Anti-Cancer
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms

Intercalating agent
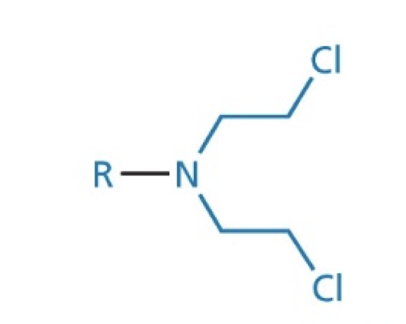
dialkylating agent nitrogen mustard structure
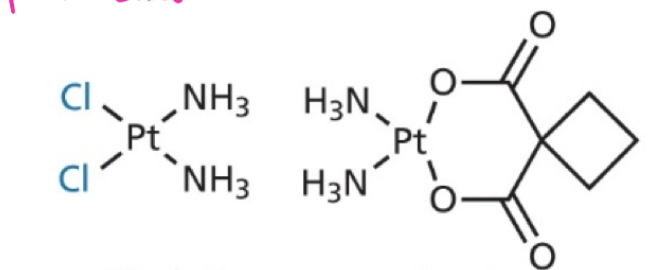
dialkylating agent platin structure

purines - guanidine and adenosine
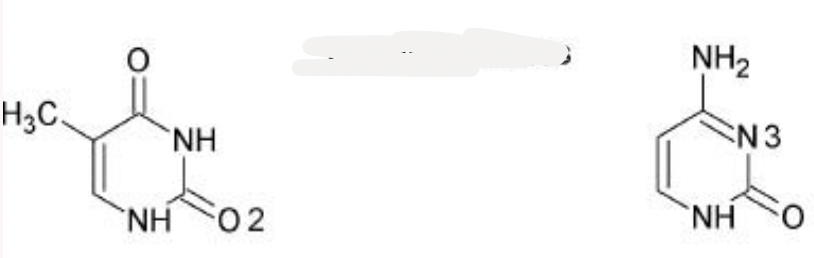
pyridines - thymine and cytosine
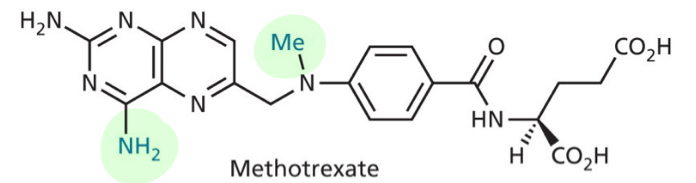
Folic acid analogue - inhibit DHFR
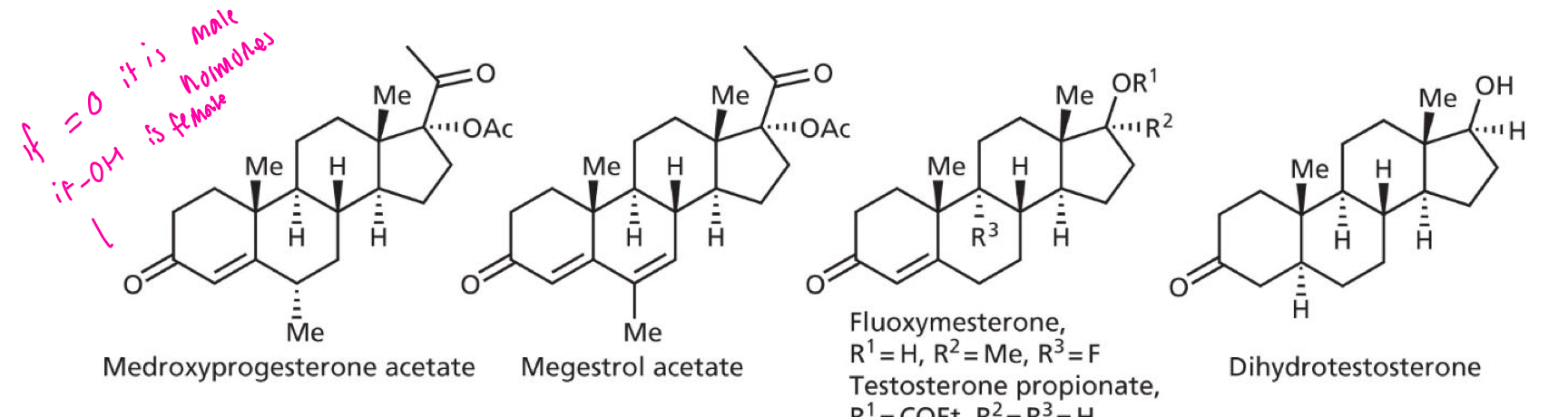
HORMONAL
anti-metabolites - vinca
Anti-metabolite - paclitaxel taxane based
kinase inhibitor
intercalating agent MOA
MOA: Planar aromatic rings that SLIDE between DNA base pairs, distorting the DNA helix and inhibiting replication/transcription
alkylating agent MOA
MoA: Covalently bind to nucleophilic DNA sites, causing mispairing or cross-linking (e.g. guanine to cytosine usually, now to thymine)→ inhibition of replication. Add an alkyl to DNA
anti-metabolites MOA
MoA: Mimic natural nucleotides, disrupting nucleotide biosynthesis or incorporation - disrupt mitosis
what does folic acid analogues inhibit?
DHFR
hormone analogues
MOA: administering opposing gender’s hormones
Drugs acting on structural proteins MOA
MOA: Disrupt cell mitosis by Ix with tubulin - (structural protein and building block for microtubules which are polymerised and depolymerised during cell division) - ANTIMITOTIC AGENT
Paclitaxel (taxane based) MOA
MoA: Promotes tubulin polymerisation → prevents depolymerisation (stimulate formation of spindle and prevent disassembling - as need to form and dissemble)
Vinca alkaloids MOA
MoA: Bind tubulin and induces depolymerisation → prevent polymerisation → spindle collapse
kinase inhibitors moa
MOa: Inhibit ATP-binding site of overactive protein kinases involved in cancer cell signalling.
types of kinase inhibitors
Type I: Active conformation – bind to ATP binding site and block access to ATP - Gefitinib, Erlotinib
Type II: Inactive conformation – bind to enzyme and stabilise inactive conformation - Imatinib, Nilotinib - more selective but random mutation risk
Allosteric/Irreversible: Trametinib, Afatinib, Ibrutinib - contain NCOC=C (amide to alkyne)
What drugs are the only ones with halogens
kinase inhibitors and alkylating agents
what drugs undergo bioactivation
pro-drugs - anti-metabolites usually, alkylating agents
What drugs are enzyme inhibitors
antimetabolites and kinase inhibitors