Histology- animal anatomy
1/182
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
183 Terms
What are the 7 levels of organization?
chemicals, cells organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms
What is the smallest level of an organization is considered a living thing?
The cellular level
What are the 4 properties of the tissue level?
Group of specialized cells, they arise from a common ancestor, they perform special functions, and sometimes have substances surrounding the cell
what is made of two or more different tissues with specific functions
Organs
What is cell division
The process where the cells reproduce and it has nuclear division and cytoplasmic division
what is included in the nuclear division
Mitosis and meiosis
what is in cytoplasmic division
cytokinesis
what is somatic cell division
Cell division that results in an increase in body cells and involves mitosis and cytokinesis
What is reproductive cell division
cell division that results in the production of sex cell and consists of meiosis and cytokinesis
what are homologous chromosomes
two chromosomes that make up a chromosome pair
what is a cell with a full set of chromosomes called
a diploid cell
What is a cell with only one chromosome from each pair called
a haploid cell
How many chromosome and chromosome pairs does cattle have
60; 30
How many chromosome and chromosome pairs does a horse have
64; 32
How many chromosome and chromosome pairs does a dog have
78; 39
How many chromosome and chromosome pairs does a cat have
38; 19
How many chromosome and chromosome pairs does a human have
46; 23
what is the cell cycle
an orderly sequence of events by which a cell duplicates its contents and divides in two.
what does the cell cycle consist of
Interphase and the mitotic phase
What does mitosis phase consist of
Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase
what are the 3 parts of interphase
G1, S, and G2
What is G1 phase of mitosis
where the cytoplasmic increase
What happens in the S phase of mitosis
the replication of chromosomes
What is the G2 phase of mitosis
where cytoplasmic growth increases
what are two routine stains
Hematoxylin and eosin
Which routine dye is basic
Hematoxyline
which routine dye is acidic
eosin
what are 4 specific stains and what do they stain?
periodic acid Schiff stain stains carbs, Best’s carmine stains glycogen, acid phosphate stains lysosomes, and Sudan black/ oil red stains lipids
Name 5 cell organelles
7 listed: nucleus, Nucleolus, Endoplasmic Reticulum, Golgi complex, Lysosome, ribosomes, and mitochondria
what is a euchromatic nucleus
a nucleus that has lighter stained, less dense chromatin
What is a heterochromatic nucleus
a nucleus with tightly packed chromatin
What are 4 apical cell surface modifications
Microvilli, cilia, flagella, and stereocilia
What is a cell junction
they are points of contact between adjacent plasma membranes
What are 3 functions of cell junctions
To form a fluid tight seal between cells, anchor cells together or to extracellular material, act as a channel that allows ion and molecules to pass from cell to cell within a tissue
What are the 5 most important kind of cell junctions
tight junctions, adherens junctions, desmosomes, hemidesmosomes, and gap junctions
what are two functions of microvilli
to increase surface area and help with absorption
what is the purpose of cilia and flagella
to act as a form of locomotion
what is the difference between cilia and flagella and stereocilia
cilia and flagella are short with a uniform height and stereocilia are long with irregular height
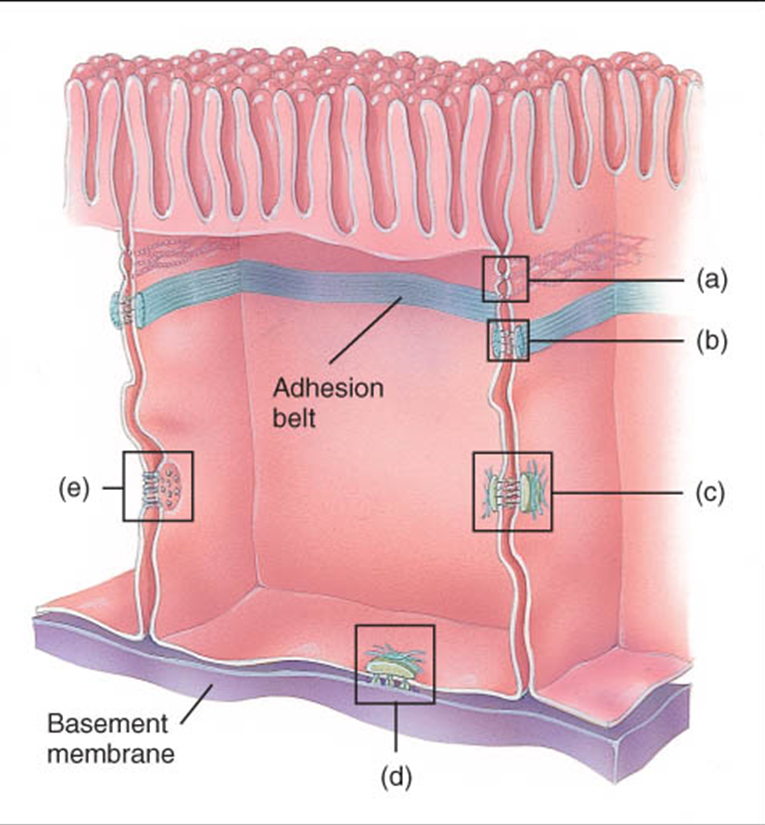
label the cell junctions
A- tight junction, B- adherens junction, C- desmosome, D- hemidesmosome, E- Gap junctions
What is the purpose of a tight junction and where can it be found
Purpose- to form a watertight seal between cells and is found between cells that line the GI tract and bladder
What is the purpose of an adherens junction
to hold epithelial cells together
what is the purpose of cell junctions and what cells can they be found in
to allow cell communication with ions and small molecules and can be found in muscle and nerve cells to spread impulses
What is the purpose of desmosomes and where can they be found
purpose is to resist cellular separation and cell disruption and can be found in the cellular support of cardiac muscles
What is the function of hemidesmosomes
to connect cells to an extracellular material such as the basement membrane,
What are 5 aspects of epithelial tissue
they are closely packed cells with very little connective tissue, the cells sit on a basement membrane, they are avascular, they have a limited nerve supply, and they have rapid cell division ( high mitotic rate)
what keeps epithelial tissue together since they have little connective tissue
Cell junctions
What are the 3 typed of surfaces on epithelial cells and where are they located
Apical surface- the free/ unattached surface, basal surface- against the basement membrane, lateral surface- surface nect to cells on either side.
what does avascular mean
without blood vessels or nerve supply
What are 5 functions of epithelial cells
Protection filtration, lubrication, digestion and absorption.
What are the 3 cell types/ shapes of the epithelium
Squamous, cuboidal, and columnar
What are the 3 number/ arrangement of layers of the epithelium
simple, stratified and pseudostratified
What are the 9 types of cells and number of layers
simple squamous, simple cuboidal, simple columnar, stratified squamous keratinized, stratified squamous nonkeratinized, stratified cuboidal, stratified columnar, pseudostratified columnar, and transitional
what is cornified the same as in classifying epithelial cells
keratinized
what tissue type is this?
simple squamous
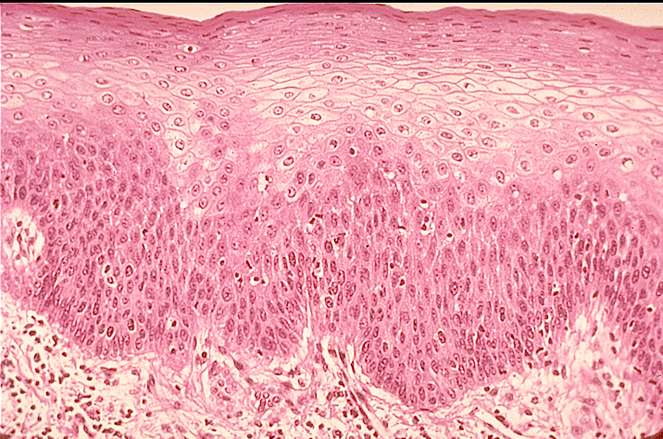
what tissue type is this
Stratified squamous
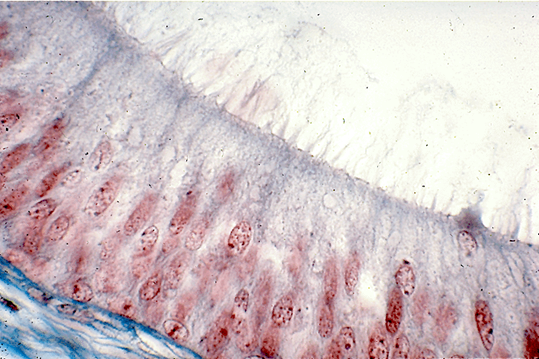
what type of tissue is this
pseudostratified columnar
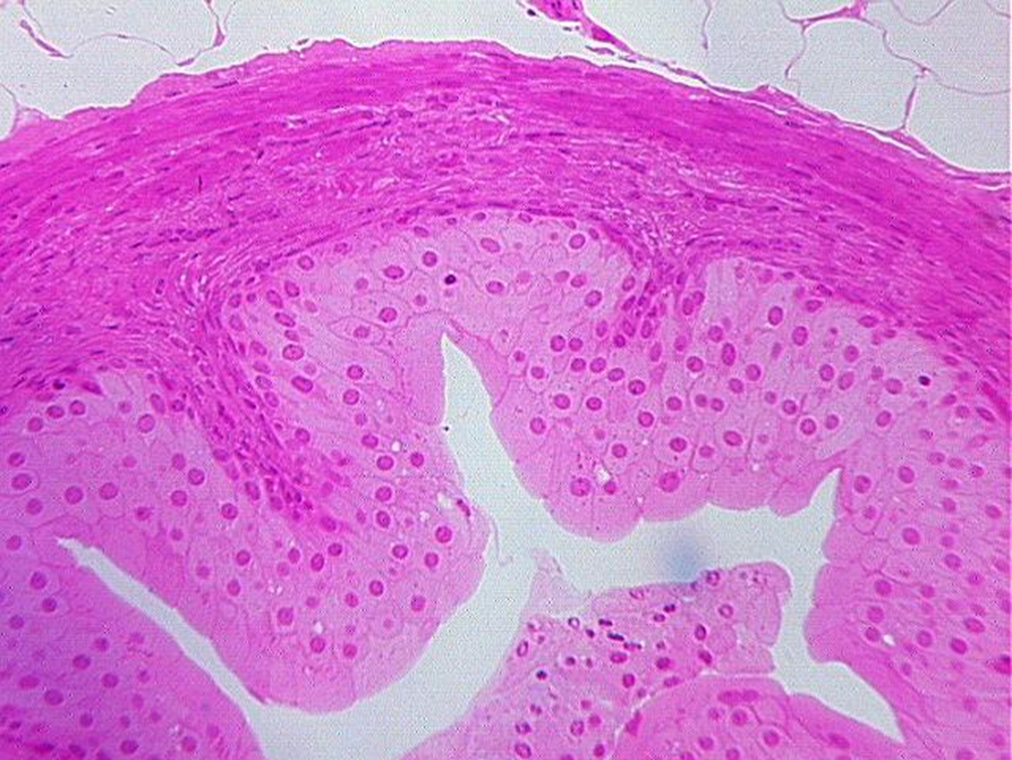
what tissue is this
transitional
True or False; glands can be unicellular or multicellular.
true
What are the 3 types of secretion of glands
serous, mucous, and mixed
what does the serous type of secretion mean?
it means protein secreting
what is an example of a gland that is serous secreting?
the pancreas
what does mucous secreting mean?
glycoprotein secretion
what does mixed secreting mean?
a mix between serous and mucous
what are the 3 modes of secretion?
merocrine, apocrine, holocrine
what is a gland and where is it
a single cell or a mass of epithelial cells adapted for secretion. It derived from epithelial cells that sank below the surface during development.
where do exocrine glands secrete ?
onto a free surface of epithelial layer
what is an example of exocrine glands?
sweat glands
Where do endocrine glands secrete?
they secrete hormones into the bloodstream
what does the hormones from the endocrine system help do?
helps maintain homeostasis
True or False: Goblet cells are unicellular glands.
True
What are the 4 classifications of exocrine glands
branched, unbranched, tubular, and acinar
True or False: compound glands have multiple versions of simple glands
True
how do merocrine glands discharge their secretions?
by exocytosis
what is an example of an merocrine gland
Saliva glands
what is exocytosis ?
when a cell forms pockets around molecules and deposits them outside of the cell without the killing or disturbing the cell
How do apocrine glands discharge their secretions
the secretion is accumulated in the apex of the cell which then pinches off from the rest of the cell.
which gland doesn’t exist in the humans?
apocrine glands
How does the holocrine gland discharge its secretions
by the secretory product accumulating in the cytosol until the cell dies and it becomes the secretory product.
what an example of holocrine gland ?
a sebaceous( oil ) gland
what is connective tissue derived from?
a type of mesoderm called mesenchyme
what subfix is given to immature cells
-blast
what do mature cells end in?
-cyte
what are fibers synthesized from?
fibroblast
what are 3 functions of connective tissue?
5 listed- support, storage of lipids, water, and electrolytes,, heat regulation, repair of damaged organs, and transport of nutrients
What are the 3 different types of fibers
collagen, elastic and reticular
what are some ways connective tissue differs from the epithelium
it is more fibrous, less cellular, has a random arrangement of cells and is vascular
what are two things that fibroblast secrete
fibers and matrix
what are fat cells called?
adipocytes
what do adipocytes do?
they store energy in the form of lipids
what are white blood cells called
leukocytes
what are the 3 types of white blood cells and what are their functions
macrophages- engulf bacteria and debris by phagocytosis, plasma cells- produce antibodies that fight against foreign substances, and mast cells- they produce histamine that dilates small blood vessels
what are the three items found in the ground substance of the extracellular matrix?
Glucosamine glycans ( GAGs), proteoglycans, adhesion proteins
why is hyaluronic acid important
it lubricates joints and it binds cells together
where can each fiber type be found ( elastic, collagen, and reticular )
collagen- bone, cartilage, tendons, ligaments, elastic- skin, blood vessels, and lungs, reticular fibers-in the walls of blood vessels, spleen and lymph nodes
what are the two classifications of connective tissue
embryonic connective tissue and mature connective tissue
what are the two types of embryonic connective tissue?
mesenchyme and mucous connective tissue
what is embryonic connective tissue?
connective tissue that is present primarily in the embryo or fetus
What tissue does all of the other connective tissues arise from
the mesenchyme
where is the mucous connective tissue found ?
in the umbilical cord of the fetus
what are the 5 types of mature connective tissue
Loose connective tissue, dense connective tissue, cartilage, bone tissue, and liquid connective tissue