intro/directional terms
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Anatomy
internal and external structures
connect between different parts + their functions
observations of the body
What two types of study are part of microscopic anatomy?
cytology, histology
cytology
study of cells
histology
study of tissues
what are the two types of anatomy
microscopic and gross
What are the 3 subcategories of gross anatomy
surface, regional, systemic
surface anatomy
general anatomical form, superficial, palpable
regional anatomy
in specific areas of the body
systemic anatomy
organ systems of the body
list the levels (6) of organization from simple to complex
chemical/molecular, cellular, tissue, organ, organ system, organism
what are the four elements that make up the body on a chemical/molecular level
C, H, O, N
What are the major classes of molecules in the body (in order from greatest to least)?
water, proteins, lipids, carbohydrates
What molecule is most prevalent in the body
water (66%)
cellular level
cells, the smallest living unit
tissue level
4 types: muscular, neural, connective, epithelial
organ level
made up of a combination of tissues
How many organ systems are there?
11
homeostasis
maintaining relatively constant environment suitable for cells, tissues, and organs
organs
failure to maintain homeostatic conditions
pathology
the study of disease
What is the language of anatomy used for (2)?
to communicate precise information
superficial anatomy
seen with the naked eye and can be used to indicate state of health
give an example of superficial anatomy
skin color, symmetry, markings, posture, movements
anatomical landmarks
prominent structures that are usually palpable
anatomical position
standing, flat feet, hands at side, palm face forward
supine
body is lying on back, toes face up, palms up
prone
body is laying on back, toes down, palms down
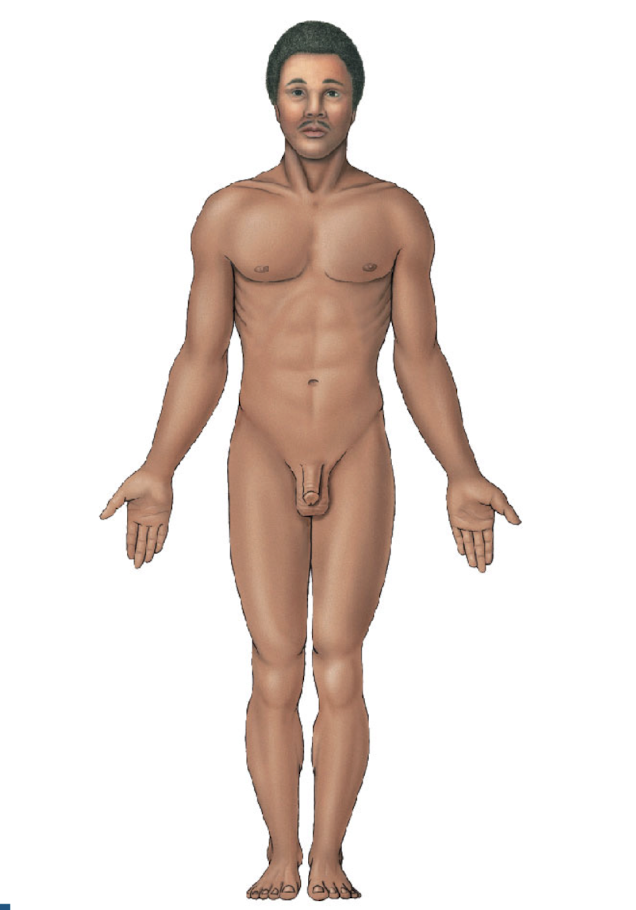
what position is this?
anatomical position
superior/ cranial
towards the head
inferior/ caudel
toward the feet
anterior/ central
toward the front of the body
posterior/ dorsal
toward the back of the body
medial
toward the midline
lateral
toward the side of the body
superficial
staying toward the surface of the body
deep
further from the surface of the body
proximal
closer to the attachment point of the body
distal
closer to the fingers
sagittal plane
spits body into left and right
midsagittal plane
through the midline
parasagittal plane
not through the midline
transverse plane
horizontal, splits body into superior and inferior sections
frontal plane
splits the body into anterior and posterior sections
oblique plane
cuts body on a diagonal