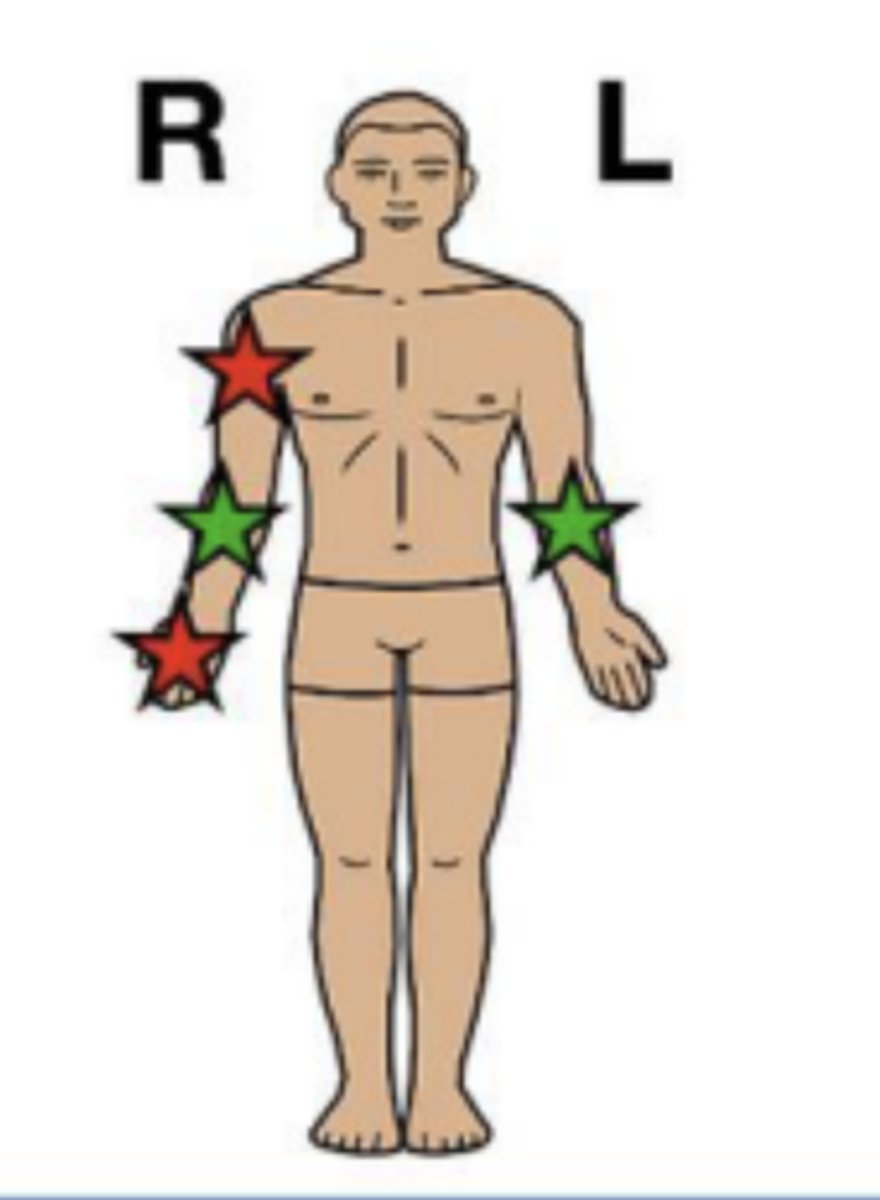
contralateral
on opposite sides of the body
"contra" = opposite
GREEN
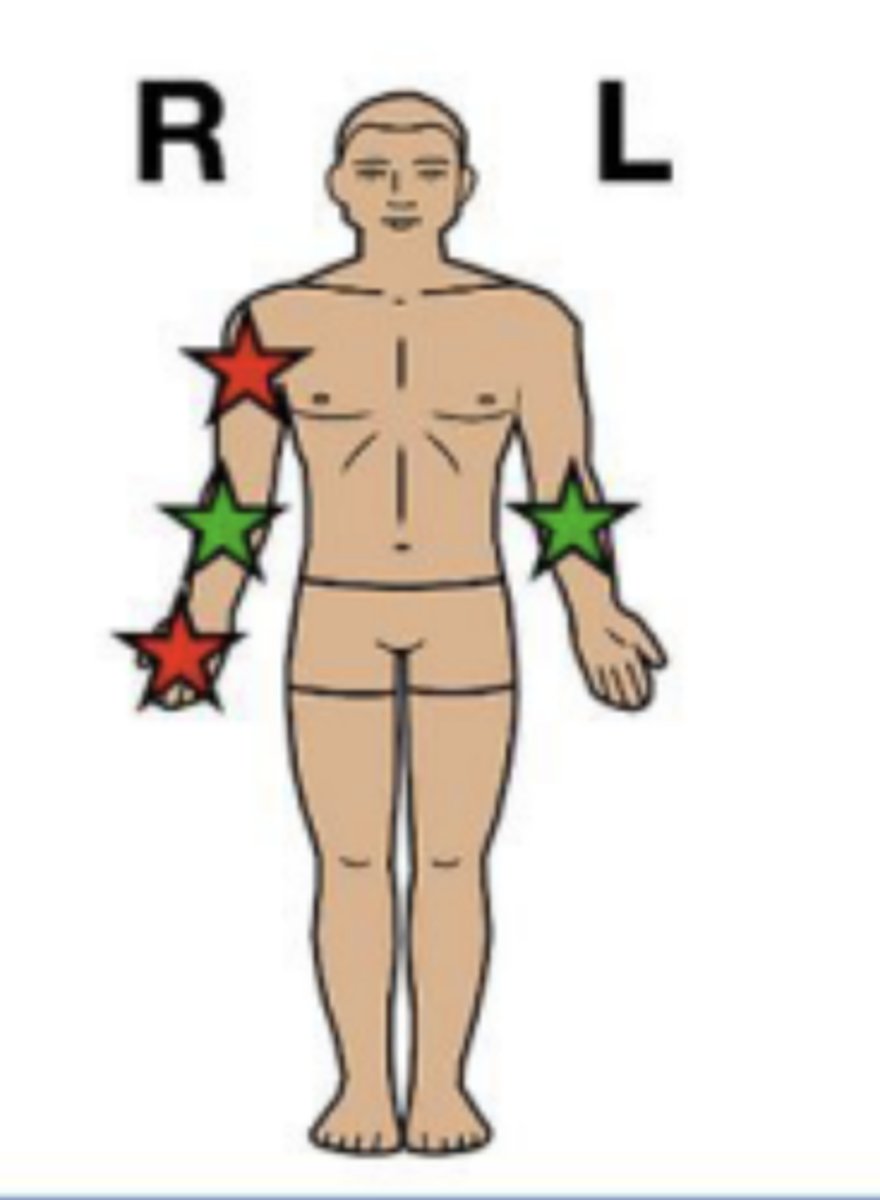
projection
defined as the path of the CR as it exits the x-ray tube, passing through the patient to the IR
identified by the entrance and exit points of the body
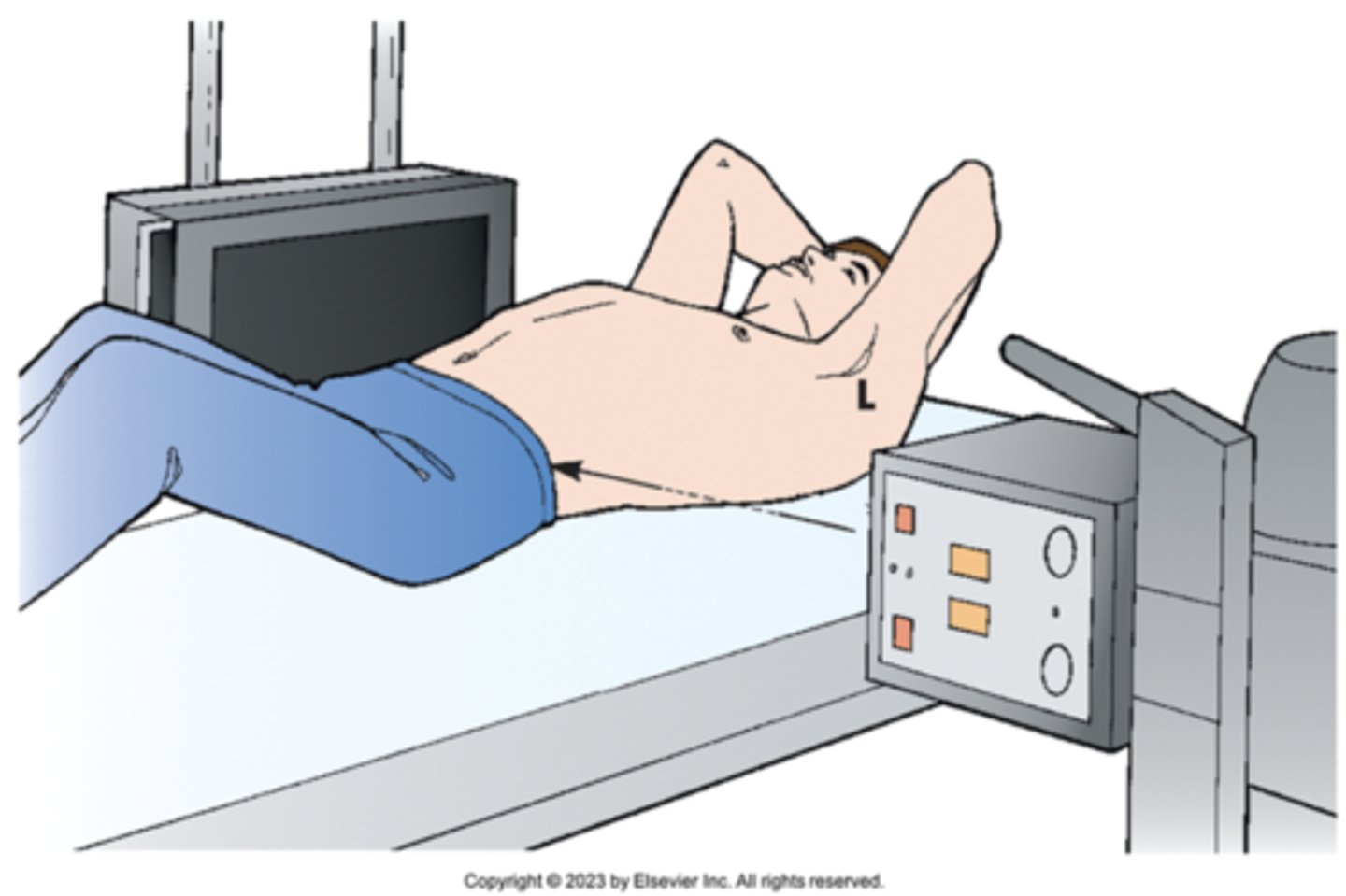
antero-posterior (AP)
central ray passes perpendicular to the coronal plane, from anterior to posterior
FRONT TO BACK
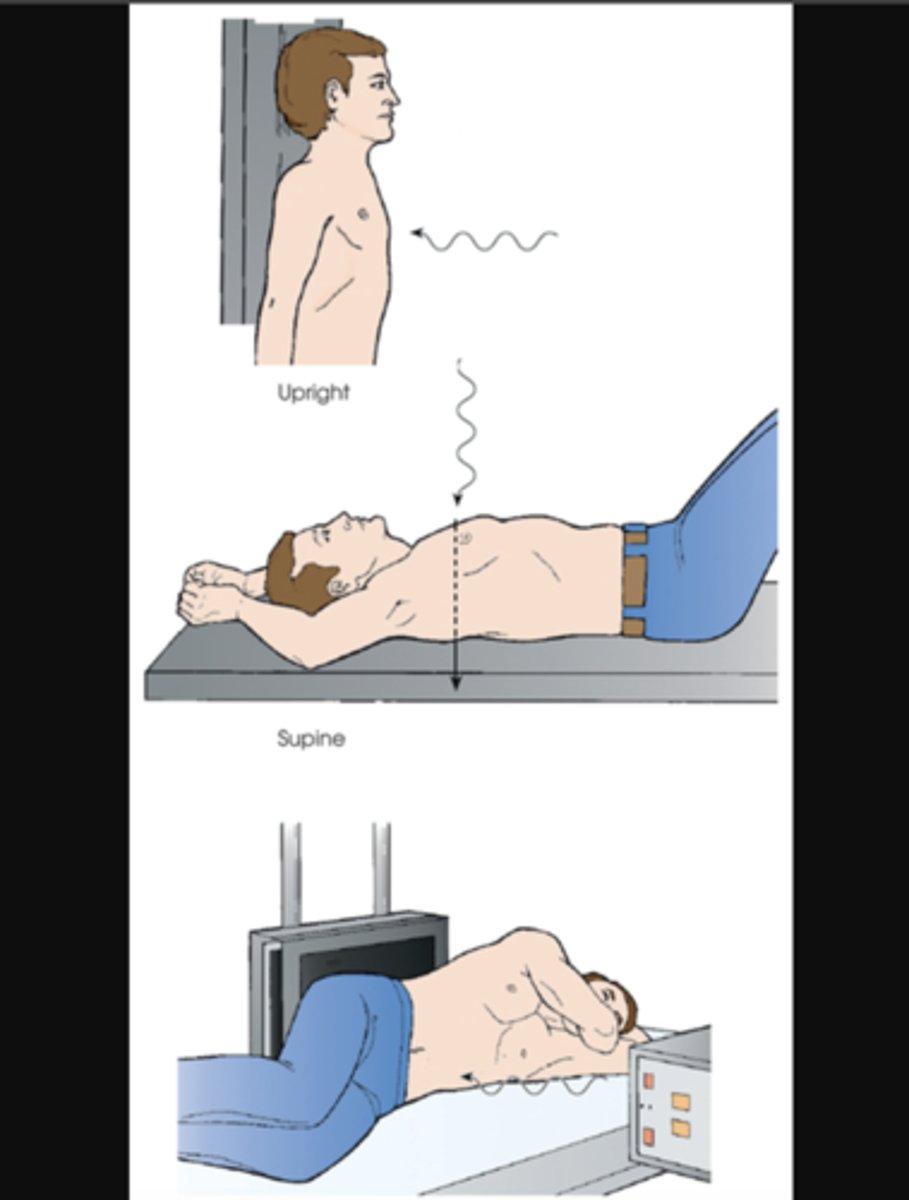
postero-anterior (PA)
central ray passes, perpendicular to the coronal plane, from posterior to anterior
lateral
central ray, perpendicular to the sagittal plane and parallel to the coronal plane, passes from one side of the body to the other
travels transversely along the coronal plane
specify side of the body closest to the IR
SIDE VIEW
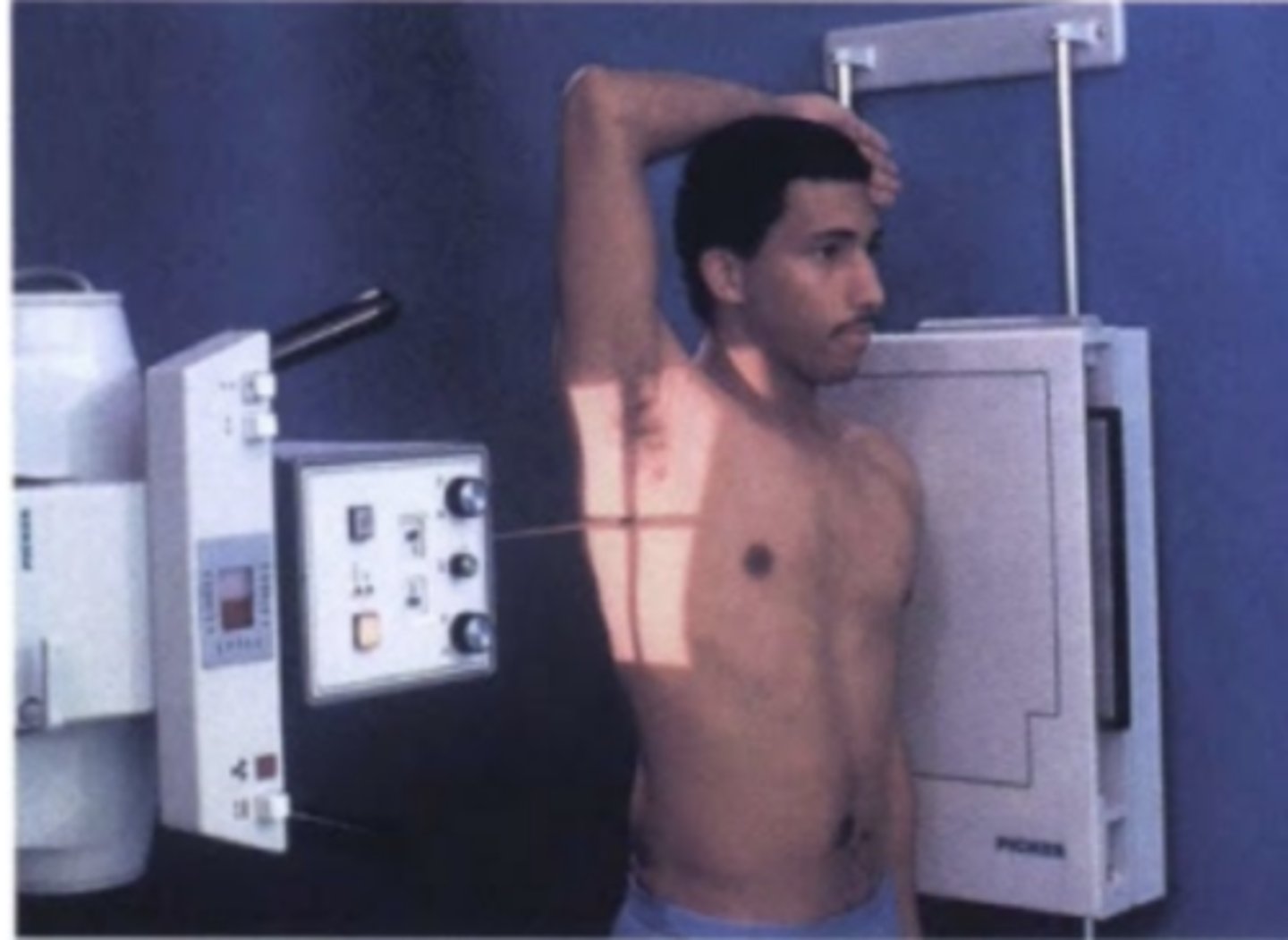
oblique
central ray passes through the body / body part through a plane which is at an angle to the transverse plane/coronal plane
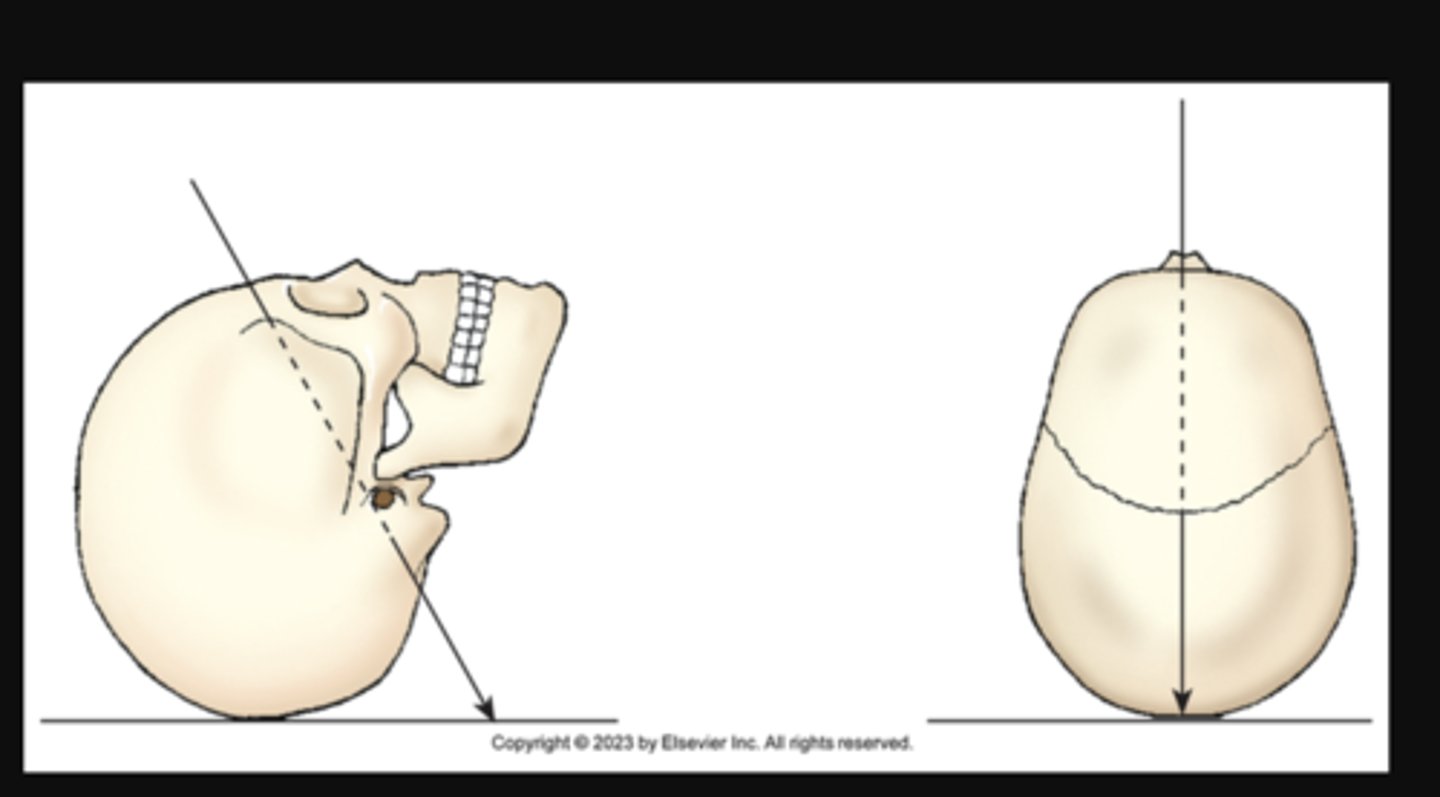
axial
longitudinal angulation of the central ray toward the head (cephalad) or the feet (caudad)
AP X projection of skull. Central ray enters anterior aspect at an angle and exits posterior aspect.
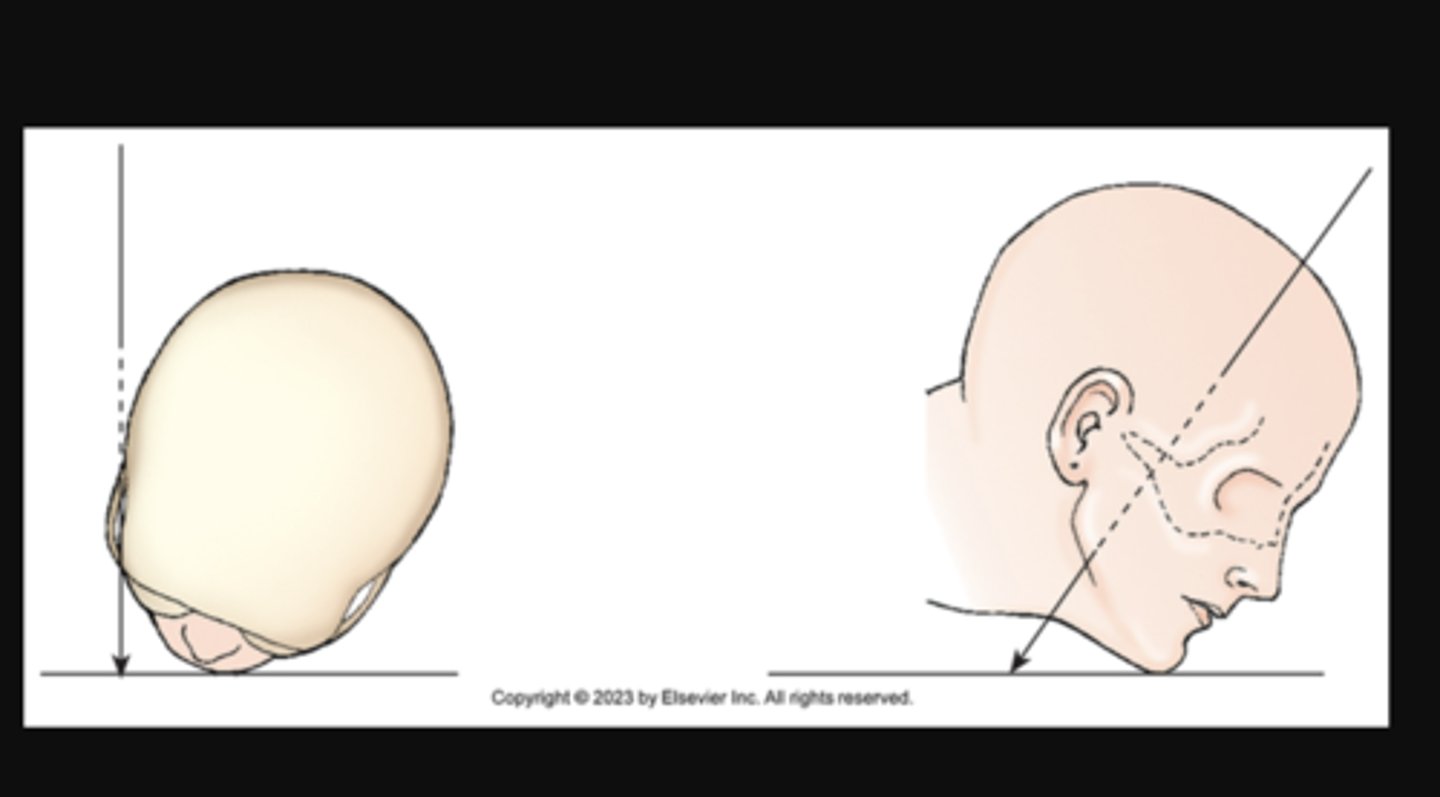
tangential
central ray passes along side (or parallel to the long axis of the body or part SKIMMING)
CR directed along the outer margin of a curbed body surface
X projection of zygomatic arch. Central ray skims surface of the skull.
Position
upright; seated; supine; prone
Overall posture of the patient or general body position
also refers to the specific placement of the body or part in relation to the table or IR
A) Patient positioned for PA projection of the chest. The anterior aspect of the chest is closest to IRs. (B) Patient positioned for AP projection of the chest. The posterior aspect of the chest is closest to IRs.
View
used to describe the body part as seen by the IR exact opposite of the projection, the preferred term in the United States
EXACT OPPOSITE OF PROJECTION
Refers to the image as seen on the IR (what’s visible in the final radiograph).
In the U.S., “view” is often used as the preferred clinical term when describing the picture rather than the projection.
Example: A PA chest view means the final image looks like it was taken with the patient’s anterior chest against the IR.👉 Think: What does the radiograph actually show?
View: PA chest view (the film/image shows the chest from a front perspective)
method
refers to a specific radiographic projection developed by an individual
✅ In short:The Robert Method = an AP projection of the first CMC joint of the thumb used to evaluate Bennett’s fracture.
1. Robert Method
AP projection of the first carpometacarpal (CMC) joint of the thumb.
Used to evaluate Bennett’s fracture (base of the first metacarpal).
2. Towne Method
AP axial projection of the skull.
Visualizes the occipital bone, foramen magnum, and petrous pyramids.
3. Caldwell Method
PA axial projection of the skull.
Best demonstrates the frontal sinuses and superior orbital rims.
4. Waters Method
PA projection with OML at 37° angle.
Used for facial bones, orbits, and maxillary sinuses.
5. Grashey Method
AP oblique projection of the shoulder joint.
Demonstrates the glenoid cavity without superimposition.
6. Lawrence Method
Transthoracic lateral projection of the shoulder.
Useful for proximal humerus fractures.
7. Stecher Method
PA axial projection of the wrist (scaphoid).
Angles beam or elevates IR to elongate the scaphoid and avoid foreshortening.
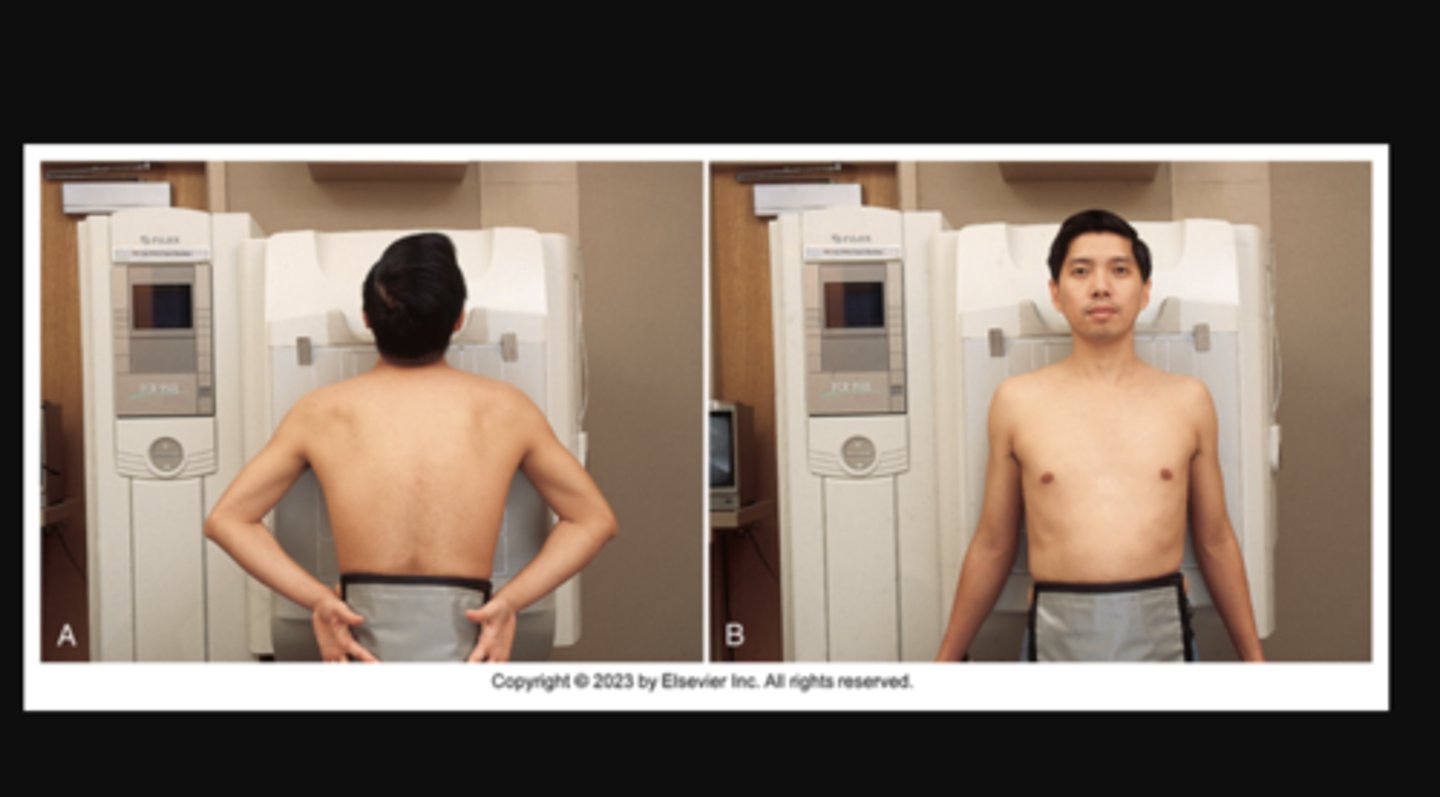
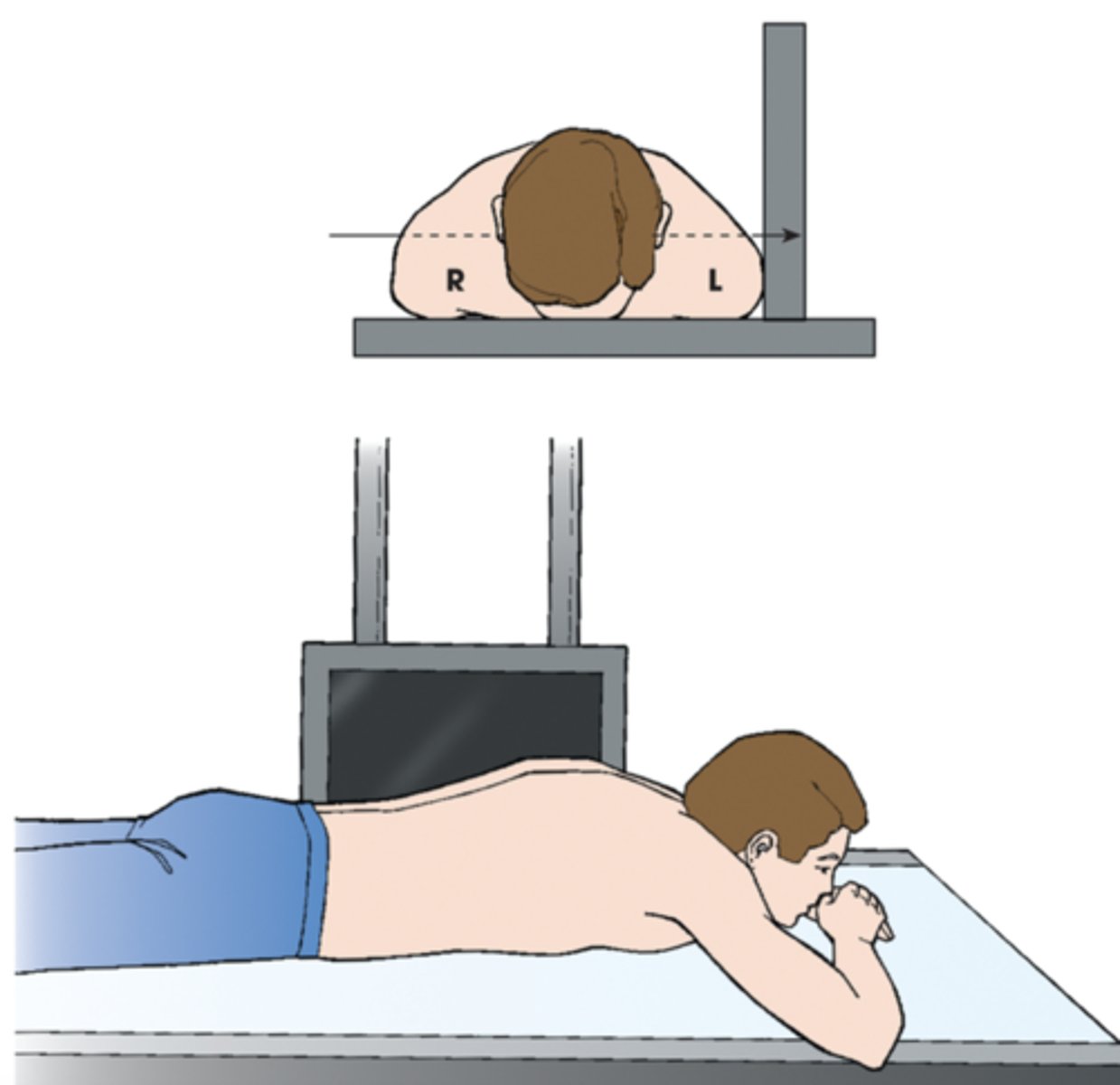
LAO (left anterior oblique)
A patient placed in the X position for PA oblique projection of the chest
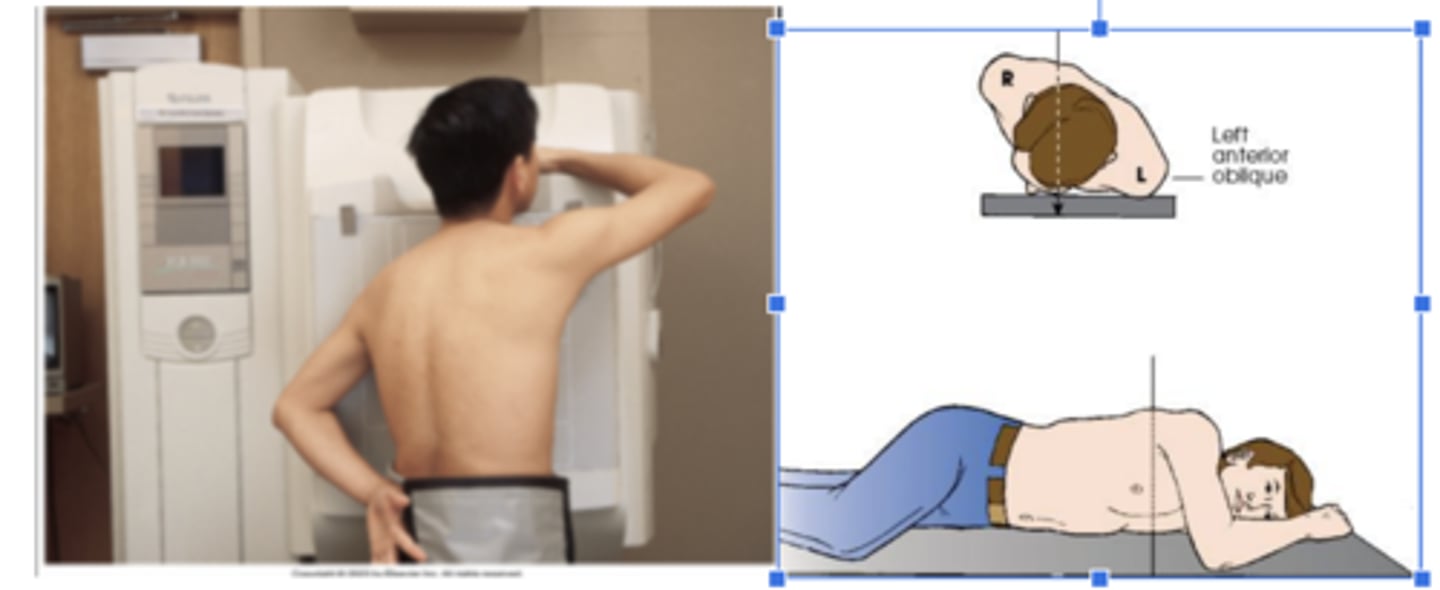
RAO (right anterior oblique)
X radiographic position of chest results in PA oblique projection
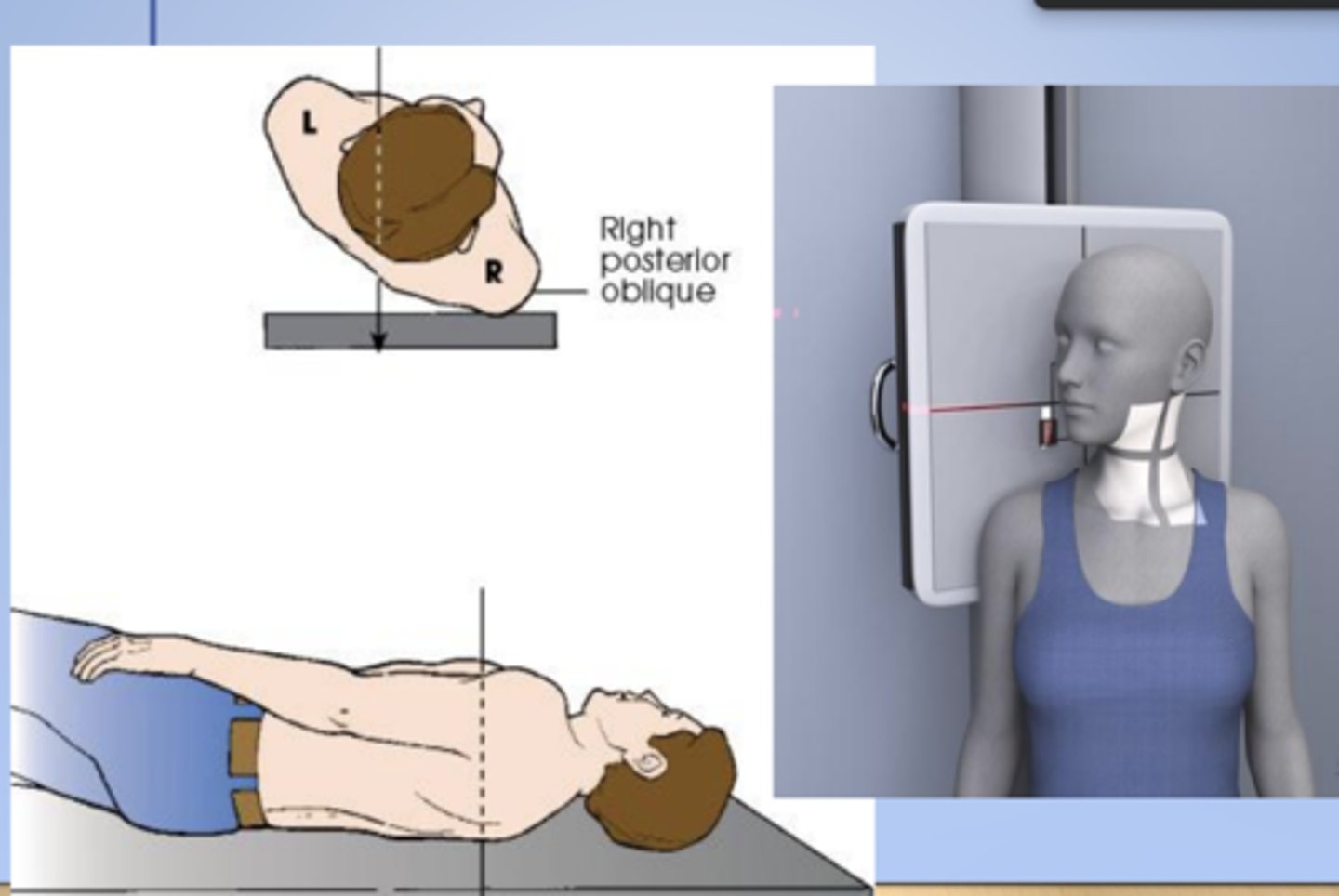
RPO (right posterior oblique)
X radiographic position of chest results in AP oblique projection.
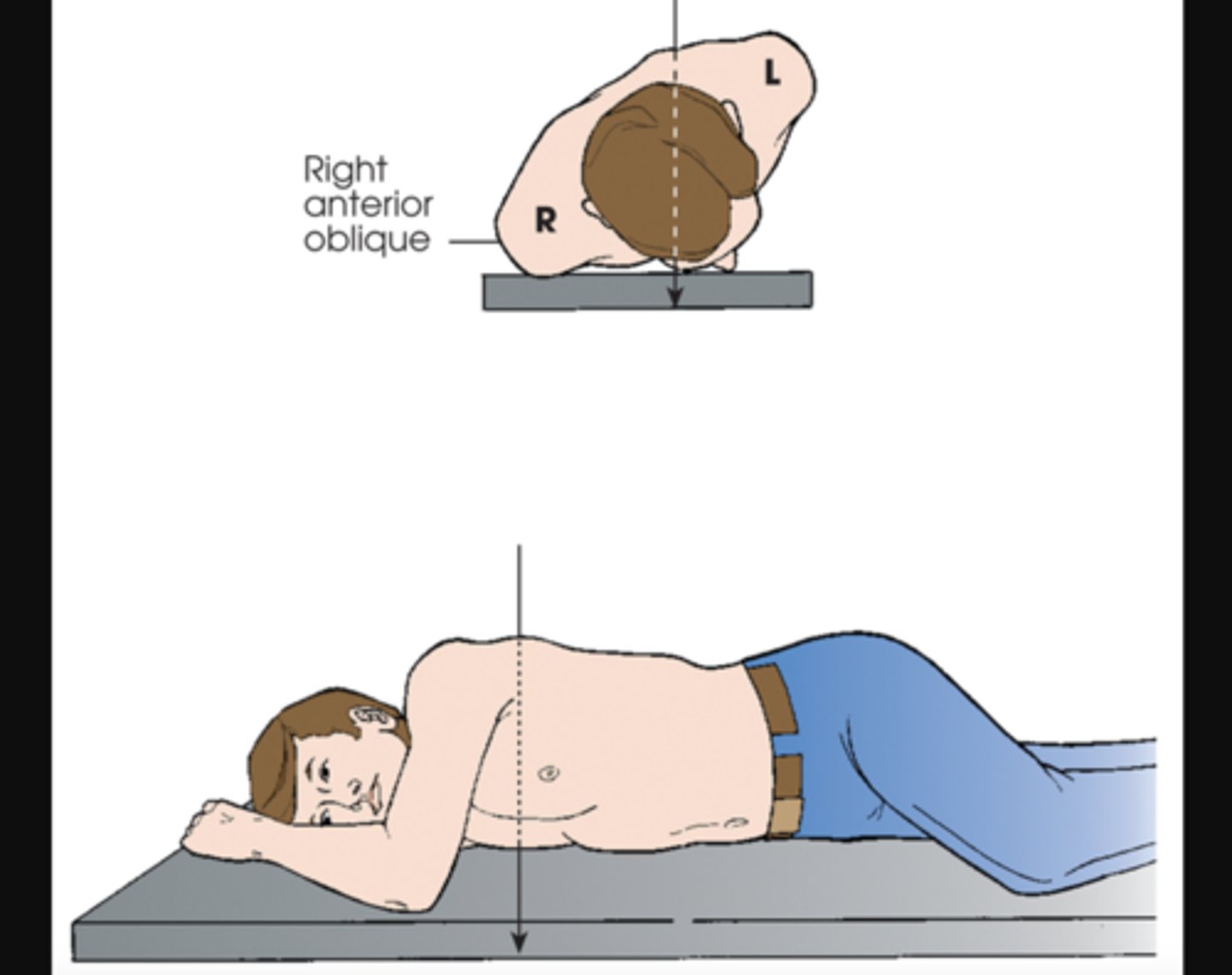
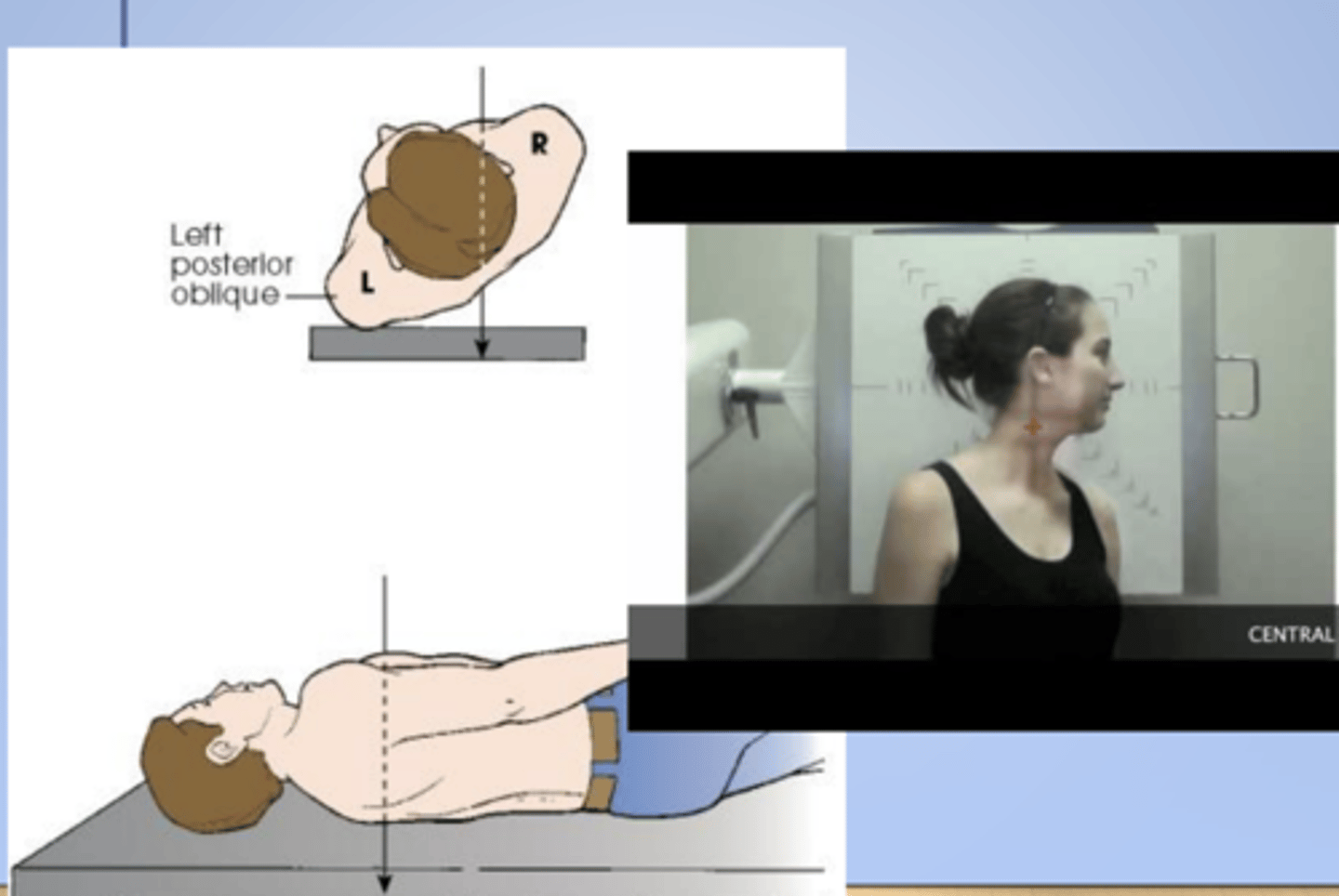
LPO (left posterior oblique)
X radiographic position of chest results in AP oblique projection.
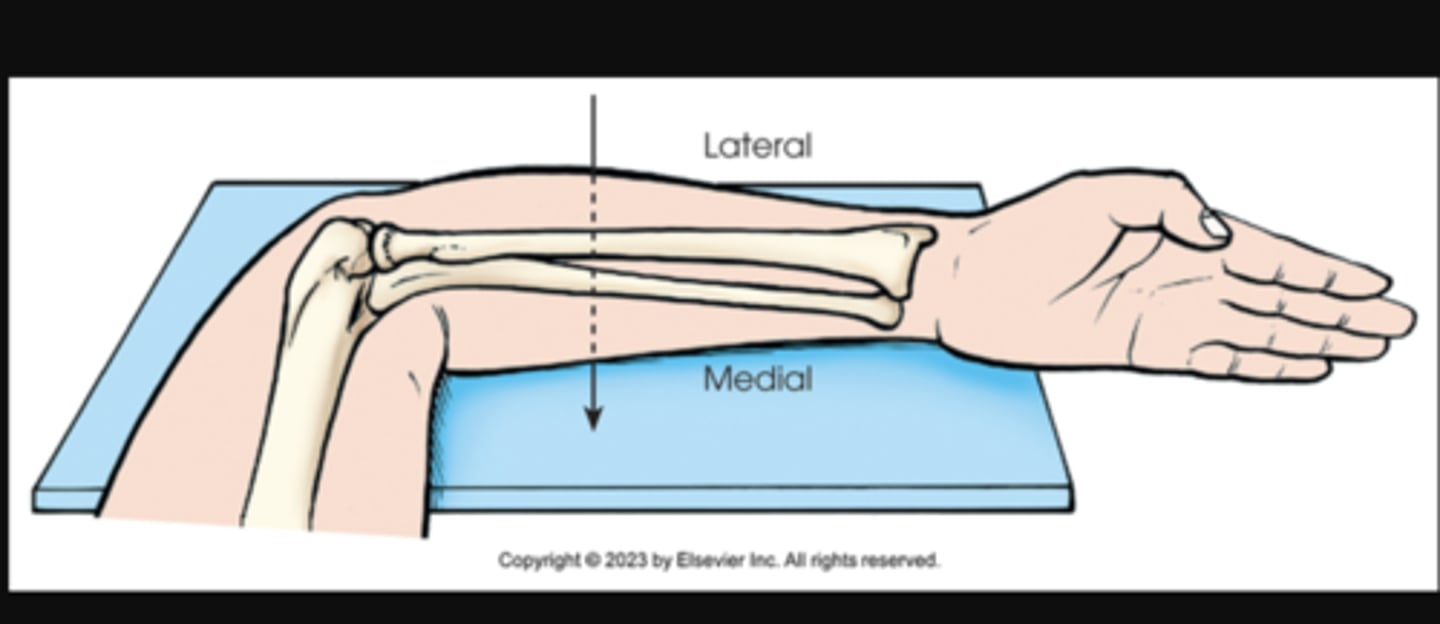
lateromedial
X projection of forearm. Central ray enters lateral aspect of forearm and exits medial aspect.
mediolateral
Lateral hand with radial surface to IR
True AP or AP Projection
Central Ray Perpendicular to the coronal (frontal) plane
Central Ray Parallel to the sagittal plane
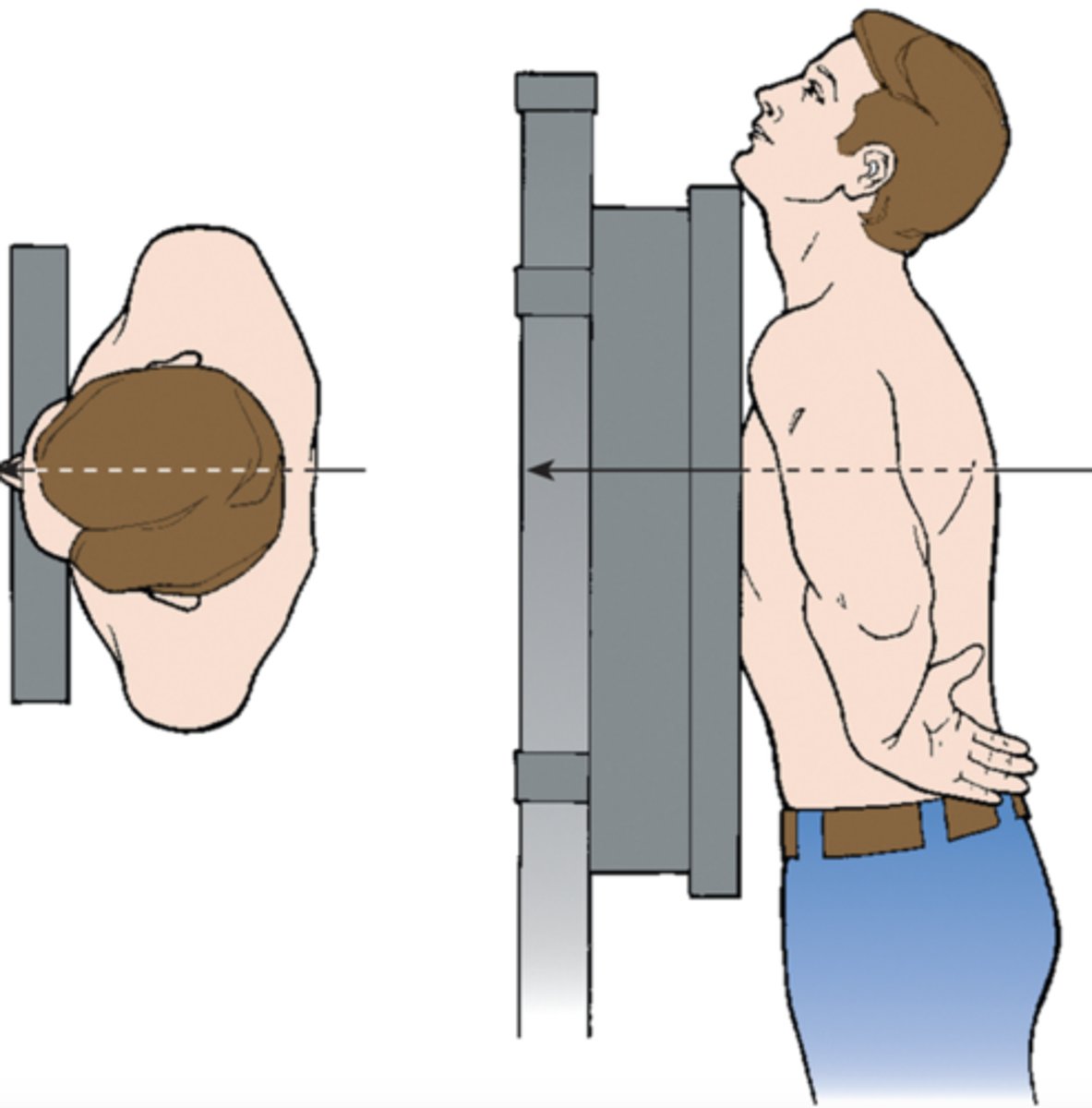
True lateral projection
Central Ray Parallel to the normal plane
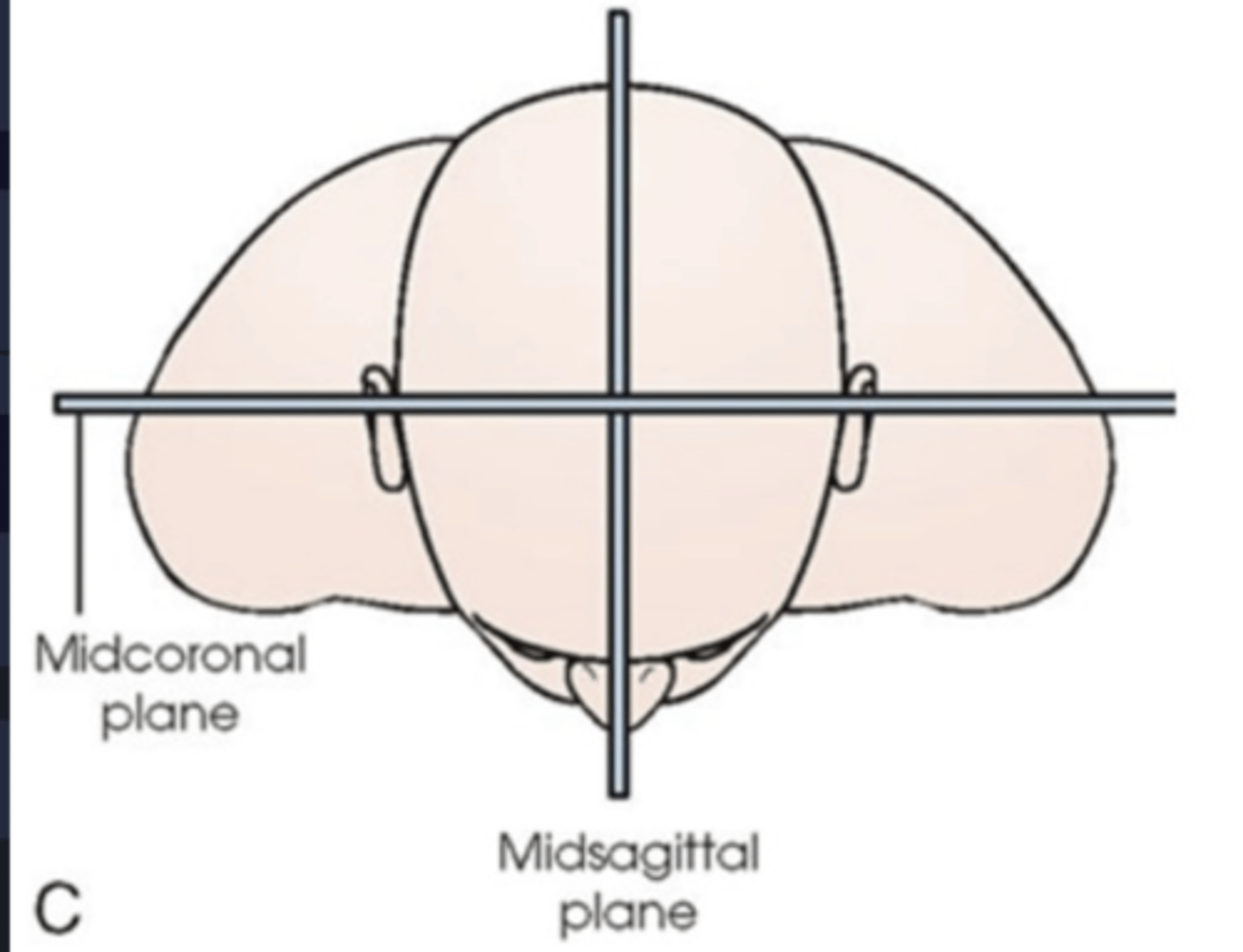
Coronal plane for Chest xray
perpendicular to sagittal plane
MCP (midcoronal plane)
perpendicular to IR (IR is on right side)
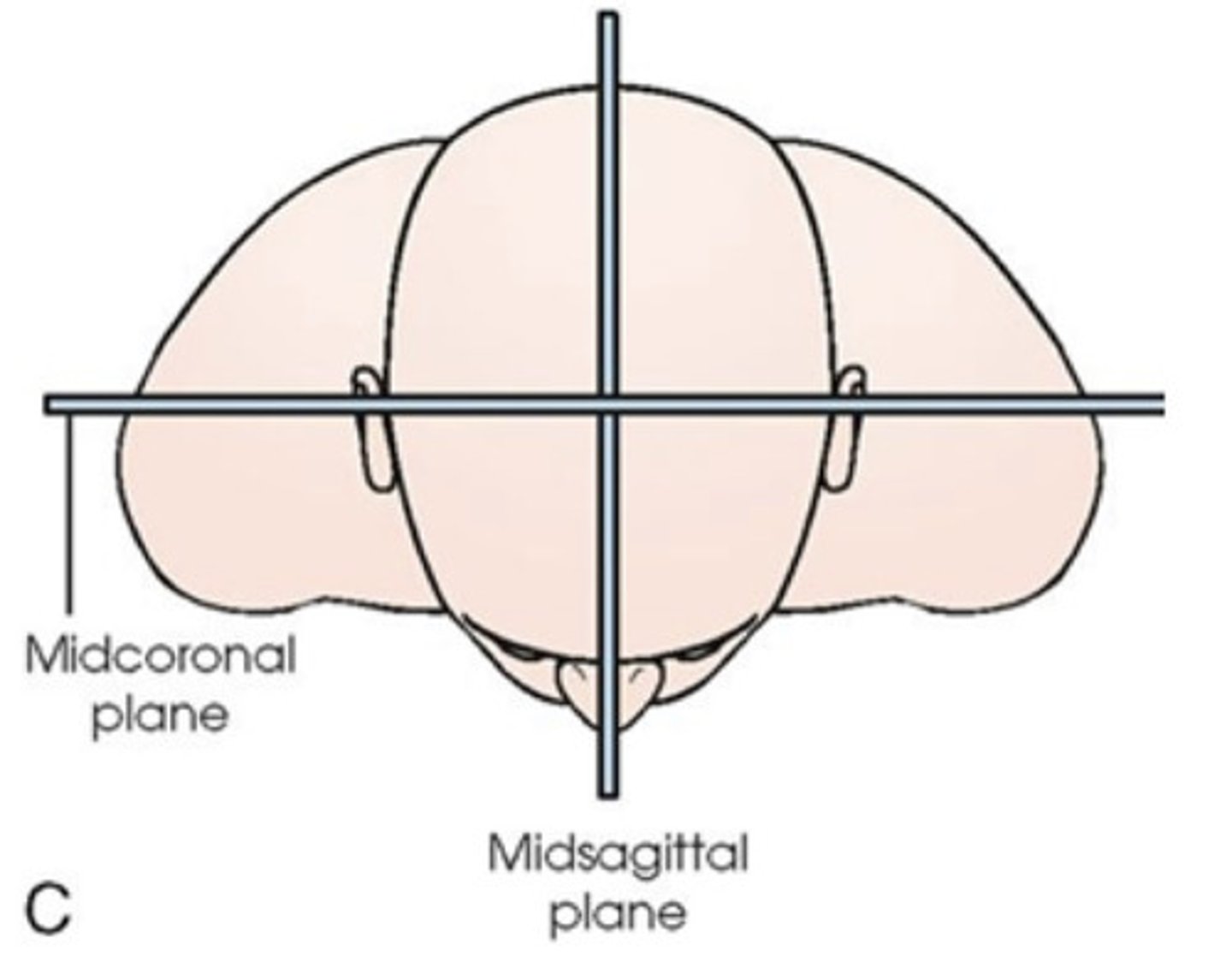
MSP (midsagittal plane)
parallel to IR (IR is on the right side)
upright
erect or vertical
seated
upright, but sitting on a stool
recumbent
lying down in any position
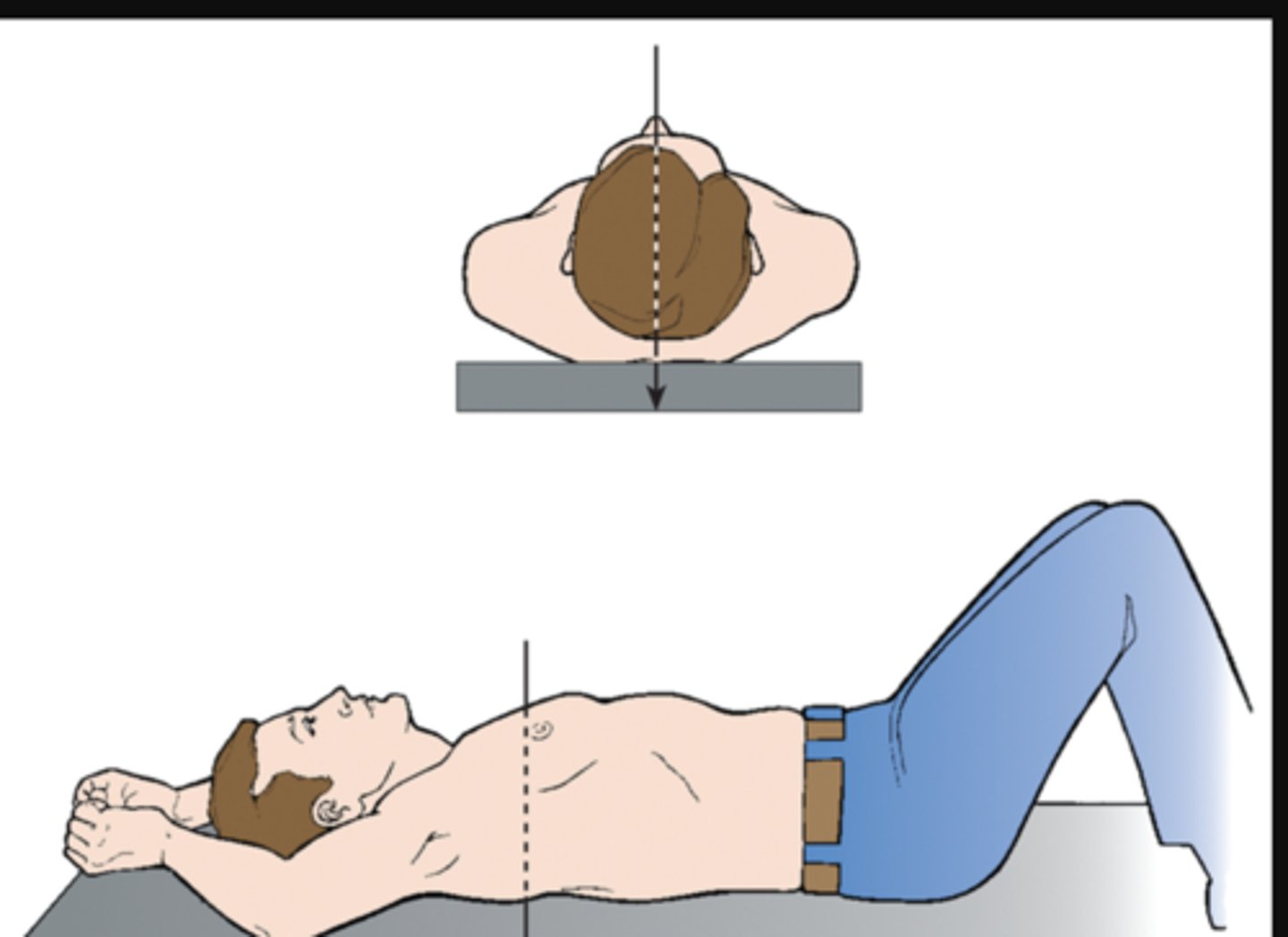
supine (dorsal recumbent position)
lying on the back
knees can be flexed for comfort
The most common surgical position. The patient lies flat on their back on the operating room bed. The spinal column should be in alignment to the bed. This position is often used for facial, abdominal, and extremity procedures.
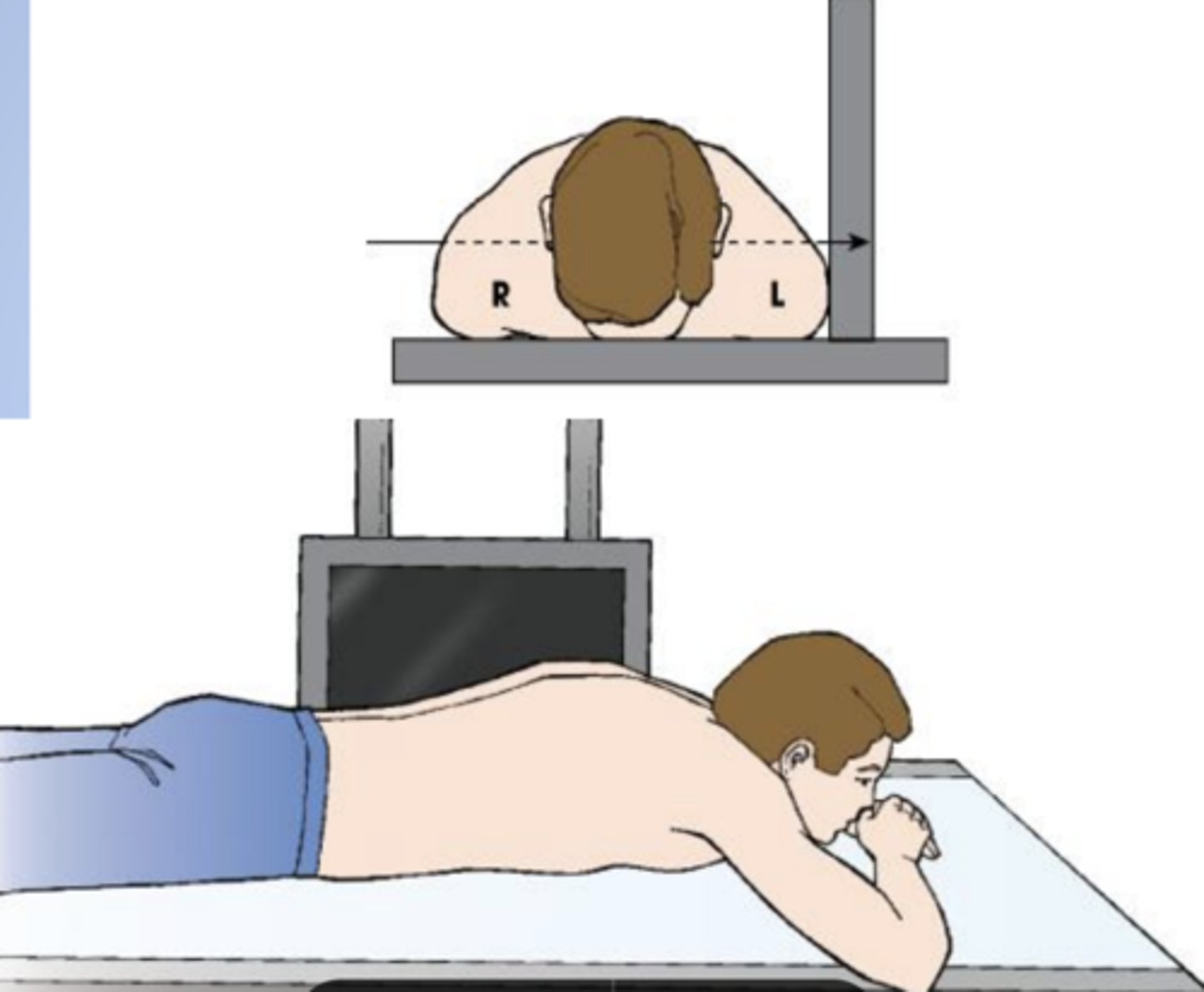
prone (ventral decubitus or recumbent)
lying face down
has the patient lying on their stomach, allowing access to the posterior cranial fossa, spine, buttocks, rectum, and posterior lower extremities.
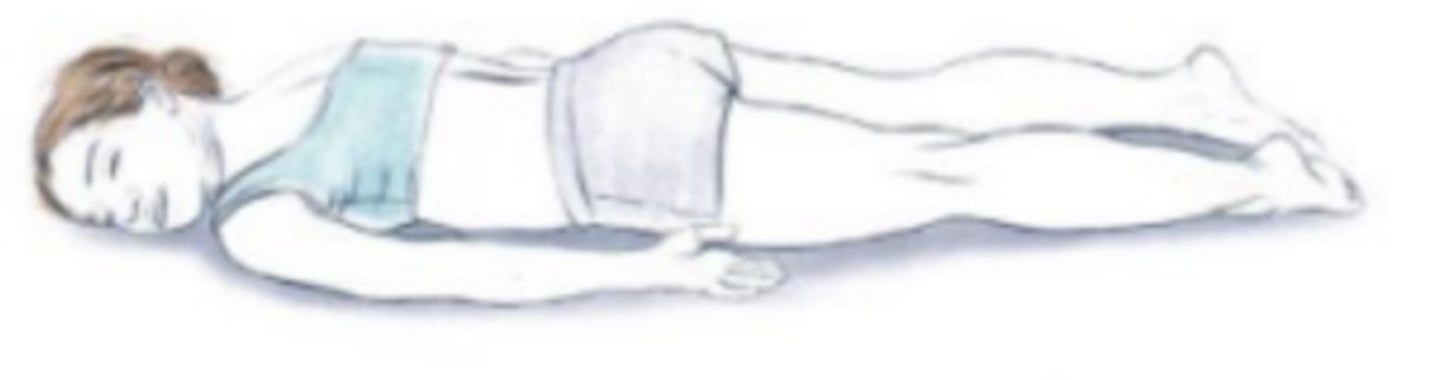
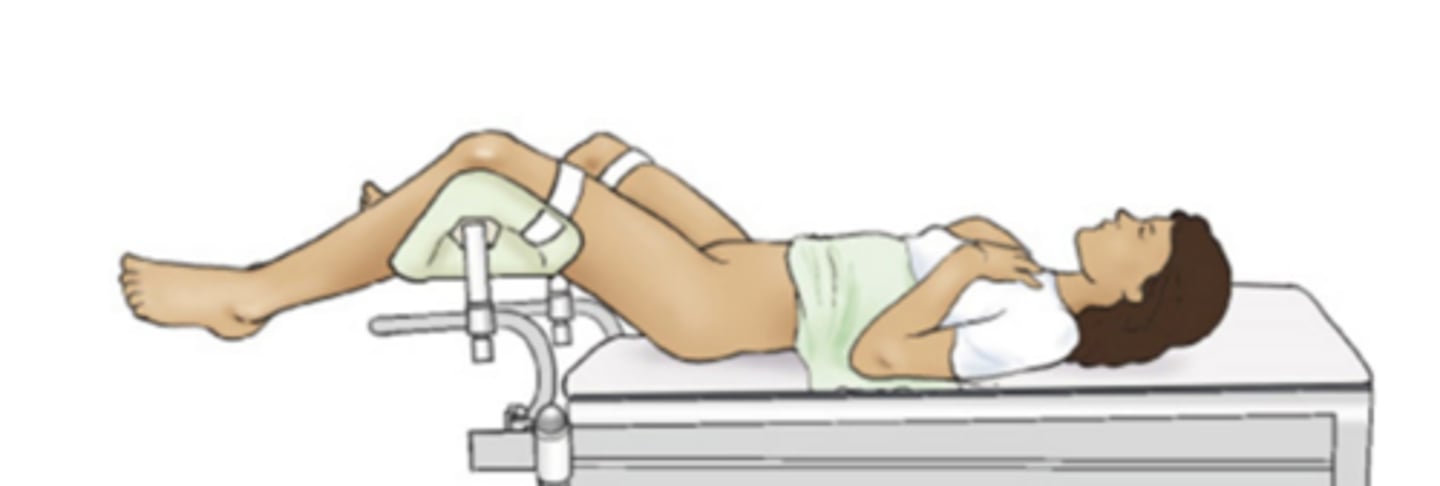
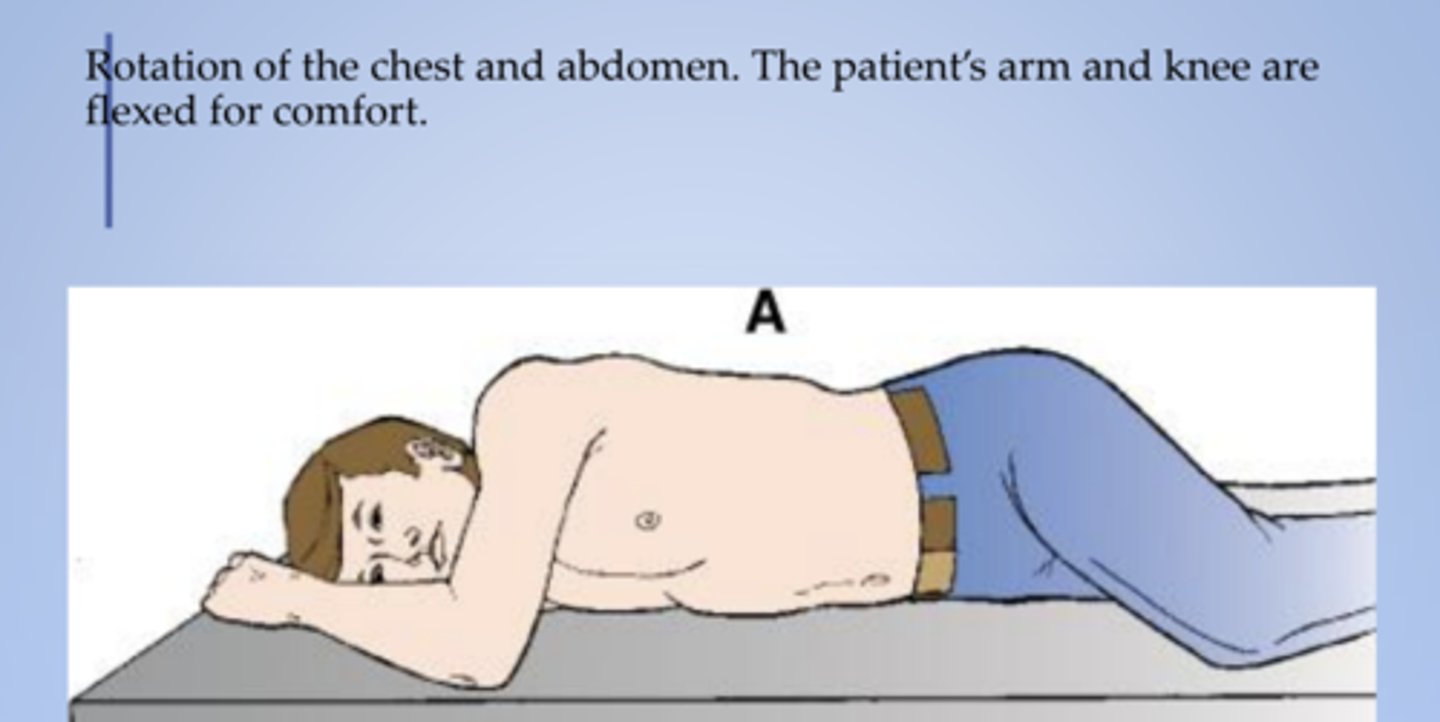
Sims (lateral position)
recumbent with patient lying on left anterior side with left leg extended and right knee and thigh partially flexed
Named after the gynecologist James Marion Sims, this position is usually used for rectal examination, treatments, and enemas. The patient lies on their left side, with right hip and knee bent.
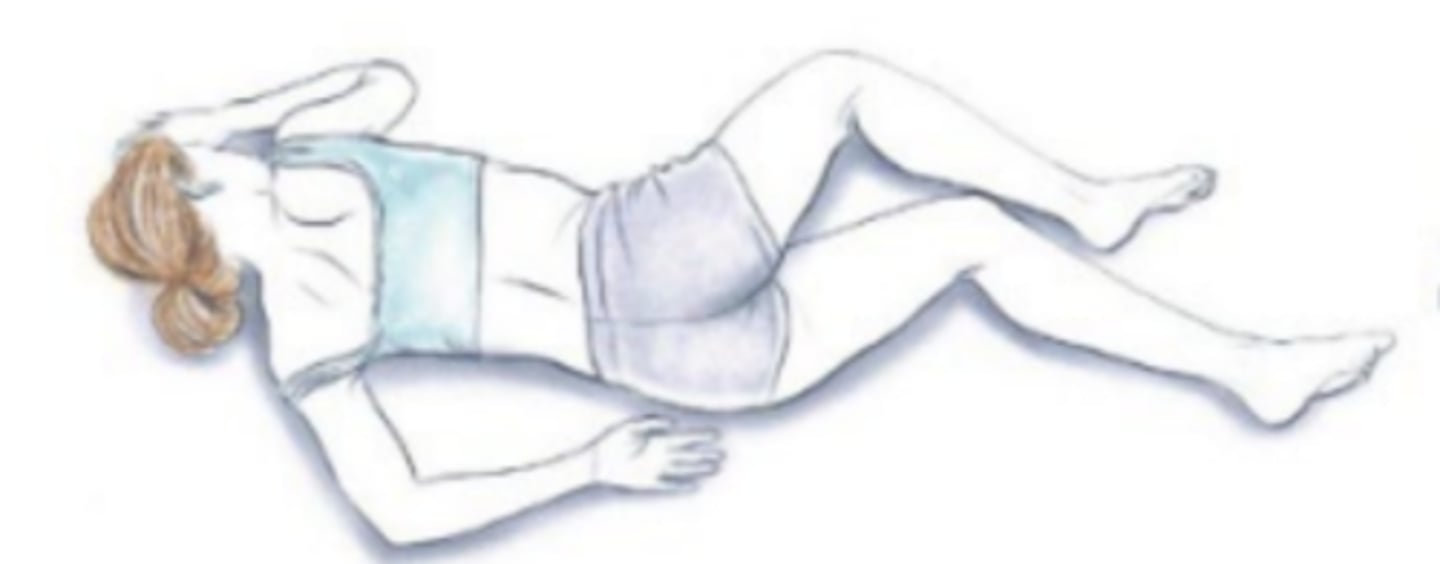
Lateral recumbent (lateral decubitus position)
it is utilized for a variety of surgical procedures including thoracic, hip, and shoulder surgery.
***remember to identify starrting with "left/right X position"
Recumbent position with a horizontal CR Named
according to the body surface on which the patient
is lying
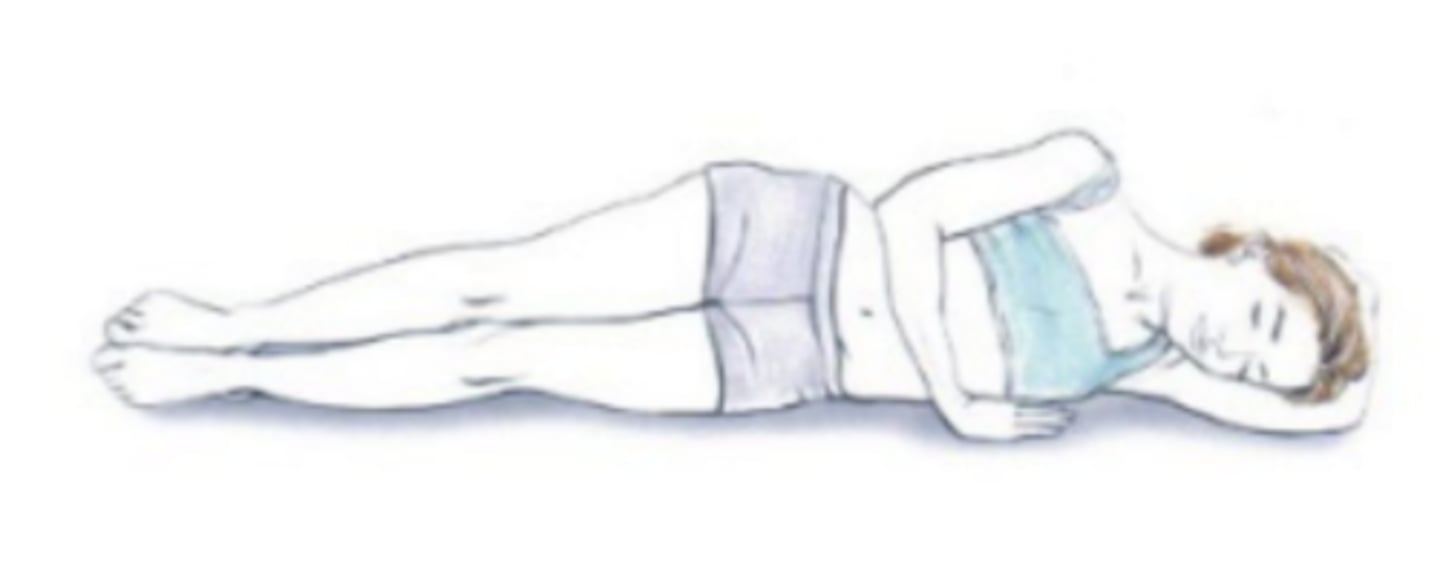
Fowlers
position: supine with the head elevated
When the top of the bed is raised up, the patient's body can be inclined at an angle ranging from 15 to 90 degrees. The legs may be either straight or bent at the knees
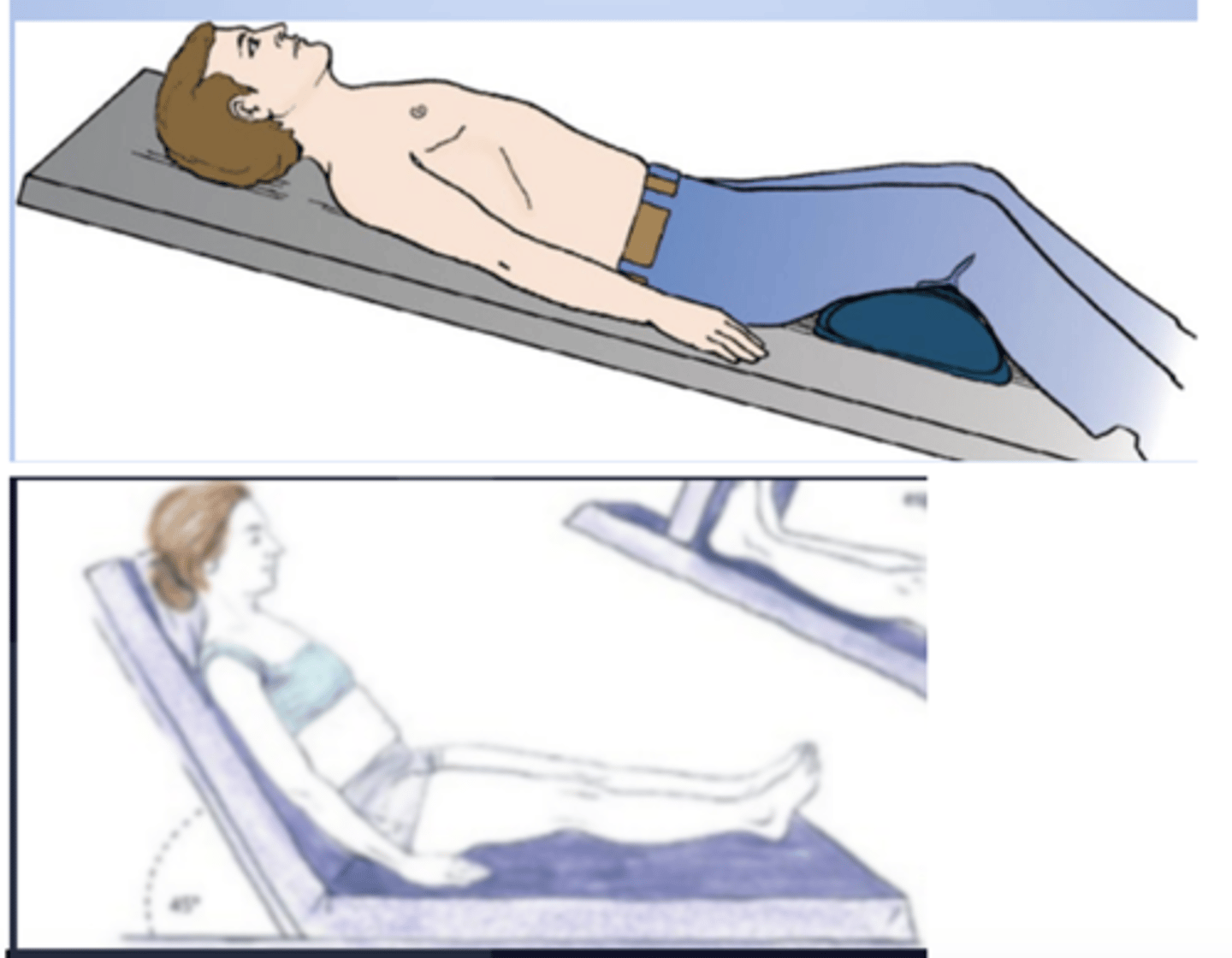
Trendelenburg
Supine with the head lower than the feet
the patient is laid flat on their back at a 15-30 degree incline, with the feet elevated above the head. This position is used in surgery, especially involving the abdomen and genitourinary system, as it allows better access to the pelvic organs.
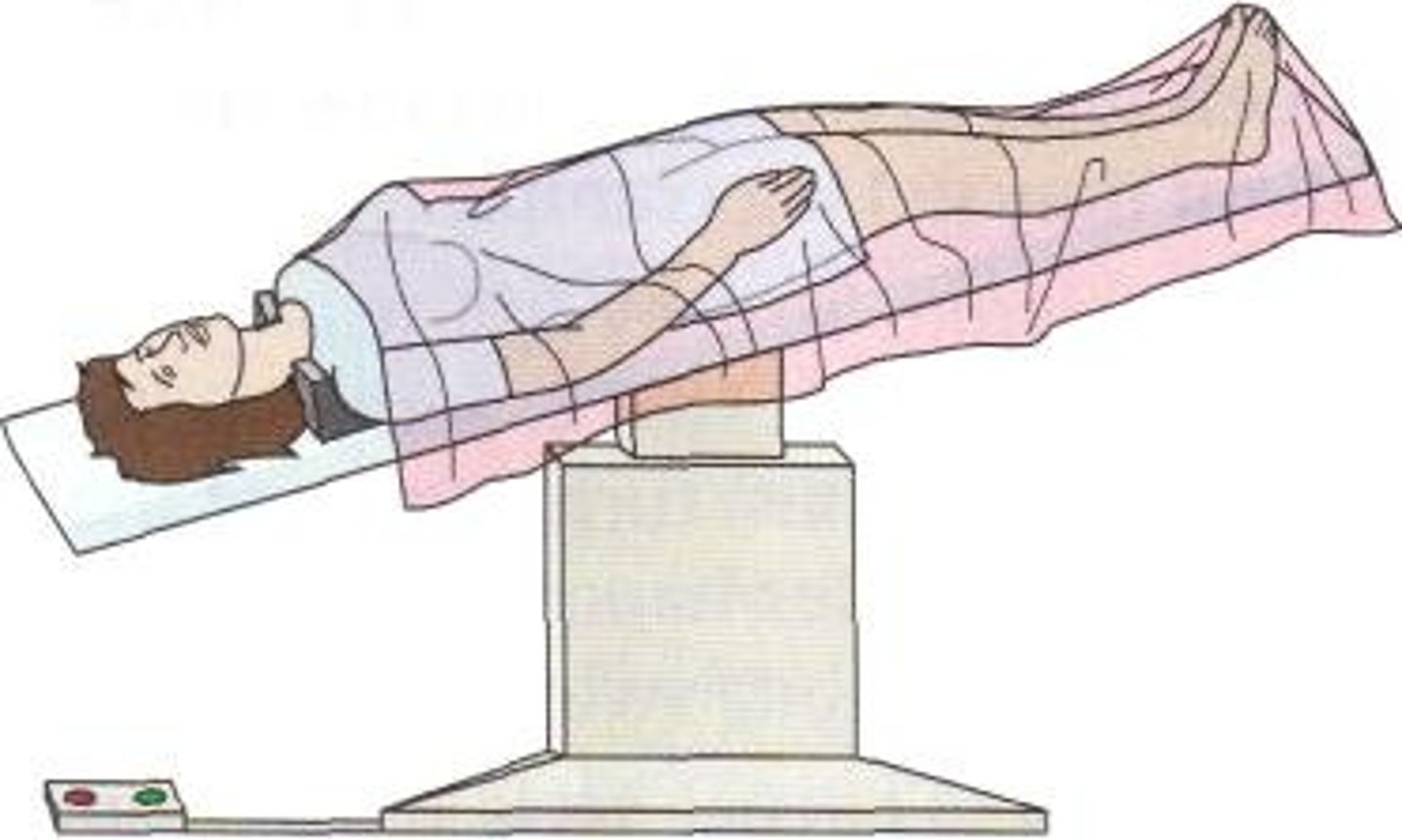
Lithotomy (Position)
where the patient is on their back with legs elevated and supported in stirrups for pelvic/urogenital access.
The patient lies supine (on their back).
The hips and knees are flexed, and the legs are placed in stirrups.
Commonly used in:
Gynecological exams and procedures (pelvic exams, childbirth, hysterectomy).
Urological surgeries (bladder, prostate).
Colorectal procedures.
ventral decubitus
patient is prone & horizontal beam is used
Left X radiographic position of abdomen results in left lateral projection. Note horizontal orientation of central ray.
dorsal decubitus
patient is supine & horizontal beam is used
Right X radiographic position of abdomen results in right lateral projection. Note horizontal orientation of central ray.
Left lateral decubitus
radiographic position of abdomen results of the abdomen results in an AP projection. Note horizontal orientation of central ray
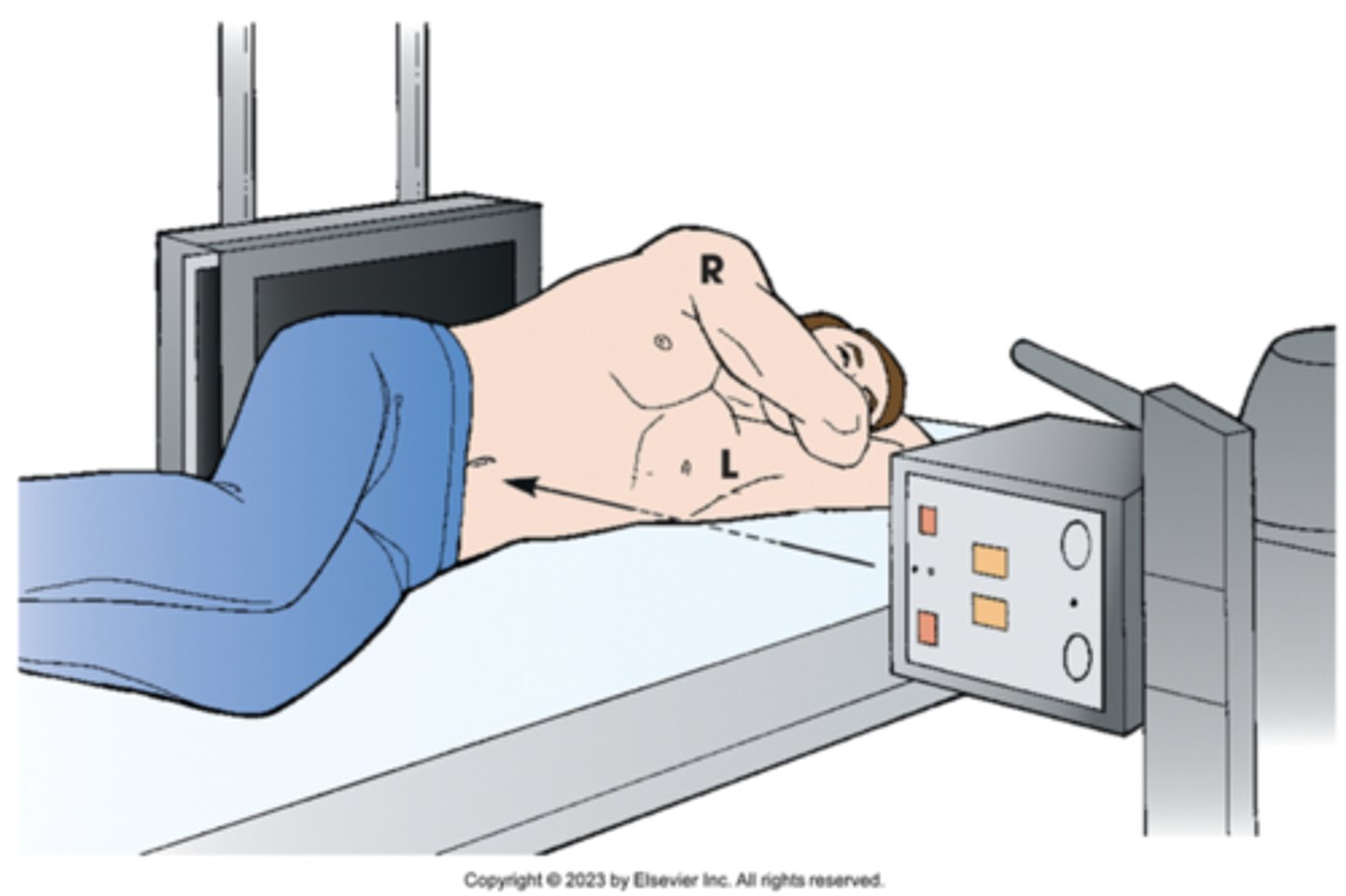
right dorsal decubitus
radiographic position of abdomen results in right lateral projection. Note horizontal orientation of central ray.
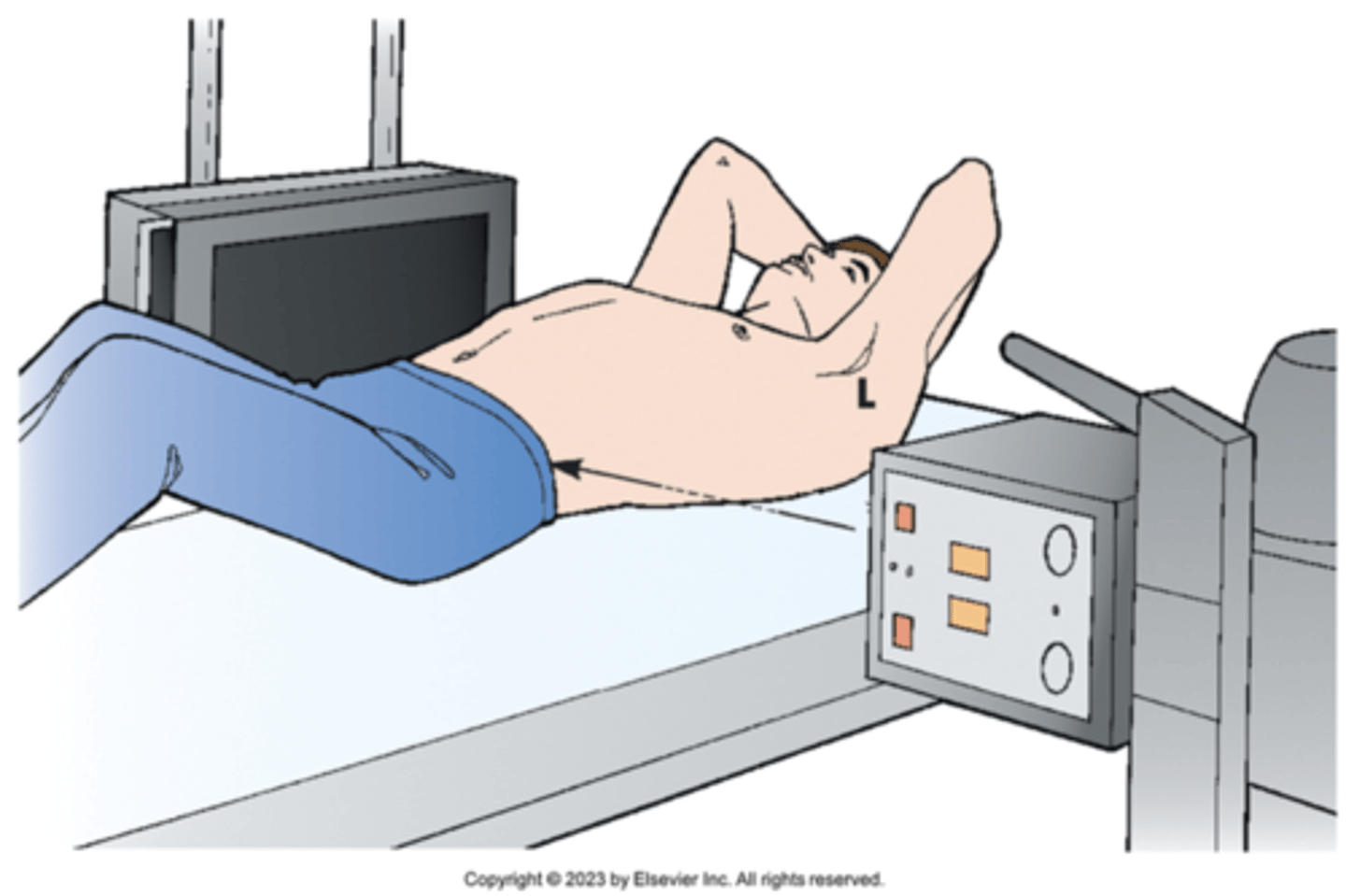
lordotic
upright position in which the patient is leaning backward
radiographic position of the chest results
in an AP axial projection. Note that the central
ray is not angled; however, it enters the chest
axially as a result of body position.
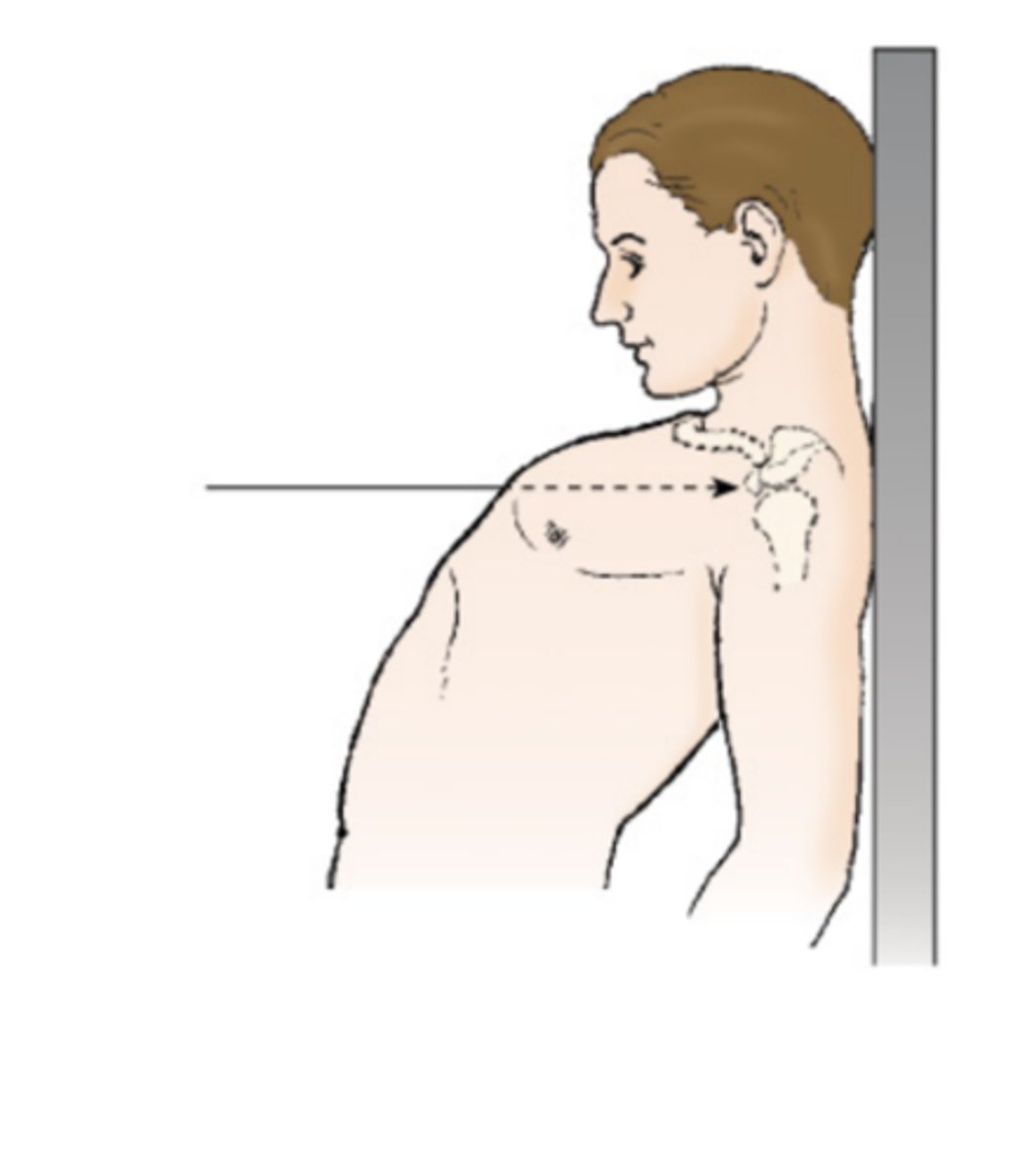
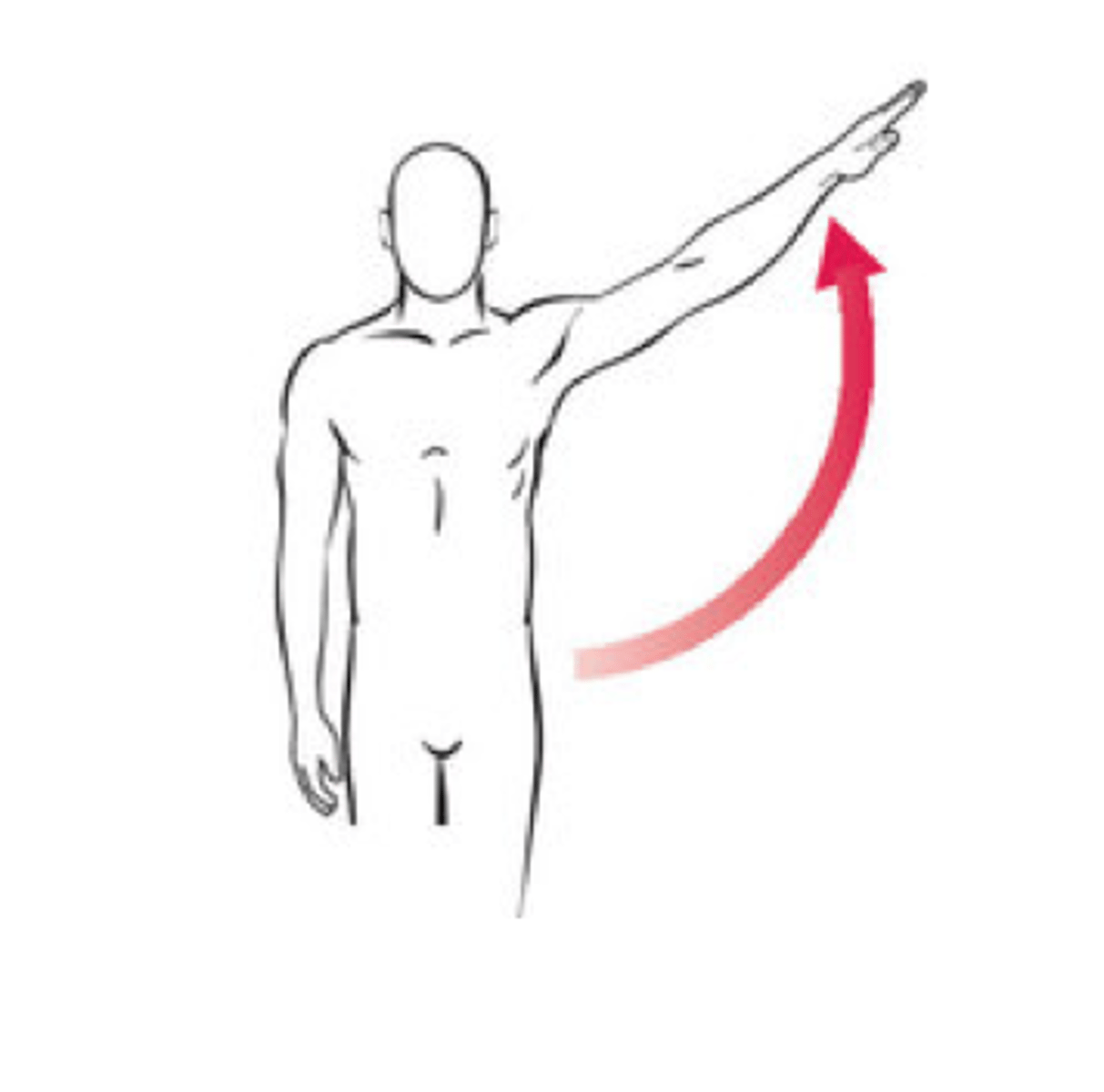
Abduction (Abduct)
movement of a part away from the central axis of the body
Adduction (adduct)
Movement of a part toward the central axis of the body
Extension
Straightening of a joint
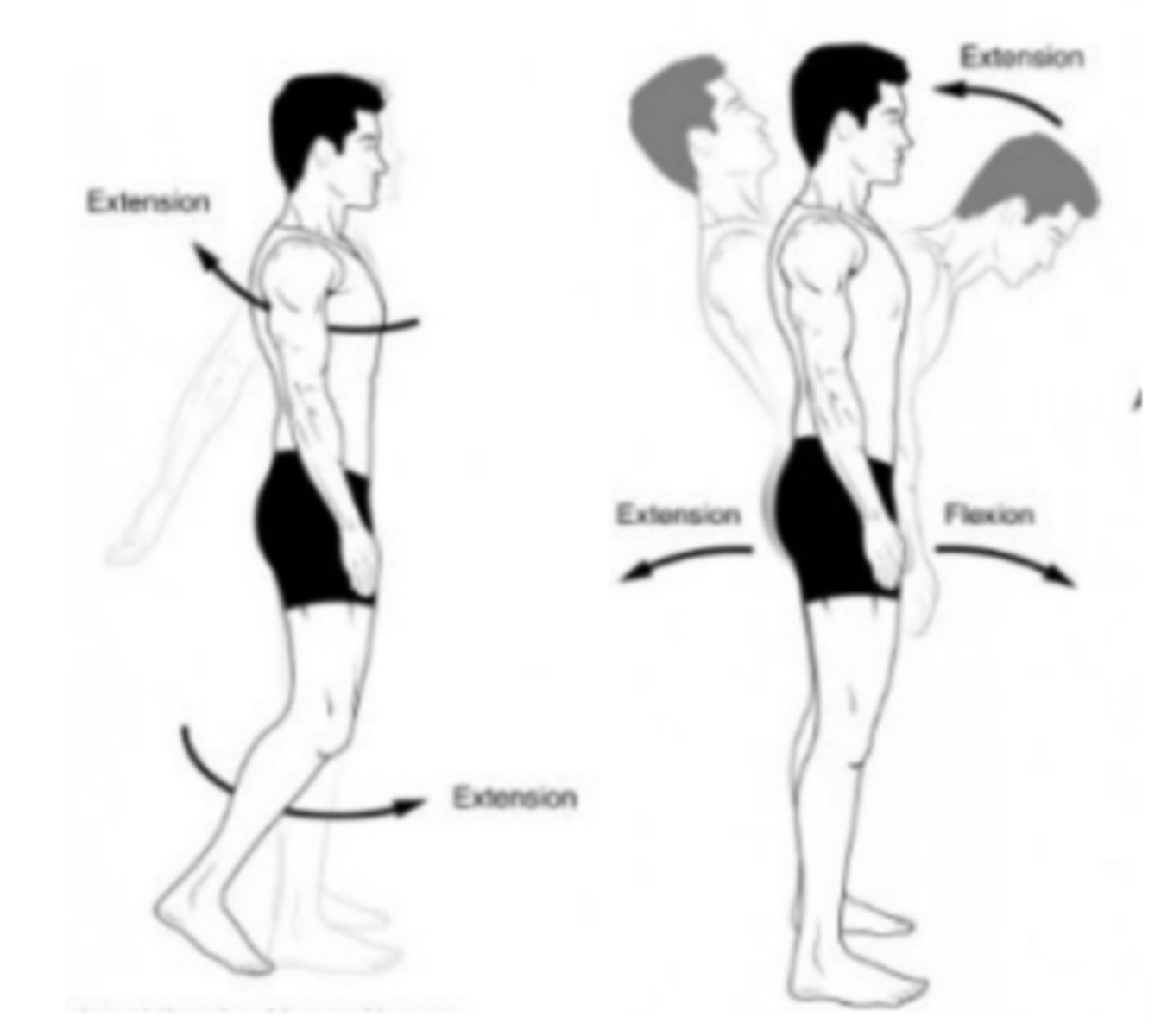
Flexion
Bending of a joint
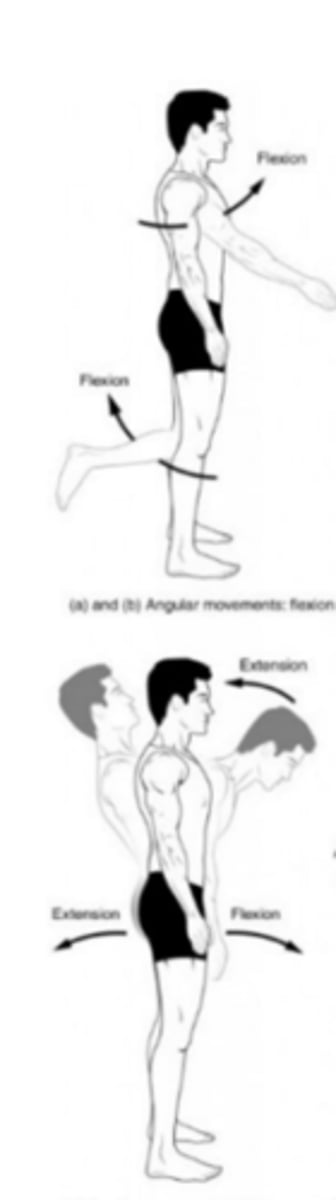
Hyperextension
Forced or Excessive Extension
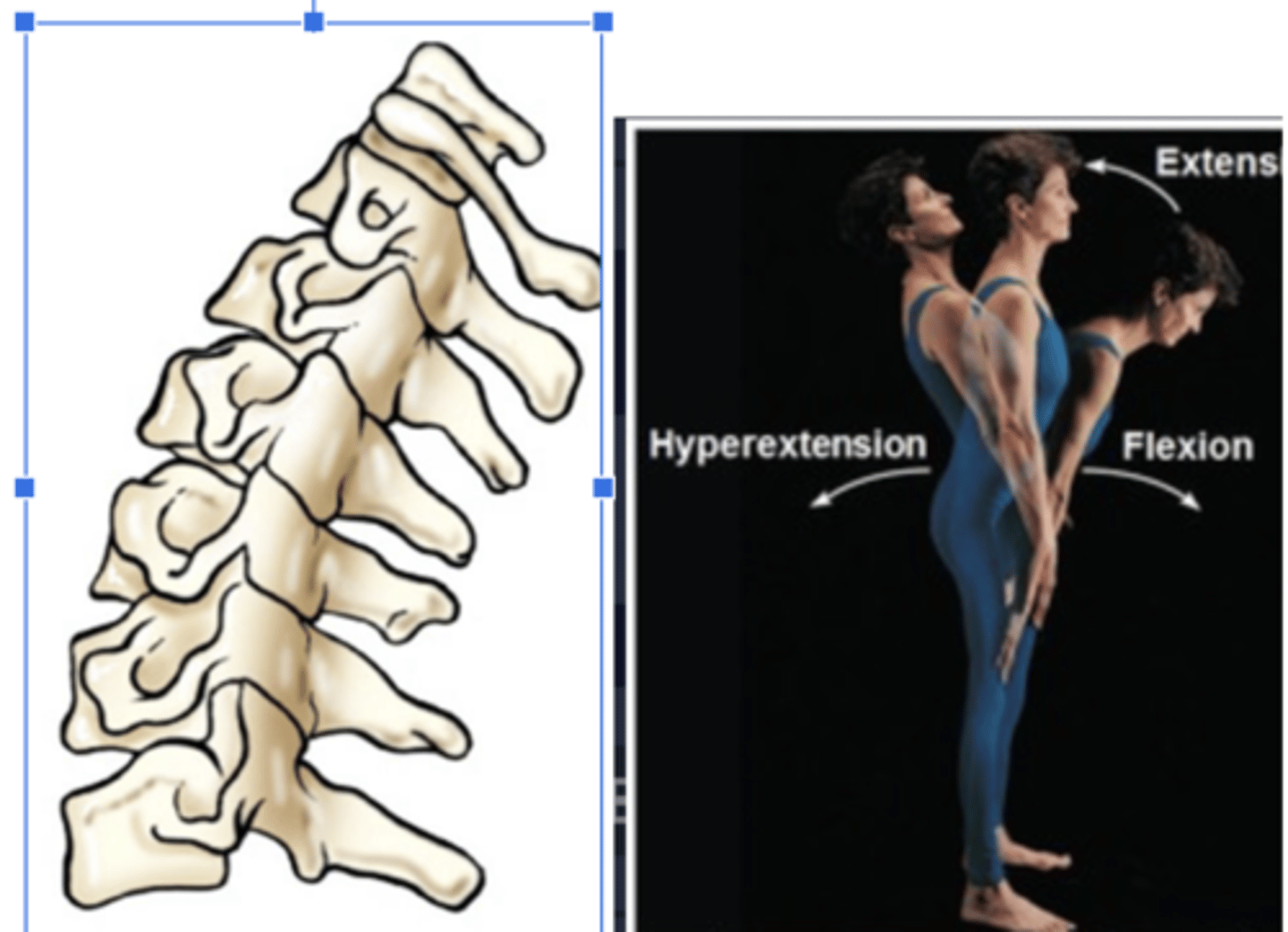
Hyperflexion
Forced overflexion
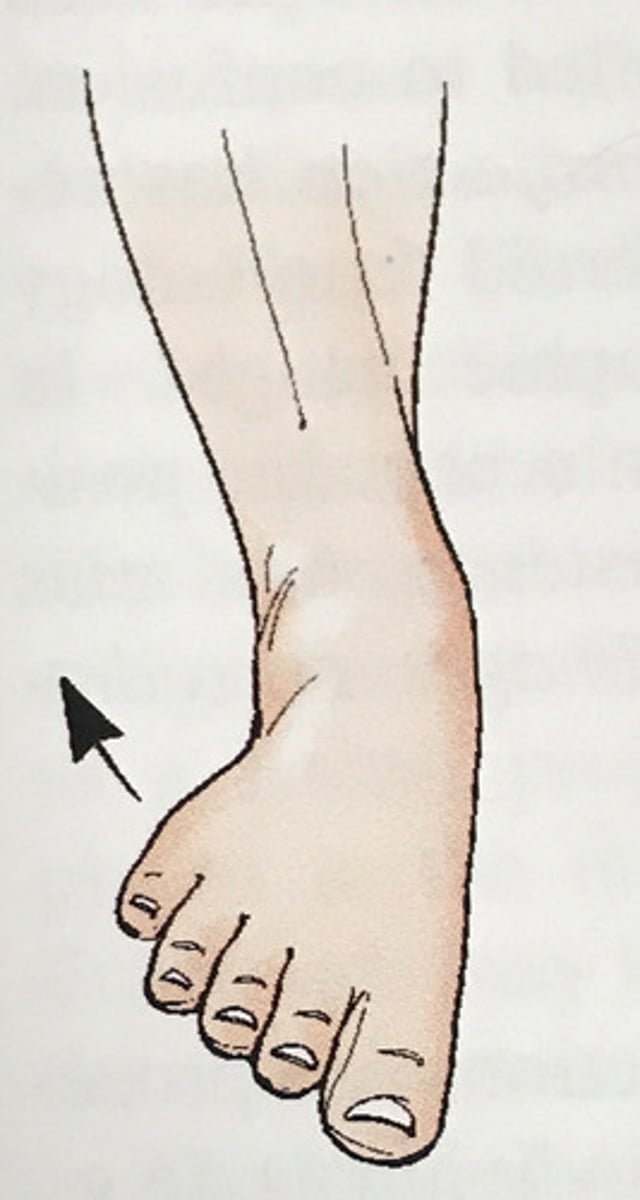
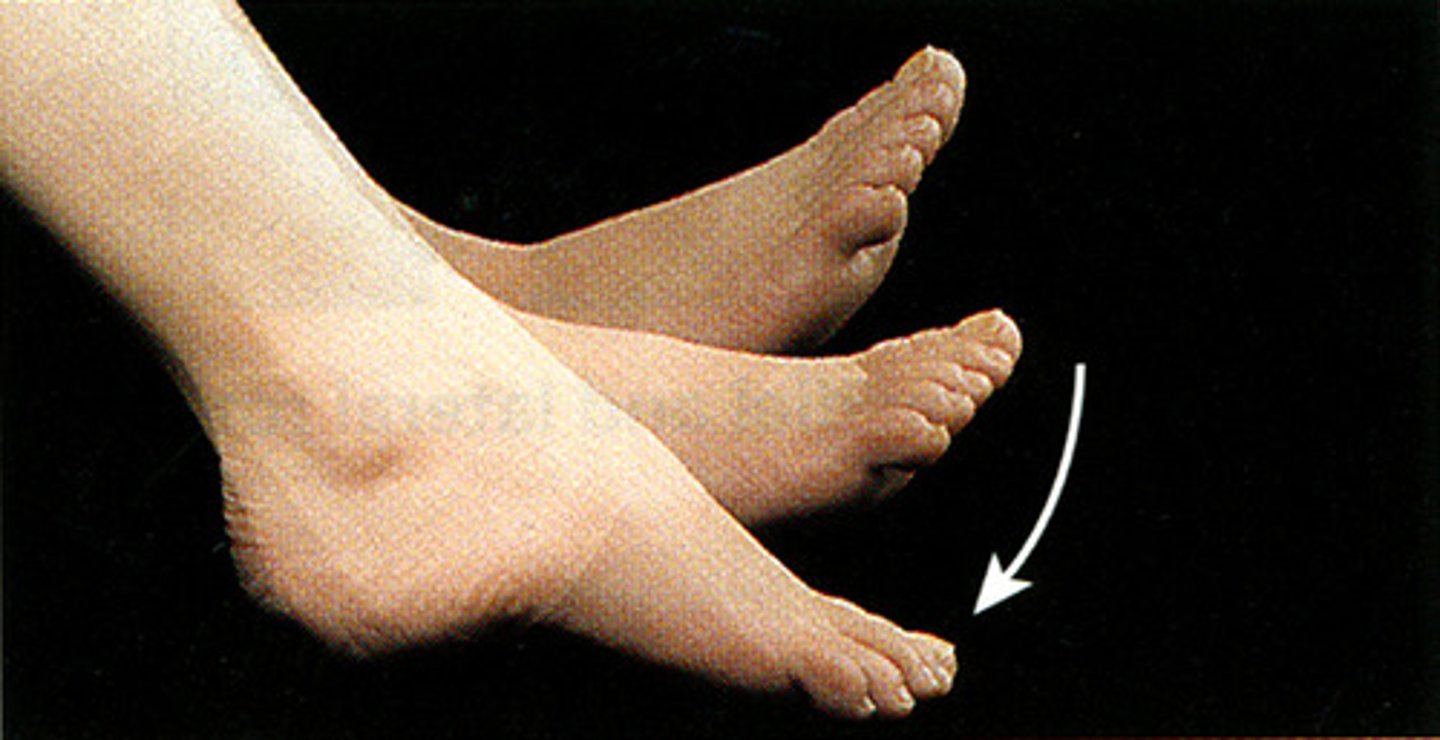
Evert / eversion
Outward turning of the foot at the ankle
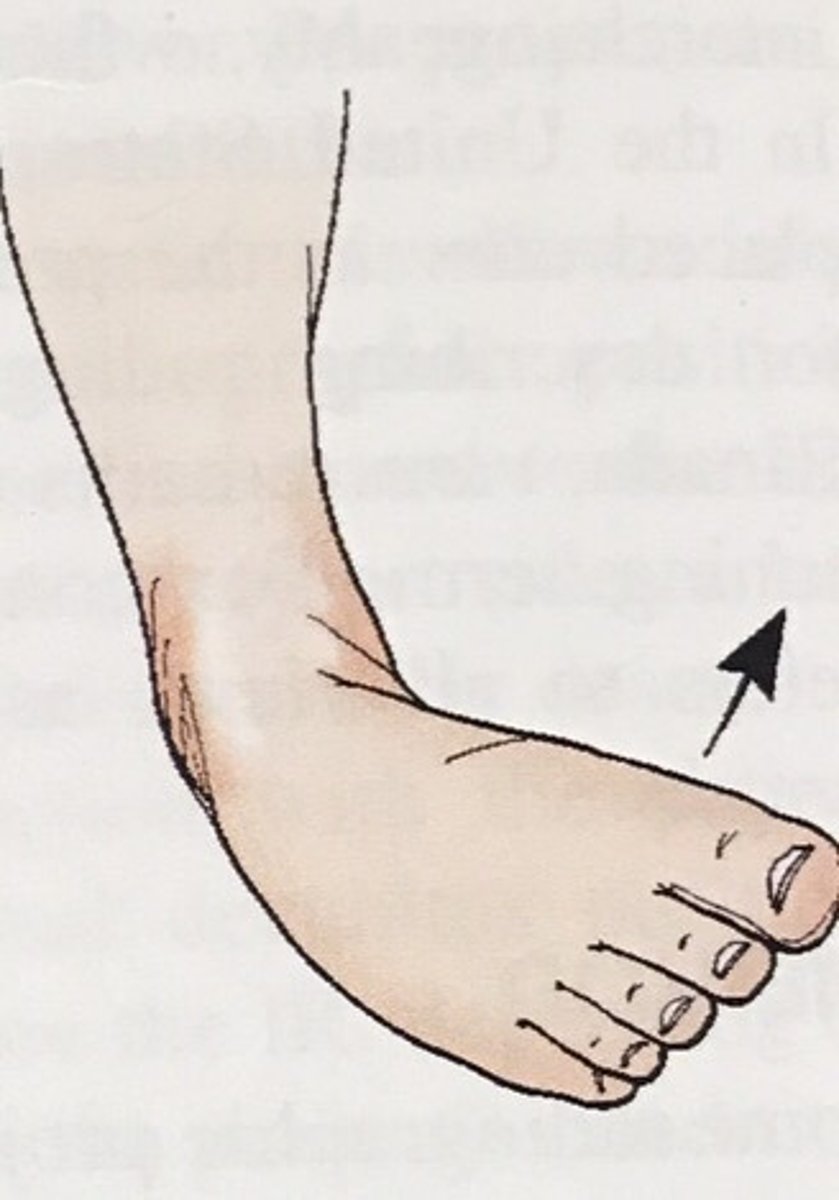
Invert / inversion
inward turning of the foot at the ankle
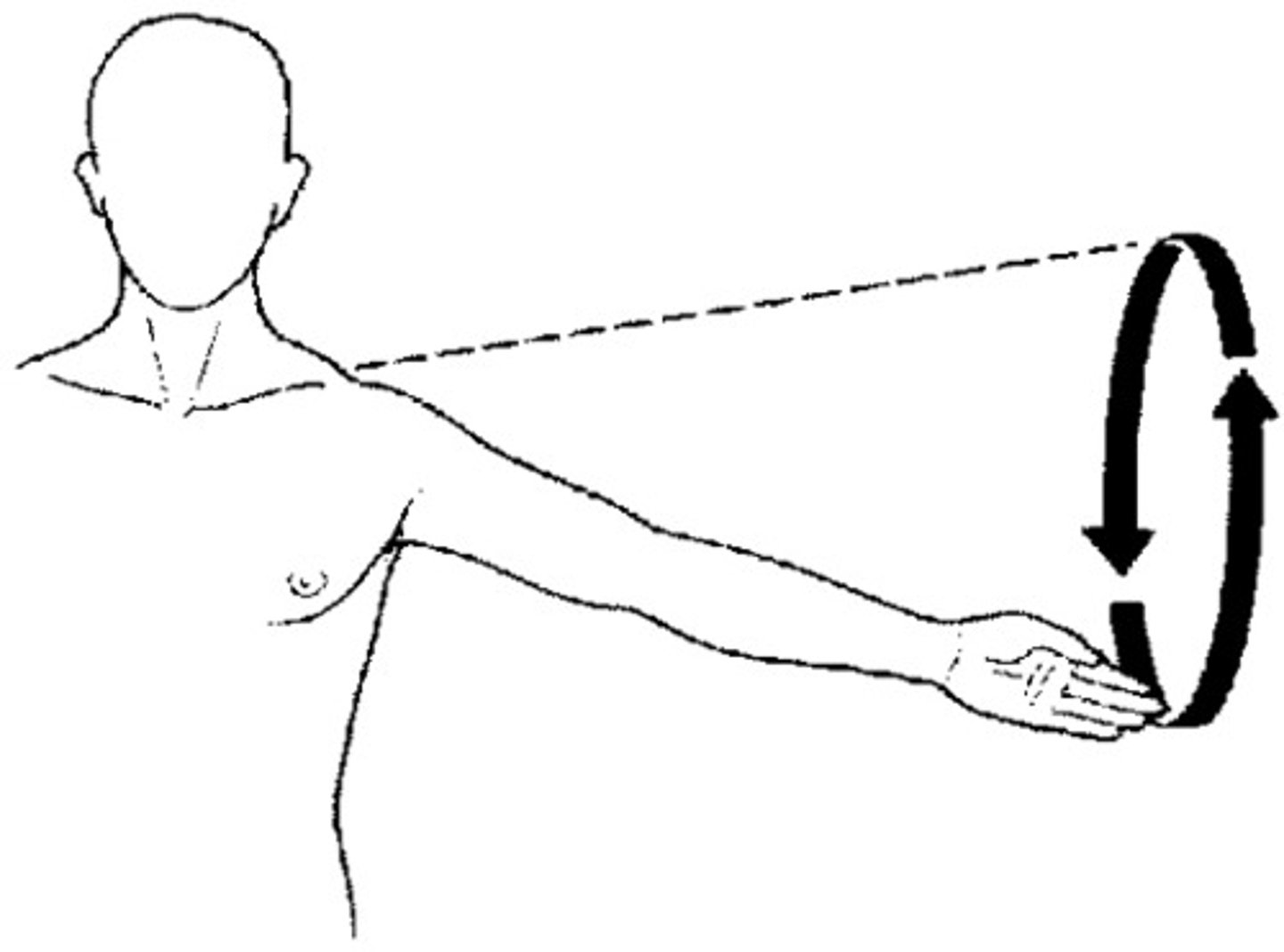
circumduction
circular movement of a limb
tilt
tipping or slanting a body part slightly
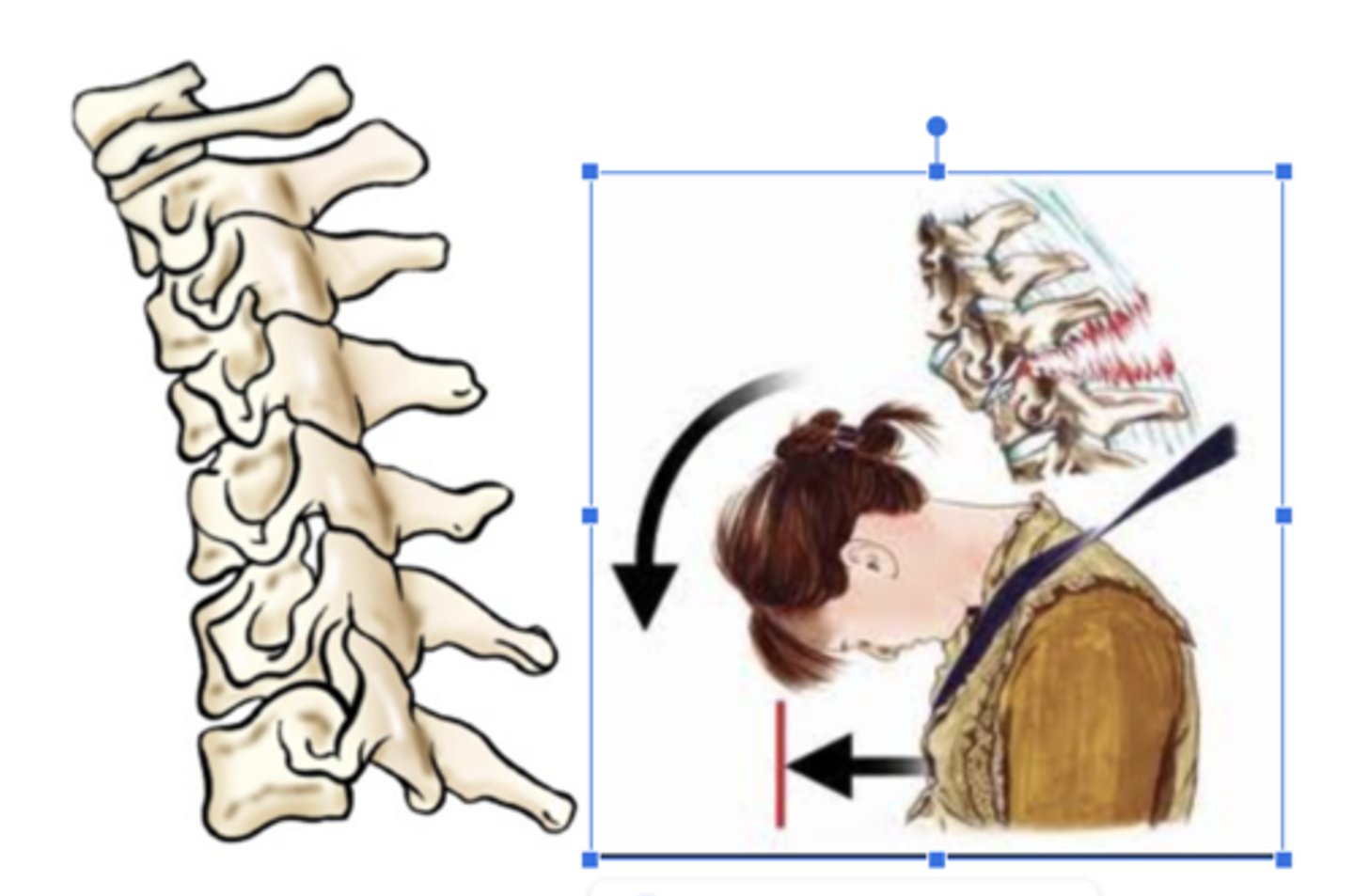
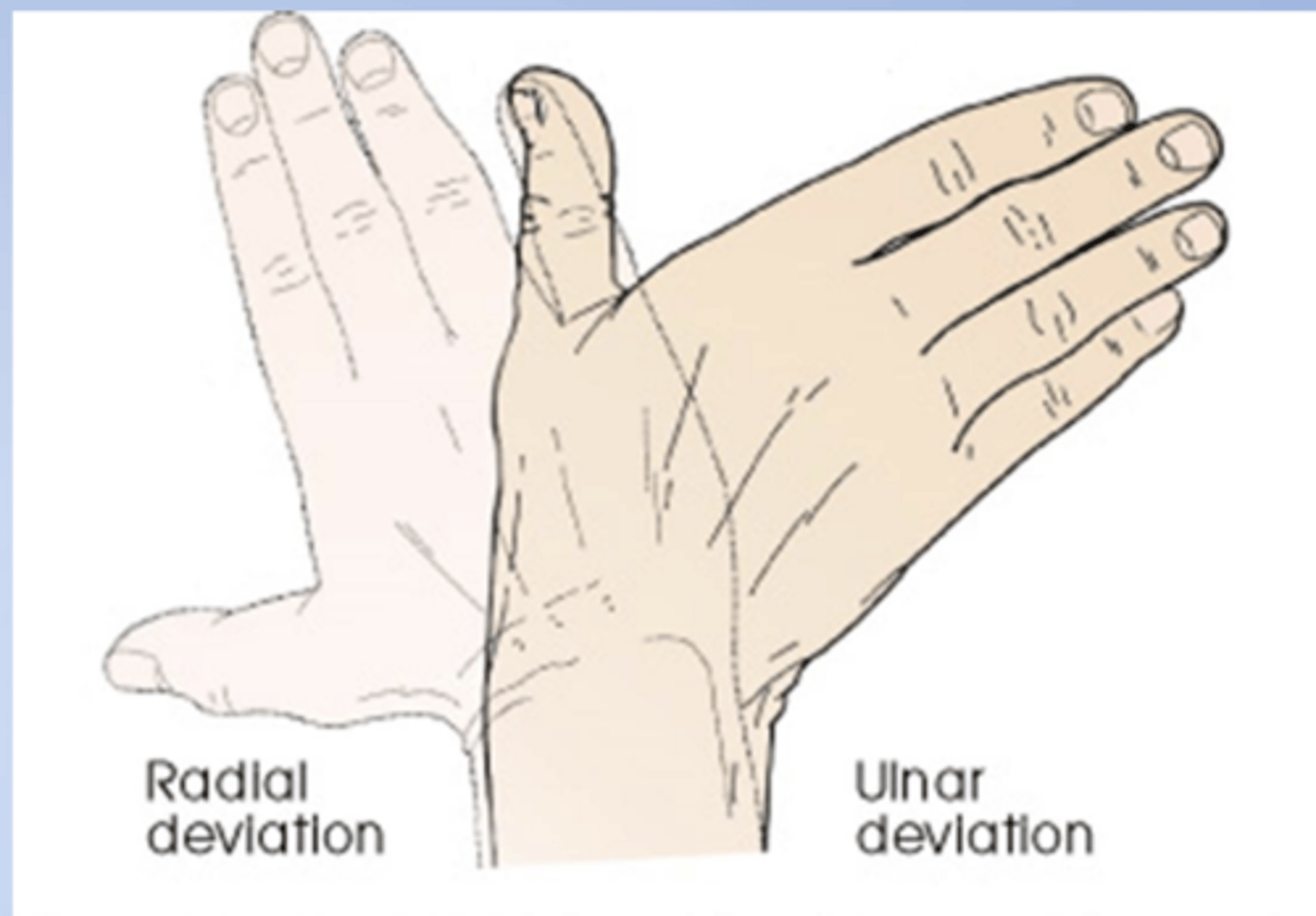
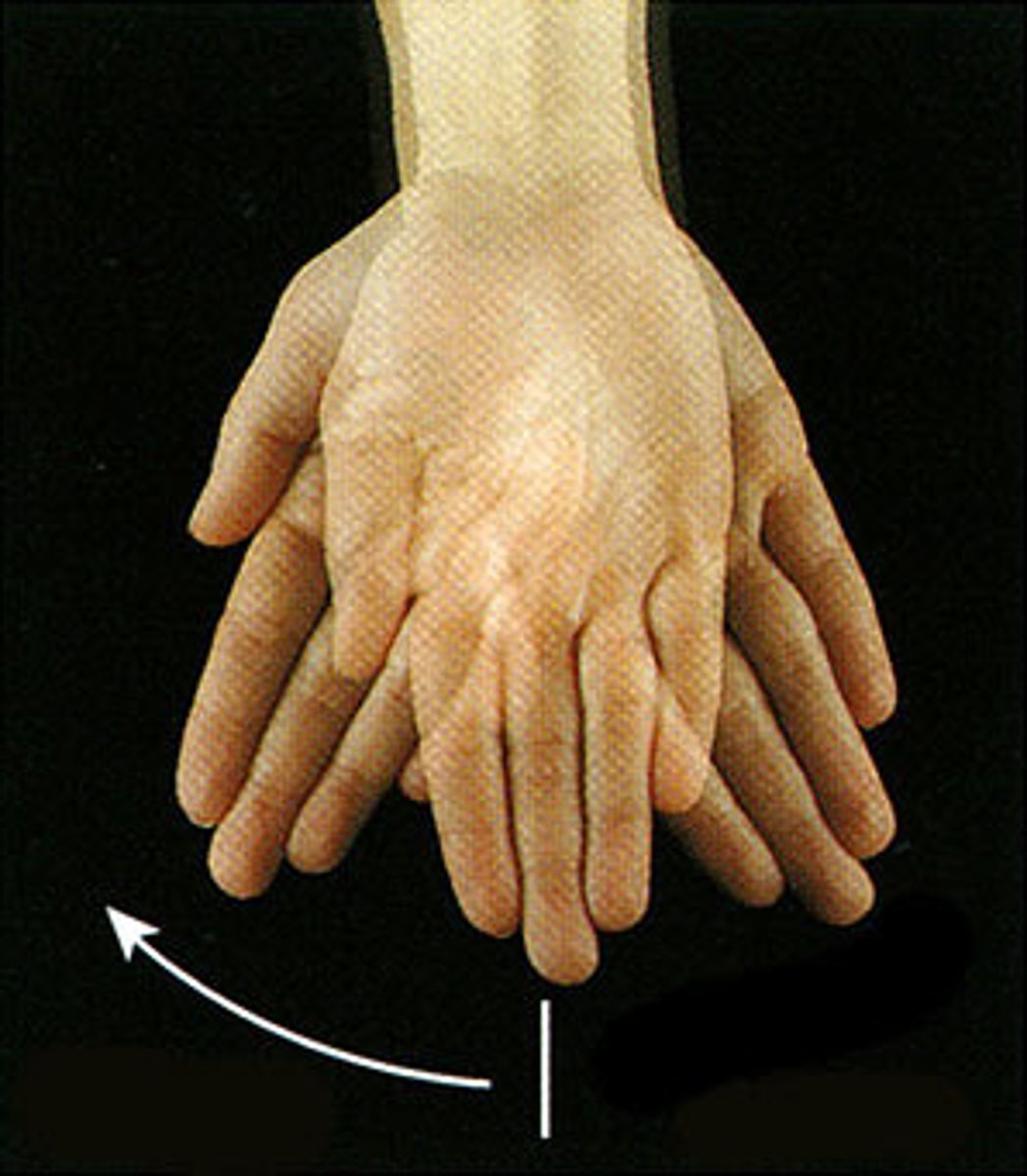
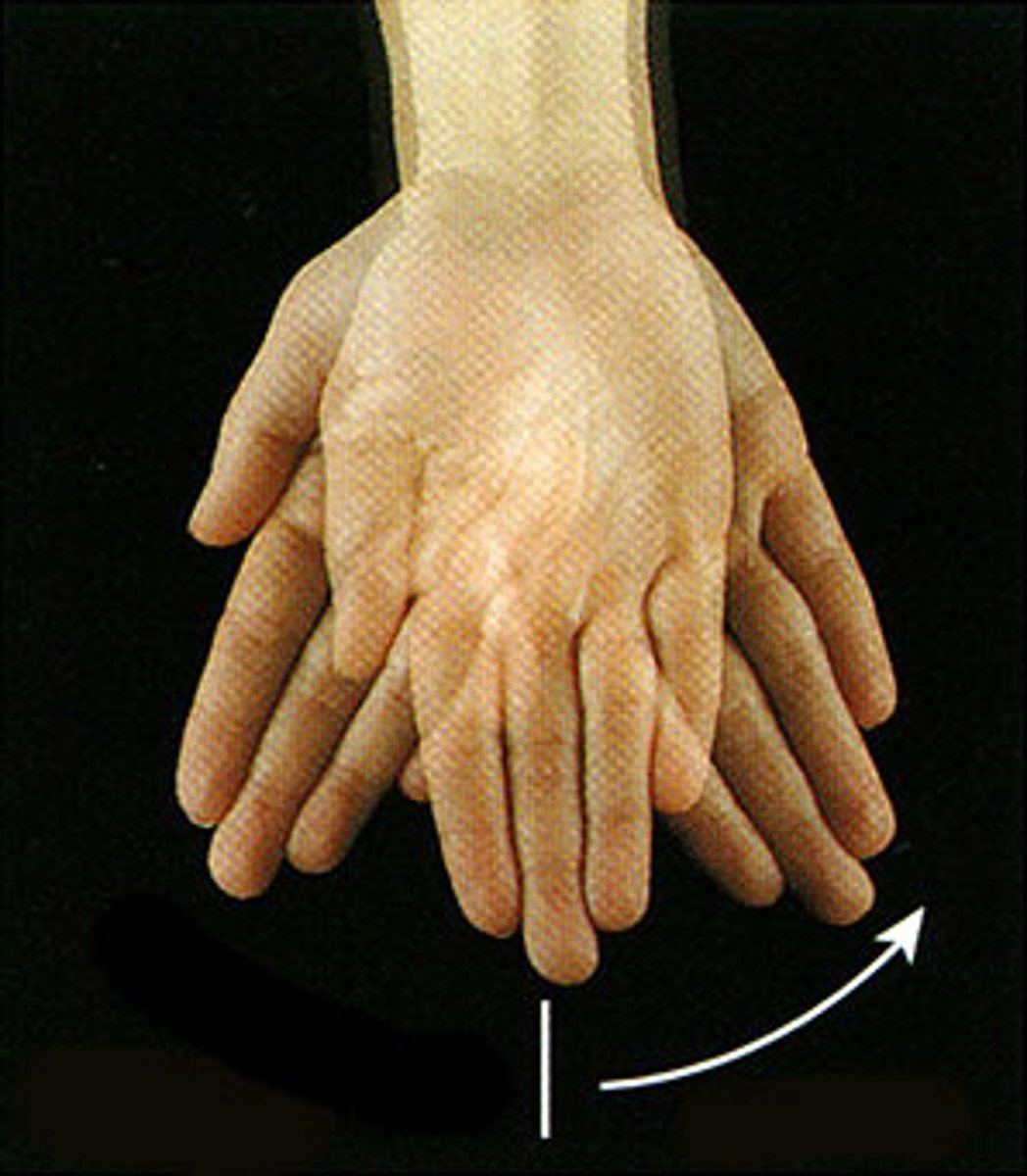
deviation
a turning away from the regular or standard course
Radial deviation of the hand (turned to the
radial side) and ulnar deviation (turned to
the ulnar side).
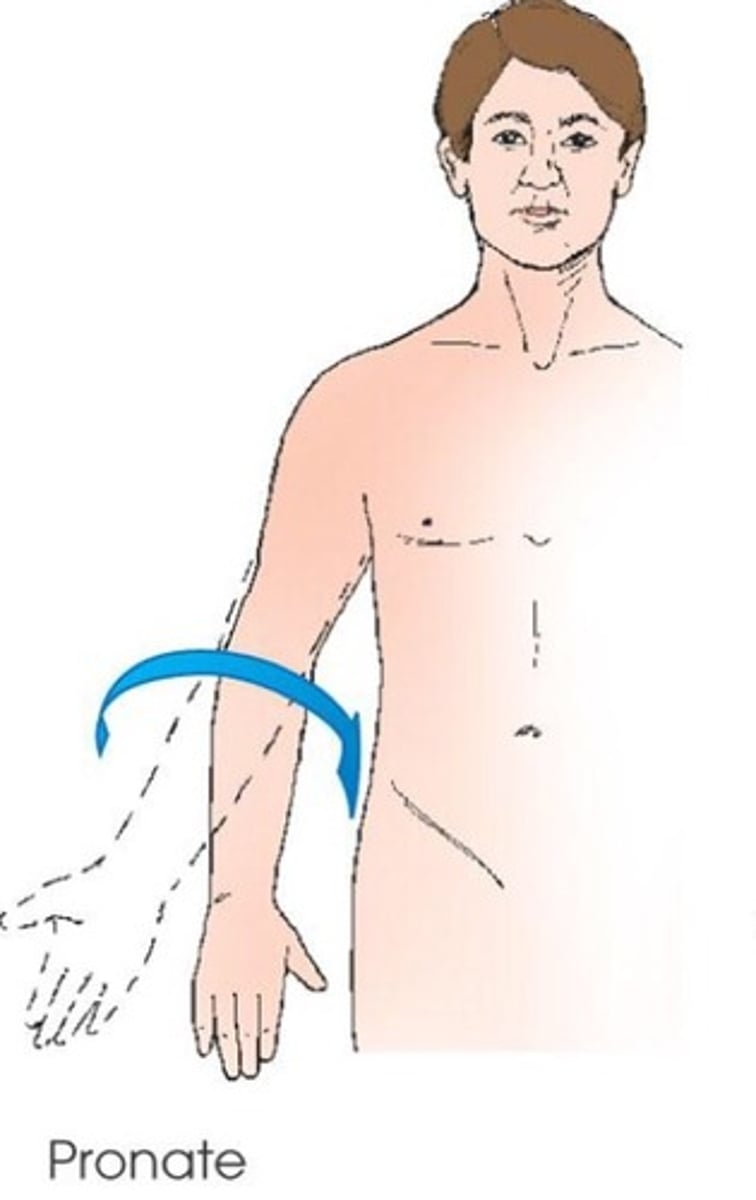
pronate (pronation)
rotation of forearm so that the palm is down
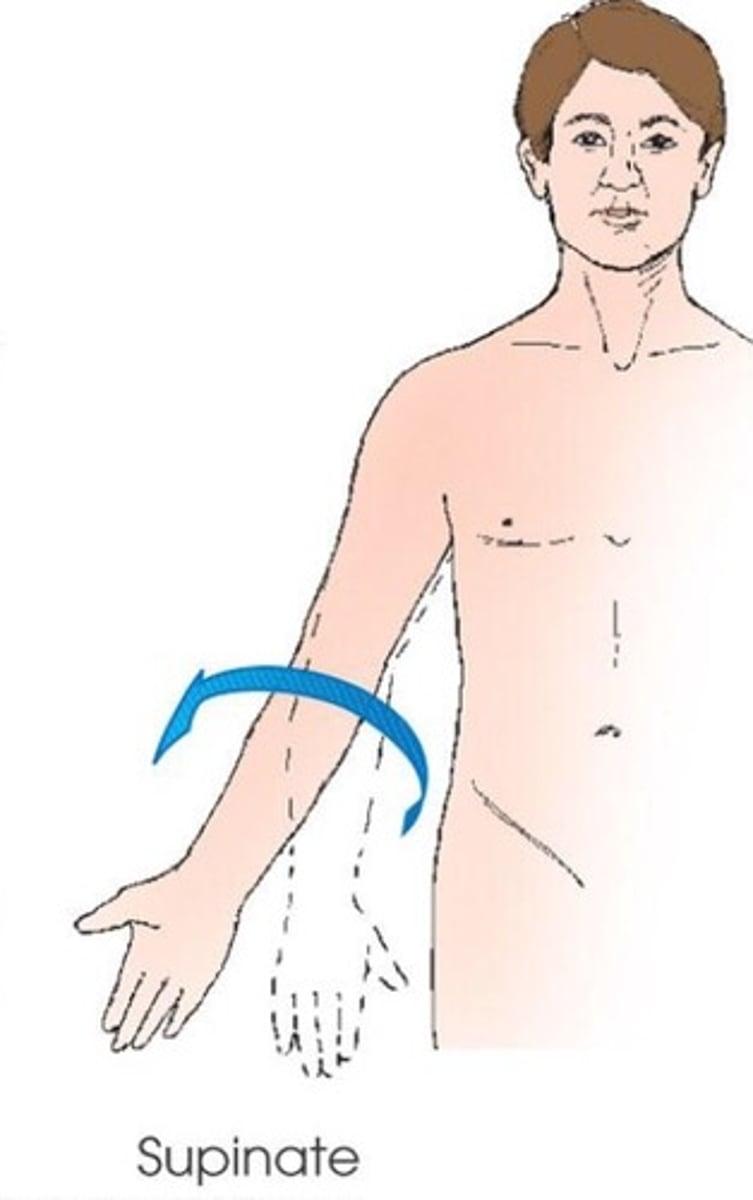
supinate (supination)
rotation of forearm so that the palm is up
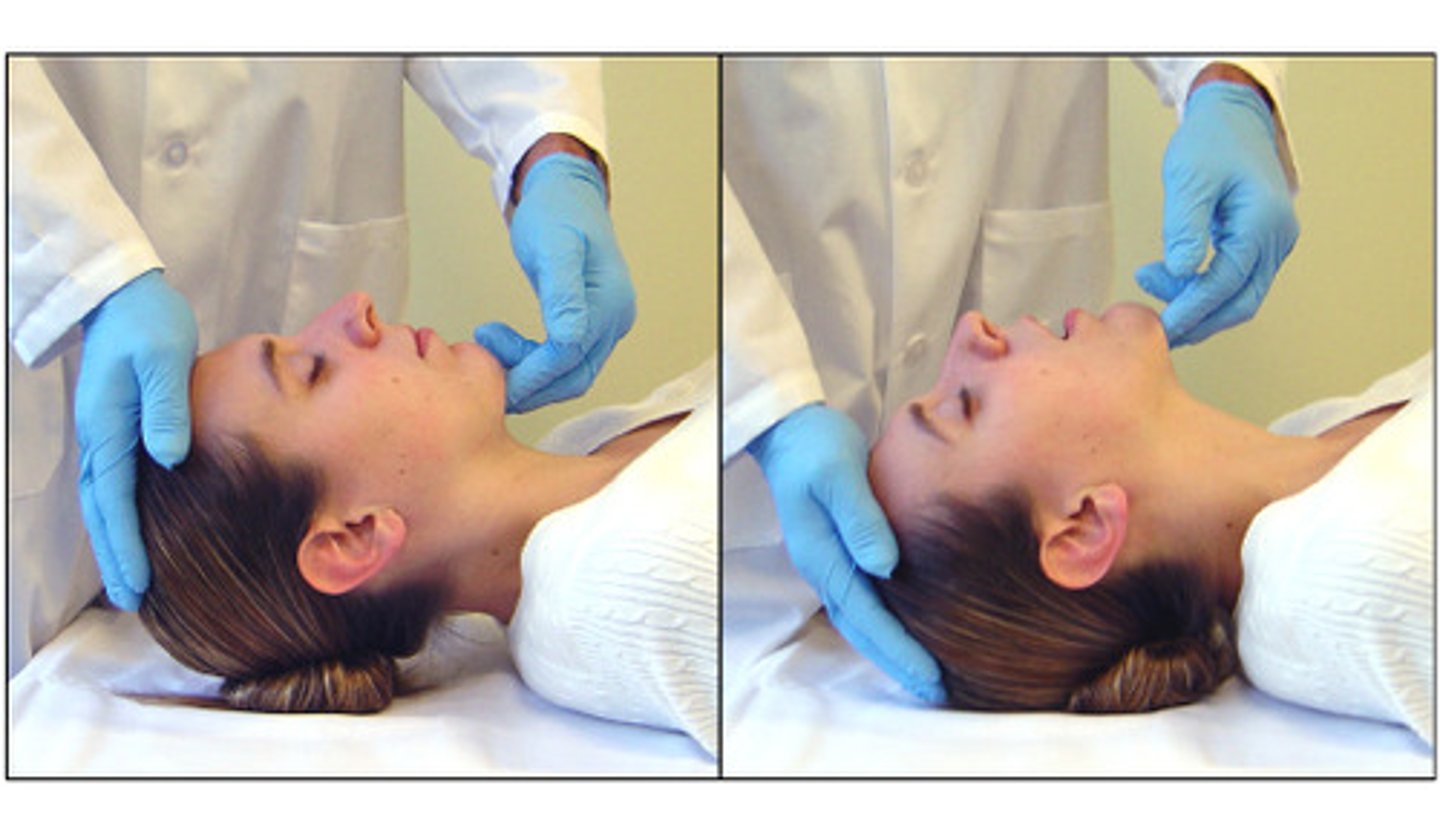
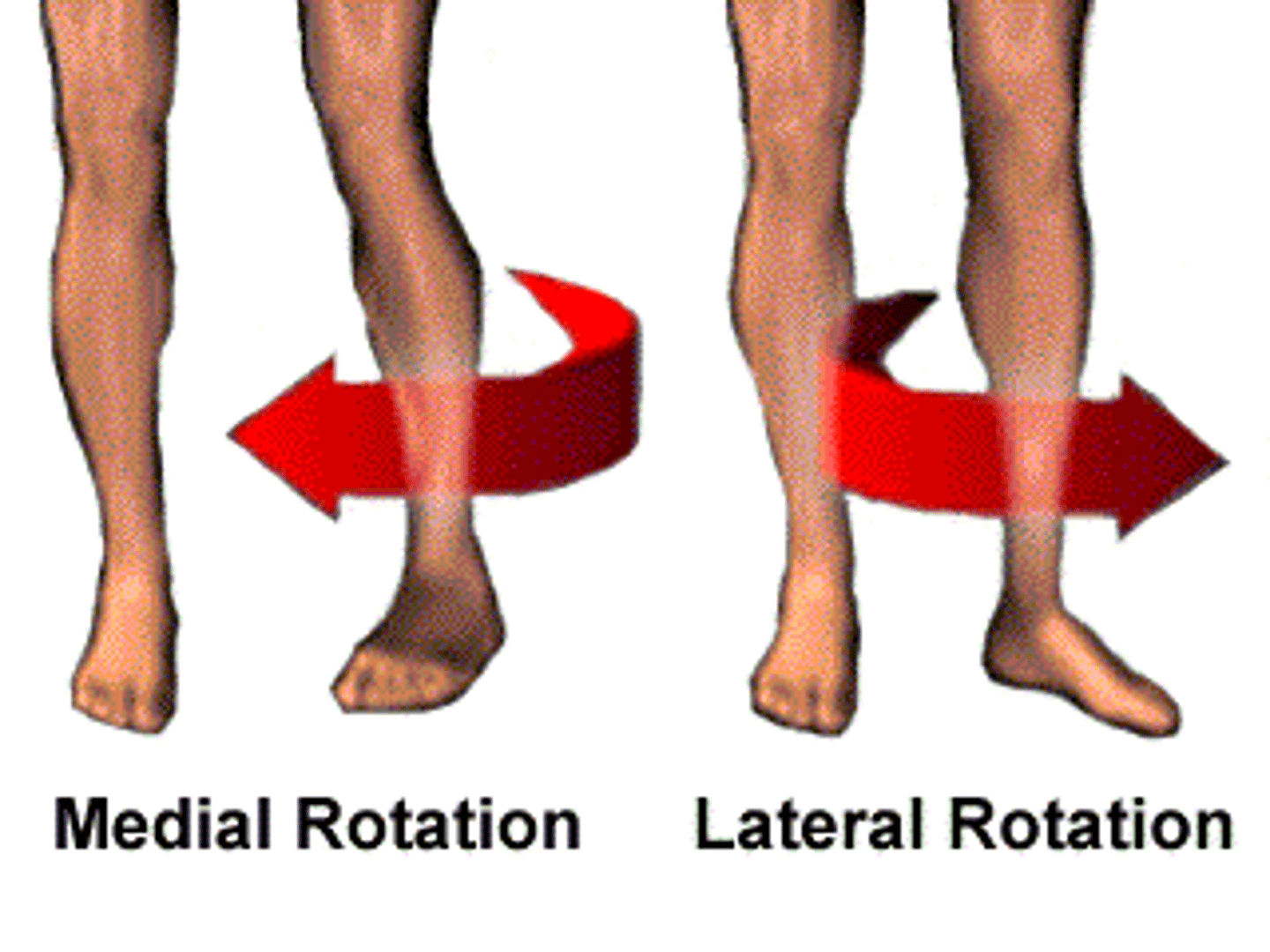
rotate (rotation)
turning of the body or part around its axis
rotation of a limb is either medial (toward midline) or lateral (away from midline)
medial rotation
Rotation toward the midline
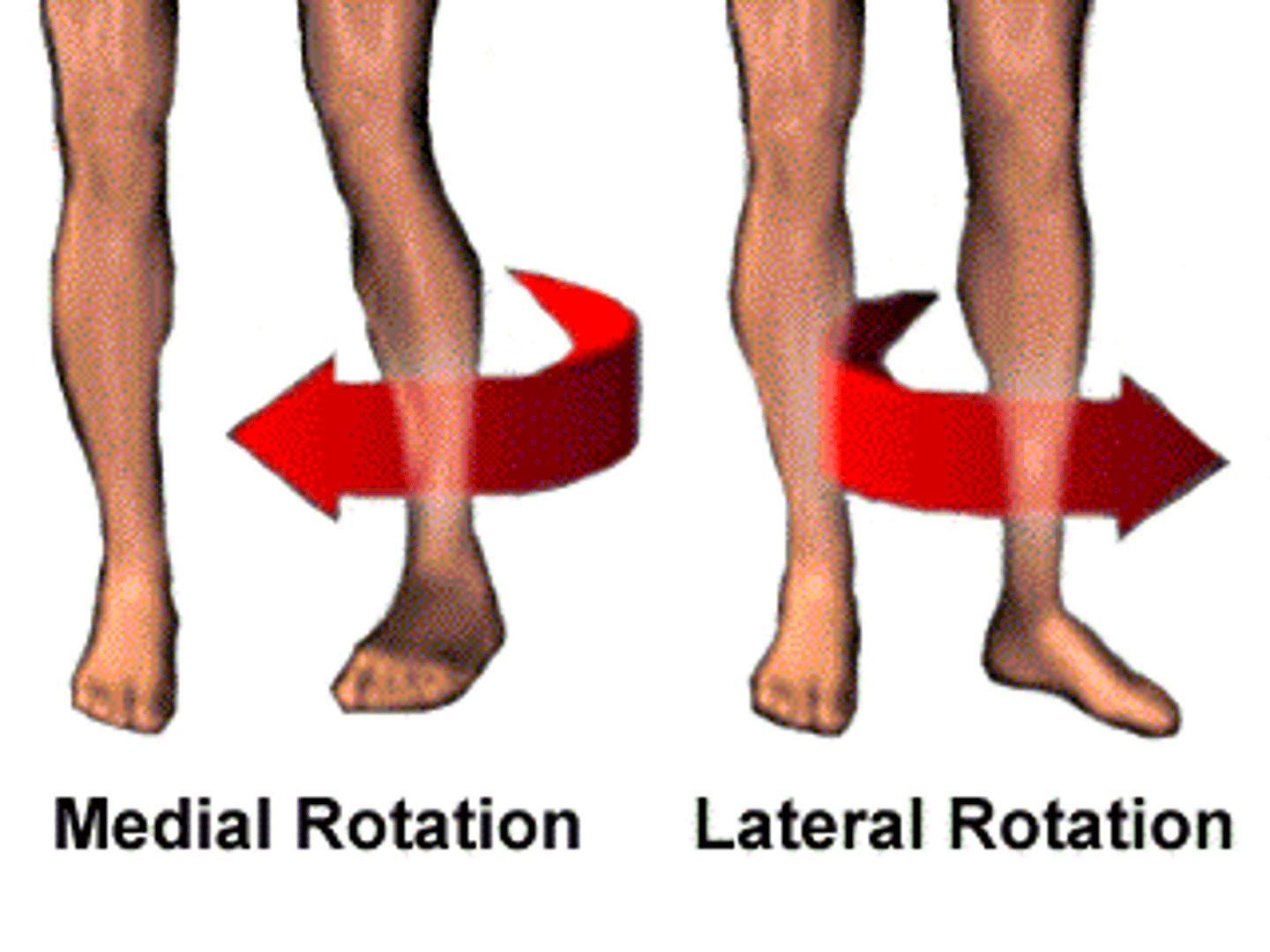
lateral rotation
rotation away from the midline
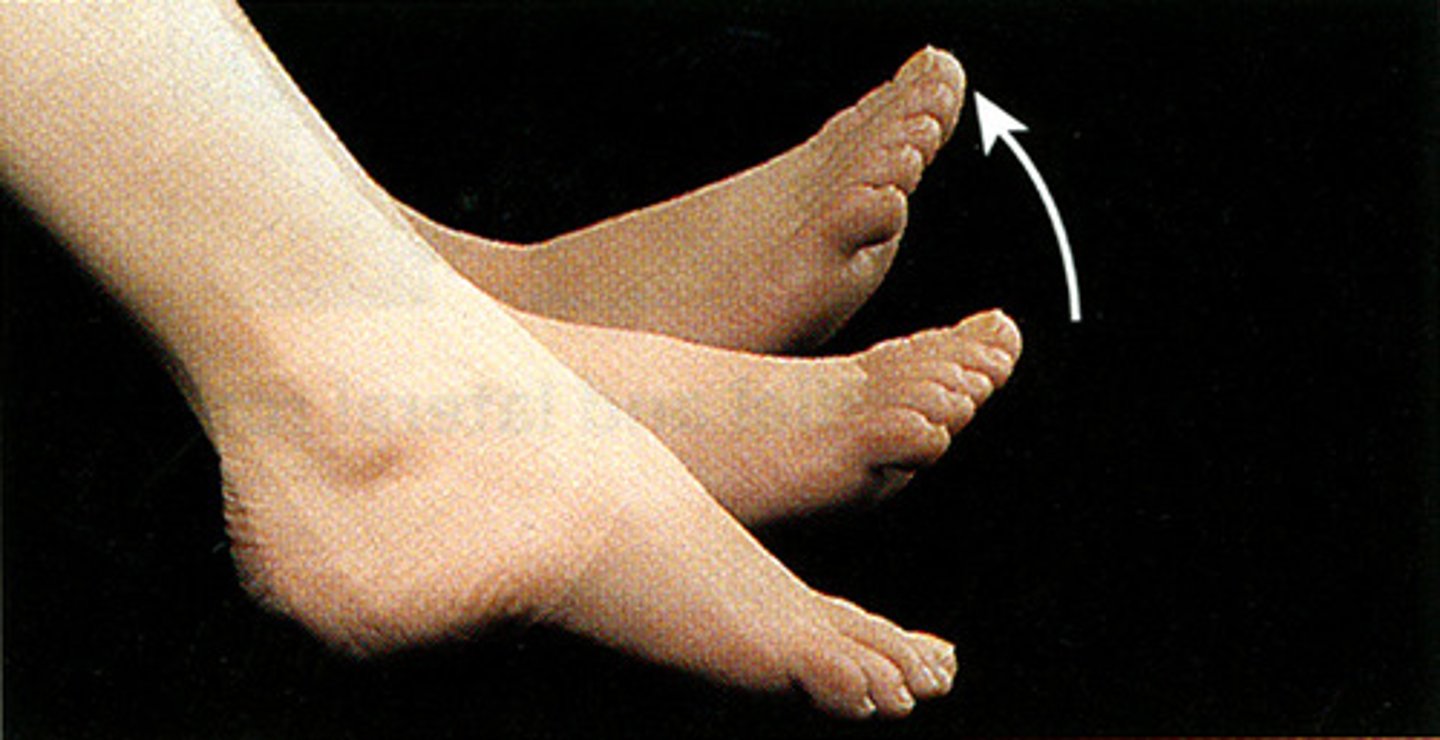
dorsiflexion
Bending the foot upward toward the shin (decreasing the angle between the dorsum of the foot and the leg).
MOVEMENT IS AT ANKLE JOINT
**great for stretching**
toes up
Plantar Flexion
Bending the foot downward (pointing toes, like pressing a gas pedal).
MOVEMENT IS AT ANKLE JOINT
**the foot pedal**
Radial Deviation
Turning or bending the wrist toward the thumb (radius) side.
Ulnar Deviation
Turning or bending the wrist toward the little finger (ulna) side
left ventral decubitus
radiographic position of the abdomen results in a left lateral projection. Note the horizontal orientation of the central ray
oblique positions
Body is rotated so that the coronal plane is not parallel with the table or IR
angle of rotation is specific for anatomy of interest
named according to side and surface of body closer to table or IR
abbreviations: RPO, LPO, RAO, and LAO
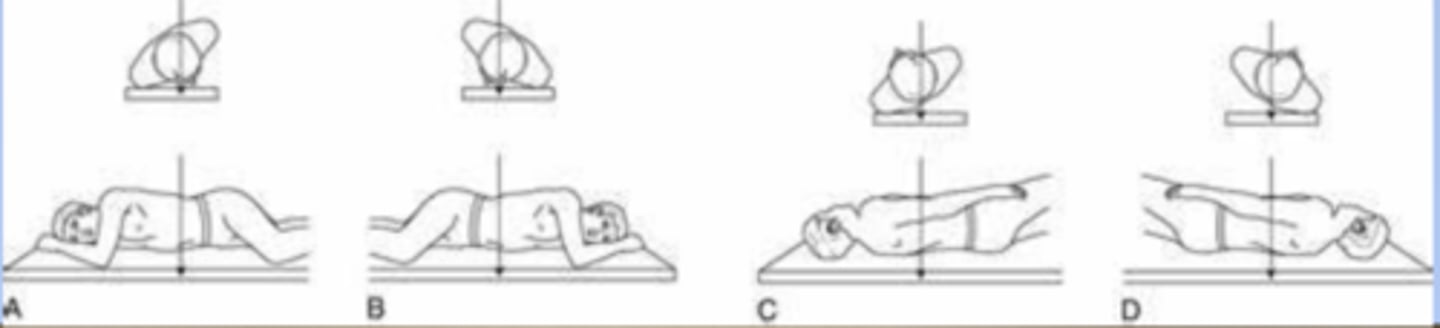
right lateral
radiographic position of the chest results in a lateral projection:
a lateral position is named according to the side of the patient that is placed closer to the IR
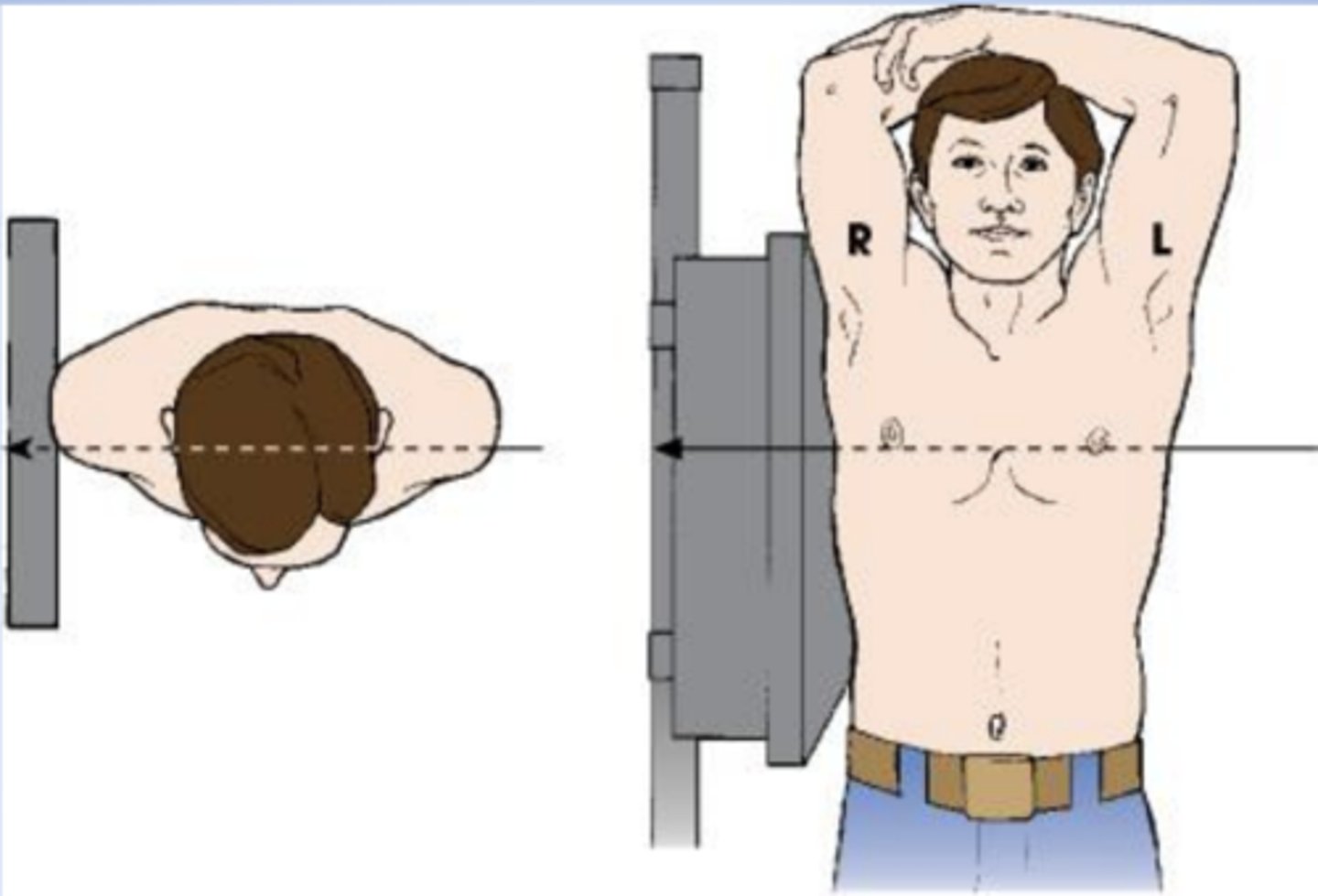
AP projection of skull
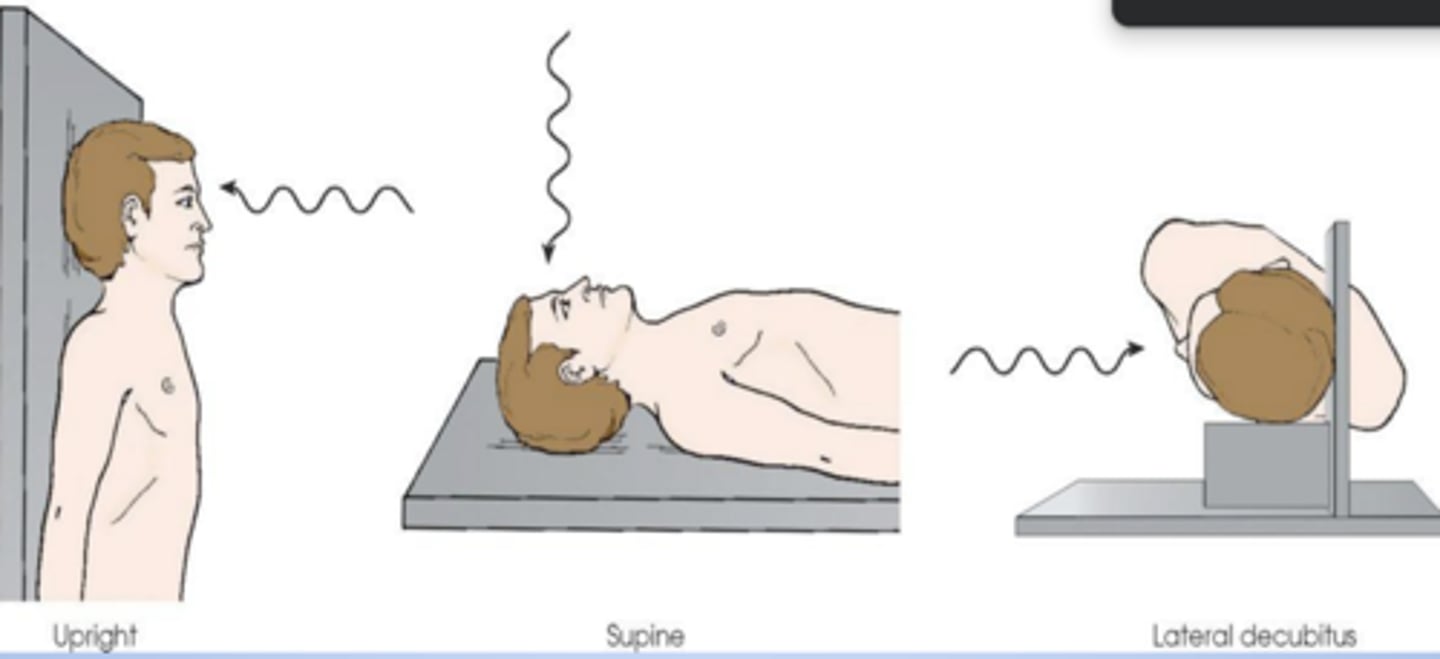
Patient's head placed in upright, supine, and lateral decubitus positions for a radiograph. All three body positions produce:
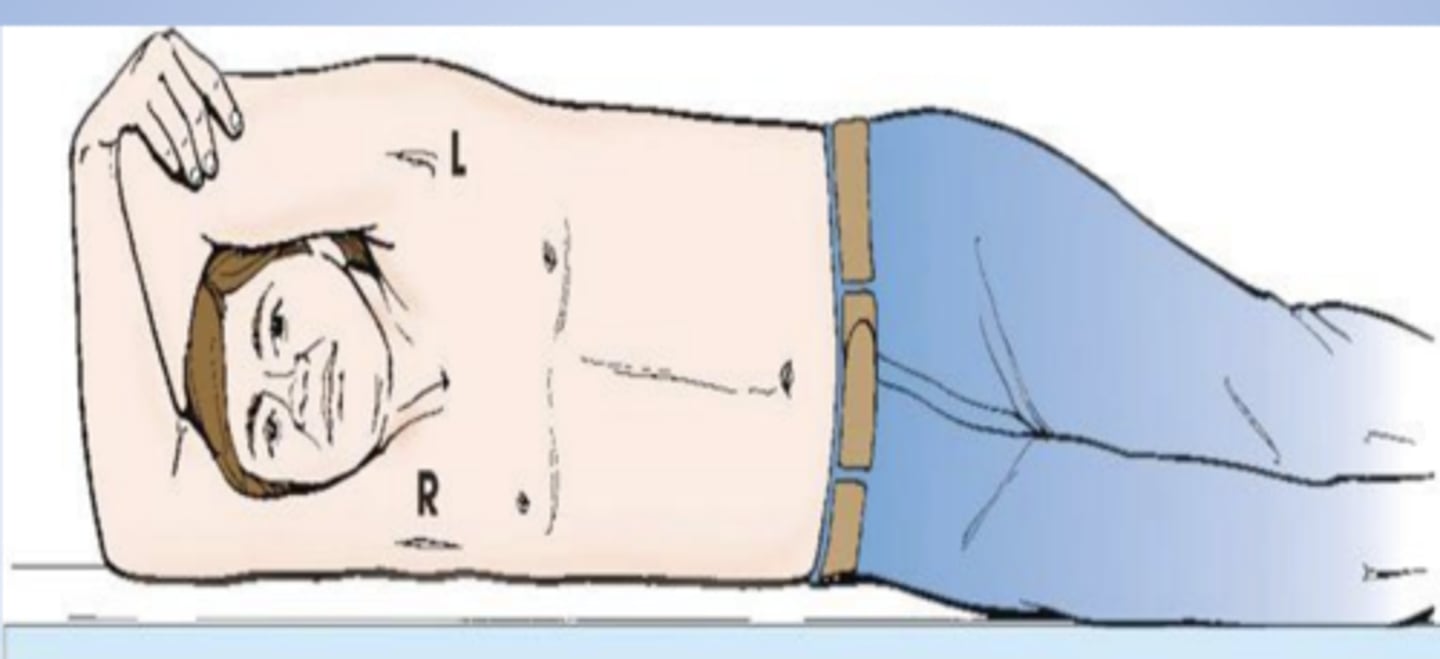
Right lateral recumbent
position?
ventral recumbent
prone position of body, aka
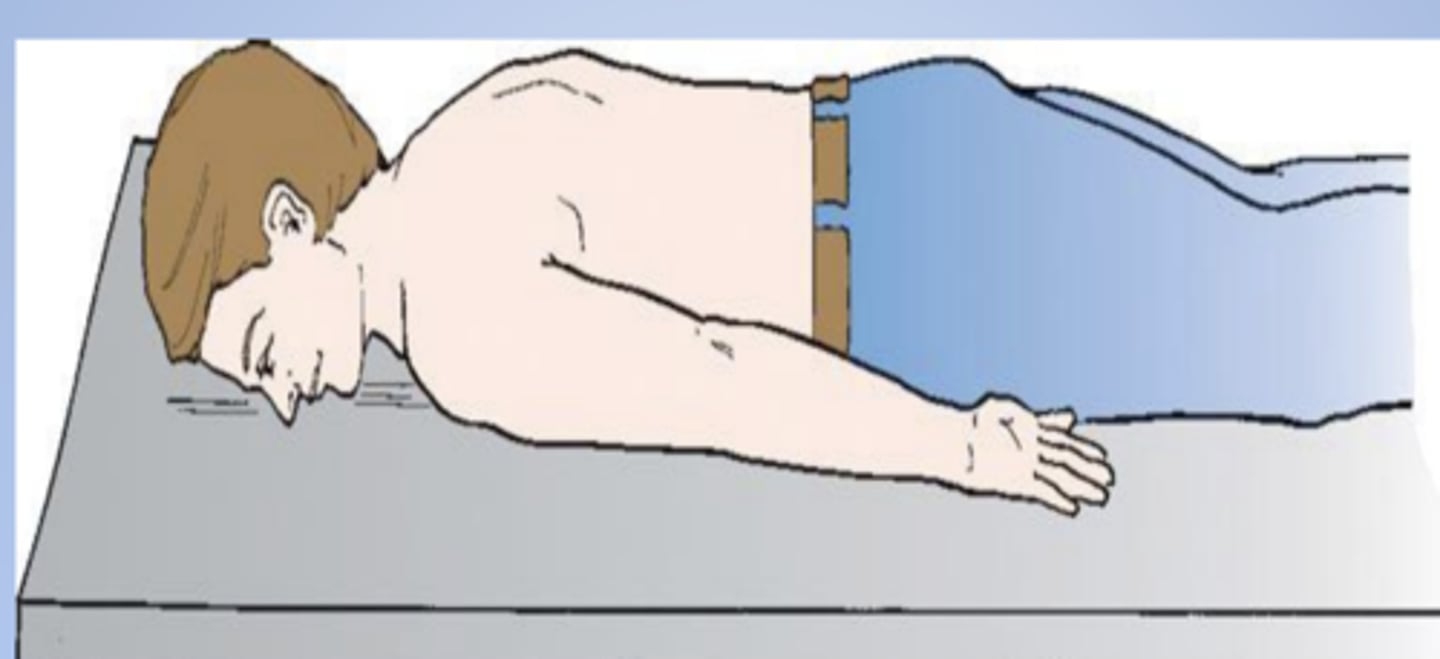
PA oblique
ID the projection:
RAO radiographic position of chest results in X
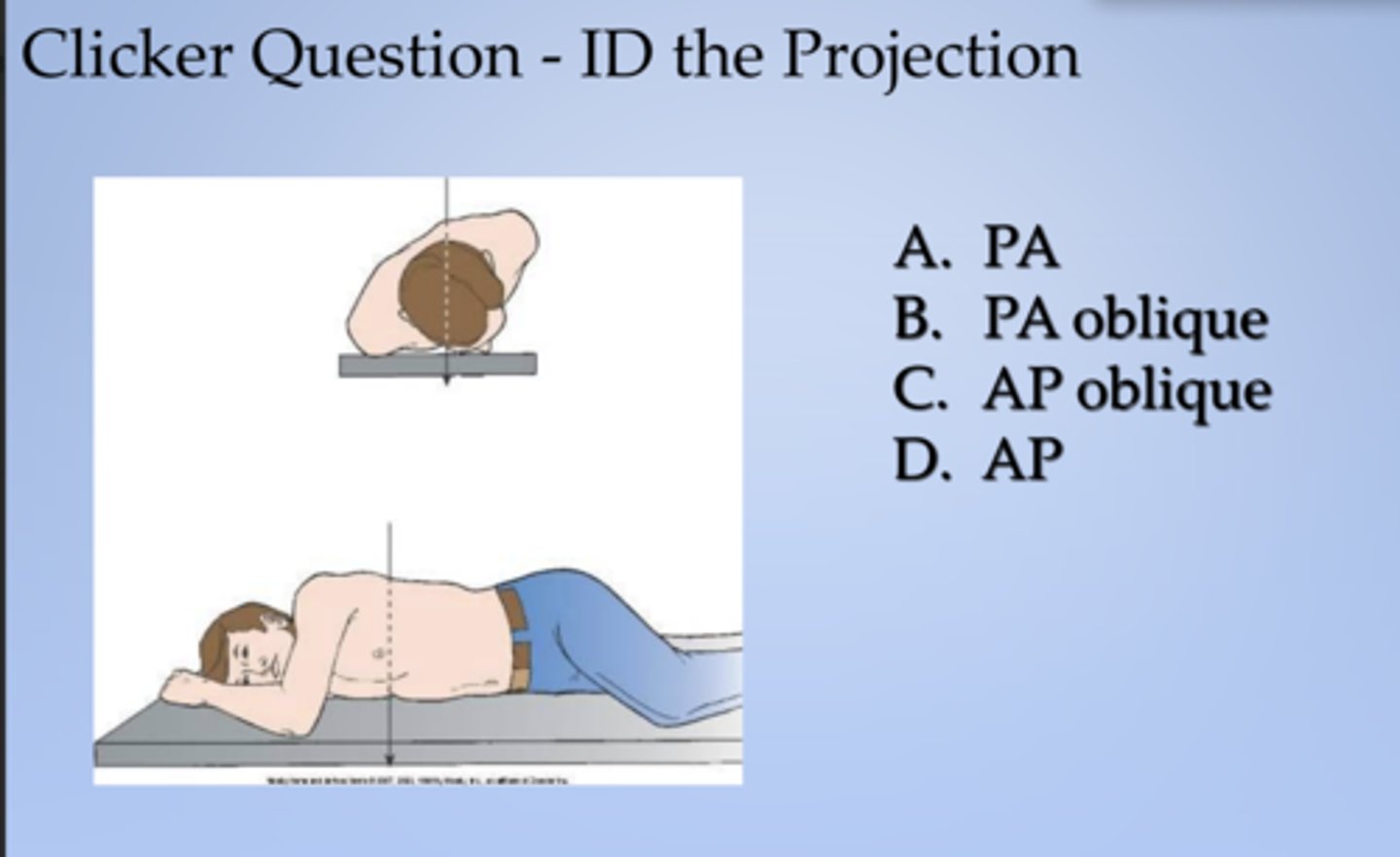
lateral
ID the projection:
Right lateral radiographic position of chest results in X projection
Left lateral radiographic position of chest results in X projection.
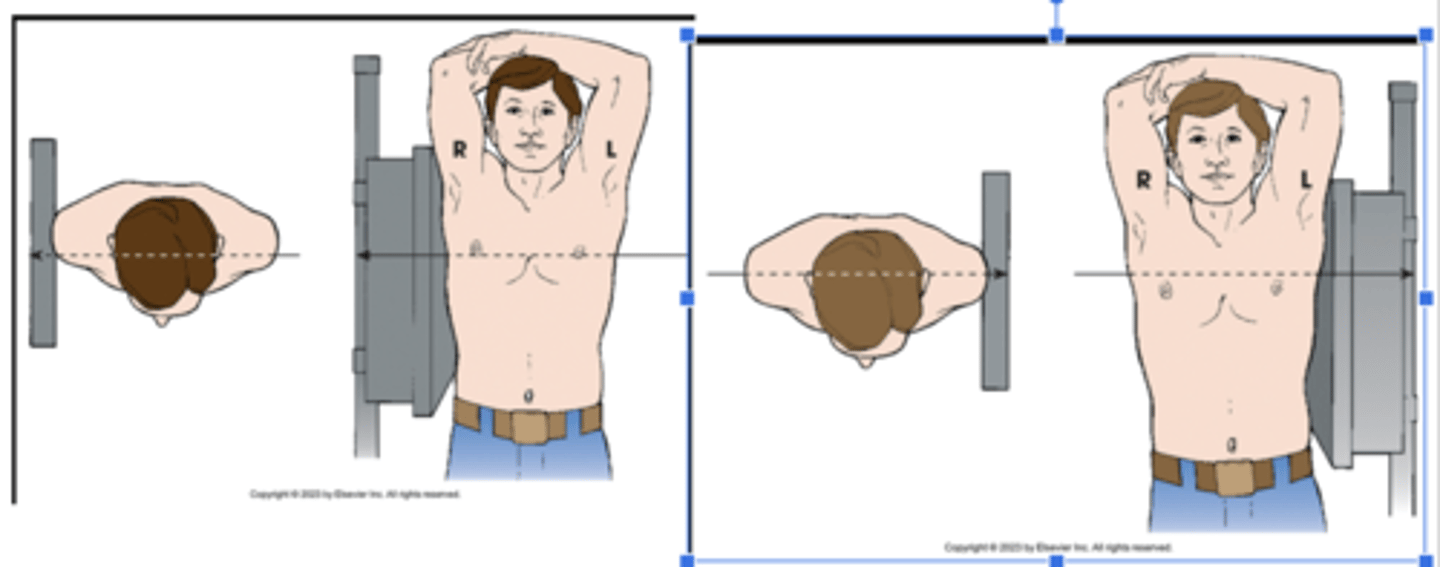
tangential
ID the projection
X projection of zygomatic arch. Central ray skims surface of the skull.
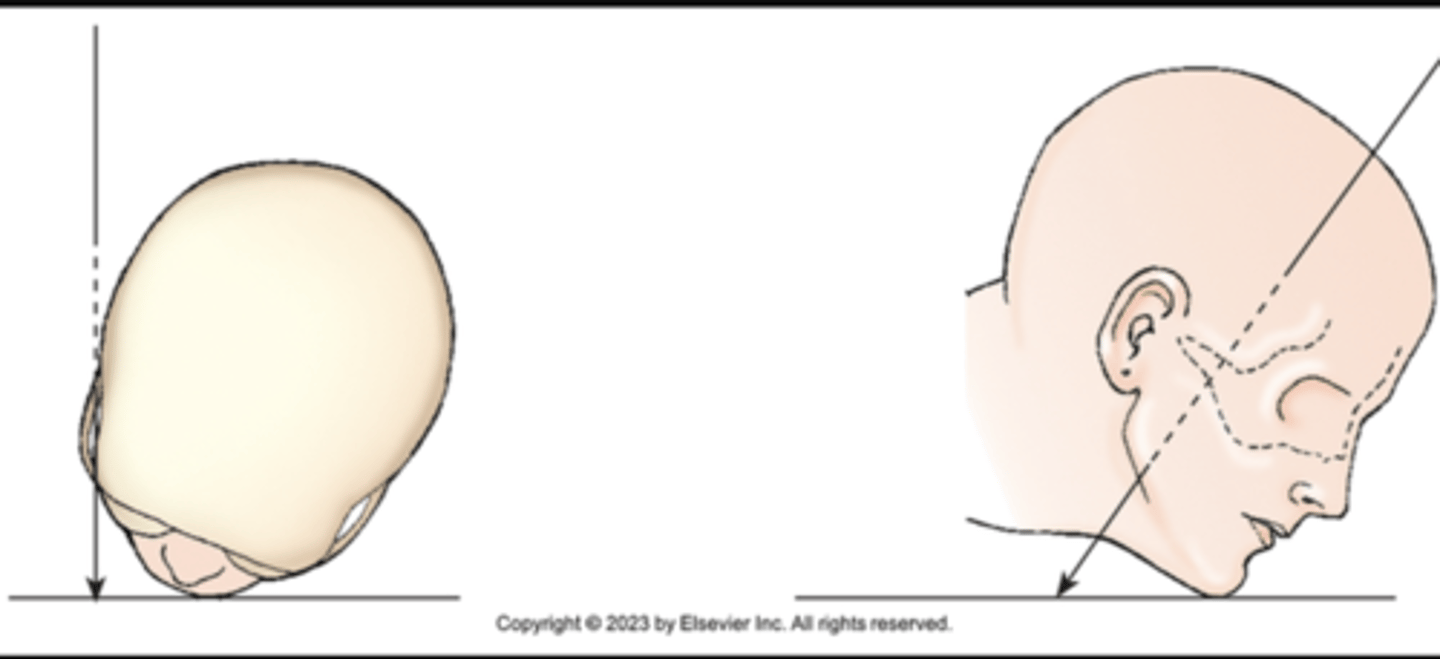
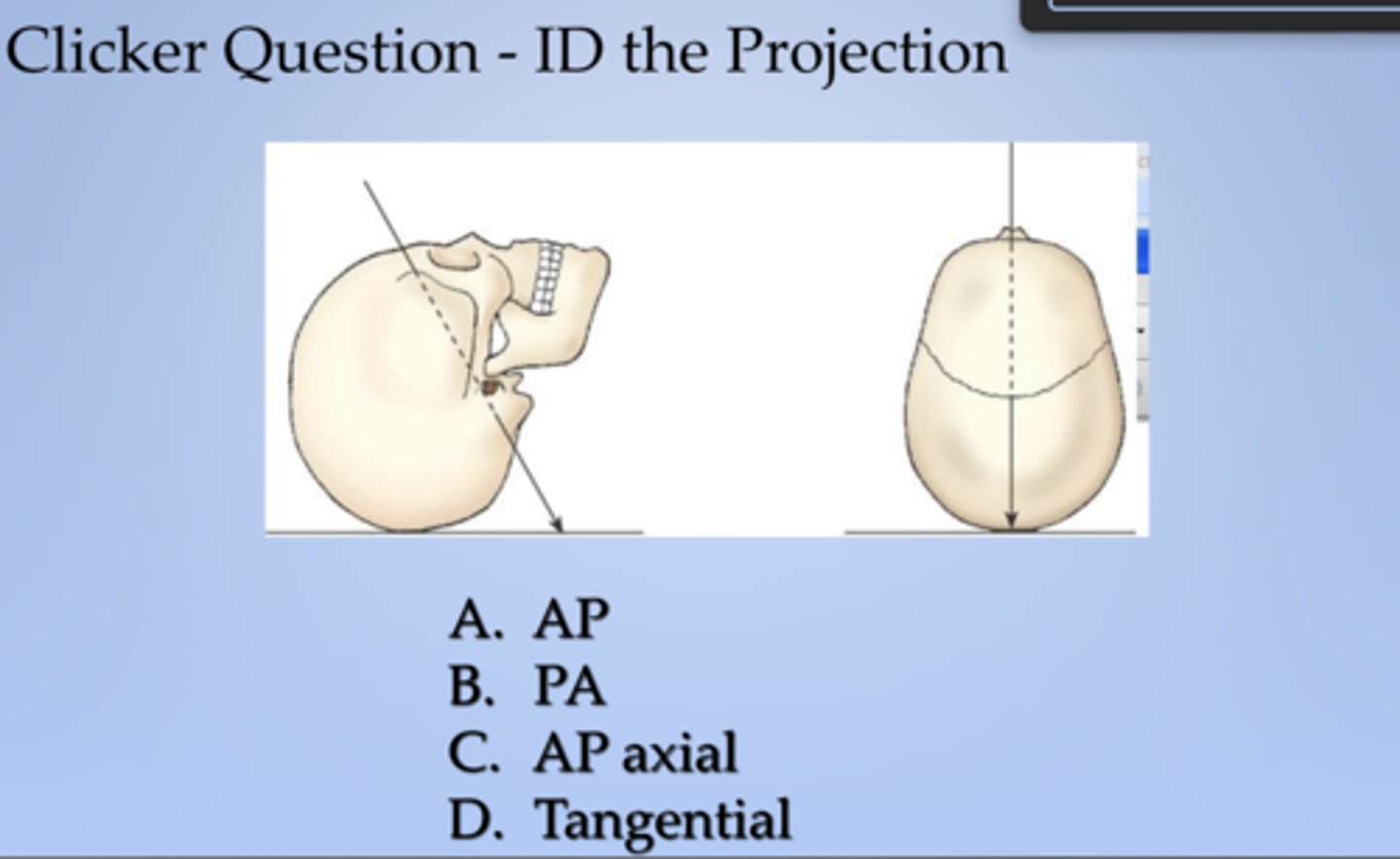
AP axial
ID the projection:
X projection of skull. Central ray enters anterior aspect at an angle and exits posterior aspect.