Module 4 - Parasites & Viruses
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
Explain the significance of parasitic diseases in the United States
- they are not very common in the U.S. because there are high levels of sanitation, adequate housing, and temperate climates
- they are more common in low and middle income countries
Groups that are affected by Neglected Tropical Diseases
- those in poverty, politically marginalized, and rural areas
- ignored by funders and pharmaceutical research
Strategies to control and eliminate NTDs
- clean water & sanitation
- vector control
- inexpensive pharmaceuticals & simple surgery
- veterinary control
Stool specimen preservatives and their uses
Formalin - concentration, EIA, acid-fast
PVA - PCR, permanent slide
Microscopic characteristics used to identify parasites
- size & shape
- internal organelles
- color & staining characteristics
- life stage form
Stool specimen preparation
- collect by using clean, wide-mouth container
- unpreserved if viewing motile forms
- preserved by two vial system
- processing --> wet mount (sometimes with iodine), concentration by centrifugation, permanent stained smears
Whole blood parasitic specimen
- use EDTA
- thick smear concentrates parasites
- thin smear allows for species identification
Other parasitic specimens (4)
- cellophane tape prep or pinworm paddle
- fluid specimens (urine & CSF should be concentrated)
- tissues, biopsy, corneal scrapings
- sputum
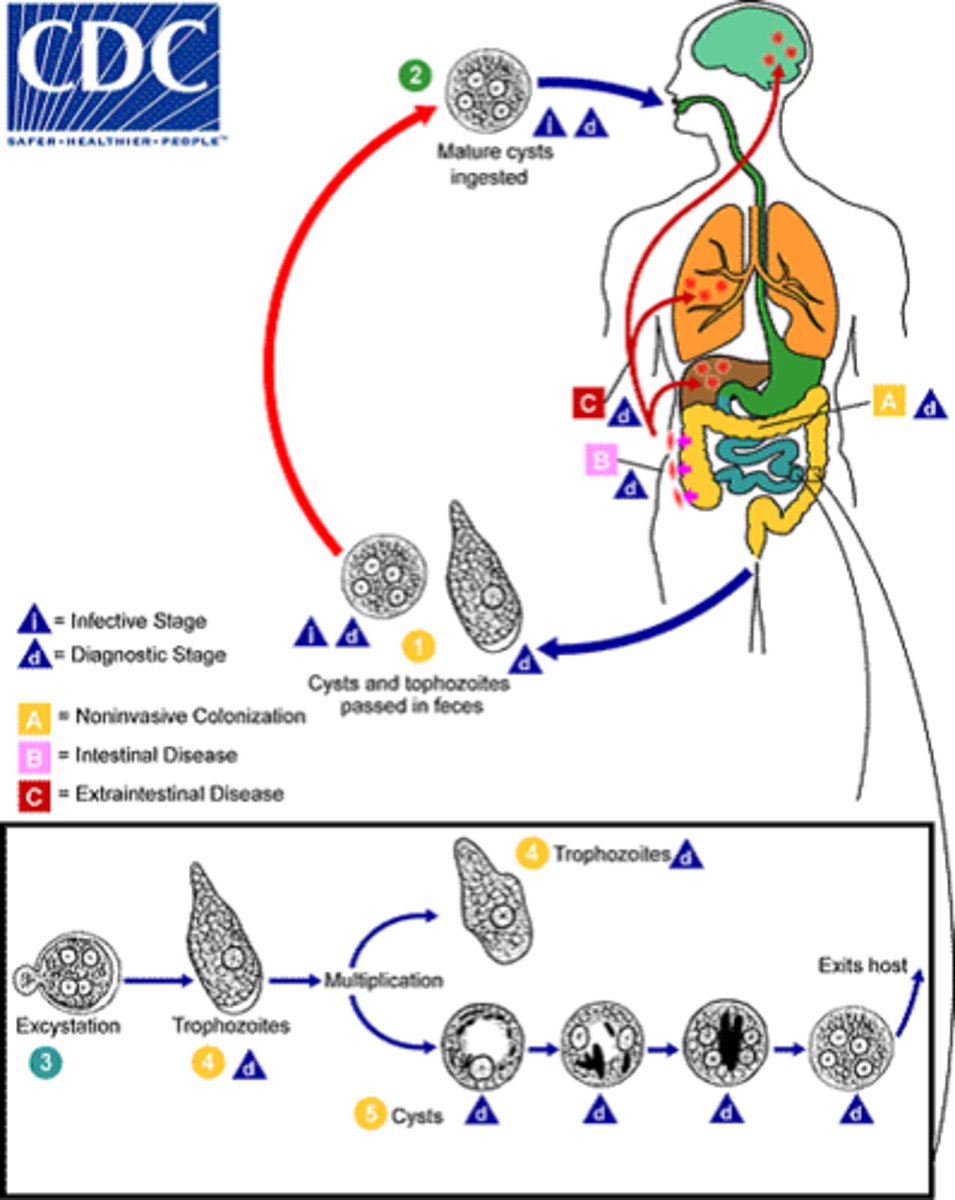
Entamoeba histolytica
disease -
symptoms -
geographic region -
transmission -
specimen -
pathogenic? -
Protozoa (Amoebae)
disease - amebic colitis, extra-intestinal infections, or asymptomatic
symptoms - mild diarrhea with periods of constipation, abdominal discomfort, abscesses in the liver or brain if serious
geographic region - worldwide
transmission - water contaminated with human feces (fecal-oral)
specimen - stool
pathogenic? - yes
Entamoeba coli
specimen -
pathogenic? -
Protozoa (Amoebae)
specimen - stool
pathogenic? - no
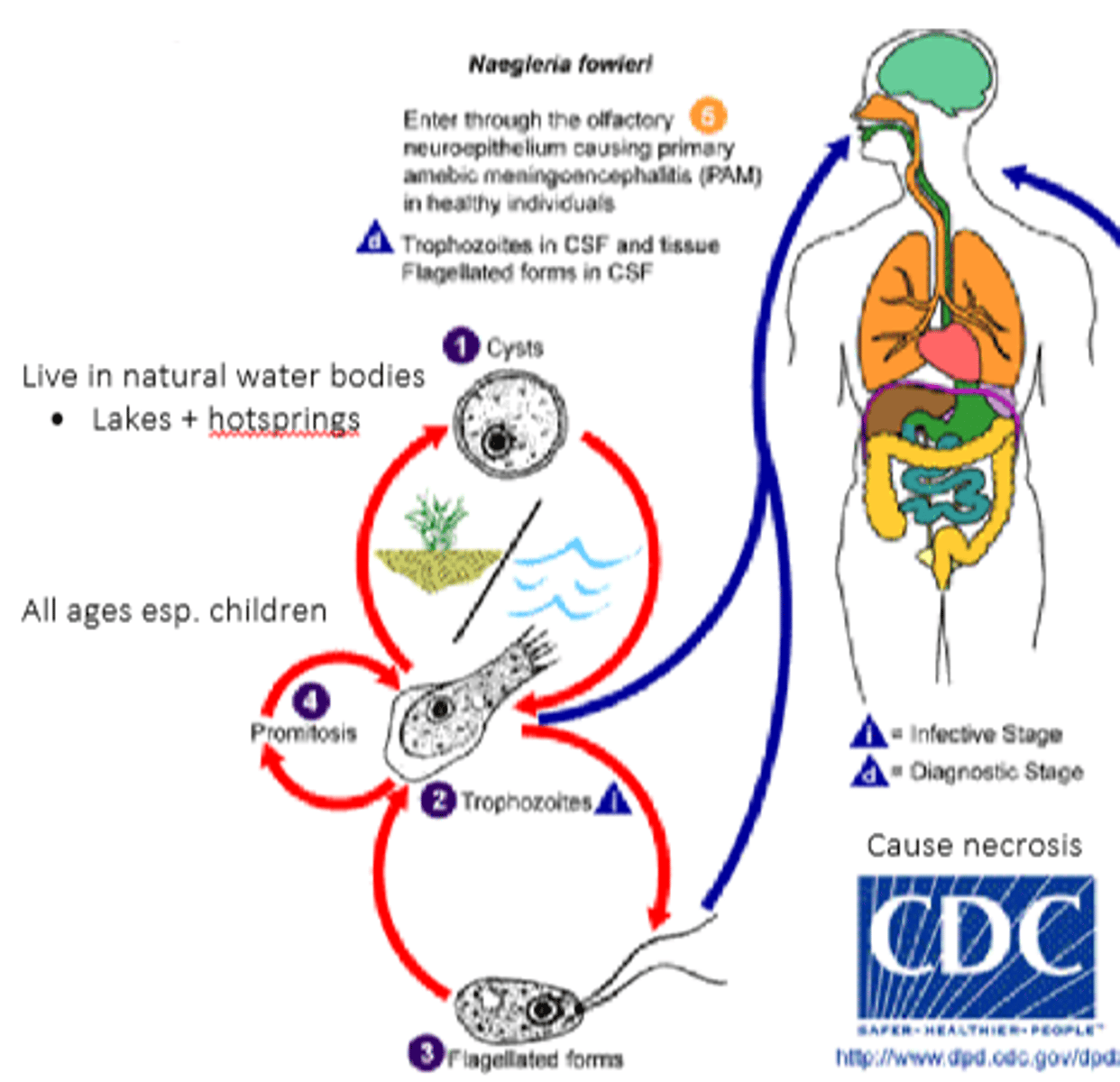
Naegleria fowleri
disease -
symptoms -
geographic region -
transmission -
specimen -
pathogenic? -
Protozoa (Amoebae)
disease - primary amoebic meningoencephalitis
symptoms - CNS infection --> headaches
geographic region - warm fresh water
transmission - force of contaminated water into the nasal cavity
specimen - CSF
pathogenic? - yes
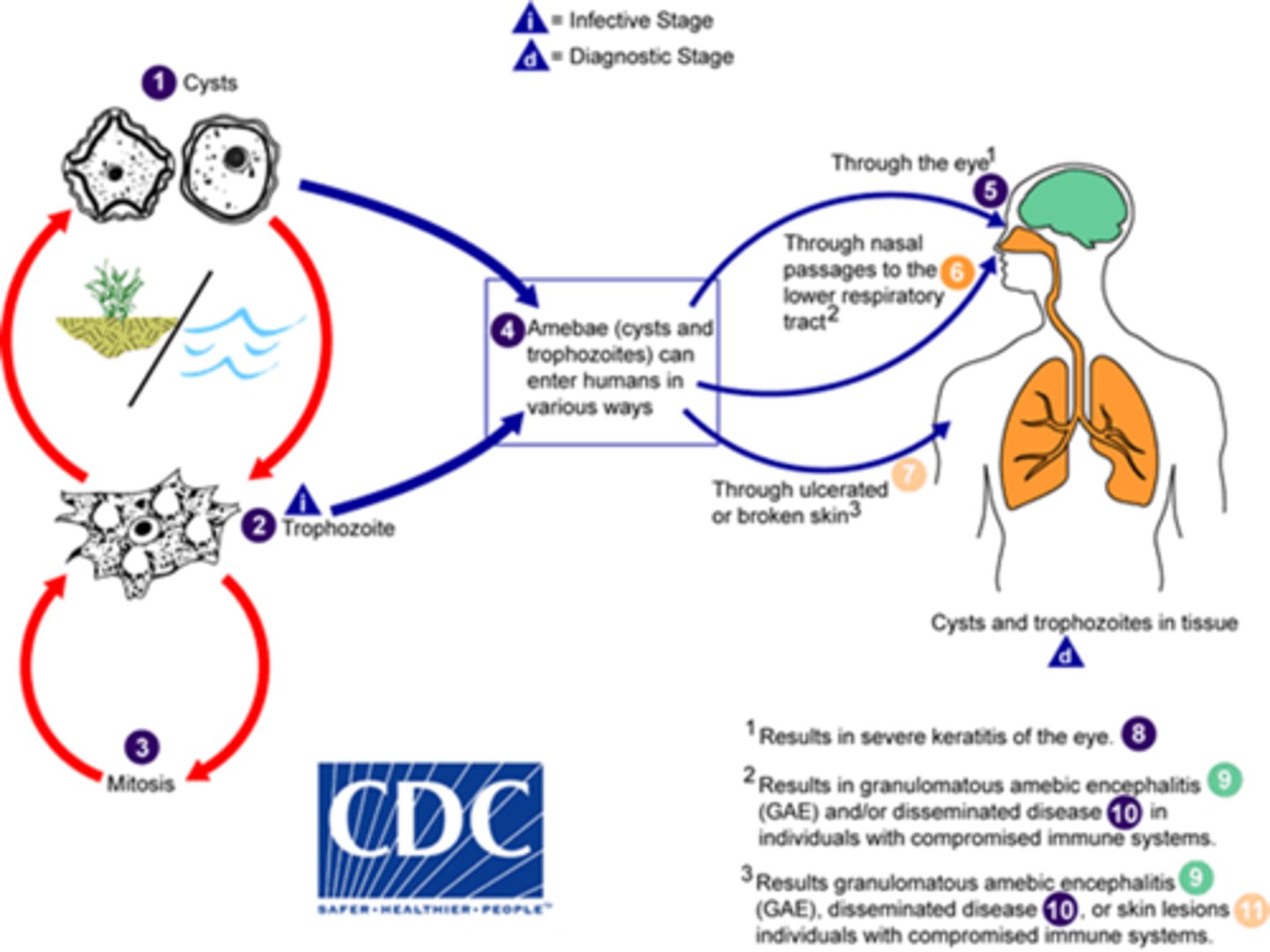
Acanthamoeba sp.
disease -
symptoms -
geographic region -
transmission -
specimen -
pathogenic? -
Protozoa (Amoebae)
disease - granulomatous amebic encephalitis (GAE), amebic keratitis, skin ulcers
symptoms - mental status changes, eye pain
geographic region - worldwide in water sources
specimen - biopsy, CSF
pathogenic? - yes
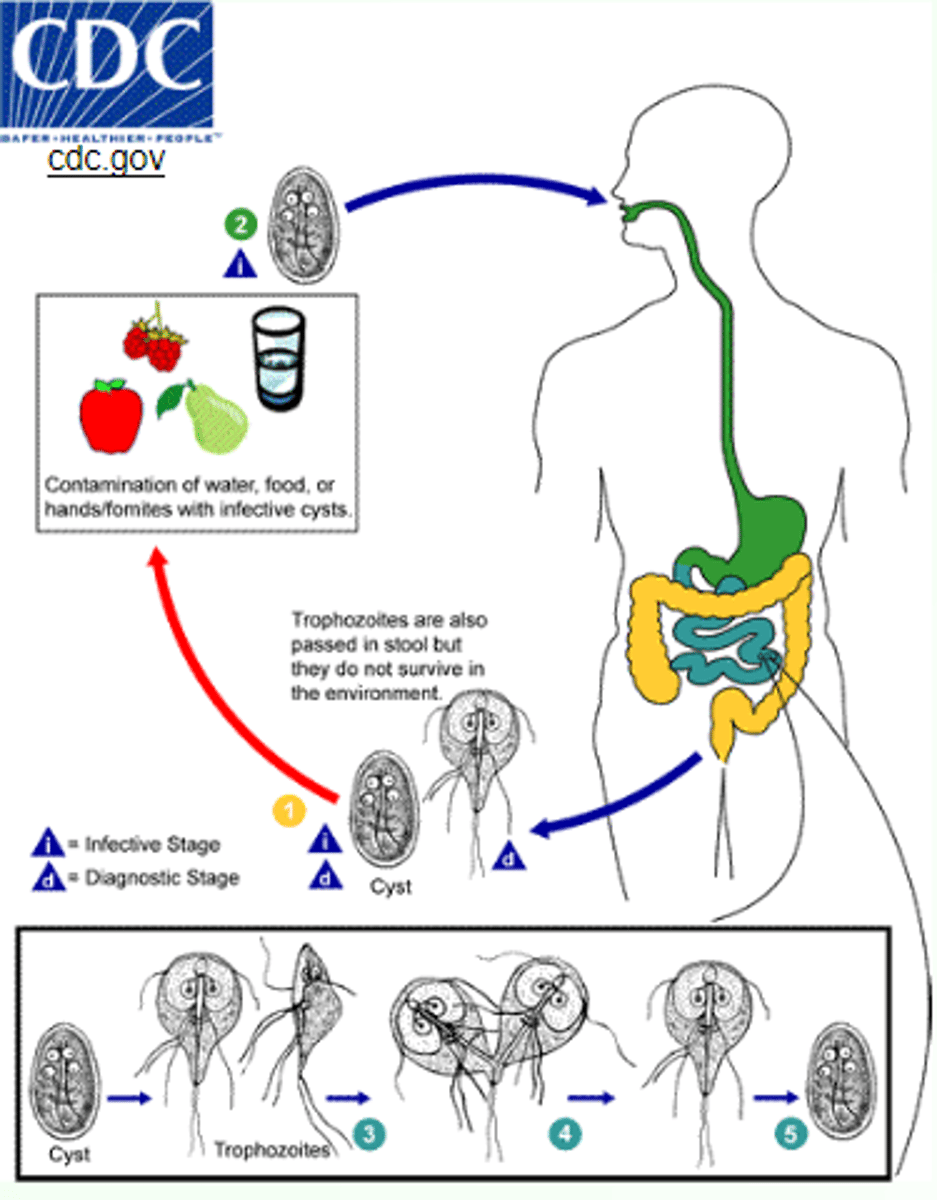
Giardia duodenalis
disease -
symptoms -
geographic region -
transmission -
specimen -
pathogenic? -
Protozoa (Flagellate)
disease - giardiasis
symptoms - diarrhea, abdominal cramps, nausea
geographic region - worldwide
transmission - ingestion of cysts by contaminated food/water, fecal-oral, sexual contact
specimen - stool
pathogenic? - yes
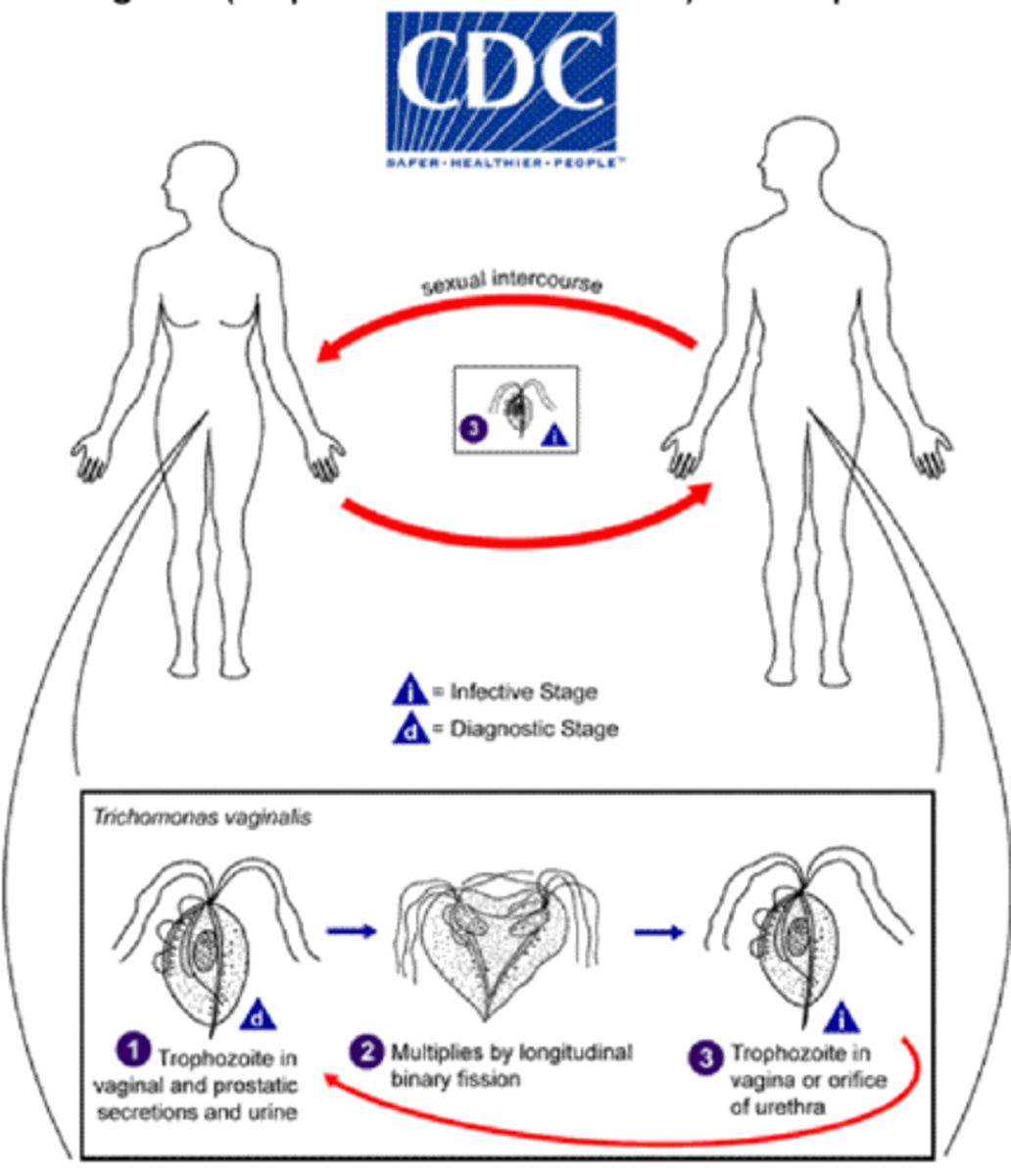
Trichomonas vaginalis
disease -
symptoms -
transmission -
specimen -
pathogenic? -
Protozoa (Flagellate)
disease - trichomoniasis
symptoms - vaginitis, uretrhitis
transmission - sexually transmitted
specimen - vaginal or urethral fluid, urine sediment
pathogenic? - yes
Trypanosomiasis cruzi
disease -
symptoms -
geographic region -
transmission -
specimen -
pathogenic? -
Protozoa (Flagellate)
disease - Chaga's disease
symptoms - painful red lesions caused by replication of amastigotes
geographic region - Central & South America
transmission - triatomine bug bite
specimen - blood
pathogenic? - yes
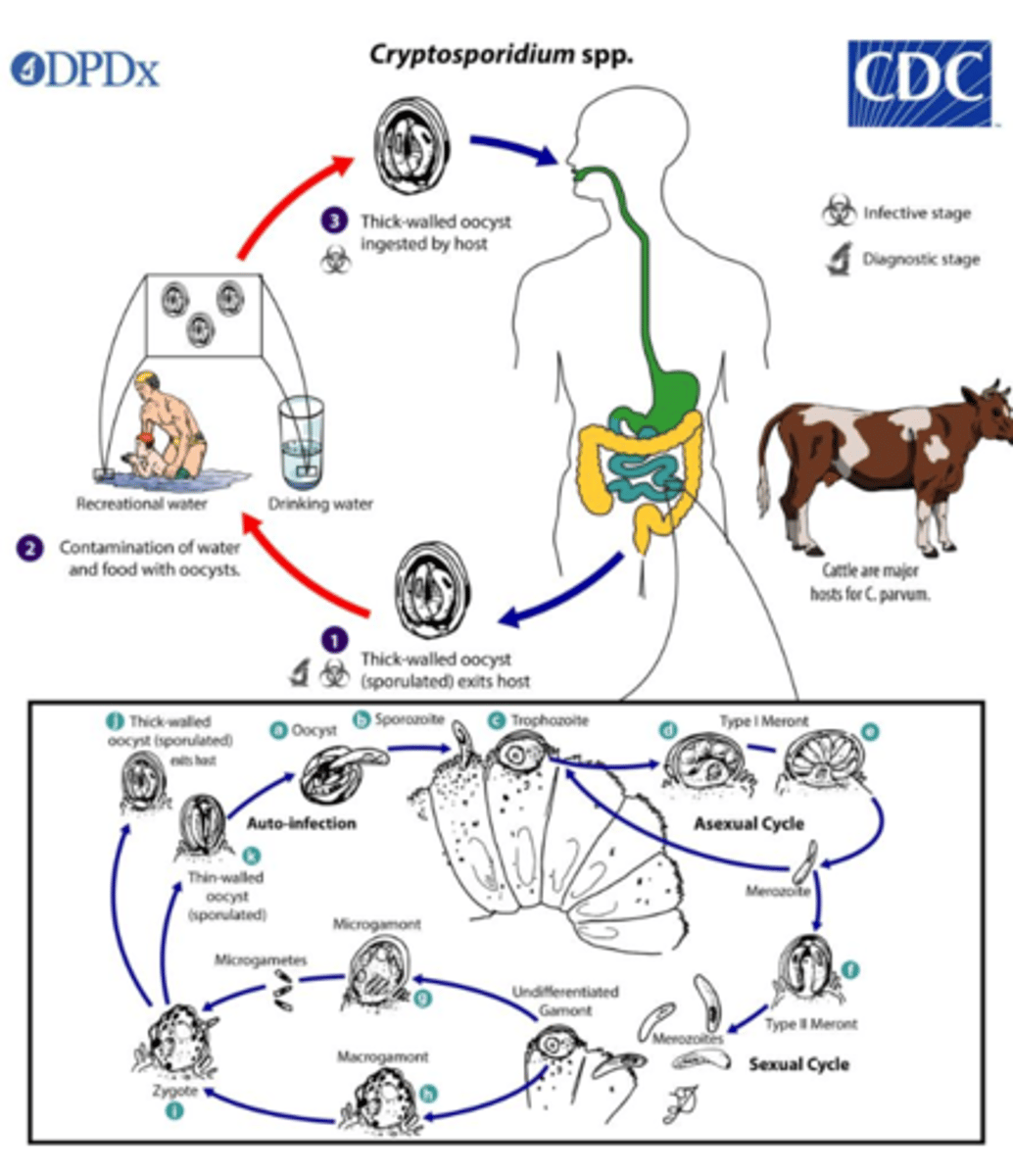
Cryptosporidium parvum
disease -
symptoms -
geographic region -
transmission -
specimen -
pathogenic? -
Protozoa (Apicomplexa)
disease - cryptosporidiosis
symptoms - healthy --> self-limiting diarrhea, immunocompromised --> malabsorption & wasting
geographic region - worldwide
transmission - ingestion of water with oocysts
specimen & identification - stool; acid-fast stain, EIA, fluorescent Ab stain
pathogenic? - yes
Cyclospora caytanesis
disease -
symptoms -
geographic region -
transmission -
specimen & identification -
pathogenic? -
Protozoa (Apicomplexia)
disease - cyclosporiasis
symptoms - persistant diarrhea, myalgia, fatigue, vomitting, malaise, abdominal cramps, bloating, flatus
geographic region - tropical and subtropical regions
transmission - ingestion of oocysts
specimen & identification - stool; autofluorescence on wet mount, acid-fast stain
pathogenic? - yes
Plasmodium vivax
disease -
symptoms -
geographic region -
transmission -
specimen & identification -
pathogenic? -
life cycle -
prevention -
Protozoa (Apicomplexia)
disease - malaria
symptoms - fever attacks every second day, anemia, splenomegaly
geographic region - central & south America, Africa, southern Europe/Asia
transmission - mosquito (vector)
specimen & identification - blood in EDTA; thin & thick smears
pathogenic? - yes
life cycle - different in humans than mosquito; in humans lifecycle occurs in liver and blood
prevention - chemoprophylaxis, insecticide tents, preventative treatment (pregnant women)
Plasmodium ovale
disease -
symptoms -
geographic region -
transmission -
specimen & identification -
pathogenic? -
life cycle -
prevention -
Protozoa (Apicomplexia)
disease - malaria
symptoms - fever attacks every second day, anemia, splenomegaly
geographic region - central & south America, Africa, southern Europe/Asia
transmission - mosquito (vector)
specimen & identification - blood in EDTA; thin & thick smears
pathogenic? - yes
life cycle - different in humans than mosquito; in humans lifecycle occurs in liver and blood
prevention - chemoprophylaxis, insecticide tents, preventative treatment (pregnant women)
Plasmodium malariae
disease -
symptoms -
geographic region -
transmission -
specimen & identification -
pathogenic? -
life cycle -
prevention -
Protozoa (Apicomplexia)
disease - malaria
symptoms - fever attacks every third day, anemia, splenomegaly
geographic region - central & south America, Africa, southern Europe/Asia
transmission - mosquito (vector)
specimen & identification - blood in EDTA; thin & thick smears
pathogenic? - yes
life cycle - different in humans than mosquito; in humans lifecycle occurs in liver and blood
prevention - chemoprophylaxis, insecticide tents, preventative treatment (pregnant women)
Plasmodium falciparum
disease -
symptoms -
geographic region -
transmission -
specimen & identification -
pathogenic? -
life cycle -
prevention -
Protozoa (Apicomplexia)
disease - malaria
symptoms - fever attacks every second day, anemia, splenomegaly
geographic region - Africa
transmission - mosquito (vector)
specimen & identification - blood in EDTA; thin & thick smears
pathogenic? - yes
life cycle - different in humans than mosquito; in humans lifecycle occurs in liver and blood
prevention - chemoprophylaxis, insecticide tents, preventative treatment (pregnant women)
Babesia sp.
disease -
symptoms -
geographic region -
transmission -
specimen & identification -
pathogenic? -
Protozoa (Acomplexia)
disease - babesiosis
symptoms - asymptomatic or flu-like, anemia
geographic region - North America
transmission - tick-borne
specimen & identification - blood; intracellular, ring-form
pathogenic? - yes
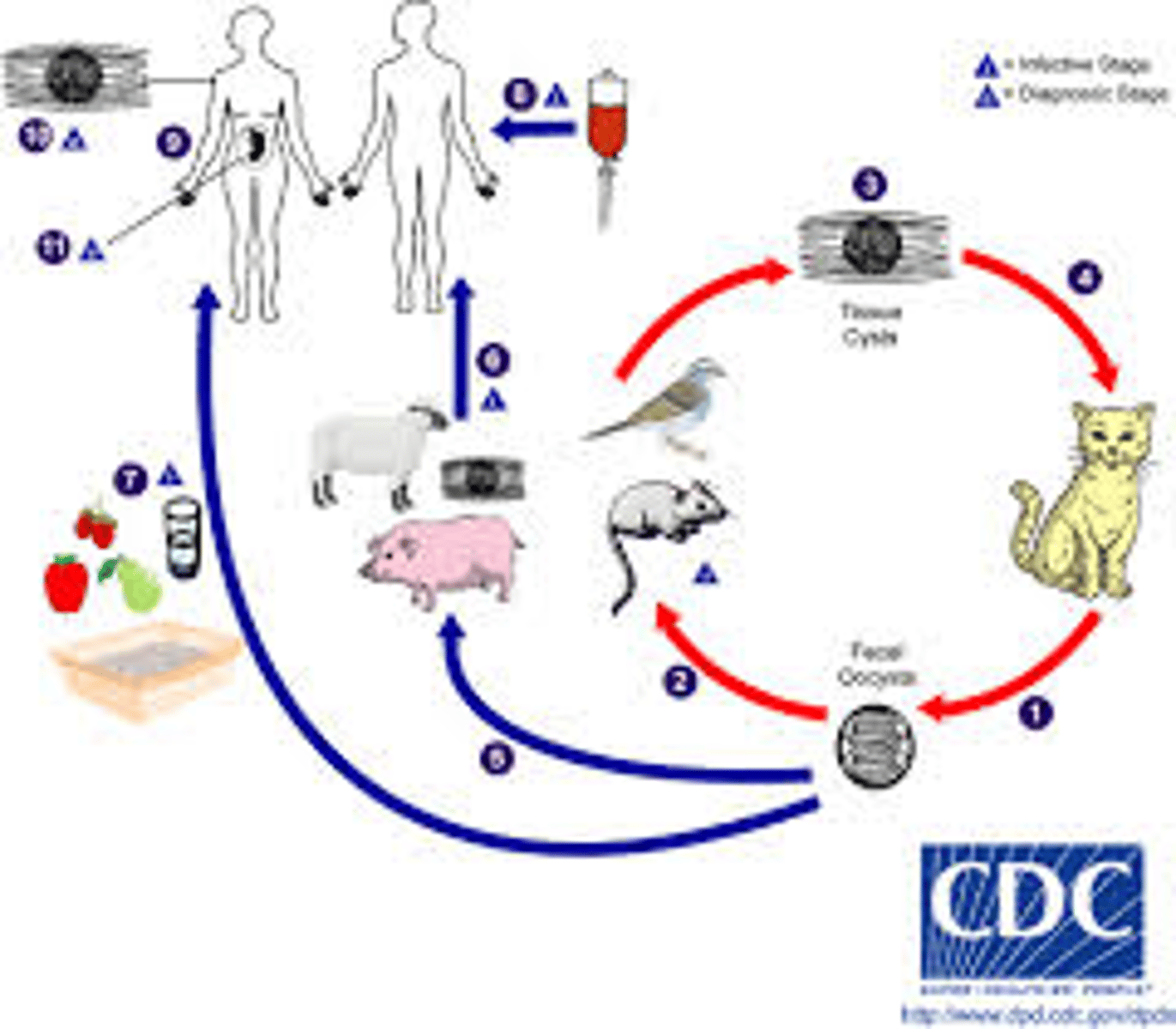
Toxoplasma gondii
disease -
symptoms -
geographic region -
transmission -
specimen & identification -
pathogenic? -
Protozoa (Acomplexia)
disease - toxoplasmosis
symptoms - mono-like in healthy but organ inflammation in immunocompromised
geographic region - worldwide
transmission - ingestion *worry about transmission to fetus
specimen & identification - test for IgG & IgM Ab, biopsy staining
pathogenic? - yes
Enterobius vermicularis (pinworm)
symptoms -
transmission -
specimen & identification -
lifecycle -
pathogenic? -
Helminth (Nematode)
symptoms - intense itching
transmission - fecal-oral
specimen & identification - tape prep/pinworm paddle
lifecycle - female migrated from intestines to perianal folds and deposits eggs at night
pathogenic? - yes
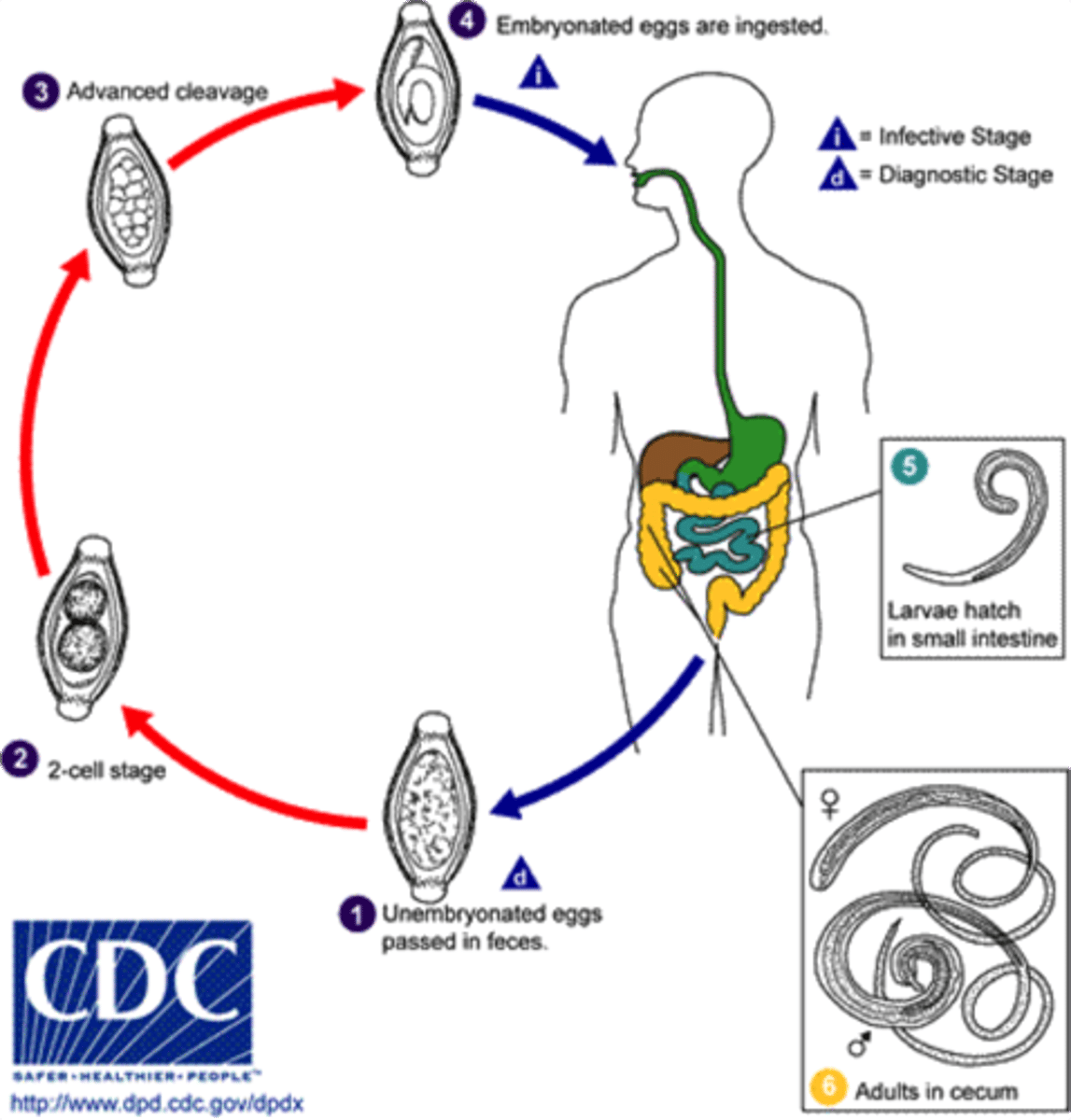
Trichuris trichiura (whipworm)
disease -
symptoms -
geographic region -
transmission -
specimen & identification -
pathogenic? -
Helminth (Nematode)
disease - trichuriasis
symptoms - mostly asymptomatic, but if heavy worm burden --> other serious symptoms
geographic region - worldwide
transmission - soil, fecal-oral
specimen & identification - microscopic examination of stool
pathogenic? - yes
Strongyloides stercoralis (threadworm)
disease -
symptoms -
geographic region -
transmission -
specimen & identification -
pathogenic? -
Helminth (Nematode)
disease - gut or lung infection
symptoms - mostly asymptomatic, but sometimes red rash at original site or disseminated
geographic region - worldwide
transmission - soil transmitted, penetration of skin
specimen & identification - microscopic examination of sputum & stool
pathogenic? - yes
Trichinella spiralis
disease -
symptoms -
transmission -
specimen & identification -
pathogenic? -
Helminth (Nematode)
disease - trichinosis or trichinellosis
symptoms - may be asymptomatic or GI or muscle encystment
transmission - ingestion of meat with encysted larvae
specimen & identification - ELISA, muscle biopsies, eosiniphilia
pathogenic? - yes
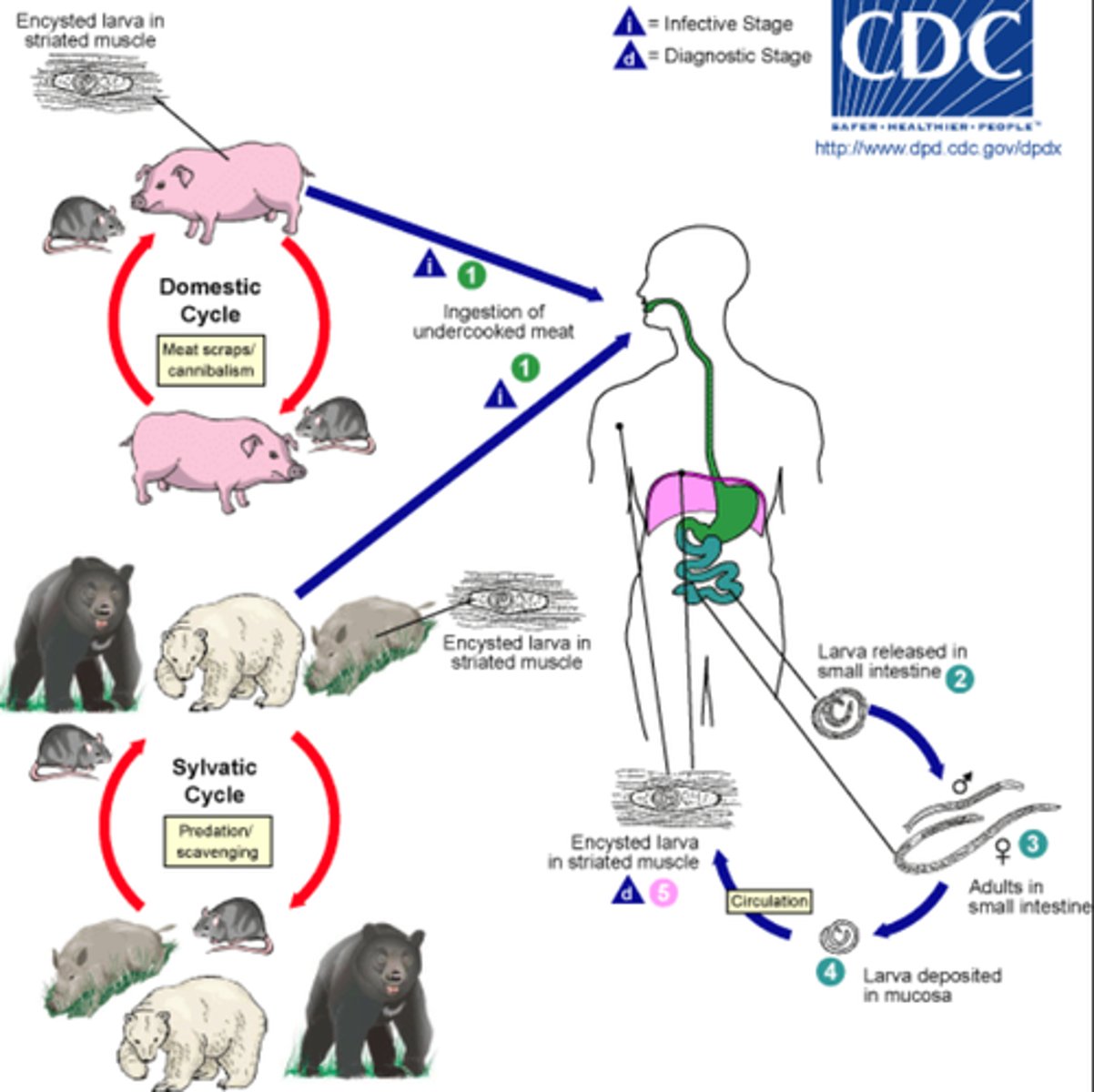
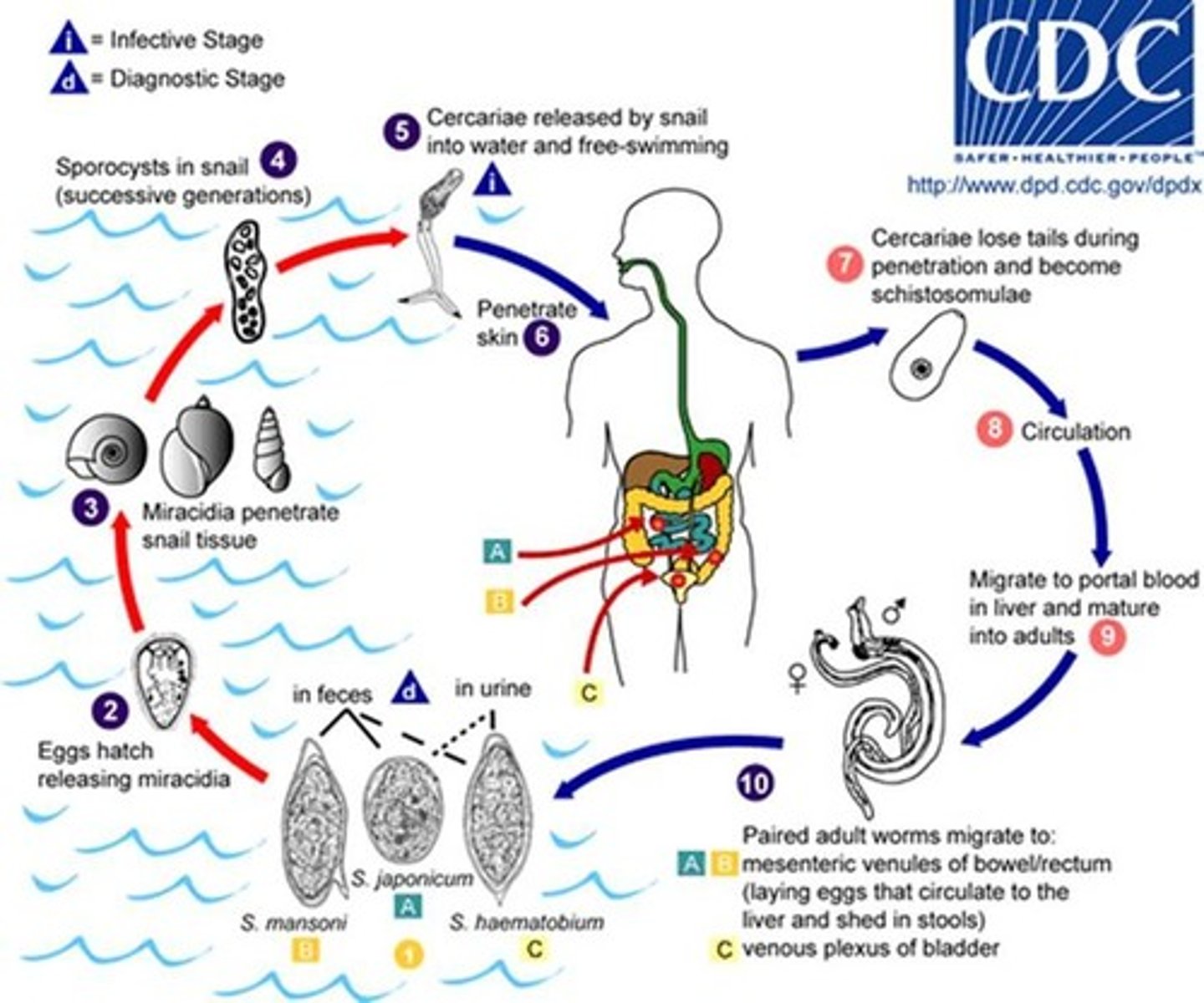
Schistosoma haematobium
disease -
symptoms -
geographic region -
transmission -
specimen & identification -
pathogenic? -
Helminth (Trematode)
disease - bladder fluke
symptoms - hematuria, anemia, bladder fibrosis, associated with bladder cancer
geographic region - freshwater of southern Africa, Egypt, and middle east
transmission - penetration of skin by free-living cercariae
specimen & identification - urine; EIA or microscopic examination
pathogenic? - yes
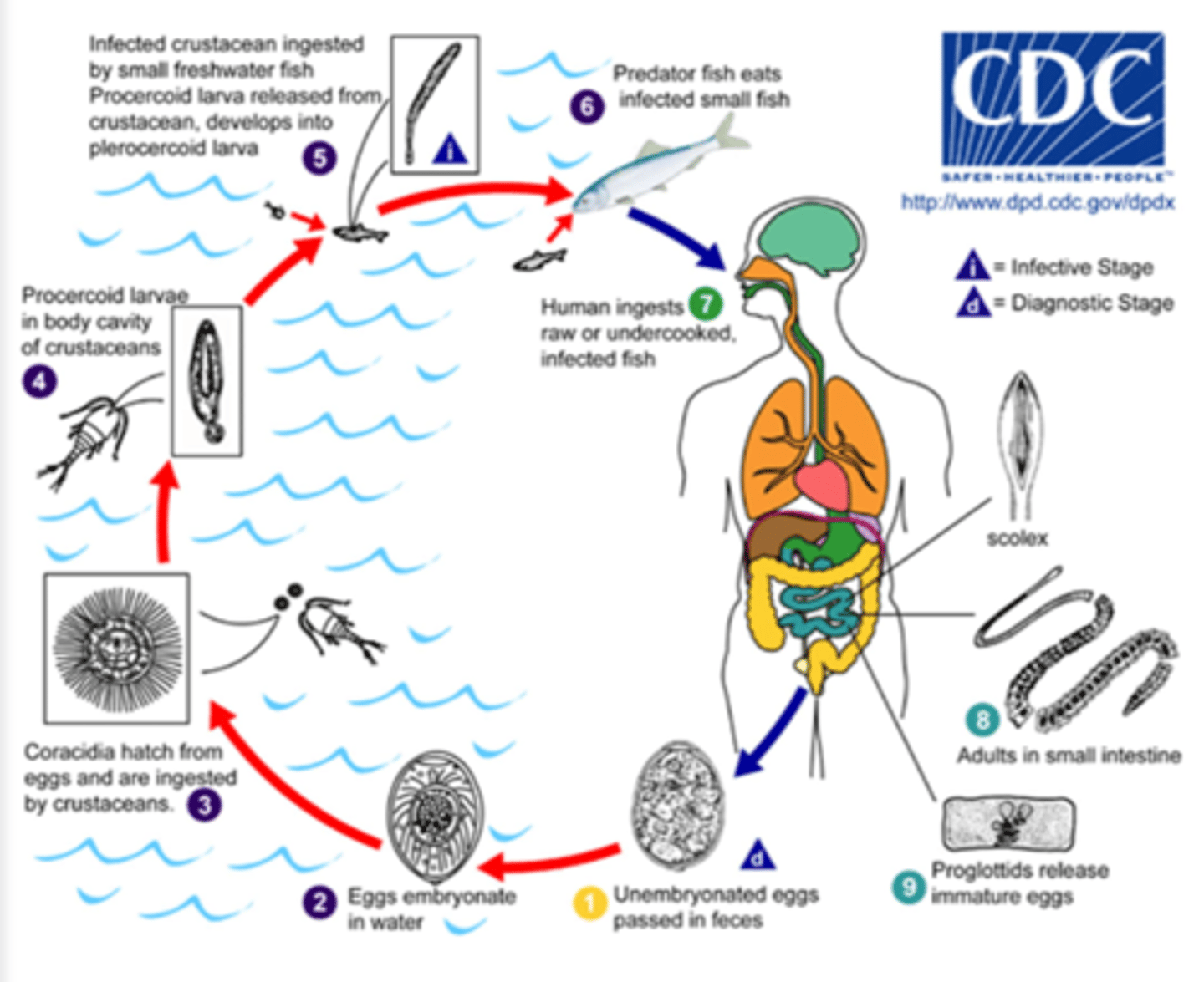
Diphyllobothrium latum
disease -
symptoms -
geographic region -
transmission -
specimen & identification -
pathogenic? -
Helminth (Cestode)
disease - intestinal infection
symptoms - asymptomatic, abdominal pain, weight loss, vitamin B12 deficiency
geographic region - parts of U.S., Scandinavia, Latin America, Asia, Africa
transmission - larva ingested in uncooked/undercooked fish
specimen & identification - microscopic examination of stool
pathogenic? - yes
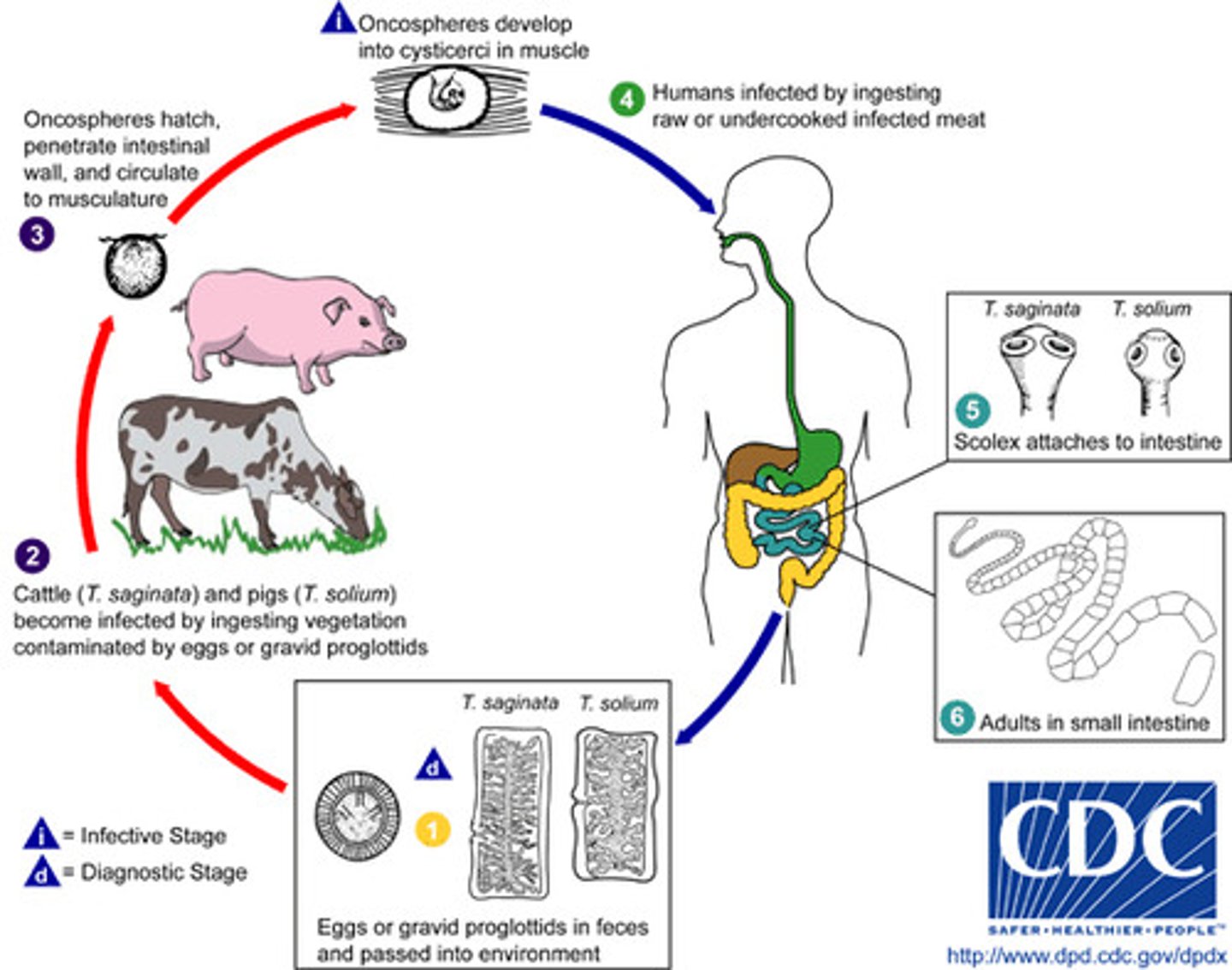
Taenia saginata
disease -
symptoms -
transmission -
specimen & identification -
pathogenic? -
Helminth (Cestode)
disease - Taeniasis
symptoms - asymptomatic, mild GI
transmission - ingestion of cysticercus larvae in undercooked beef
specimen & identification - microscopic examination of stool
pathogenic? - no
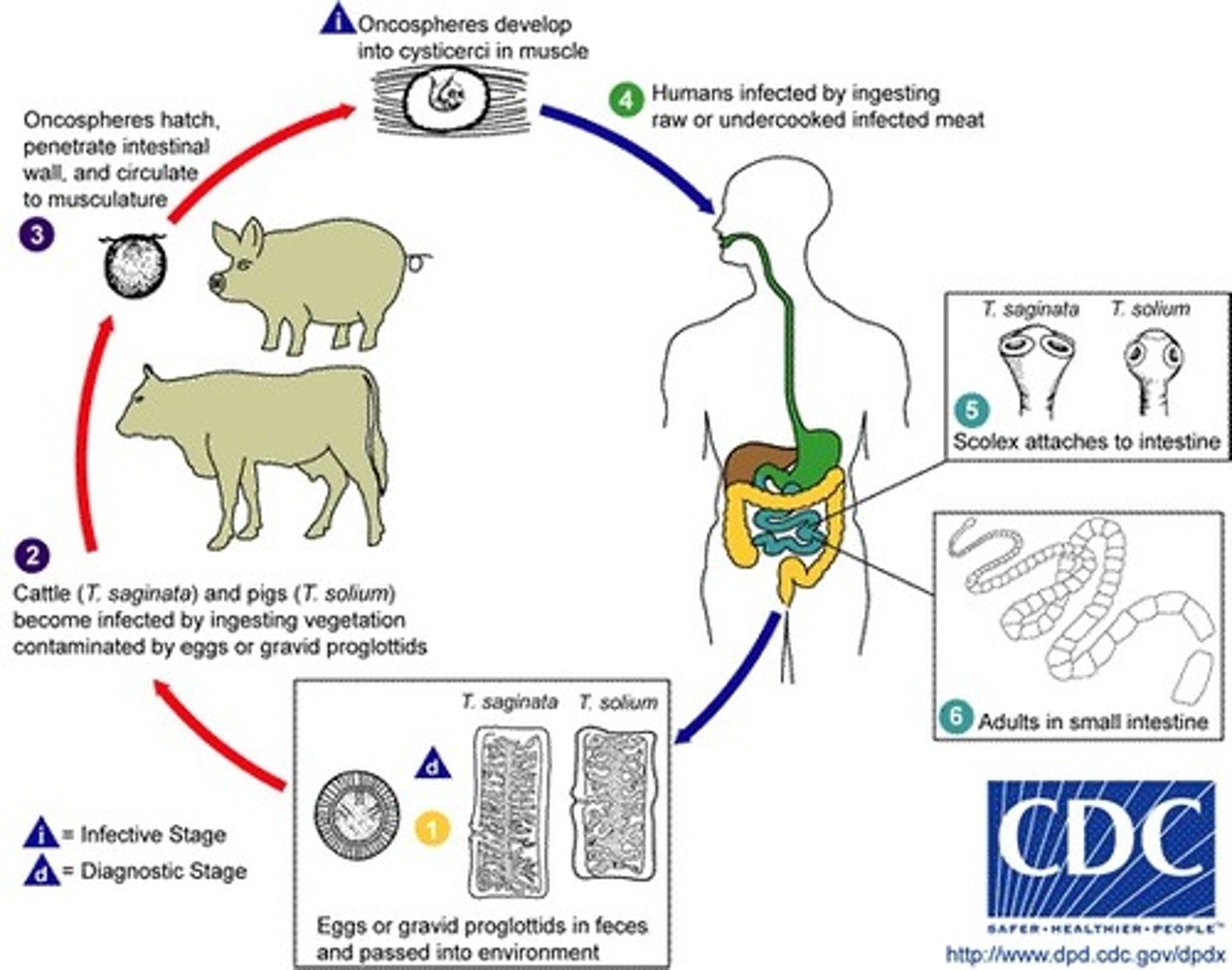
Taenia solium
disease -
symptoms -
transmission -
specimen & identification -
pathogenic? -
Helminth (Cestode)
disease - cysticercosis
symptoms - infection of other organs with cysticercus
transmission - ingestion of cysticercus larvae in undercooked pork
specimen & identification - microscopic examination of stool, immunoassay
pathogenic? - yes
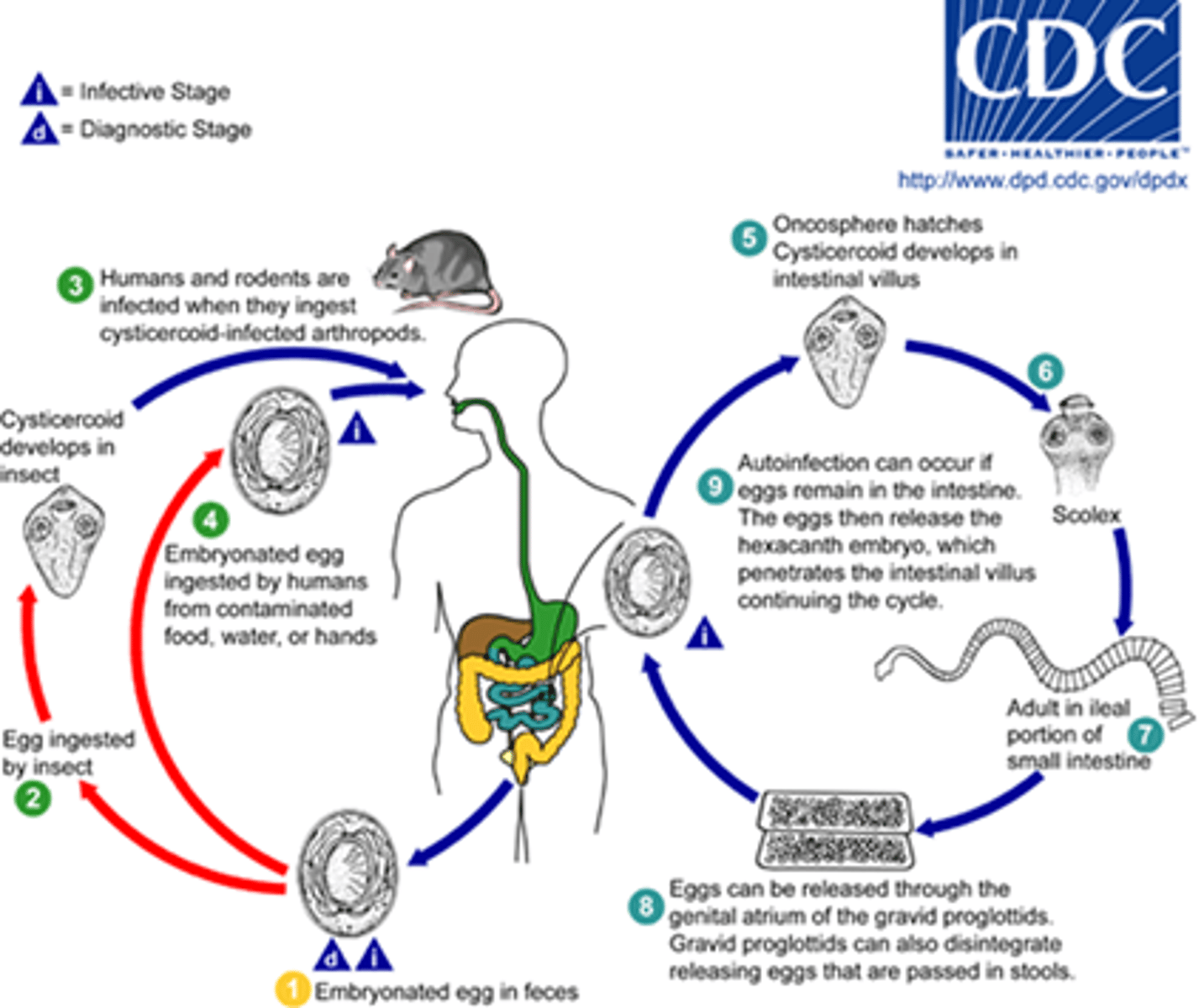
Hymenolepsis nana
symptoms -
geographic region -
transmission -
specimen & identification -
pathogenic? -
Helminth (Cestode)
symptoms - asymptomatic or symptoms if heavy word burden
geographic region - most common tapeworm in U.S., but found globally
transmission - ingestion of embryonated egg or arthropod with cysticercoid larva
specimen & identification - microscopic examination of stool
pathogenic? - yes
Dipylidium caninum
disease -
symptoms -
transmission -
specimen & identification -
pathogenic? -
Helminth (Cestode)
disease - intestinal infection
symptoms - asymptomatic or mild symptoms
transmission - contact with dog and cat tapeworm
specimen & identification - microscopic examination of stool
pathogenic? - yes
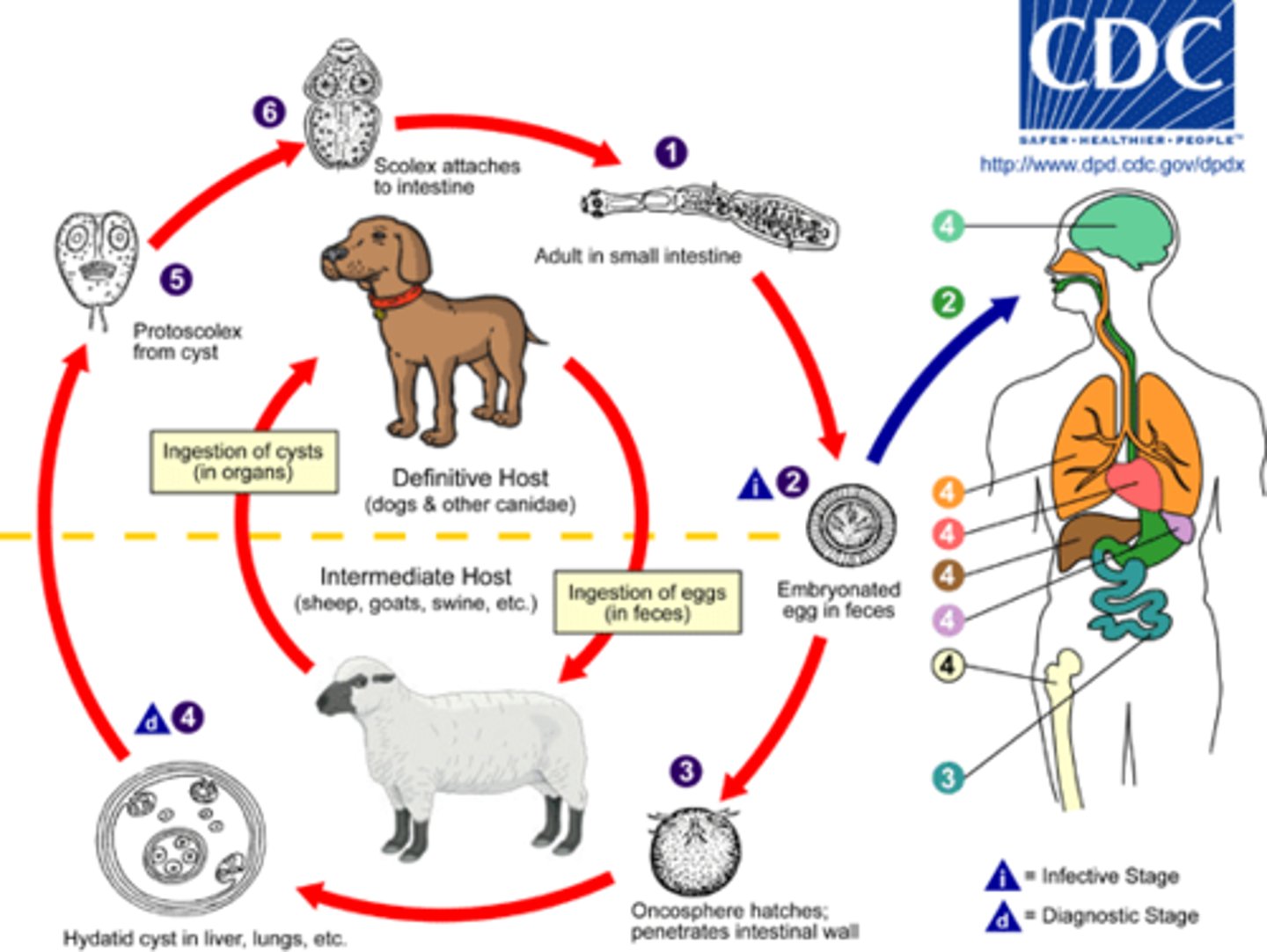
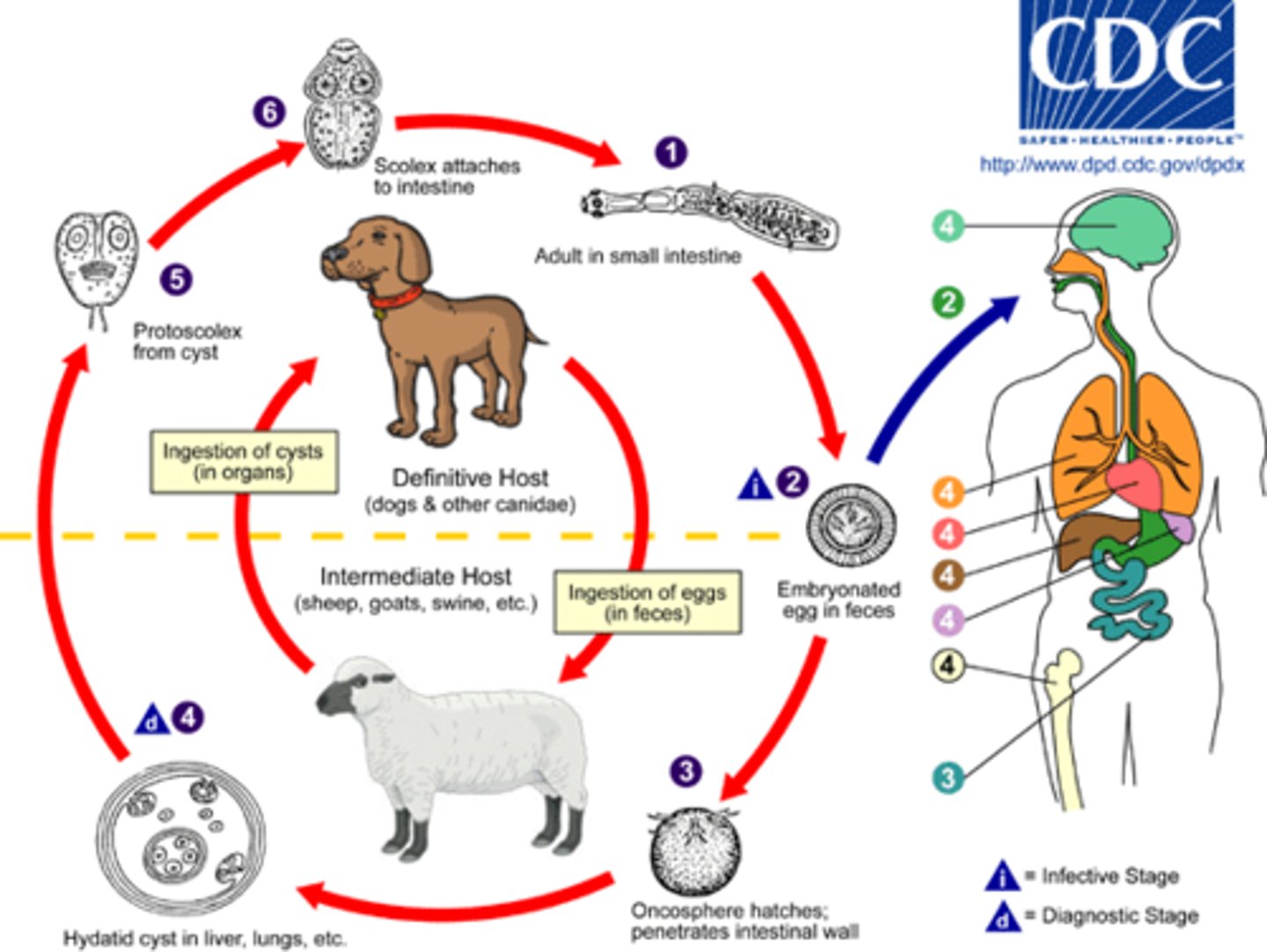
Echinococcus granulosus
disease -
symptoms -
geographic region -
transmission -
specimen & identification -
pathogenic? -
Helminth (Cestode)
disease - intestinal infection
symptoms - hydatid cysts
geographic region - worldwide
transmission - ingestion of eggs
specimen & identification - radiologic imaging, serology
pathogenic? - yes
Echinococcus multilocularis
disease -
symptoms -
geographic region -
transmission -
pathogenic? -
Helminth (Cestode)
disease - alveolar echinococcosis
symptoms - hydatid cysts
geographic region - Eurasia & North America
transmission - ingestion of eggs
pathogenic? - yes
Ixodes scapularis
diseases transmitted -
geographical region -
visual identification -
Ectoparasite (tick)
diseases transmitted - babesiosis, erlichiosis, relapsing fever borreliosis, lyme disease, anaplasmosis, powassan virus disease (B.E.R.L.A.P.)
geographical region - Eastern US
visual identification - mouthparts longer than basis capituli, inornate, no festoons, no eyes, anterior anal groove
Amblyoma americanum
diseases transmitted -
geographical region -
visual identification -
Ectoparasite (tick)
diseases transmitted - heartland, erlichiosis, Tularemia, southern tick rash illness (H.Er.T.S.)
geographical region - Southeastern US
visual identification - mouthparts longer than basis capituli, ornate, eyes, festoons, white spot (lonestar), posterior anal groove
Pediculus humanis (subspecies: capitis & corporis)
diseases transmitted -
visual identification -
Ectoparasite (lyse)
diseases transmitted - only by corporis --> endemic typhus, trench fever, louse-borne relapsing fever
visual identification - louse body longer than wide, nit (egg) is flattened operculum
Pediculus pubis (pubic lyse)
transmission -
visual identification -
Ectoparasite (lyse)
transmission - sec
visual identification - body wide as it is long, nit (egg) is raised and conical operculum
Sarcoptes scabiei
diseases transmitted -
geographical region -
visual identification -
transmission -
Ectoparasite (scabies)
diseases transmitted - human scabies (human itch mite)
geographical region - worldwide
visual identification - roundish mite with 4 pairs of legs, oval-shaped egg
transmission - direct, prolonged, skin to skin contact
Viral structure (4)
- viral genomes (DNA or RNA) in a protein coat known as a capsid
- genome + capside = nucleocapsid
- entire virus = virion
- sometimes an envelope
Explain host cell tropism
Viruses show host specificity because the viral anti-receptor only binds to certain host cell receptors
What is viral neutralization by antibodies
Patient antibodies prevent cell culture identification
Viral Classification System
- DNA
- DS, linear or circular
- SS, linear or circular
- RNA
- DS, linear
- SS, linear --> positive (mRNA), negative, ambisense (circular), segmented
What is the role of mRNA in viral replication
All types of nucleic acids get transcribed into mRNA and translated into proteins
First step of viral replication
attachment
- virus attaches to the target cell by receptors (tropism)
- anti-receptors on virus + host cell receptors
Second step of viral replication
Entry/penetration
- naked virions directly penetrate the membrane
- enveloped virions enter by endocytosis
- once into the cell the virions lose their protein coat releasing the genome (RNA-->cytoplasm, DNA-->nucleus)
Third step of viral replication
replication & translation (biosynthesis)
- viral genome directs host cell to make viral proteins and replicate the genome
*host cell metabolism may stop
Fourth step of viral replication
Assembly of viral particles
- capsid protein subunits form capsomers
- capsomers combine to form capsid
- capsid and genome combine to form nucleocapsid
Fifth step of viral replication
Release
- naked viruses release by lysis (kills host cell)
- enveloped viruses release by budding
Why are RNA viruses more prone to rapid mutation than DNA viruses
Because RNA polymerase does not have an exonuclease proofreading function
Basis of viral culture & identification
- grow virus in culture cells
- detect by: cytopathic effect, hemadsorption, immunostaining, neutralization
Basis of Ag detection by EIA & immunofluorescence
- identifies viral Ags to identify and classify viruses
Basis of PCR and RT PCR
- rapid, high volume, specific
- non-culturable viruses
- quantitative can be used to monitor therapy effectiveness
What cell culture can enteroviruses grow in?
PMK, HDF
What cell culture can influenza grow in?
PMK, HDF
What cell culture can adenovirus grow in?
PMK, HDF, HeP-2, A549
What cell culture can HSV grow in?
PMK, HDF, HeP-2, A549
What cell culture can SARS-CoV-2 grow in?
VERO
Rotavirus
genome type -
disease -
transmission -
diagnostic test -
genome type - segmented dsRNA
disease - viral gastroenteritis in infants and children
transmission - fecal-oral
diagnostic test - EIA for Ag detection, RT PCR
Norovirus
genome type -
disease -
transmission -
diagnostic test -
genome type - ssRNA
disease - viral gastroenteritis "stomach flu"
transmission - fecal-oral --> very low infectious dose
diagnostic test - PCR, EIA but low sensitivity
Poliovirus
genome type -
disease -
transmission -
genome type - ssRNA
disease - asymptomatic or mild flu-like, paralytic polio
transmission - fecal-oral
Hepatitis A
genome type -
disease -
transmission -
diagnostic test -
genome type - ssRNA
disease - acute flu-like symptoms and jaundice
transmission - fecal-oral
diagnostic test - IgM detection, nucleic acid testing
Hepatitis C
genome type -
disease -
transmission -
diagnostic test -
genome type - ssRNA
disease - acute asymptomatic and self-limiting, or chronic leading to liver cirrhosis
transmission - blood borne --> IV-drug use, mom to child
diagnostic test - ELISA for HCV Ab, qualitative & quantitative HCV RNA, HCV genotyping
What are the steps of viral replication that are targeted by anti-virals? (3)
- protein coat release
- replication & translation
- release of virus from infected cells
Rubella
genome type -
disease/symptoms -
transmission -
diagnostic testing -
genome type - ssRNA, enveloped
disease/symptoms - German measles --> rash, lymphadenopathy, mild fever
Congenital --> development impairment
transmission - respiratory / placental
diagnostic testing - viral culture preferred, IgM 4x rise in titer
Measles
genome type -
disease/symptoms -
transmission -
diagnostic testing -
genome type - ssRNA enveloped
disease/symptoms - fever, cough, rash, Koplick's spots, SSPE (encephalitis)
transmission - respiratory aerosol
diagnostic testing - IgM, PCR, viral culture
Rabies
genome type -
disease/symptoms -
transmission -
diagnostic testing -
genome type - ssRNA enveloped (bullet shaped)
disease/symptoms - flu-like, CNS
transmission - zoonotic by bite injecting saliva, travels via peripheral nerves to CNS
diagnostic testing - saliva: RT PCR, serum & CSF: Ab tests, skin biopsy & brain tissue: DFA
hCoVs
genome type -
disease/symptoms -
transmission -
diagnostic testing -
genome type - ssRNA, enveloped
disease/symptoms - mild coldlike, GI tract
transmission - airborne
diagnostic testing - multiplex molecular panels
MERS-CoV
genome type -
disease/symptoms -
transmission -
diagnostic testing -
genome type - ssRNA, enveloped
disease/symptoms - respiratory, GI, kidney failure
transmission - zoonotic (camels), airborne
diagnostic testing - molecular testing
SARS-CoV
genome type -
disease/symptoms -
transmission -
diagnostic testing -
genome type - ssRNA, enveloped
disease/symptoms - high fever, respiratory
transmission - zoonotic, airborne
diagnostic testing - no longer circulatin
SARS-CoV2
genome type -
disease/symptoms -
transmission -
diagnostic testing -
genome type - ssRNA, enveloped
disease/symptoms - mild to severe
transmission - zoonotic, droplet/airborne
diagnostic testing - rapid Ag test, multiplex molecular panels, culture, swabs
influenza A/B
genome type -
disease/symptoms -
transmission -
diagnostic testing -
genome type - ssRNA segmented, enveloped
disease/symptoms - flu-like
transmission - droplet
diagnostic testing - rapid Ag tests, PCR, culture
HIV
genome type -
disease/symptoms -
transmission -
diagnostic testing -
genome type - retrovirus (enveloped ssRNA)
disease/symptoms - CD4+ cells are targeted; acute --> chronic --> AIDS
transmission - blood, body fluids
diagnostic testing - screening (Ab detection), combo immunoassay (HIV 1/2 Ab & p24 Ag), Ab differential assay, HIV 1 RNA assay
Herpes Simplex Virus 1 & 2 (HSV)
genome type -
disease/symptoms -
transmission -
diagnostic testing -
genome type - dsDNA
disease/symptoms - oral & congenital herpes --> recurrent disease, neonatal herpes, ocular herpes, HSV encephalitis
transmission - direct contact with virus secretions
diagnostic testing - viral culture (fast), DFA typing, serology, PCR
Varicella Zoster Virus (VZV)
genome type -
disease/symptoms -
transmission -
diagnostic testing -
genome type - dsDNA
disease/symptoms - chicken pox & shingles
transmission - contact with fluid from skin vesicles or through aerosols
diagnostic testing - clinical findings, viral culture, DFAs, PCR
Epstein-Barr Virus
genome type -
disease/symptoms -
transmission -
diagnostic testing -
genome type - dsDNA
disease/symptoms - mononucleosis
transmission - contact with saliva
diagnostic testing - monospot test (heterophile antibodies), VCA antibodies, early Ag antibodies, EBV nuclear Ag antibodies
Antibodies found in an individual susceptible to mono
Anti-EA - negative
Anti-VCA IgM - negative
Anti-VCA IgG - negative
Anti-NA IgG - negative
Antibodies found in a individual with a primary mono infection?
Anti-EA - positive
Anti-VCA IgM - positive
Anti-VCA IgG - positive
Anti-NA IgG - negative
Antibodies found in a individual who was previously infected with mono?
Anti-EA - negative
Anti-VCA IgM - negative
Anti-VCA IgG - positive
Anti-NA IgG - positive
Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
genome type -
disease/symptoms -
transmission -
diagnostic testing -
genome type - dsDNA
disease/symptoms -
HEALTHY --> asymptomatic, goes latent, rarely reactivated
IMMUNOCOMPROMISED --> high risk for CMV disease
transmission - vertical or horizontal, contact with someone shedding the virus, contact with body fluids, blood transfusion or transplant
diagnostic testing - culture (slow growth), pp65 antigen detection, PCR
Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
genome type -
disease/symptoms -
transmission -
diagnostic testing -
genome type - dsDNA
disease/symptoms - cervical cancer from high-risk strains and variety of warts from low-risk strains
transmission - sexual contact
diagnostic testing - NAT test for detection of HPV, partial and extended genotyping for strain differentiation
Hepatitis B Virus (HBV)
genome type -
disease/symptoms -
transmission -
diagnostic testing -
genome type - partially circular dsDNA
disease/symptoms - Acute & Chronic hepatitis
transmission - bloodborne
diagnostic testing - serology --> identification of antigens and antibodies in serum
What is found in an individual's serum who is susceptible to HBV?
Nothing!
What is found in an individual's serum who is immune from infection of HBV?
Anti-HBs
Anti-HBc IgG
What is found in an individual's serum who is immune from vaccination of HBV?
Anti-HBs
What is found in an individual's serum who has an acute infection with HBV?
HBsAg
HBeAg
Anti-HBc IgM
What is found in an individual's serum who has a chronic infection with HBV?
HBsAg
HBeAg
Anti-HBe
Anti-HBc IgG
Parvovirus B19
genome type -
disease/symptoms -
transmission -
diagnostic testing -
genome type - ssDNA
disease/symptoms - Parvovirus B19 also known as Fifth disease which has a characteristic symptom of a "slapped-cheek" appearance
transmission - respiratory droplets, blood or blood products, vertical
diagnostic testing - serology, PCR