Transcriptomics and Single Cell RNA Seq I
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
2-3-25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
central dogma exceptions
reverse transcription
RNA RNA replication (virus)
prions - proteins replication themselves
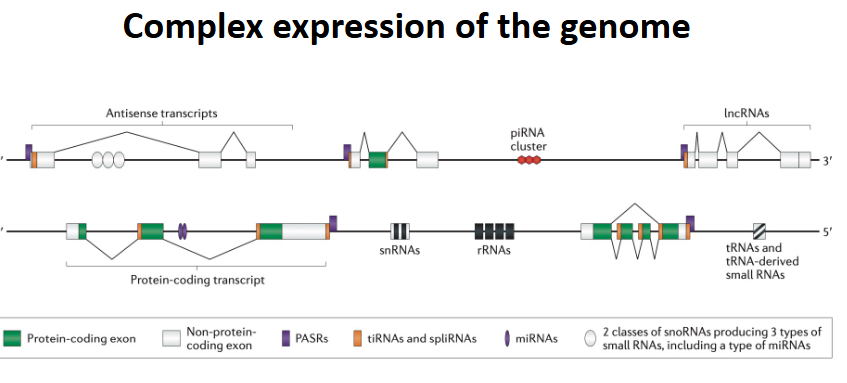
complex expression of the genome
more than just mRNA (protein coding)
miRNA - -bind to RNA and limit expression and cause degradation
tRNA - amino acid builder
rRNA - ribosomal rna
snRNA (RNA splicing)
lncRNA
microarray originally
probes of known DNA and RNA hybridize with fluorescent probes
issues with microarrays
only known species (requires a reference)
specific hybridization cause background (impacts sensitivity)
expensive
need custom probes / microarray
RNA Seq
advantages include: high throughput, low background noise, wide range of RNA exp. detectable
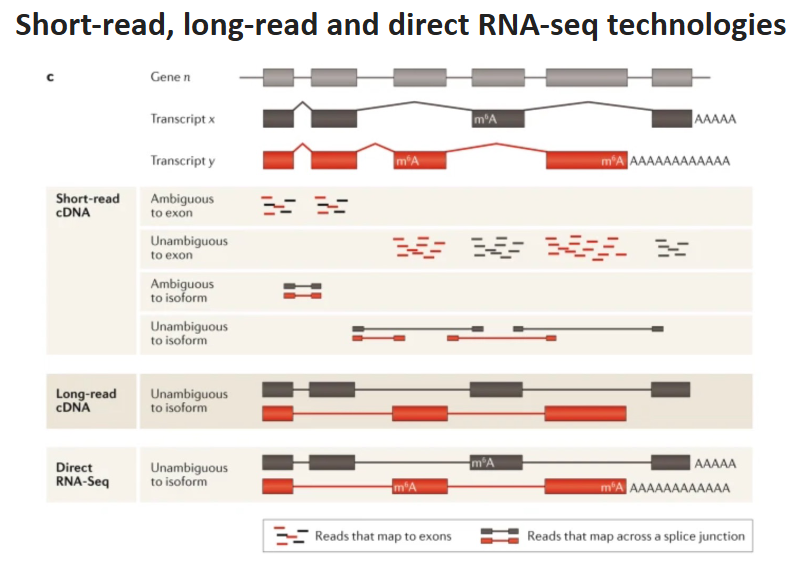
short read, long read and direct RNA seq technologies
illumina short read cDNA - difficult for isoforms or haplotyping
long read (nanopore and pacbio)
direct is nanopore (includes modifications)
RNA sequencing
use poly adentylation /selection for mRNA sequencing
need oligo-dt enrichment to select for transcripts containing poly A (mRNA only like 1-5% of all RNA, some lncRNA have polya)
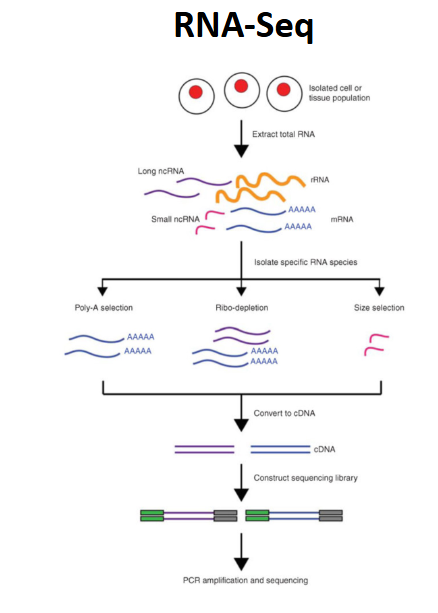
total RNA sequencing
profile both coding and non-coding transcripts
it is critical to remove ribosomal RNA (rRNAs), as otherwise up to 95% of reads might come from rRNAs
what are the two types of rRNA depletion
rRNA depletion via pull out
probe w/ typical rRNA sequences (magnetic bead capture)
via selective degradation
ribonuclease H and DNAse I
ssDNA bind to RNA and RNA will be degraded by ribonucl. and ssDNA will be degraded by DNAse
requirements for strand information
“unstranded” RNA seq gives no info for transcript orientation
need to know polarity to know DNA
can come from antisense transcripts (rarely)
stranded RNA seq facilitates gene annotation and accurate assessment of gene expression
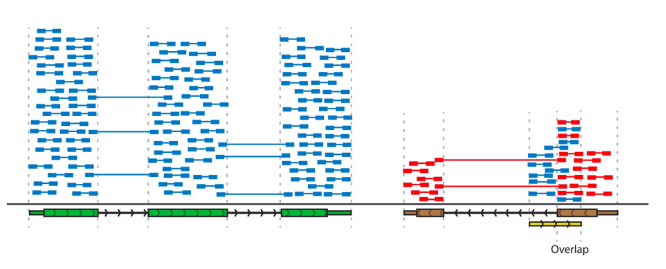
RNA stranded sequencing
allows sense and antisense transcripts to be differeniated
in the dUTP based method, strand specificty is achieved by the second-strand cDNA incorporating dUTPs instead of dTTPs. Digestion of dUTPs by uracil-DNA glycosylase (UGDase) prevents this strand from being PCR amplified, conferring single strand specificity
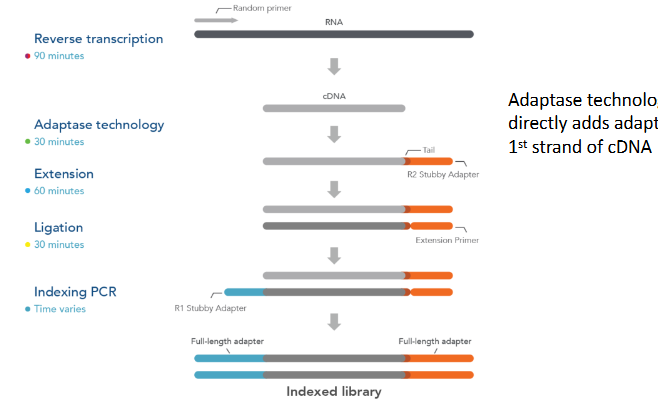
adaptase technology directly adds adapter to 1st strand of cDNA
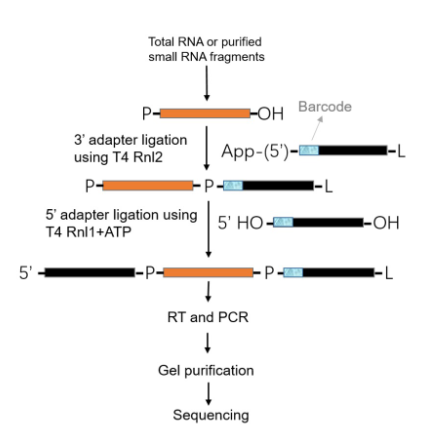
small RNA sequencing
as miRNA molecules are of short length, they are extended by ligation or polyadenylation, which introduce primer-binding sites of RT and subsequent amplification
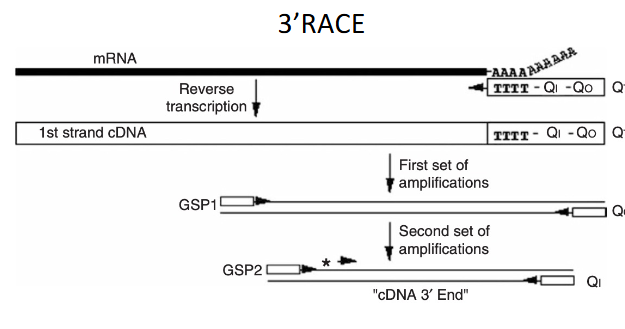
rapid amplification of cDNA Ends (RACE)
a procedure for amplification of nucleic acid sequences from a mRNA template between a defined internal site and unkown sequences at either the 3’ or the 5’ end of the mRNA
rbetter for second set of PCR amplification (more specific)
approaches to force the specific acquisition of full length 5’ cDNAs
approach 1: ligating an anchor primer to the 5’ end of the mRNA before performing the reverse transcription step
approach 2: cap-switching RACE. this method takes advantage of the propensity of Moloney murine leukemia virus reverse transcriptase to add an extra 2-4 cytosines to the 3’ ends of newly synthesized cDNA strands upon reaching the cap structure at the 5’ end of the mRNA template
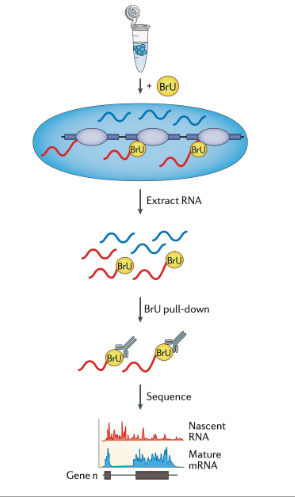
run-on methods e.g. GRO-seq (nascent RNA analysis)
rely on the incorporation of nucleotide analogues that enable nascent RNA to be enriched from the total RNA pool and that allow measurement of transient RNA transcription
Bru pull down to enrich the nascent RNA
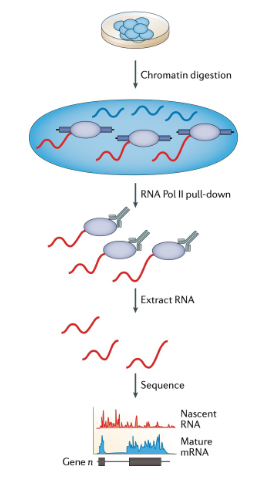
RNA Pol II directed methods (mNET-seq) (nascent RNA analysis)
Poll II associated RNA is pulled down using anti-FLAG or various antibodies directed against Pol II C terminal domain
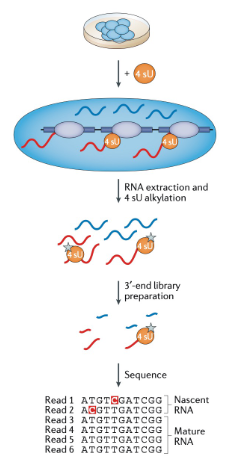
metabolic labeling SLAM-seq (nascent RNA analysis)
nucleotide analogue 4-thiouridine (4 sU) is used for pulse labeling. Iodoacetamide is added after rna extraction, to alkylate 4 sU residues that have been incorporated into the growing nascent RNA strand. This modification induces reverse-transcription-dependent thymine-to-cytosine nucleotide substitutions which are detected as mutations in a sequencing analysis, thereby directly identifying the 4 sU incorporation sites
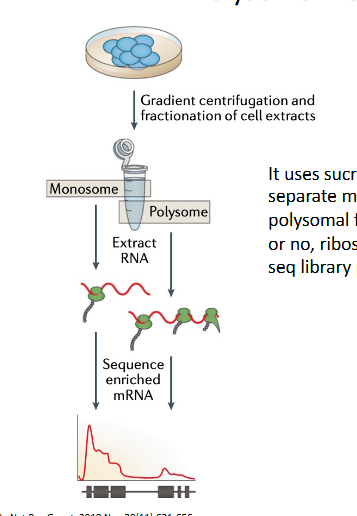
polysome profiling (translatome analysis)
transcription doesn’t directly relate to protein synthesis
It uses sucrose gradient ultra centrifugation to separate mRNAs boud by multiple ribosomes from those bound by a single or no ribosome for RNA seq library preparation
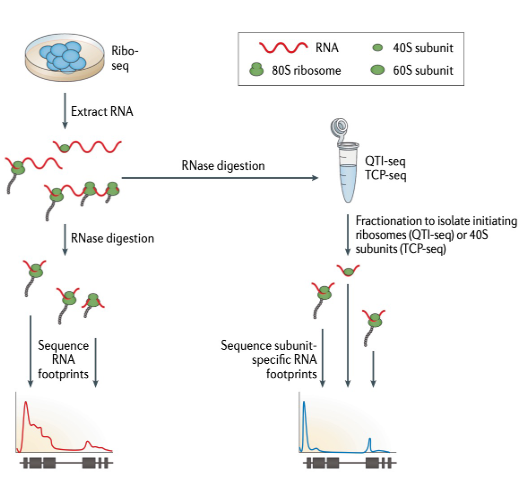
ribosome footprinting (translatome analysis)
it uses cyclohexamide to inhibit translation elongation and cause ribosomes to stall on mRNAs. Digestion of mRNA with RNase I leaves ribosome protected footprints of 20-30 nucleotides, which are processed to generate an rna-seq library
structurome (beyond analysis of gene expression)
nuclease methods use enzymes that digest either ssRNA or dsRNA. The RNA remaining after nuclease digestion is used as the input for RNA-seq library preparation
chemical mapping methods use chemical probes that react with RNA molecules and mark structured or unstructured nucleotides. These marks either block reverse transcription ir resukt in cDNA misincorporation, allowing the mapping and analysis of RNA-seq reads to reveal strucurome
RNA-RNA interaction analysis (beyond analysis of gene expression)
RNA molecules are crosslinked so as to preserve interactions, before fragmentation and proximity ligation
adapters → sequence
RNA-protein interaction analysis
RNA-protein interaction methods rely on immunoprecipitation, utilizing an antibody against the RNA binding protein of interest to capture its bound RNA for analysis
.fastq format
four lines repeating
@title and optional description / sequence identifier
sequence
+ (and optional repeat of title line)
quality scores corresponding to sequnce
RNA Sequencing
high throughput method
count the number of reads (transcript)
can probe entire genome for expression (non-targeted approach)
splicing information
alternative splicing and novel isoforms
possible to phase
can get variant information