NURS 3366: MECHANISMS OF DEFENSE
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/115
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapters mentioned: Mechanisms of Defense: Inflammation and Immune Function
Last updated 5:05 AM on 2/28/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
116 Terms
1
New cards
Innate (AKA “*natural”*) resistance
the defense mechanisms we are __*born with*__
2
New cards
%%1st Line of Defense%%
%%Non-specific, Immediate, physical barriers%%
3
New cards
%%EX of defensive roles for 1st:%%
1. protection from hazardous environment
2. desquamation of skin
3. secretion of sweat (has anti-fungal/anti-bacterial properties)
4
New cards
%%*stressors that can breach* this defense%%
lacerations, abrasions, & punctures
5
New cards
eyes Defense
Tears and Eyelashes
6
New cards
*stressors that can breach* eyes defenses
1. **Sjogren’s Syndrome:** autoimmune disease that
dries up all lubricating fluids in the body
2. **Dry Eye Syndrome:** manufacturing of tears slows down; due to aging
7
New cards
respiratory system defenses
1. viscosity of mucus
2. cilia of cells in bronchi
3. cough reflex
8
New cards
*stressors that can breach* respiratory defenses:
1. cigarette smoking changes bronchial cells—no more cilia. (__**metaplasia**__)
2. __cough reflex suppression__ such as in head injury or stroke
9
New cards
GI system defenses
1. saliva - contains protective enzymes
2. stomach - HCL destroys most microbes
3. gag reflex / vomiting
4. bowels - normal contain “good flora” & defecation
10
New cards
*stressors that can breach* GI defenses
1. **Sjogren’s Syndrome** - dries up saliva, so less protection in mouth
2. anything that changes the bowel flora can leave us open to invading microbes; ex of something that might change the bowel flora: __**antibiotics**__
11
New cards
genitourinary (GU) system defenses
1. flow of urine - washes away microbes
2. vaginal secretions slightly acidic - kills bacteria
12
New cards
*stressors that can breach* GU defenses
1. decreased urine flow → kidney stones/failure
2. anything the changes vag. pH (EX: douching)
13
New cards
==2nd Line of Defense==
==INFLAMMATION, non-specific, immediate==
14
New cards
SHEP
swelling, heat, erythema (redness), pain
15
New cards
___________ is a normal, important body mechanism that helps us defend against stressors and begin the healing process.
Inflammation
16
New cards
Inflammation is
acute and short-lived (2 weeks)
17
New cards
mast cell degranulation leak chemical granules called
local inflammatory mediators
18
New cards
What are the three local inflammatory mediators?
Histamine, Leukotrienes, & Prostaglandin (HLP)
19
New cards
HLP causes capillaries to
vasodilate and become more permeable
20
New cards
If more inflammation is needed, what systemic inflammatory mediators will come to the area via the bloodstream?
__acute phase reactants (APR)__
21
New cards
What are the three APR?
__*CRP (*__*C-reactive protein)* , complement, *circulating prostaglandins*
22
New cards
Function of APR
opsonize (coat) and directly kill bacteria
23
New cards
*serous* exudate
clear, gold color of plasma leaking out in the area (blister)
24
New cards
*serosanguinous*
if there is blood (similar to blister)
25
New cards
*purulent exudate*
also, known as *pus,* thick & whitish or yellowish color, a microbe is present
26
New cards
Chemotactic substances
biochemical mediators that summon OTHER substances to a certain area, or to increase in amount.
27
New cards
Granulating tissue
pink, healthy, healing tissue
28
New cards
Degranulation
breaking apart of mast cells with spillage of granules of biochemical mediators into tissue.
29
New cards
local external example
laceration or abrasion to skin.
30
New cards
local internal examples
1. pleuritis—inflammation of pleura when irritated by, for example, a lung cancer cell.
2. thyroiditis—thyroid is inflamed because of autoimmune attack.
31
New cards
S&S of (normal) systemic inflammation:
1. malaise, aches & pains
2. FEVER (response from increased PG’s & APR)
32
New cards
fever can dilate blood vessels →
too much vasodilation = low BP
33
New cards
fever increases metabolic rate→
may cause decompensation in very ill, debilitated, and/ or elderly patients.
34
New cards
Systemic Inflammation Lab Test
1. CBC will show increased WBCs: Leukocytosis and Neutrophilia
2. serum CRP will often be elevated
35
New cards
“__**Not enough**__” inflammation
Anyone with not enough inflammation will be __extra susceptible__ to infections.
36
New cards
Quantitative Defect
Leukopenia and Neutropenia
37
New cards
Qualitative Defect
1. **chemotactic defects**: won’t respond appropriately when “summoned.”
2. **impaired function**; ex—phagocytes damaged by diabetes mellitus have decreased ability to fight microbes.
38
New cards
__“____**too much**__” inflammation
inflammation goes into “overdrive” and/or becomes chronic; **EX**: __SIRS__, __sepsis__, __septic shock,__ & __chronic inflammation__ disorders
39
New cards
**SIRS** – *systemic inflammatory response syndrome*
excessive systemic inflammation contributes to widespread impaired tissue function and organ damage.
40
New cards
SIRS S&S
1. unexplained change in mental status (confusion, not as awake and alert as normal).
2. fever of more than 100.4° F
3. increased HR
4. increased RR
5. abnormal white blood cell count (WBC)
41
New cards
Sepsis
SIRS + Infection
42
New cards
Septic Shock
sepsis + low BP
* __*extreme*__ __vasodilation__ = no arterial vessel “tone” as arteries become too relaxed, “floppy”
* __*extreme*__ __vasodilation__ = no arterial vessel “tone” as arteries become too relaxed, “floppy”
43
New cards
Septic Shock S&S
SIRS S&S + low BP
* causes __ischemia__ to organs so patient can have __renal failure, respiratory failure, heart failure or death.__
* causes __ischemia__ to organs so patient can have __renal failure, respiratory failure, heart failure or death.__
44
New cards
non-medicinal interventions for inflammation
Ice on the area of swelling → cold numbs pain → vasoconstriction of bv → diminished swelling and pain
45
New cards
medicinal therapeutics
anti-inflammatory medications and prostaglandins (PGs)
46
New cards
anti-inflammatory medications MOA
__*suppress the effects of prostaglandins*__ : STEROIDS, and NSAIDs—“non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs
47
New cards
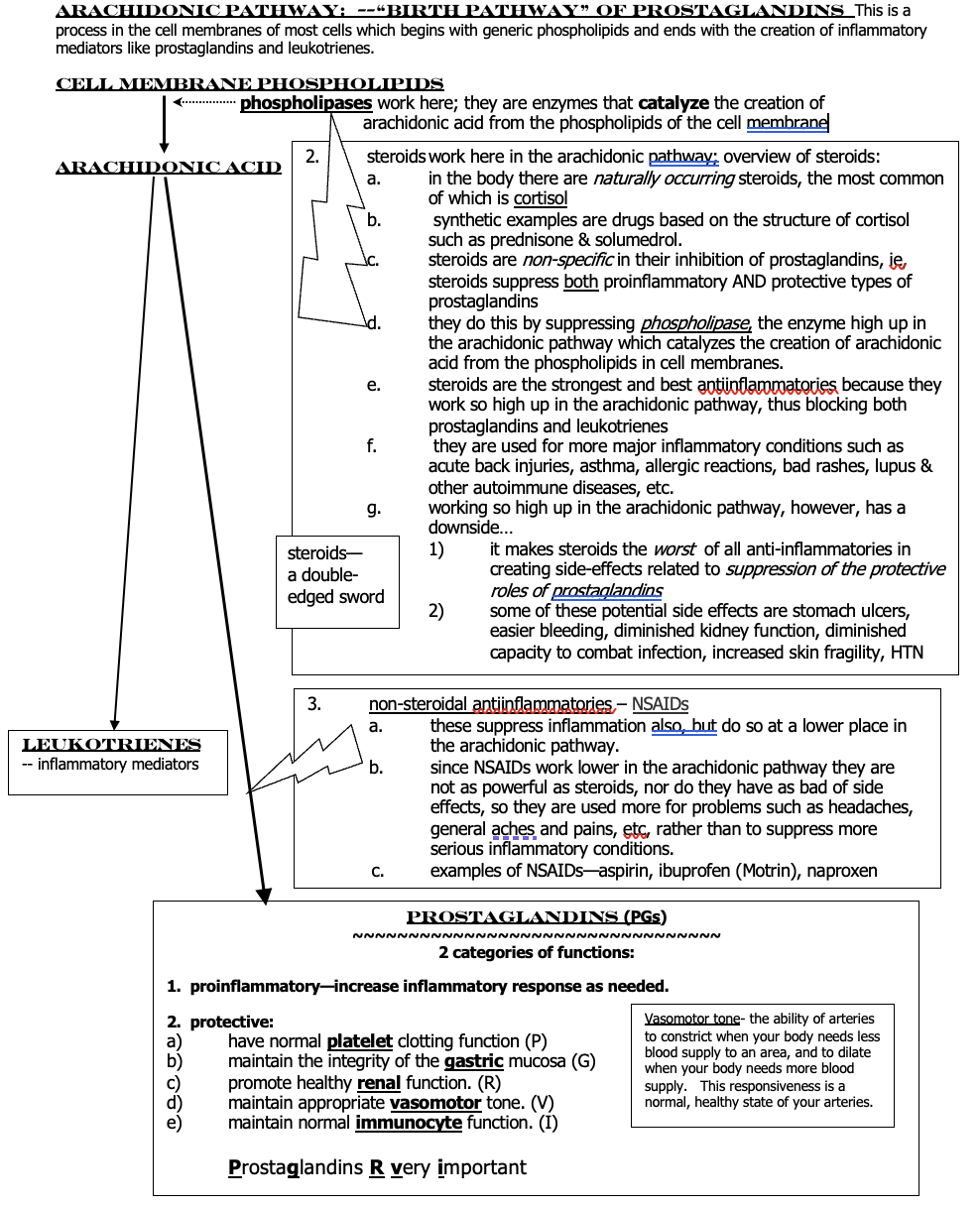
Prostaglandins (PGs)
Pro-inflammatory PG’s - stimulate further inflammation by increasing vascular permeability and also induce fever &
pain
Protective PG’s - PGRVI
pain
Protective PG’s - PGRVI
48
New cards
*side effects* of anti-inflammatory drugs
have to do with suppressing the *“protective”* and *“pro-inflammatory”* effect
\* (ideal effect would be to be __specific__ and suppress *pro-inflammatory* __only__.)
\* (ideal effect would be to be __specific__ and suppress *pro-inflammatory* __only__.)
49
New cards
arachidonic pathway
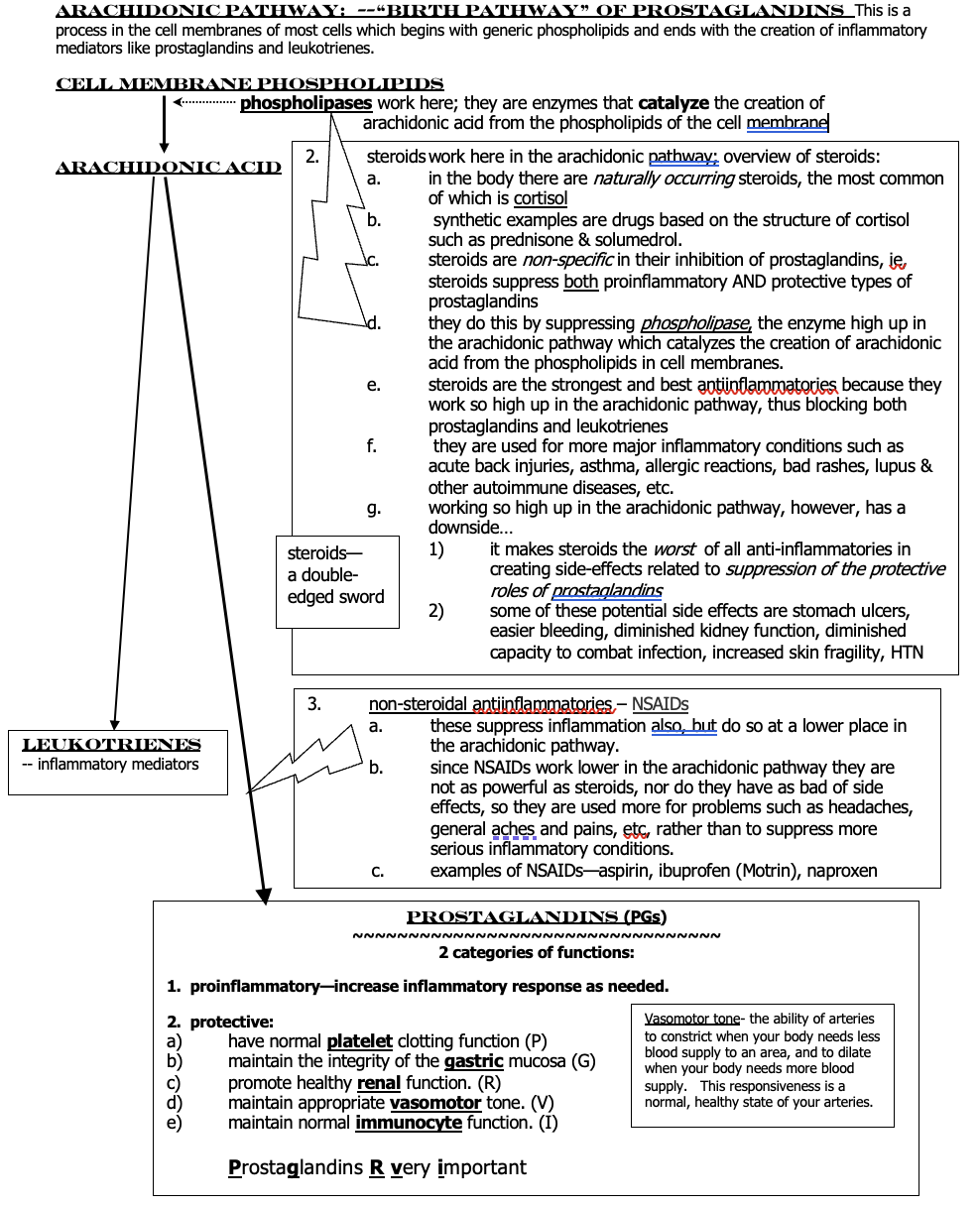
birth pathway to PG’s
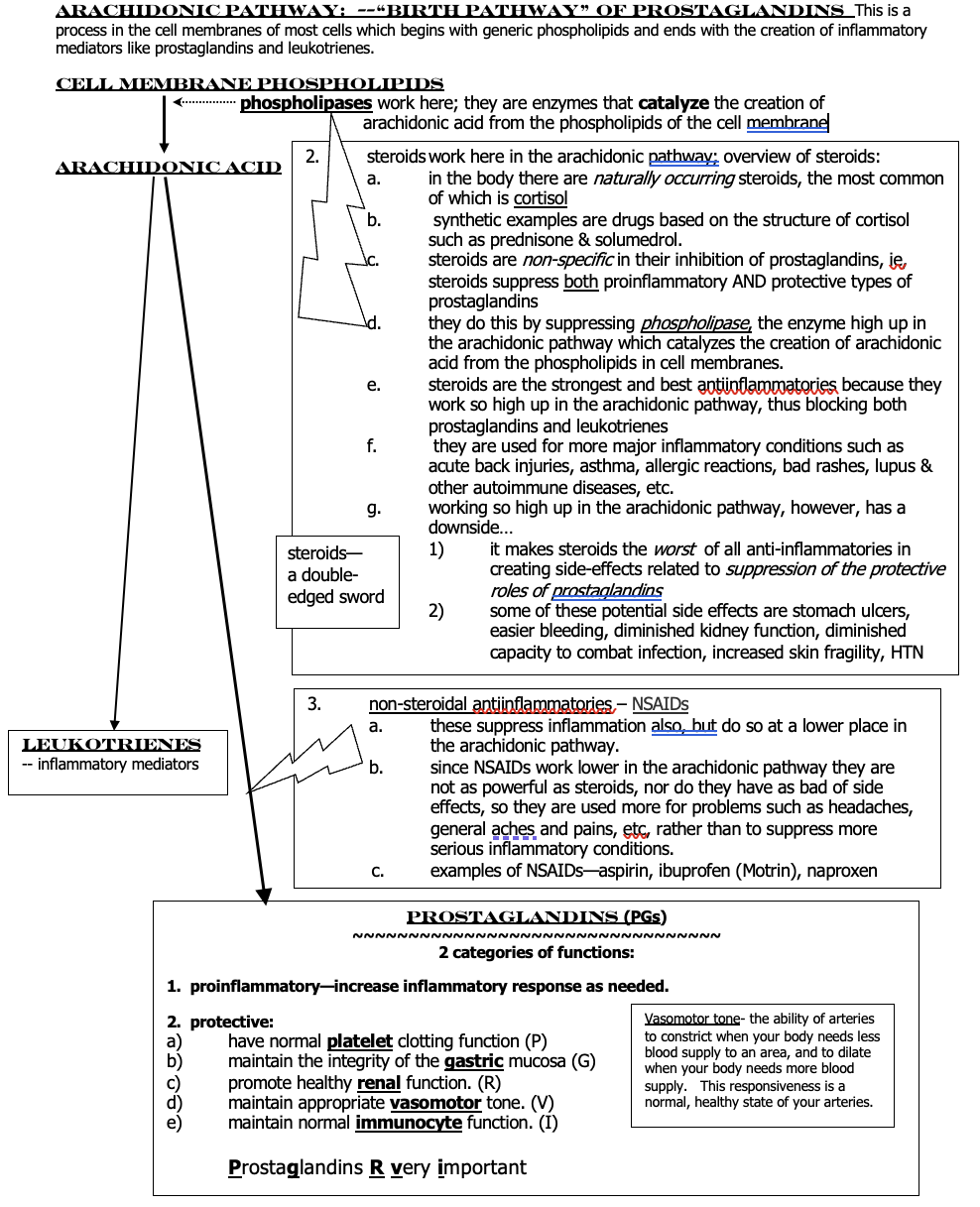
50
New cards
__phospholipases__
they are enzymes that catalyze the creation of arachidonic acid from the phospholipids of the cell membrane
51
New cards
Protective PG’s
1. have normal __**platelet**__ clotting function (**P**)
2. maintain the integrity of the __**gastric**__ mucosa (**G**)
3. promote healthy __**renal**__ function. (**R**)
4. maintain appropriate __**vasomotor**__ tone. (**V**)
5. maintain normal __**immunocyte**__ function. (**I**)
52
New cards
Protective PG’s: Steroid *Side Effects*
**P** - easy bleeding and bruising
**G** - ulcers
**R** - kidney failure
**V** - vasoconstriction → HTN
**I** - higher risk of infections
when pt is taking a steroid for a long time ⬆️
**G** - ulcers
**R** - kidney failure
**V** - vasoconstriction → HTN
**I** - higher risk of infections
when pt is taking a steroid for a long time ⬆️
53
New cards
steroids
________ suppress __both__ proinflammatory AND protective PG’s high up in the arachidonic pathway by blocking prostaglandins and leukotrienes
54
New cards
Steroids are used to treat
acute back injuries, asthma, allergic reactions, bad rashes, lupus & other autoimmune diseases
55
New cards
__non-steroidal antiinflammatories__ – __NSAIDs__
work lower in the arachidonic pathway and are used for headaches, general aches, and pains
56
New cards
examples of NSAIDs
aspirin, ibuprofen (Motrin), naproxen
57
New cards
^^Acquired (AKA “*adaptive”*) immunity-- 3rd line of defense^^
^^*delayed, specific, & immunocyte involvement*^^
58
New cards
Which T-cell is known as an introductory cell?
CD4 cells (helper-T)
59
New cards
__B-lymphocytes (B-cells)__
1. differentiate into __plasma cells__
2. create __antibodies__ to the microbe that has attacked the body → memory B-cells
60
New cards
Antigens
“name tag,” “invader”: substance that induces the formation of Ab bc it’s recognized by the immune system as a threat
* response to antigens that are foreign to our bodies is normal; response to our own “self” antigens is abnormal.
* response to antigens that are foreign to our bodies is normal; response to our own “self” antigens is abnormal.
61
New cards
Antibodies
IgG & IgE: “protect & defend”: made by immune system in response to & counteract a specific antigen
62
New cards
T-Cell in charge →
Cell-Mediated Immunity
63
New cards
B-Cell in charge →
Humoral Immunity
64
New cards
__**Active**__ acquired immunity
*their own immunocyte system developed the antibodies that established immunity*
65
New cards
__***NATURAL***__ active acquired immunity
when a person’s plasma cells build up Ab in response to a microbially induced illness
* Summary: you get an infection when someone sneezes on you and you create your own Ab or memory T-cells so you’ll never get that dz again.
* Summary: you get an infection when someone sneezes on you and you create your own Ab or memory T-cells so you’ll never get that dz again.
66
New cards
__***ARTIFICIAL***__ active acquired immunity
when a person’s plasma cells build up Ab in response to receiving inoculations (vax) of a weakened or inactive microbe
67
New cards
__**Passive**__ acquired immunity
*they have been given someone else’s antibodies; they did* __*not*__ *develop the antibodies on their own*
68
New cards
__***NATURAL***__ @@passive@@ acquired immunity
mom → baby; via placenta/breast milk; MatAb
* Summary: mom’s Ab are temporary & only protect for approx. 2-3 mths, then disintegrate
* Summary: mom’s Ab are temporary & only protect for approx. 2-3 mths, then disintegrate
69
New cards
__***ARTIFICIAL***__ @@passive@@ acquired immunity
Ab injected during treatment; emergencies or as a stop-gap measure until active immunity develops
* Summary: exposed to a dz you’re not vaxxed against → get an IgG shot → gives Ab for right now (last 2 weeks)
* Summary: exposed to a dz you’re not vaxxed against → get an IgG shot → gives Ab for right now (last 2 weeks)
70
New cards
__*neutralization*__ (inactivation):
neutralizes viruses by preventing attachment and entrance of viruses into host cells
71
New cards
__*opsonization*__
“coats” bacteria—this promotes phagocytosis by optimizing recognition and “digestibility” of antigen for phagocytes
* makes it tastyyyyy
* makes it tastyyyyy
72
New cards
**Hypersensitivities**— “**too much**” immunocyte response
immunocyte response that is *supposed to help us* goes “too far” and *harms us*.
73
New cards
subcategories of hypersensitivity responses
allergic, autoimmune, and alloimmune
74
New cards
__allergic__ response (“allergic reaction”):
hypersensitivity to *a target antigen (environmental, medical, or pharmaceutical), called an* __allergen__*.*
75
New cards
__autoimmune__ response:
hypersensitivity to __*self-antigens*__ *(the target antigen)* – a reaction of our body to our own antigens.
76
New cards
__alloimmune__ response:
hypersensitivity to *another person’s antigens (the target antigen)*, such as when an __organ is transplanted__
77
New cards
*allergic hypersensitivity*
IgE mediated; exposure through inhalation, ingestion, injection, or skin contact → trigger primary response **SENSITIZATION** → creation of Ab that lies out in the lymph system
78
New cards
Allergic pathologic response
if an individual is genetically predisposed → IgE binds to mast cells → sensitizing the cell
79
New cards
*local allergic hypersensitivity* S&S
1. dermatitis (skin rash → itching and swelling),
2. nasal allergic rhinitis,
3. conjunctivitis - as a result of HLP release from the mast cell.
80
New cards
*systemic allergic hypersensitivity* S&S
1. anaphylaxis
2. urticaria (hives)
3. angioedema - abnormal vasodilation & edema of small bv (lips, tongue, hands)
4. N, V, D, cramps
5. wheezing - bronchial edema - leukotriene induced bronchoconstriction
6. dyspnea; possibly laryngeal edema
7. Hypotension & shock → systemic vasodilation
81
New cards
*allergic hypersensitivity* tx
1. histamine - anti-histamine
2. steroids
3. leukotriene blockers (Singulair)
82
New cards
*autoimmune hypersensitivity*
to self-antigens -- a reaction of our body to our own antigens
83
New cards
Autoimmune Hyper. EX:
__**rheumatic heart disease:**__ heart valve cells appear to be a close enough match to the strep antigen → autoAb begin attacking them → heart valve can malfunction-- become __floppy & leaky__ instead of opening & closing tightly.
\
\
84
New cards
Humoral Autoimmune Response
autoAb attack causing opsonization → phagocytized tissue cells by macrophages as if they were bacteria
85
New cards
Humoral Tissue Specific AutoImmune Dzs
Graves, Goodpasture’s Synd., Myasthenia gravis, Autoimmune hemolytic anemia
86
New cards
Cell-mediated Autoimmune Response
auto-T-cell response - “attacker” is our own T-cells
87
New cards
Cell-mediated Tissue Specific AutoImmune Dzs
Multiple sclerosis, Type-1 Diabetes, Celiac Dz
88
New cards
Systemic Autoimmune Dzs
Ab & self-antigen pair up → immune complex → irritates bc & vasculitis = surrounding tissue inflamed
89
New cards
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Ab → autoAb when encountered Nucleic Acids → attach themselves to DNA → immune complexes → circulated & deposited in connective tissue bv: kidneys, lungs, joints, skin → vasculitis
90
New cards
SLE S&S
1. **skin rashes**: “__butterfly” malar rash__ (wolf-like across face)
2. Joints: non-erosive arthritis of at least 2 peripheral joints
3. Serositis: pleura & pericardial sac inflamed → pleurisy & pericarditis
4. proteinuria - kidneys
5. seizures - neurons of brain
6. fatigue
91
New cards
SLE diagnosis
elevated CRP - non-specific
**ANA** - antinuclear Ab that looks for immune complexes
**ANA** - antinuclear Ab that looks for immune complexes
92
New cards
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
Immune Complex: Ab + Collagen → systemic S&S
* pain tends to be worse in morning & lessens as
day goes on
* pain tends to be worse in morning & lessens as
day goes on
93
New cards
RA S&S
fatigue, joint pain, swelling and deformation, inflammatory S&S of eyes, heart, lungs, almost any tissue
94
New cards
RA diagnosis
elevated CRP and + Rheumatoid (Rh) factor
95
New cards
*alloimmune hypersensitivity*
hypersensitivity to someone else’s cells; ex: organ transplant; “compatibility” issues
96
New cards
Types of *alloimmune* hyper.
Histocompatibility and ABO/Rh
97
New cards
Histocompatibility compatibility issues
test done on both donors to see if the HLA’s match on their cells
* if immunocytes attack → rejection
* S&S: pain over area, fever
* if immunocytes attack → rejection
* S&S: pain over area, fever
98
New cards
immunosuppressant drug
to minimize rejection, transplant patients are put on _________ _______ immune system “lethargic” so it won’t attack transplanted tissue.
99
New cards
ABO compatibility issues
A, B, AB, O
* receiving wrong blood type → hemolysis
* “clumping” effect → block bv in kidneys (failure) → ischemia to distal tissues (transfusion reaction) → __S&S: rash, fever, low BP, &/or body aches__
* receiving wrong blood type → hemolysis
* “clumping” effect → block bv in kidneys (failure) → ischemia to distal tissues (transfusion reaction) → __S&S: rash, fever, low BP, &/or body aches__
100
New cards
Rh factor compatibility issues
a person is either born with or w/out the Rh factor on their RBC as part of inheritance
* EX: a person w/out the Rh factor who is given RH+ blood will be __**ok**__ the 1st time they get blood since there’s no Ab development
* EX: a person w/out the Rh factor who is given RH+ blood will be __**ok**__ the 1st time they get blood since there’s no Ab development